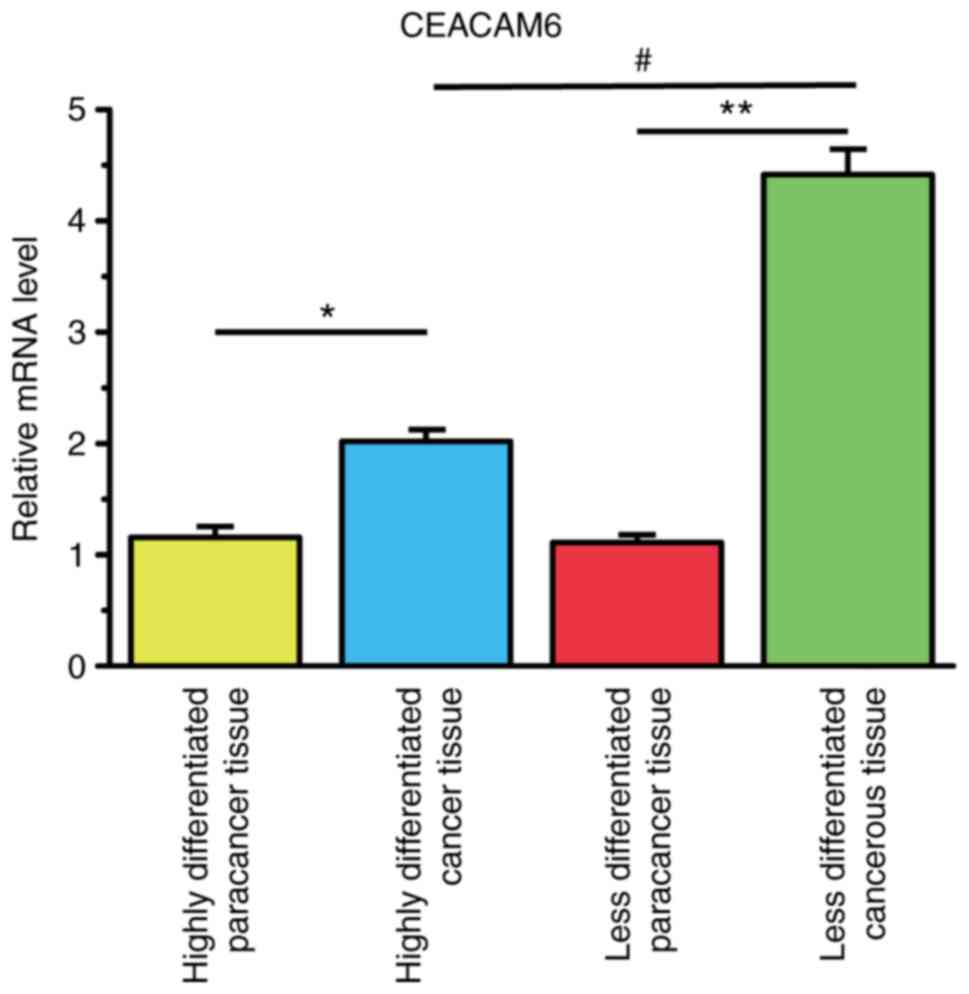
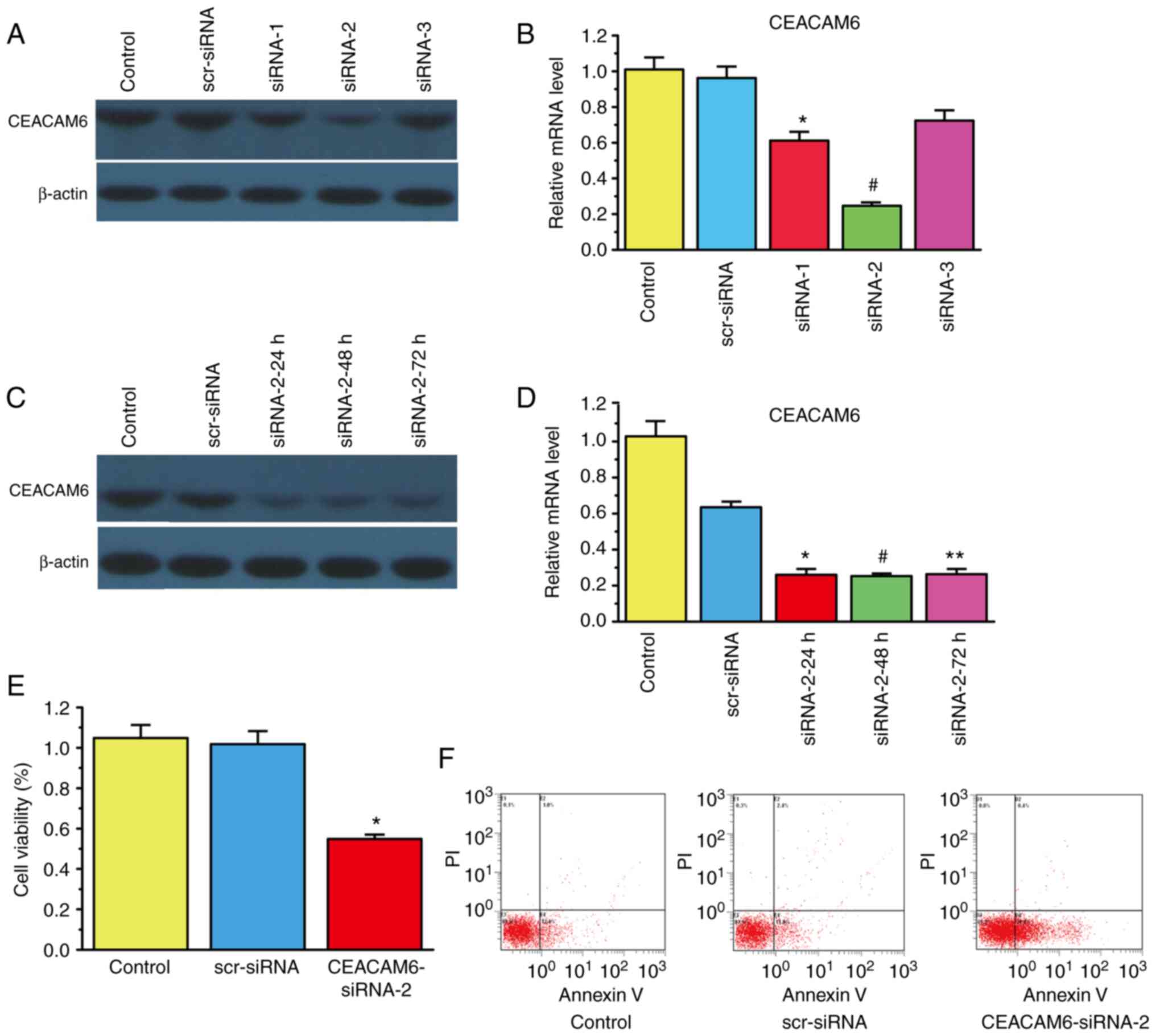
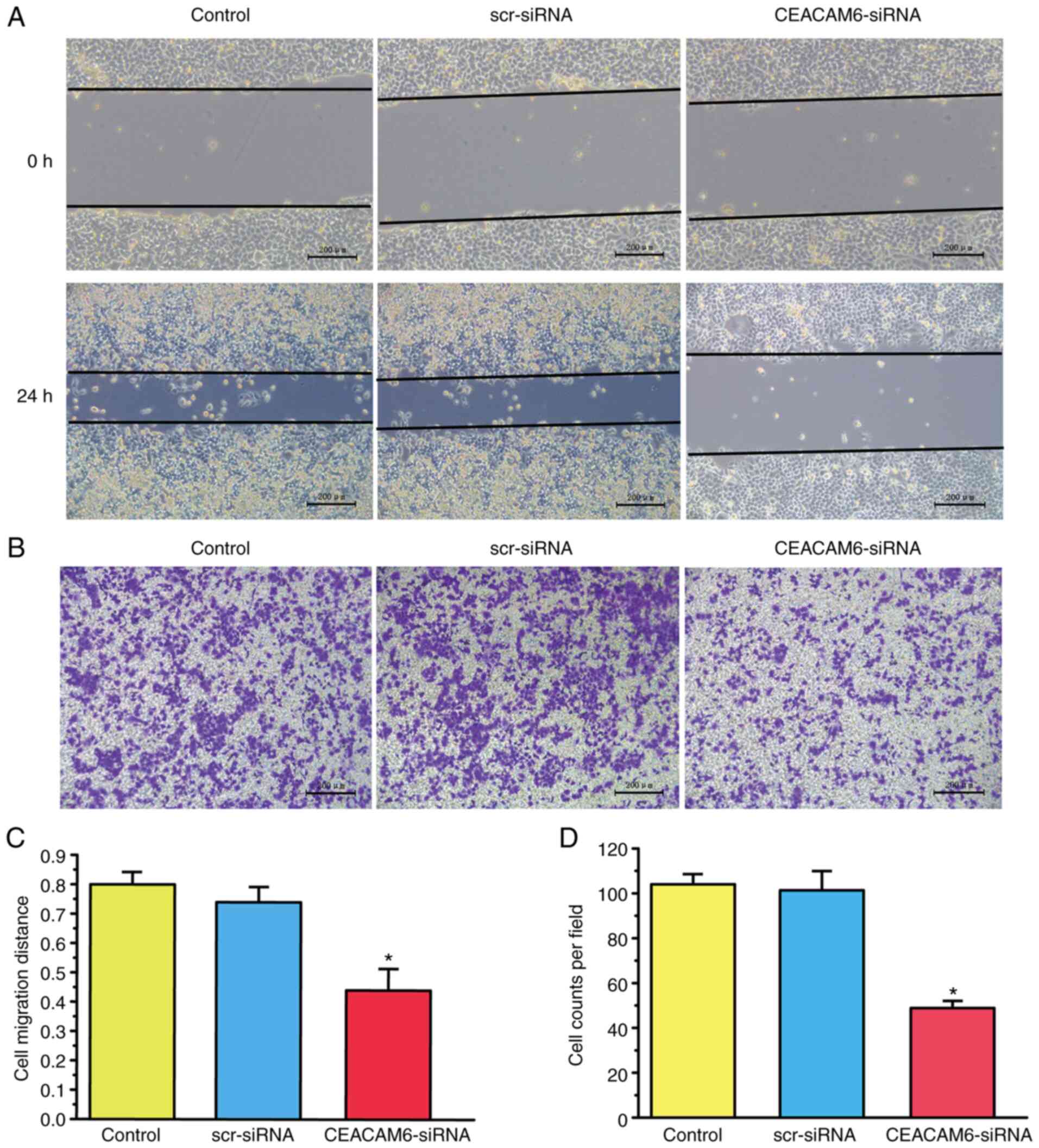
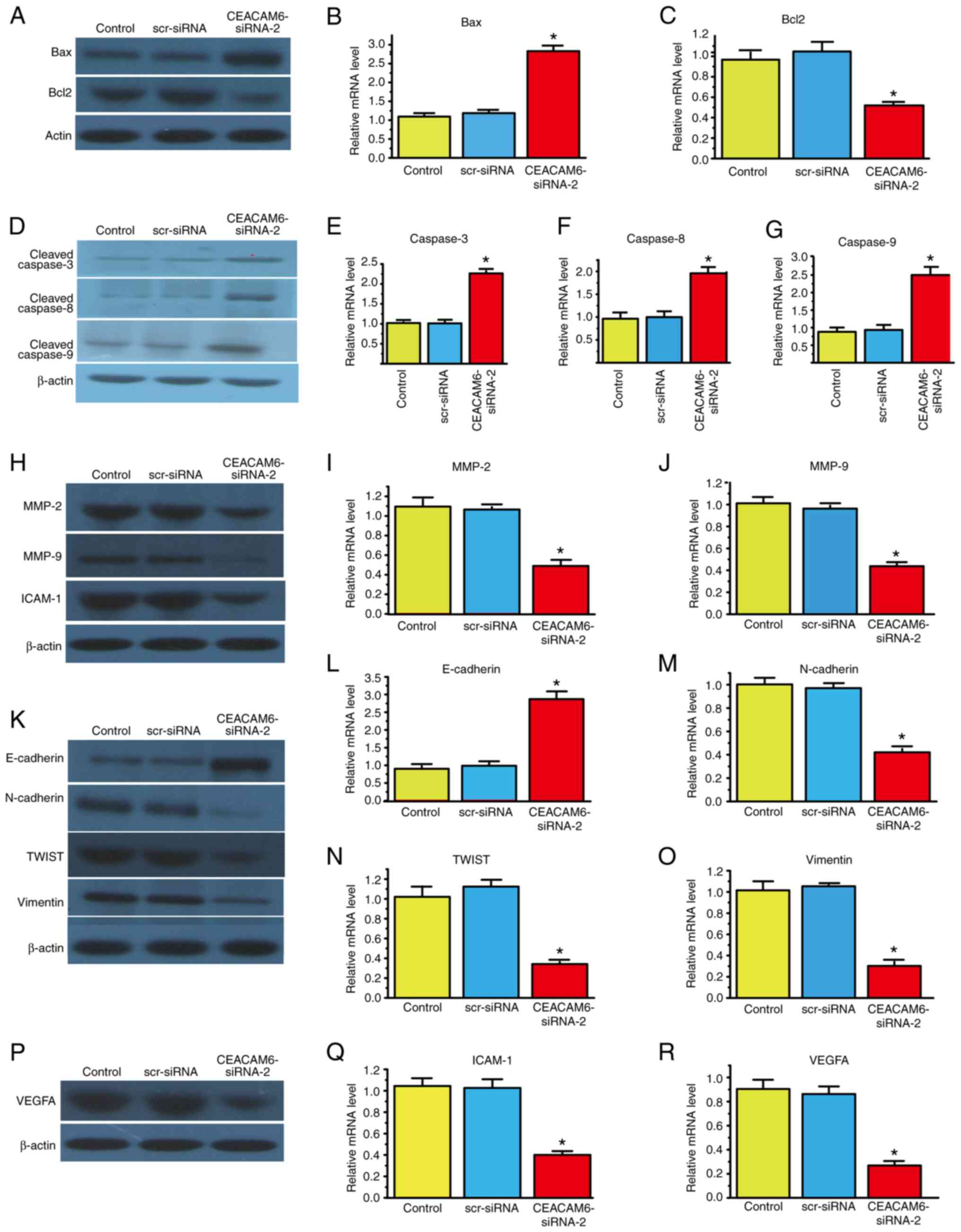
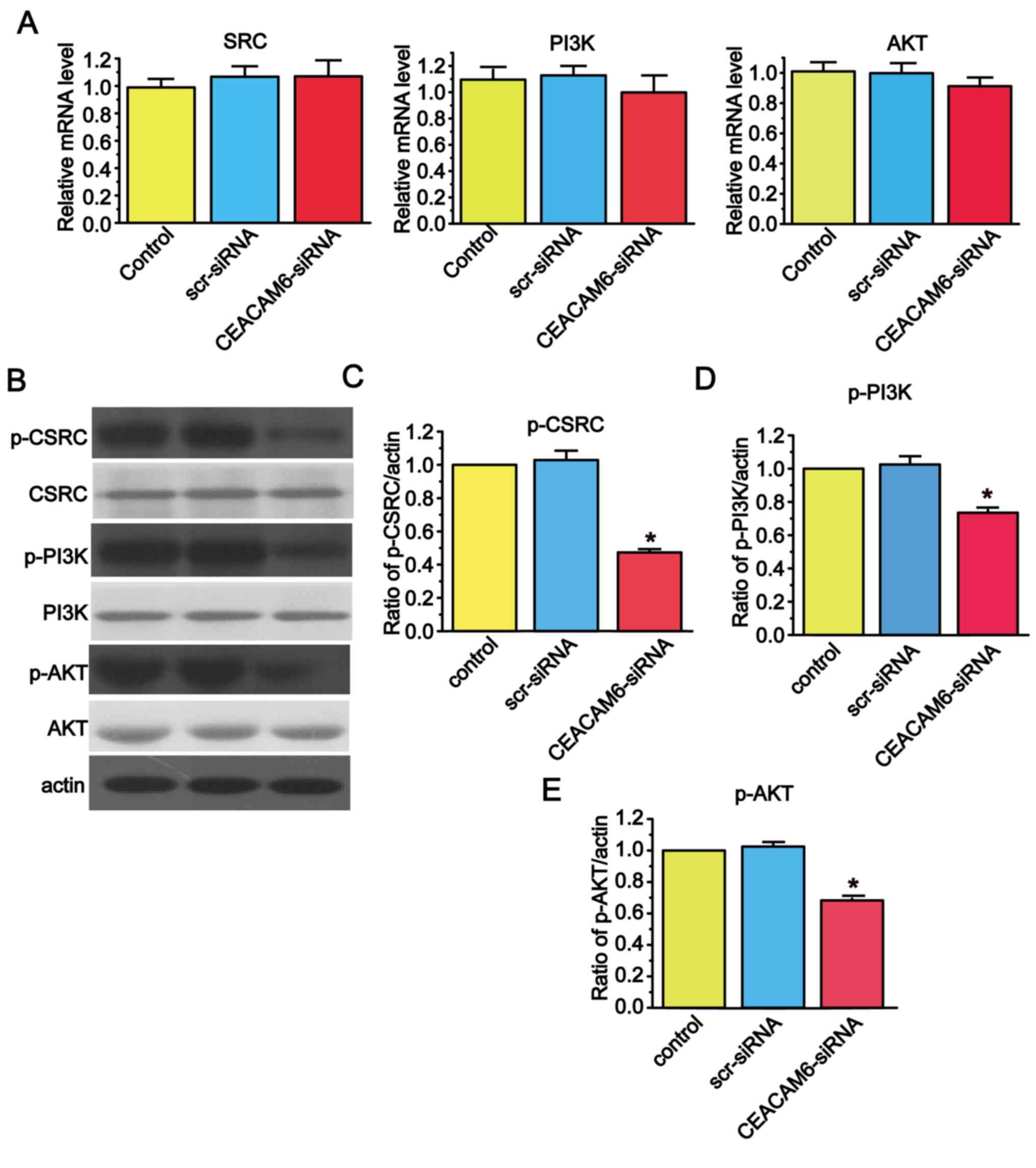
|
1
|
Bridgewater J, Galle PR, Khan SA, Llovet
JM, Park JW, Patel T, Pawlik TM and Gores GJ: Guidelines for the
diagnosis and management of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J
Hepatol. 60:1268–1289. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Saha SK, Zhu AX, Fuchs CS and Brooks GA:
Forty-year trends in cholangiocarcinoma incidence in the U.S.:
Intrahepatic disease on the rise. Oncologist. 21:594–599. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kayhanian H, Smyth EC and Braconi C:
Emerging molecular targets and therapy for cholangiocarcinoma.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. 9:268–280. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Khan SA, Taylor-Robinson SD, Toledano MB,
Beck A, Elliott P and Thomas HC: Changing international trends in
mortality rates for liver, biliary and pancreatic tumours. J
Hepatol. 37:806–813. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rizvi S, Khan SA, Hallemeier CL, Kelley RK
and Gores GJ: Cholangiocarcinoma-evolving concepts and therapeutic
strategies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 15:95–111. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Battaglia S, Benzoubir N, Nobilet S,
Charneau P, Samuel D, Zignego AL, Atfi A, Brechot C and Bourgeade
MF: Liver cancer-derived hepatitis C virus core proteins shift
TGF-beta responses from tumor suppression to epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. PLoS One. 4:e43552009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vaquero J, Guedj N, Claperon A, Nguyen
Ho-Bouldoires TH, Paradis V and Fouassier L: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in cholangiocarcinoma: From clinical evidence to
regulatory networks. J Hepatol. 66:424–441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Puisieux A, Brabletz T and Caramel J:
Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell
Biol. 16:488–494. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu JY, Zhou F, Yu L and Zhang J:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition of small airway epithelium in
patients receiving lung tumor surgery with normal lung function and
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
99:2681–2686. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Baum B, Settleman J and Quinlan MP:
Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states in
development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 19:294–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zeisberg M and Neilson EG: Biomarkers for
epithelial-mesenchymal transitions. J Clin Invest. 119:1429–1437.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rizeq B, Zakaria Z and Ouhtit A: Towards
understanding the mechanisms of actions of carcinoembryonic
antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 in cancer progression.
Cancer Sci. 109:33–42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yamanka T, Kuroki M, Matsuo Y and Matsuoka
Y: Analysis of heterophilic cell adhesion mediated by CD66b and
CD66c using their soluble recombinant proteins. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 219:842–847. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ieta K, Tanaka F, Utsunomiya T, Kuwano H
and Mori M: CEACAM6 gene expression in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 95:532–540. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rose JB, Correa-Gallego C, Li Y, Nelson J,
Alseidi A, Helton WS, Allen PJ, D'Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP, Fong Y,
et al: The role of biliary carcinoembryonic antigen-related
cellular adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) as a biomarker in
cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01501952016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Farina A, Dumonceau JM, Antinori P,
Annessi-Ramseyer I, Frossard JL, Hochstrasser DF, Delhaye M and
Lescuyer P: Bile carcinoembryonic cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEAM6)
as a biomarker of malignant biliary stenoses. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1844:1018–1025. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuespert K, Pils S and Hauck CR: CEACAMs:
Their role in physiology and pathophysiology. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
18:565–571. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ilantzis C, DeMarte L, Screaton RA and
Stanners CP: Deregulated expression of the human tumor marker CEA
and CEA family member CEACAM6 disrupts tissue architecture and
blocks colonocyte differentiation. Neoplasia. 4:151–163. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ordonez C, Screaton RA, Ilantzis C and
Stanners CP: Human carcinoembryonic antigen functions as a general
inhibitor of anoikis. Cancer Res. 60:3419–3424. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Zinner MJ, Ashley SW
and Whang EE: CEACAM6 gene silencing impairs anoikis resistance and
in vivo metastatic ability of pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells.
Oncogene. 23:465–473. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen J, Li Q, An Y, Lv N, Xue X, Wei J,
Jiang K, Wu J, Gao W, Qian Z, et al: CEACAM6 induces
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and mediates invasion and
metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol. 43:877–885. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y, Zang M, Li J, Ji J, Zhang J, Liu
X, Qu Y, Su L, Li C, Yu Y, et al: CEACAM6 promotes tumor migration,
invasion, and metastasis in gastric cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 46:283–290. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mancarella S, Serino G, Dituri F, Cigliano
A, Ribback S, Wang J, Chen X, Calvisi DF and Giannelli G:
Crenigacestat, a selective NOTCH1 inhibitor, reduces intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma progression by blocking VEGFA/DLL4/MMP13 axis.
Cell Death Differ. 27:2330–2343. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim KS, Kim JT, Lee SJ, Kang MA, Choe IS,
Kang YH, Kim SY, Yeom YI, Lee YH, Kim JH, et al: Overexpression and
clinical significance of carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell
adhesion molecule 6 in colorectal cancer. Clin Chim Acta.
415:12–19. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lewis-Wambi JS, Cunliffe HE, Kim HR,
Willis AL and Jordan VC: Overexpression of CEACAM6 promotes
migration and invasion of oestrogen-deprived breast cancer cells.
Eur J Cancer. 44:1770–1779. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kobayashi M, Miki Y, Ebina M, Abe K, Mori
K, Narumi S, Suzuki T, Sato I, Maemondo M, Endo C, et al:
Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecules as
surrogate markers for EGFR inhibitor sensitivity in human lung
adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 107:1745–1753. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zang M, Zhang B, Zhang Y, Li J, Su L, Zhu
Z, Gu Q, Liu B and Yan M: CEACAM6 promotes gastric cancer invasion
and metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via
PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. PLos One. 9:e1129082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS and Liang J:
Caspase family proteases and apoptosis. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 37:719–727. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Makler A and Asghar W: Exosomal biomarkers
for cancer diagnosis and patient monitoring. Expert Rev Mol Diagn.
20:387–400. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Deng Z, Wu J, Xu S, Chen F, Zhang Z, Jin A
and Wang J: Exosomes-microRNAs interacted with gastric cancer and
its microenvironment: A mini literature review. Biomark Med.
14:141–150. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Duxbury MS, Ito H, Ashley SW and Whang EE:
c-Src-dependent cross-talk between CEACAM6 and alphavbeta3 integrin
enhances pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell adhesion to extracellular
matrix components. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 317:133–141. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|