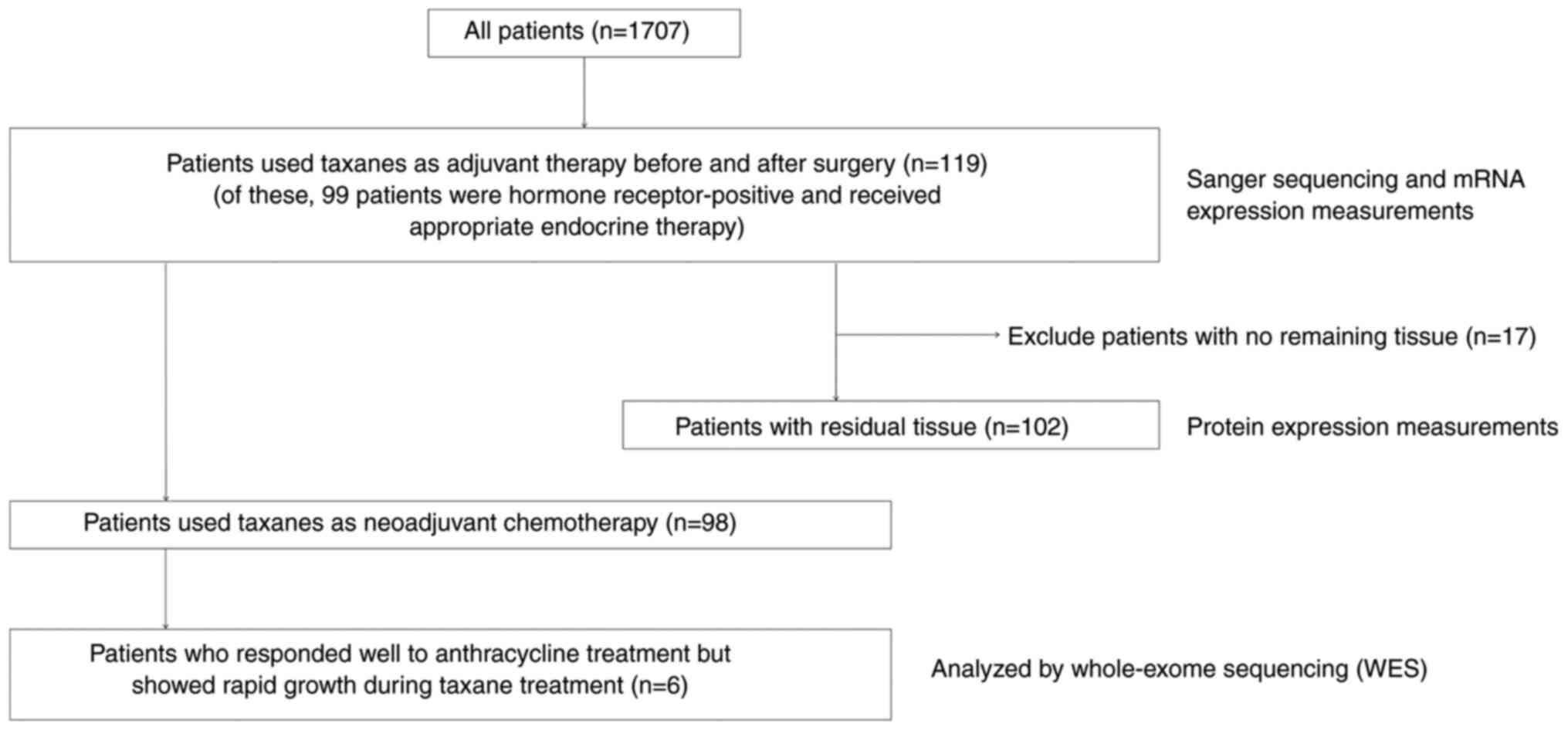
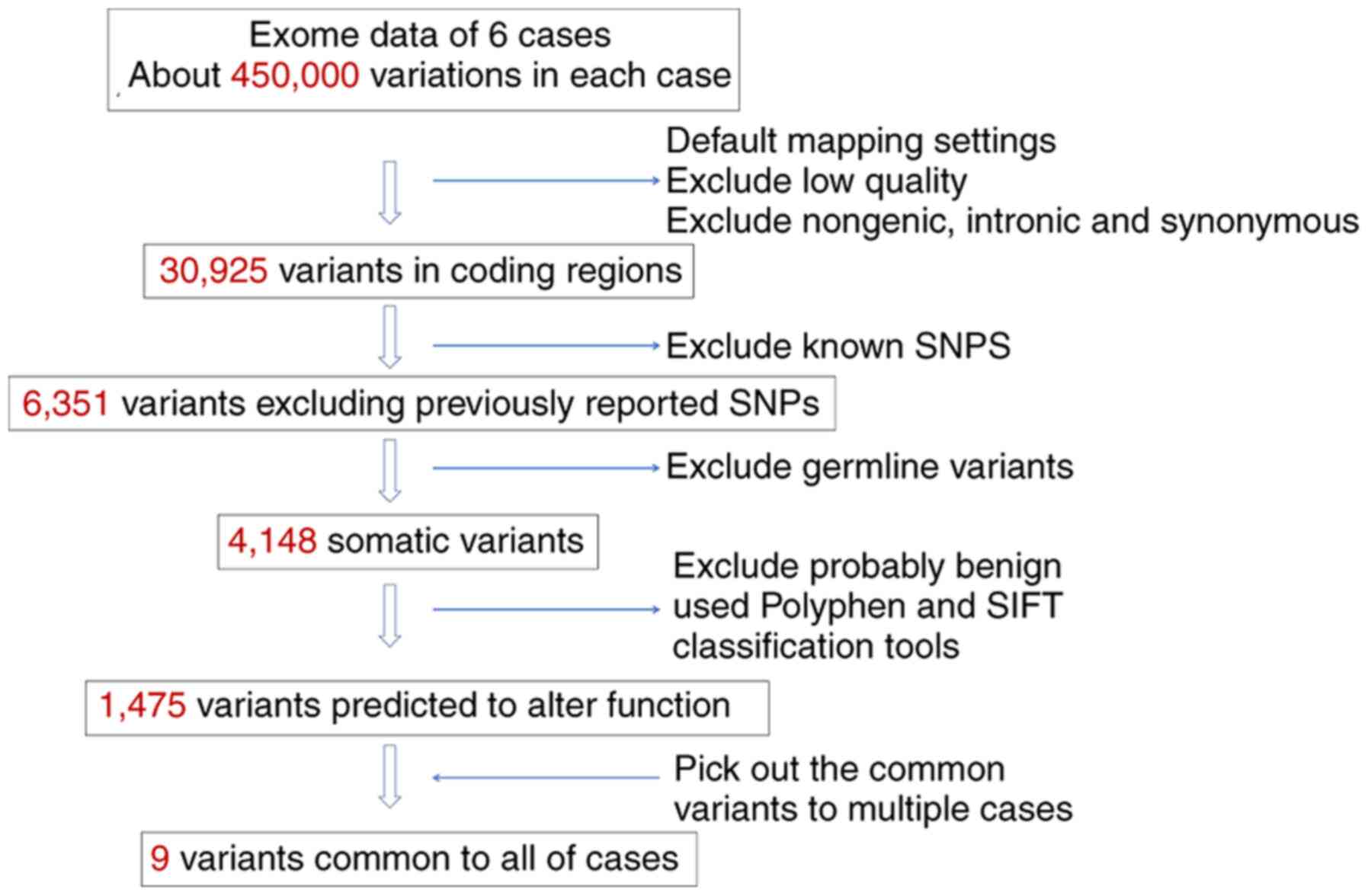
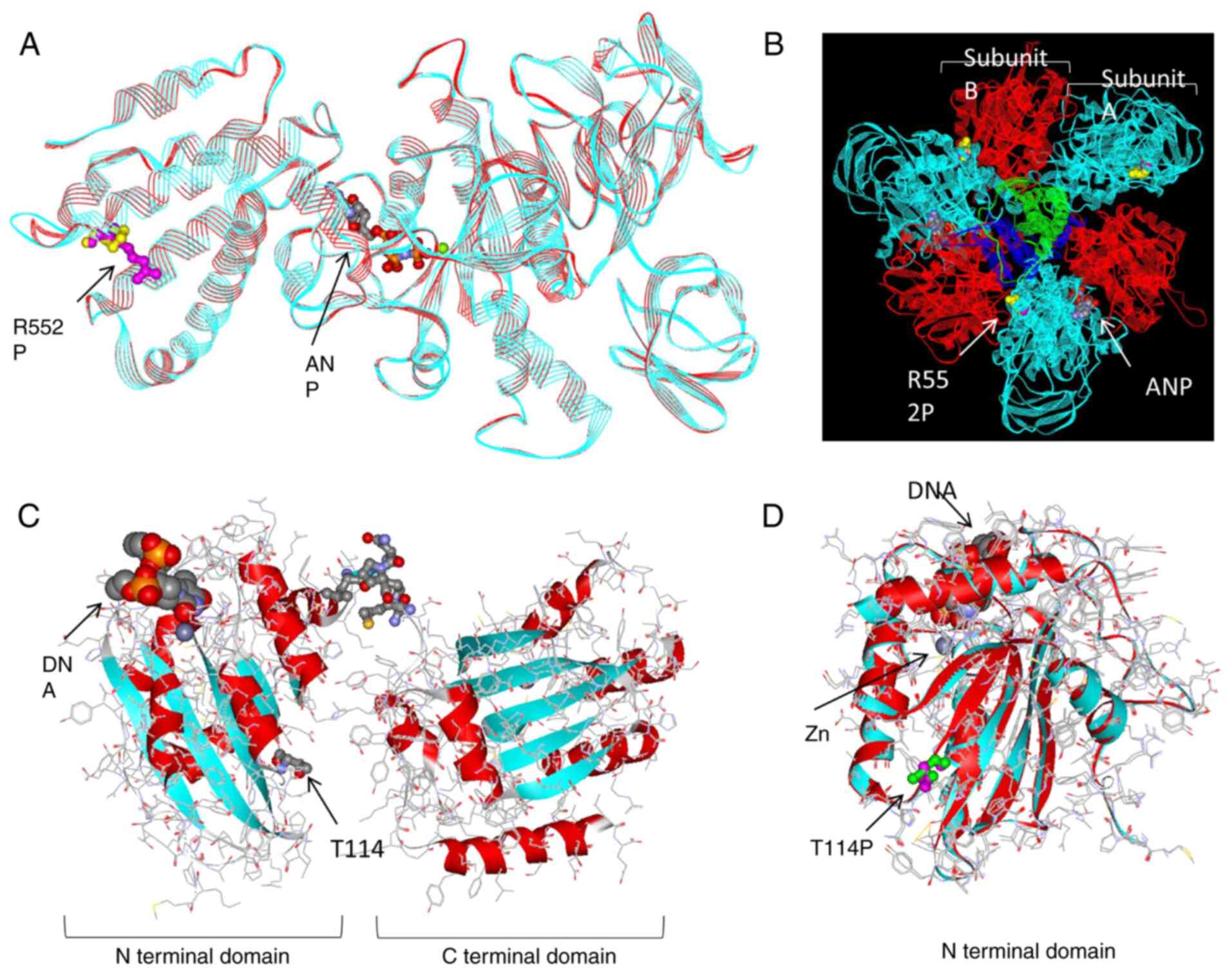
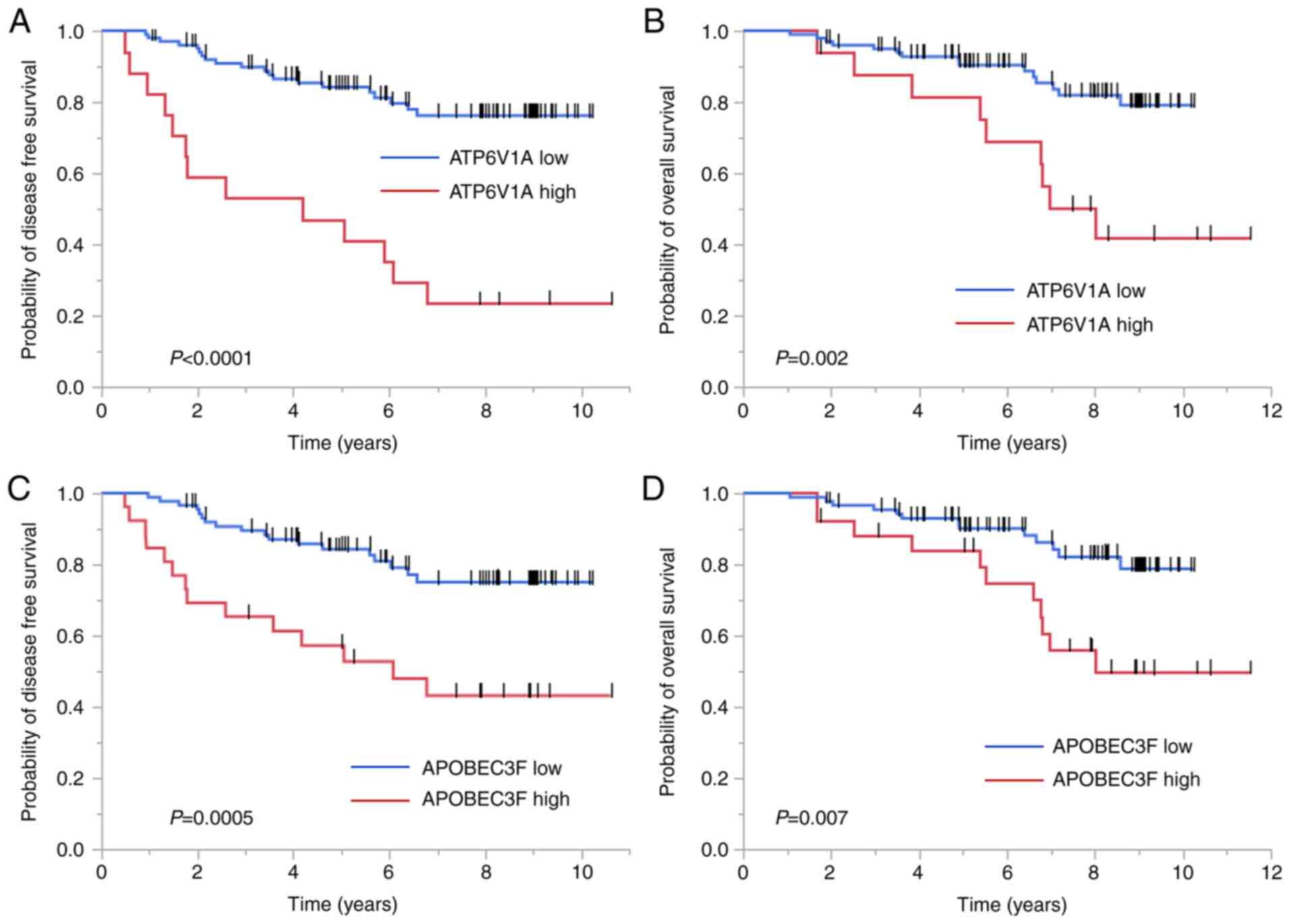
|
1
|
Mougalian SS, Soulos PR, Killelea BK,
Lannin DR, Abu-Khalaf MM, DiGiovanna MP, Sanft TB, Pusztai L, Gross
CP and Chagpar AB: Use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for patients
with stage I to III breast cancer in the United States. Cancer.
121:2544–2552. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bear HD, Anderson S, Brown A, Smith R,
Mamounas EP, Fisher B, Margolese R, Theoret H, Soran A, Wickerham
DL, et al: The effect on tumor response of adding sequential
preoperative docetaxel to preoperative doxorubicin and
cyclophosphamide: Preliminary results from national surgical
adjuvant breast and bowel project protocol B-27. J Clin Oncol.
21:4165–4174. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Caudle AS, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hunt KK,
Liu P, Pusztai L, Symmans WF, Kuerer HM, Mittendorf EA, Hortobagyi
GN and Meric-Bernstam F: Predictors of tumor progression during
neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1821–1828. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pucci P, Rescigno P, Sumanasuriya S, de
Bono J and Crea F: Hypoxia and noncoding RNAs in taxane resistance.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 39:695–709. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yin S, Zeng C, Hari M and Cabral F:
Paclitaxel resistance by random mutagenesis of alpha-tubulin.
Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 70:849–862. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matsunaga T, Saito H, Endo S, Iguchi K,
Soda M, El-Kabbani O, Hara A and Ikari A: Roles of aldo-keto
reductases 1B10 and 1C3 and ATP-binding cassette transporter in
docetaxel tolerance. Free Radic Res. 50:1296–1308. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vaidyanathan A, Sawers L, Gannon AL,
Chakravarty P, Scott AL, Bray SE, Ferguson MJ and Smith G: ABCB1
(MDR1) induction defines a common resistance mechanism in
paclitaxel- and olaparib-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Br J
Cancer. 115:431–441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bose R, Kavuri SM, Searleman AC, Shen W,
Shen D, Koboldt DC, Monsey J, Goel N, Aronson AB, Li S, et al:
Activating HER2 mutations in HER2 gene amplification negative
breast cancer. Cancer Discov. 3:224–237. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang L, Ye F, Bao L, Zhou X, Wang Z, Hu P,
Ouyang N, Li X, Shi Y, Chen G, et al: Somatic alterations of TP53,
ERBB2, PIK3CA and CCND1 are associated with chemosensitivity for
breast cancers. Cancer Sci. 110:1389–1400. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Endo Y, Dong Y, Yoshimoto N, Asano T, Hato
Y, Yamashita H, Sato S, Takahashi S, Fujii Y and Toyama T: HER2
mutation status in Japanese HER2-negative breast cancer patients.
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 44:619–623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wanifuchi-Endo Y, Asano T, Kondo N, Hato
Y, Dong Y, Hisada T, Nishikawa S, Kato H, Takahashi S, Okuda K, et
al: Effects of serum estradiol and progesterone on
estrogen-regulated gene expression in breast cancers of
premenopausal patients. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 49:12–21. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M and Clark
GM: Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by
immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol. 11:155–168.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty
KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, Dowsett M, Fitzgibbons PL, Hanna WM, Langer
A, et al: American society of clinical oncology/college of american
pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth
factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
25:118–145. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hirsch FR, Varella-Garcia M, Bunn PA Jr,
Maria MV, Veve R, Bremmes RM, Barón AE, Zeng C and Franklin WA:
Epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung carcinomas:
Correlation between gene copy number and protein expression and
impact on prognosis. J Clin Oncol. 21:3798–3807. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
John T, Liu G and Tsao MS: Overview of
molecular testing in non-small-cell lung cancer: Mutational
analysis, gene copy number, protein expression and other biomarkers
of EGFR for the prediction of response to tyrosine kinase
inhibitors. Oncogene. 28 (Suppl 1):S14–S23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Endo Y, Yamashita H, Takahashi S, Sato S,
Yoshimoto N, Asano T, Hato Y, Dong Y, Fujii Y and Toyama T:
Immunohistochemical determination of the miR-1290 target arylamine
N-acetyltransferase 1 (NAT1) as a prognostic biomarker in breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:9902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hayes DF, Ethier S and Lippman ME: New
guidelines for reporting of tumor marker studies in breast cancer
research and treatment: REMARK. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
100:237–238. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, Taube
SE, Gion M and Clark GM; Statistics Subcommittee of the NCI-EORTC
Working Group on Cancer Diagnostics, : REporting recommendations
for tumor MARKer prognostic studies (REMARK). Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 100:229–235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Fais S, De Milito A, You H and Qin W:
Targeting vacuolar H+-ATPases as a new strategy against
cancer. Cancer Res. 67:10627–10630. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nishi T and Forgac M: The vacuolar
(H+)-ATPases-nature's most versatile proton pumps. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 3:94–103. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stransky L, Cotter K and Forgac M: The
function of V-ATPases in cancer. Physiol Rev. 96:1071–1091. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun-Wada GH and Wada Y: Role of
vacuolar-type proton ATPase in signal transduction. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1847:1166–1172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Whitton B, Okamoto H, Packham G and Crabb
SJ: Vacuolar ATPase as a potential therapeutic target and mediator
of treatment resistance in cancer. Cancer Med. 7:3800–3811. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sasazawa Y, Futamura Y, Tashiro E and
Imoto M: Vacuolar H+-ATPase inhibitors overcome
Bcl-xL-mediated chemoresistance through restoration of a
caspase-independent apoptotic pathway. Cancer Sci. 100:1460–1467.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
von Schwarzenberg K, Lajtos T, Simon L,
Müller R, Vereb G and Vollmar AM: V-ATPase inhibition overcomes
trastuzumab resistance in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 8:9–19. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tavares-Valente D, Baltazar F, Moreira R
and Queirós O: Cancer cell bioenergetics and pH regulation
influence breast cancer cell resistance to paclitaxel and
doxorubicin. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 45:467–475. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pakula AA and Sauer RT: Genetic analysis
of protein stability and function. Annu Rev Genet. 23:289–310.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
MacArthur MW and Thornton JM: Influence of
proline residues on protein conformation. J Mol Biol. 218:397–412.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Muley H, Fadó R, Rodriguez-Rodríguez R and
Casals N: Drug uptake-based chemoresistance in breast cancer
treatment. Biochem Pharmacol. 177:1139592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fan S, Niu Y, Tan N, Wu Z, Wang Y, You H,
Ke R, Song J, Shen Q, Wang W, et al: LASS2 enhances
chemosensitivity of breast cancer by counteracting acidic tumor
microenvironment through inhibiting activity of V-ATPase proton
pump. Oncogene. 32:1682–1690. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu P, Chen H, Han L, Zou X and Shen W:
Expression and role of V1A subunit of V-ATPases in gastric cancer
cells. Int J Clin Oncol. 20:725–735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cotter K, Liberman R, Sun-Wada G, Wada Y,
Sgroi D, Naber S, Brown D, Breton S and Forgac M: The a3 isoform of
subunit a of the vacuolar ATPase localizes to the plasma membrane
of invasive breast tumor cells and is overexpressed in human breast
cancer. Oncotarget. 7:46142–46157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Katara GK, Jaiswal MK, Kulshrestha A,
Kolli B, Gilman-Sachs A and Beaman KD: Tumor-associated vacuolar
ATPase subunit promotes tumorigenic characteristics in macrophages.
Oncogene. 33:5649–5654. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jarmuz A, Chester A, Bayliss J, Gisbourne
J, Dunham I, Scott J and Navaratnam N: An anthropoid-specific locus
of orphan C to U RNA-editing enzymes on chromosome 22. Genomics.
79:285–296. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Burns MB, Temiz NA and Harris RS: Evidence
for APOBEC3B mutagenesis in multiple human cancers. Nat Genet.
45:977–983. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Roberts SA, Lawrence MS, Klimczak LJ,
Grimm SA, Fargo D, Stojanov P, Kiezun A, Kryukov GV, Carter SL,
Saksena G, et al: An APOBEC cytidine deaminase mutagenesis pattern
is widespread in human cancers. Nat Genet. 45:970–976. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Burns MB, Lackey L, Carpenter MA, Rathore
A, Land AM, Leonard B, Refsland EW, Kotandeniya D, Tretyakova N,
Nikas JB, et al: APOBEC3B is an enzymatic source of mutation in
breast cancer. Nature. 494:366–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sieuwerts AM, Schrijver WA, Dalm SU, de
Weerd V, Moelans CB, Hoeve NT, van Diest PJ, Martens JWM and van
Deurzen CH: Progressive APOBEC3B mRNA expression in distant breast
cancer metastases. PLoS One. 12:e01713432017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Sieuwerts AM, Willis S, Burns MB, Look MP,
Gelder ME, Schlicker A, Heideman MR, Jacobs H, Wessels L,
Leyland-Jones B, et al: Elevated APOBEC3B correlates with poor
outcomes for estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancers. Horm
Cancer. 5:405–413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang Z, Tao Y, Xu X, Cai F, Yu Y and Ma L:
Bufalin inhibits cell proliferation and migration of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells via APOBEC3F induced intestinal immune network for
IgA production signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
503:2124–2131. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang Z, Zhuang L, Yu Y, Zhou W, Lu Y, Xu
Q, Tang B and Chen X: Overexpression of APOBEC3F in tumor tissues
is potentially predictive for poor recurrence-free survival from
HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Discov Med. 20:349–356.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
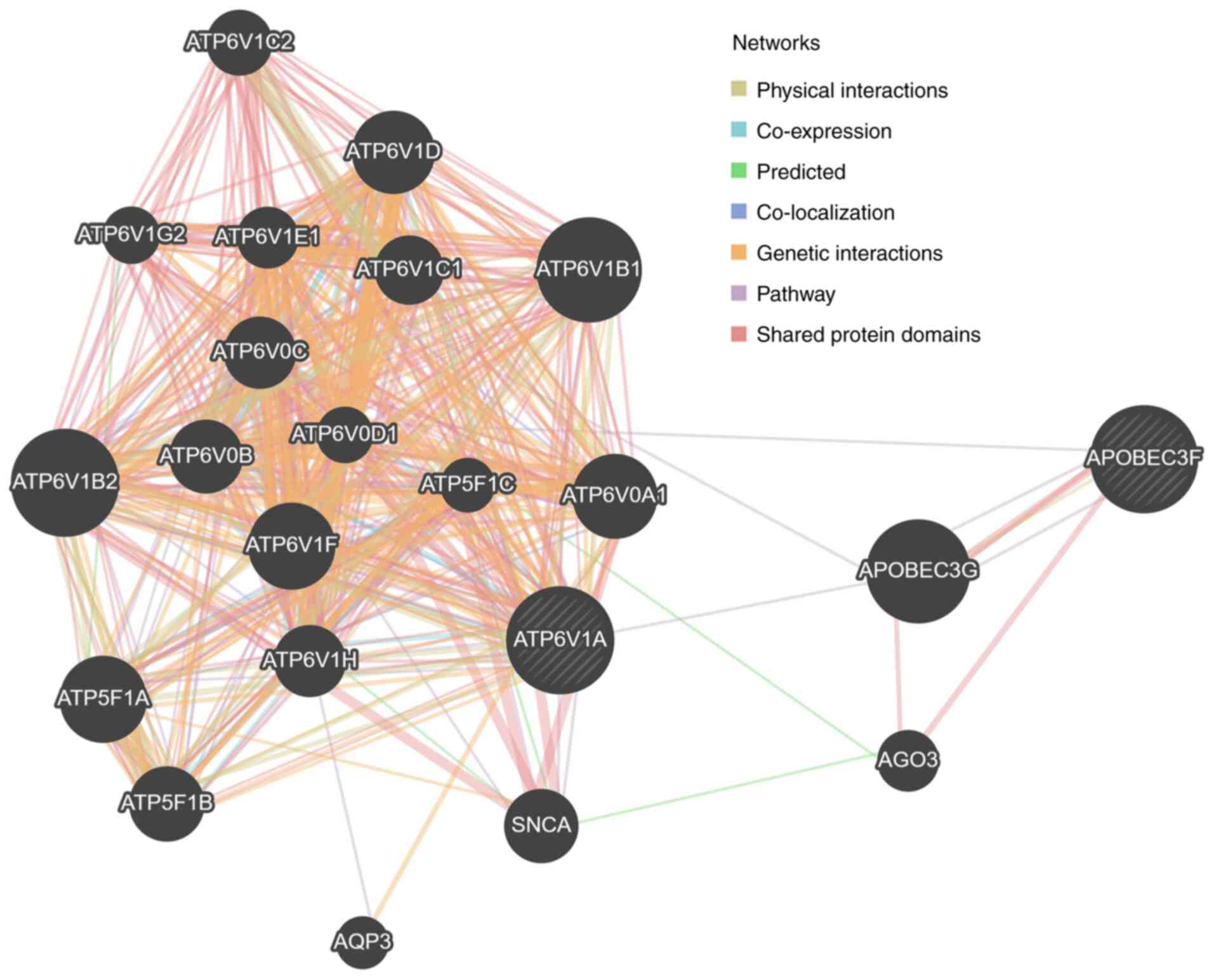
Warde-Farley D, Donaldson SL, Comes O,
Zuberi K, Badrawi R, Chao P, Franz M, Grouios C, Kazi F, Lopes CT,
et al: The GeneMANIA prediction server: Biological network
integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:W214–W220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chung CY, Shin HR, Berdan CA, Ford B, Ward
CC, Olzmann JA, Zoncu R and Nomura DK: Covalent targeting of the
vacuolar H(+)-ATPase activates autophagy via mTORC1 inhibition. Nat
Chem Biol. 15:776–785. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|