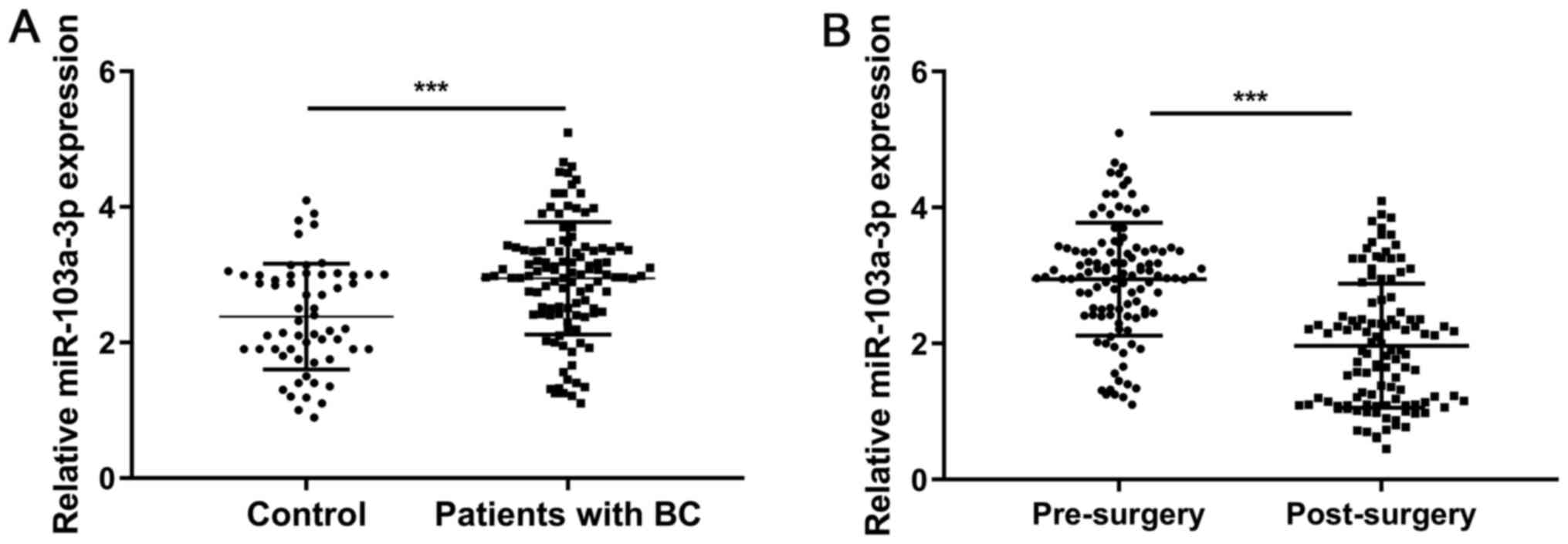
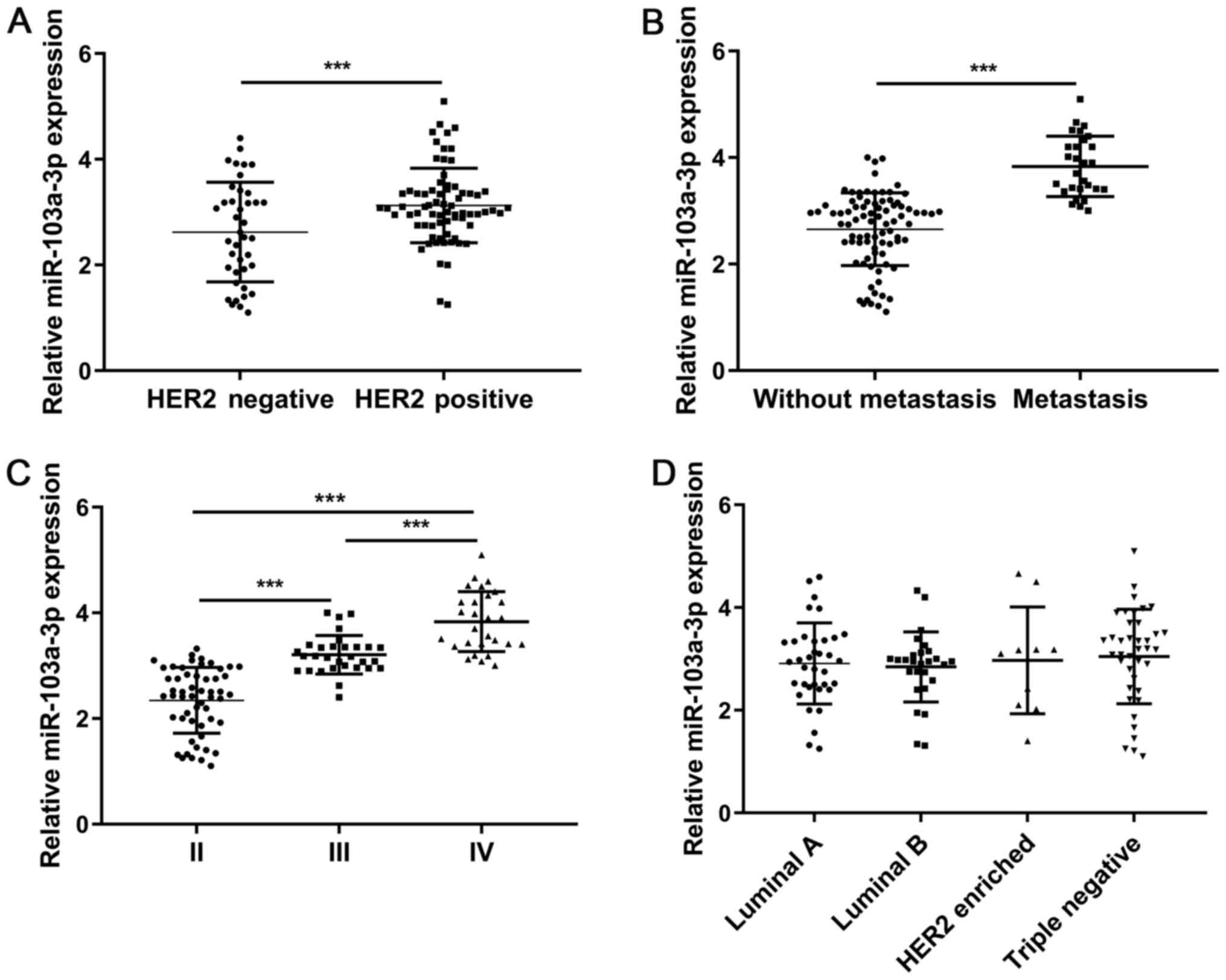
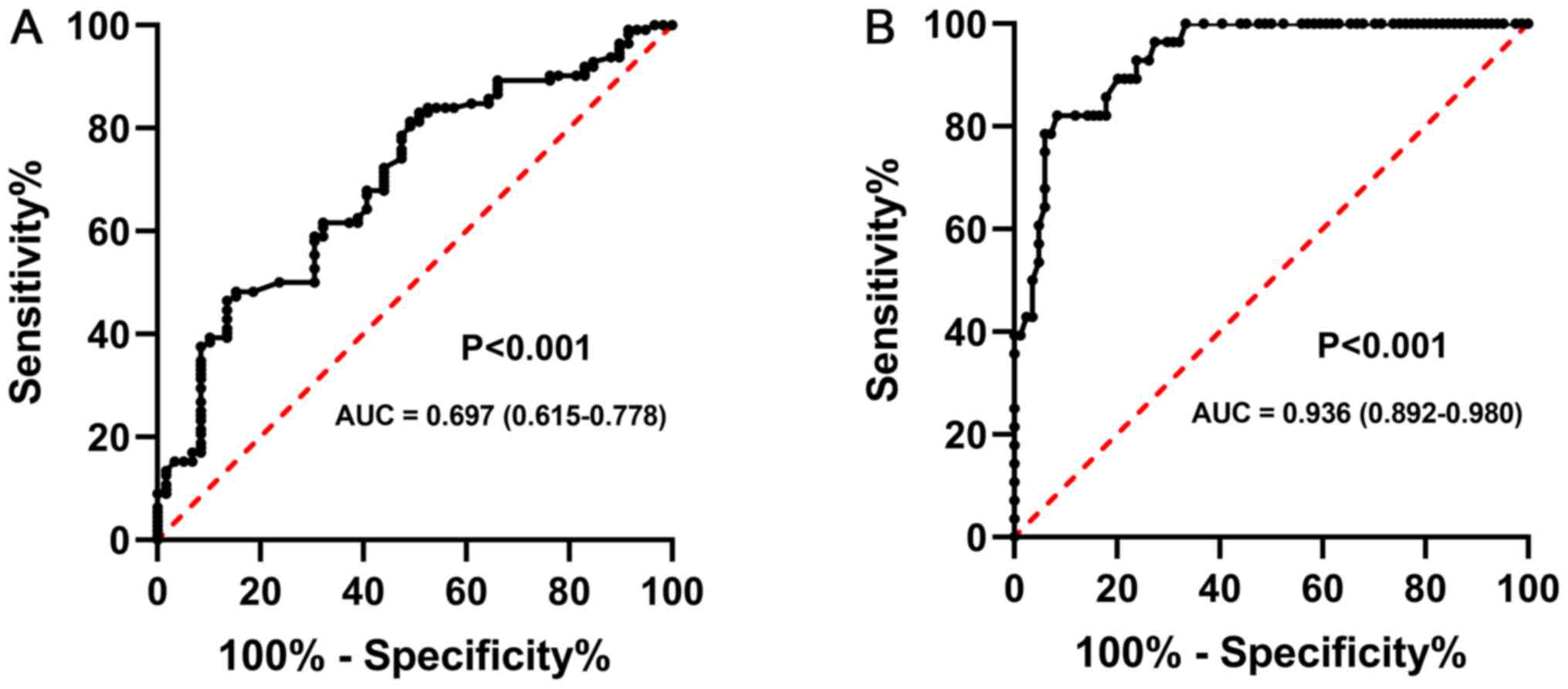
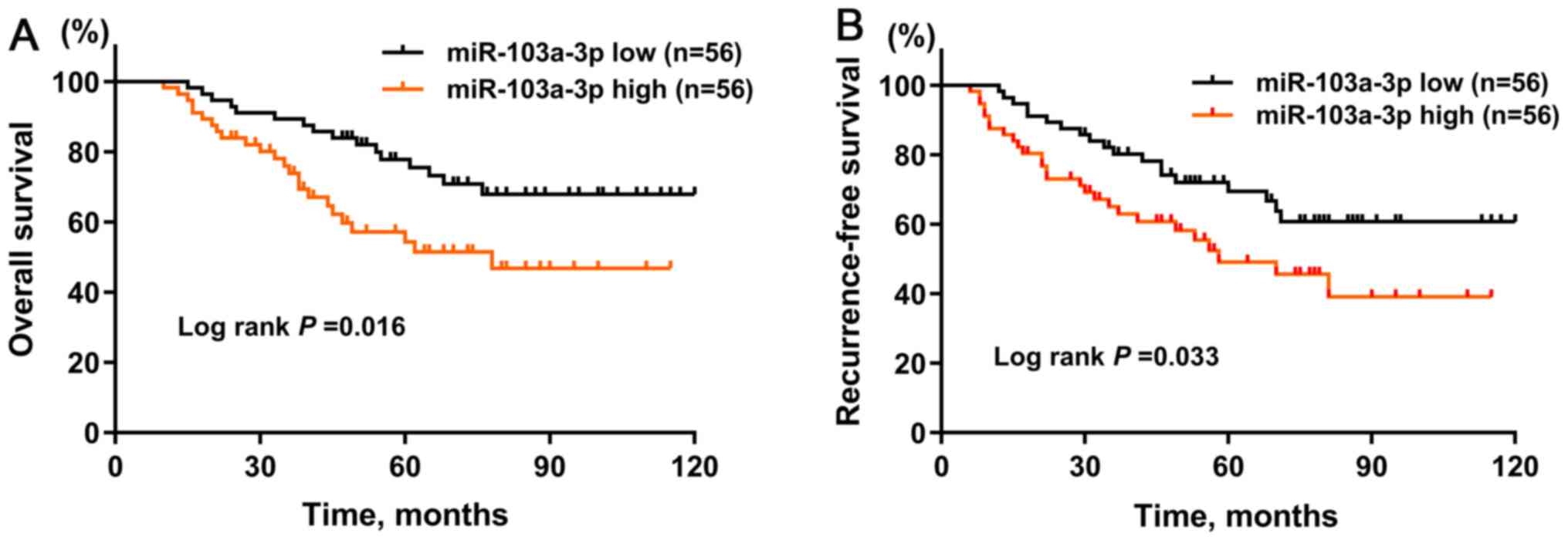
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
O'Shaughnessy J: Extending survival with
chemotherapy in metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist. 10 (Suppl
3):20–29. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cardoso F, Spence D, Mertz S,
Corneliussen-James D, Sabelko K, Gralow J, Cardoso MJ, Peccatori F,
Paonessa D, Benares A, et al: Global analysis of
advanced/metastatic breast cancer: Decade report (2005–2015).
Breast. 39:131–138. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Viale G: The current state of breast
cancer classification. Ann Oncol. 23 (Suppl 10):x207–x210. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bertoli G, Cava C and Castiglioni I:
MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy
prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics.
5:1122–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tutar Y: miRNA and cancer; computational
and experimental approaches. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 15:4292014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mishra S, Yadav T and Rani V: Exploring
miRNA based approaches in cancer diagnostics and therapeutics. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 98:12–23. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li B, Zhang F and Li H: miR-1225-5p
inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration
and invasion, and may be a prognostic biomarker. Exp Ther Med.
20:1722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Acunzo M, Romano G, Wernicke D and Croce
CM: MicroRNA and cancer - a brief overview. Adv Biol Regul. 57:1–9.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hamam R, Hamam D, Alsaleh KA, Kassem M,
Zaher W, Alfayez M, Aldahmash A and Alajez NM: Circulating
microRNAs in breast cancer: Novel diagnostic and prognostic
biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chong ZX, Yeap SK and Ho WY: Roles of
circulating microRNA(s) in human breast cancer. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 695:1085832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ozawa PM, Jucoski TS, Vieira E, Carvalho
TM, Malheiros D and Ribeiro EM: Liquid biopsy for breast cancer
using extracellular vesicles and cell-free microRNAs as biomarkers.
Transl Res. 223:40–60. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang ML, Sun WH, Wu HQ, Liu ZD and Wang
P: Knockdown of microRNA-103a-3p inhibits the malignancy of thyroid
cancer cells through Hippo signaling pathway by upregulating LATS1.
Neoplasma. 67:1266–1278. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang H, Zhu M, Shan X, Zhou X, Wang T,
Zhang J, Tao J, Cheng W, Chen G, Li J, et al: A panel of
seven-miRNA signature in plasma as potential biomarker for
colorectal cancer diagnosis. Gene. 687:246–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu X, Miao J, Zhang M, Wang X, Wang Z, Han
J, Tong D and Huang C: miRNA-103a-3p promotes human gastric cancer
cell proliferation by targeting and suppressing ATF7 in vitro. Mol
Cells. 41:390–400. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang G, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Li T, Bao Y and
Zhang S: Inhibition of miR-103a-3p suppresses the proliferation in
oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via targeting RCAN1. Neoplasma.
67:461–472. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weber DG, Casjens S, Johnen G, Bryk O,
Raiko I, Pesch B, Kollmeier J, Bauer TT and Brüning T: Combination
of miR-103a-3p and mesothelin improves the biomarker performance of
malignant mesothelioma diagnosis. PLoS One. 9:e1144832014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fu M, Chen CW, Yang LQ, Yang WW, Du ZH, Li
YR, Li SL and Ge XY: MicroRNA 103a 3p promotes metastasis by
targeting TPD52 in salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
57:574–586. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ge J, Mao L, Xu W, Fang W, Wang N, Ye D,
Dong Z, Guan H and Guan C: miR-103a-3p suppresses cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting tumor protein D52 in
prostate cancer. J Invest Surg. 34:984–992. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Lei J, Wang J, Lian CL, Hua L,
Yang LC and Wu SG: Validation of the 8th edition of the American
Joint Committee on Cancer Pathological Prognostic Staging for young
breast cancer patients. Aging (Albany NY). 12:7549–7560. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Scully OJ, Bay BH, Yip G and Yu Y: Breast
cancer metastasis. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 9:311–320.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Koi Y, Tsutani Y, Nishiyama Y, Ueda D,
Ibuki Y, Sasada S, Akita T, Masumoto N, Kadoya T, Yamamoto Y, et
al: Predicting the presence of breast cancer using circulating
small RNAs, including those in the extracellular vesicles. Cancer
Sci. 111:2104–2115. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li M, Zou X, Xia T, Wang T, Liu P, Zhou X,
Wang S and Zhu W: A five-miRNA panel in plasma was identified for
breast cancer diagnosis. Cancer Med. 8:7006–7017. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Xu Y, Jin X, Wang Z, Wu Y, Zhao
D, Chen G, Li D, Wang X, Cao H, et al: A circulating miRNA
signature as a diagnostic biomarker for non-invasive early
detection of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 154:423–434.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Valihrach L, Androvic P and Kubista M:
Circulating miRNA analysis for cancer diagnostics and therapy. Mol
Aspects Med. 72:1008252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Usuba W, Urabe F, Yamamoto Y, Matsuzaki J,
Sasaki H, Ichikawa M, Takizawa S, Aoki Y, Niida S, Kato K, et al:
Circulating miRNA panels for specific and early detection in
bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 110:408–419. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu XL, Ren LF, Wang HP, Bai ZT, Zhang L,
Meng WB, Zhu KX, Ding FH, Miao L, Yan J, et al: Plasma microRNAs as
potential new biomarkers for early detection of early gastric
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 25:1580–1591. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kirschner MB, Edelman JJ, Kao SC, Vallely
MP, van Zandwijk N and Reid G: The impact of hemolysis on cell-free
microRNA biomarkers. Front Genet. 4:942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Iempridee T, Wiwithaphon S, Piboonprai K,
Pratedrat P, Khumkhrong P, Japrung D, Temisak S, Laiwejpithaya S,
Chaopotong P and Dharakul T: Identification of reference genes for
circulating long noncoding RNA analysis in serum of cervical cancer
patients. FEBS Open Bio. 8:1844–1854. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Barzaman K, Karami J, Zarei Z,
Hosseinzadeh A, Kazemi MH, Moradi-Kalbolandi S, Safari E and
Farahmand L: Breast cancer: Biology, biomarkers, and treatments.
Int Immunopharmacol. 84:1065352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|