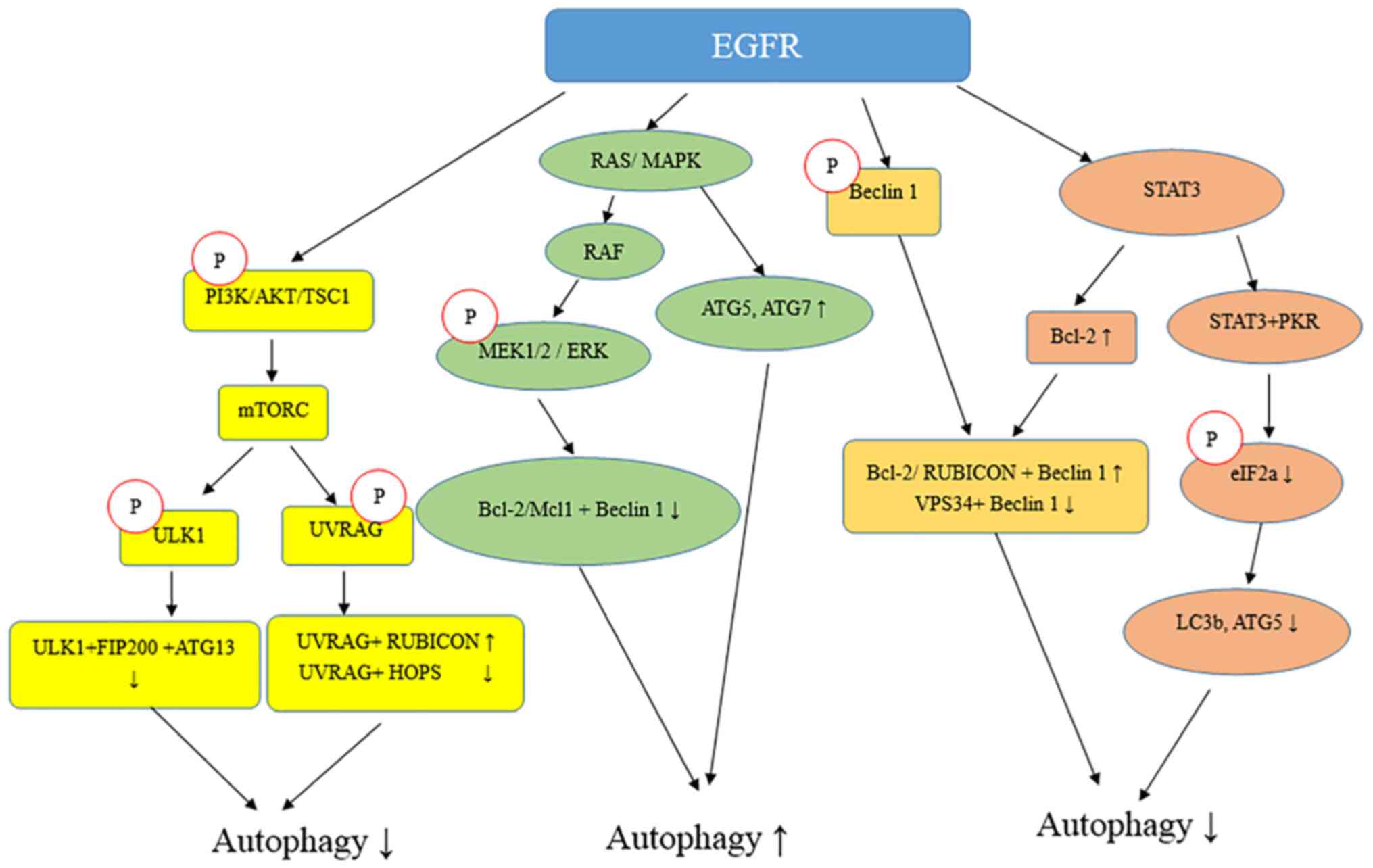
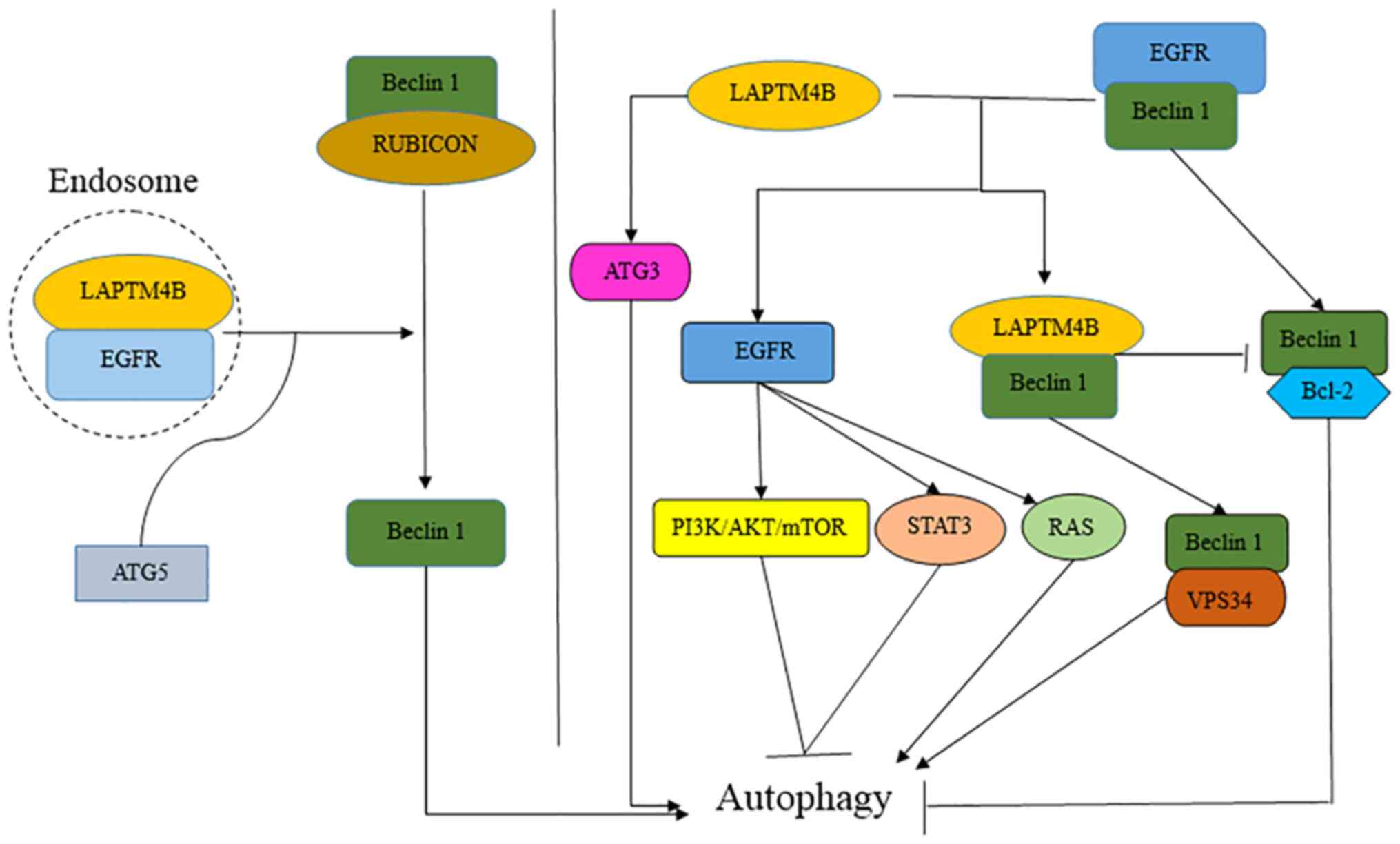
|
1
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdelmohsen K, Abe A, Abedin
MJ, Abeliovich H, Arozena AA, Adachi H, Adams CM, Adams PD, Adeli
K, et al: Guidelines for the use and interpretation of assays for
monitoring autophagy (3rd edition). Autophagy. 12:1–222. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Feng Y, He D, Yao Z and Klionsky DJ: The
machinery of macroautophagy. Cell Res. 24:24–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Henson ES and Gibson SB: Surviving cell
death through epidermal growth factor (EGF) signal transduction
pathways: Implications for cancer therapy. Cell Signal.
18:2089–2097. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jutten B and Rouschop KMA: EGFR signaling
and autophagy dependence for growth, survival, and therapy
resistance. Cell Cycle. 13:42–51. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Henson E, Chen Y and Gibson S: EGFR family
members' regulation of autophagy is at a crossroads of cell
survival and death in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 9:272017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sigismund S, Avanzato D and Lanzetti L:
Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol Oncol. 12:3–20. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mendelsohn X and Baselga J: Epidermal
growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin Oncol.
33:369–385. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Paez JG, Jänne PA, Lee JC, Tracy S,
Greulich H, Gabriel S, Herman P, Kaye KJ, Lindeman N, Boggon TJ, et
al: EGFR mutations in lung cancer: Correlation with clinical
response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 304:1497–1500. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Majem M and Remon J: Tumor heterogeneity:
Evolution through space and time in EGFR mutant non small cell lung
cancer patients. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2:226–237. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng Y, Gao S, Gao Y, Wang X and Chen Z:
Anti-EGFR antibody sensitizes colorectal cancer stem-like cells to
Fluorouracil-induced apoptosis by affecting autophagy. Oncotarget.
7:81402–81409. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han W, Pan H, Chen Y, Sun J, Wang Y, Li J,
Ge W, Feng L, Lin X, Wang X, et al: EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors
activate autophagy as a cytoprotective response in human lung
cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e186912011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wei Y, Zou Z, Becker N, Anderson M,
Sumpter R, Xiao G, Kinch L, Koduru P, Christudass CS, Veltri RW, et
al: EGFR-mediated phosphorylation of beclin 1 in autophagy
suppression, tumor progression and tumor chemoresistance. Cell.
154:1269–1284. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu XR, Zhou RL, Zhang QY, Zhang Y, Jin
YY, Lin M, Rui JA and Ye DX: Structure analysis and expressions of
a novel tetratransmembrane protein, lysosoma-associated protein
transmembrane 4 beta associated with hepatocellular carcinoma.
World J Gastroenterol. 10:1555–1559. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tooze SA and Yoshimori T: The origin of
the autophagosomal membrane. Nat Cell Biol. 12:831–835. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tan X, Thapa N, Sun Y and Anderson RA: A
kinase independent role for EGF receptor in autophagy initiation.
Cell. 160:145–160. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang F, Wu H, Zhang S, Lu J, Lu Y, Zhan P,
Fang Q, Wang F, Zhang X, Xie C and Yin Z: LAPTM4B facilitates tumor
growth and induces autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer
Manag Res. 11:2485–2497. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Y, Zhang Q, Tian R, Wang Q, Zhao JJ,
Iglehart JD, Wang ZC and Richardson AL: Lysosomal transmembrane
protein LAPTM4B promotes autophagy and tolerance to metabolic
stress in cancer cells. Cancer Res. 71:7481–7489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meng Y, Wang L, Chen D, Chang Y, Zhang M,
XU JJ, Zhou R and Zhang QY: LAPTM4B: An oncogene in various solid
tumors and its functions. Oncogene. 35:6359–6365. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang S, Zhang QY and Zhou RL: Relationship
between LAPTM4B gene polymorphism and susceptibility of primary
liver cancer. Ann Oncol. 23:1864–1869. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang B, Xu JJ, Zhou R and Zhang QY:
Association of LAPTM4B gene polymorphism with nasopharyngeal
carcinoma susceptibility in a Chinese population. Med Oncol.
30:4702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang H, Tian H, Yue W, Li L, Li S, Gao C,
Si L, Qi L, Lu M and Hu W: LAPTM4B polymorphism is associated with
nonsmall cell lung cancer susceptibility and prognosis. Oncol Rep.
31:2454–2460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shaker O, Taha F, Salah M and El-Marzouky
M: LAPTM4B gene expression and polymorphism as diagnostic markers
of breast cancer in Egyptian patients. J Med Biochem. 34:393–401.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xia LZ, Yin ZH, Ren YW, Shen L, Wu W, Li
XL, Guan P and Zhou BS: The relationship between LAPTM4B
polymorphisms and cancer risk in Chinese Han population: A
meta-analysis. Springerplus. 4:1792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang H, Xiong F, Wei X, Yang Y, McNutt MA
and Zhou RL: Overexpression of LAPTM4B-35 promotes growth and
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. Cancer
Lett. 294:236–244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Xiong F, Wei X, Yang H and Zhou R:
LAPTM4B-35, a novel tetratransmembrane protein and its PPRP motif
serve critical roles in proliferation and metastatic potential of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Sci. 100:2335–2340. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li L, Wei XH, Pan YP, Li HC, Yang H, He
QH, Pang Y, Shan Y, Xiong FX, Shao GZ and Zhou RL: LAPTM4B: A novel
cancer-associated gene motivates multidrug resistance through
efflux and activating PI3K/AKT signaling. Oncogene. 29:5785–5795.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Y, Zou L, Li Q, Haibe-Kains B, Tian R,
Li Y, Desmedt C, Sotiriou C, Szallasi Z, Iglehart JD, et al:
Amplification of LAPTM4B and YWHAZ contributes to chemotherapy
resistance and recurrence of breast cancer. Nat Med. 6:214–218.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou L, He XD, Yu JC, Zhou RL, Yang H, Qu
Q and Rui JA: Overexpression of LAPTM4B promotes growth of
gallbladder carcinoma cells in vitro. Am J Surg. 199:515–521. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou L, He XD, Cui QC, Zhou WX, Qu Q, Zhou
RL, Rui JA and Yu JC: Expression of LAPTM4B-35: A novel marker of
progression, invasiveness and poor prognosis of extrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 264:209–217. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu Y, Liu Y, Zhou R, Meng F, Gao Y, Yang
S, Li X, Yang M and Lou G: LAPTM4B polymorphisms is associated with
ovarian cancer susceptibility and its prognosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol.
42:413–419. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang Y, Yang H, McNutt MA, Xiong F, Xiu N,
Li L and Zhou R: LAPTM4B overexpression is an independent
prognostic marker in ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 20:1077–1083.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang H, Tian B, Yu H, Yao H and Gao Z:
LAPTM4B-35 protein as a potential therapeutic target in gastric
cancer. Tumour Biol. 35:12737–12742. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng XJ, Xu W, Zhang QY and Zhou RL:
Relationship between LAPTM4B gene polymorphism and susceptibility
of colorectal and esophageal cancers. Ann Oncol. 19:527–532. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Usman RM, Razzaq F, Akbar A, Farooqui AA,
Iftikhar A, Latif A, Hassan H, Zhao J, Carew JS, Nawrocki ST and
Anwer F: Role and mechanism of autophagy-regulating factors in
tumorigenesis and drug resistance. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol.
17:193–208. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Scarlatti F, Granata R, Meijer AJ and
Codogno P: Does autophagy have a license to kill mammalian cells?
Cell Death Differ. 16:12–20. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Eisenberg-Lerner A, Bialik S, Simon HU and
Kimchi A: Life and death partners: Apoptosis, autophagy and the
cross-talk between them. Cell Death Differ. 16:966–975. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang J, Ni J, Liu K, Yu Y, Xie M, Kang R,
Vernon P, Cao L and Tang D: HMGB1 promotes drug resistance in
osteosarcoma. Cancer Res. 72:230–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Pan B, Chen D, Huang J, Wang R, Feng B,
Song H and Chen L: HMGB1-mediated autophagy promotes docetaxel
resistance in human lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1652014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Tao H, Chen F, Liu H, Hu Y, Wang Y and Li
H: Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway activation reverses gemcitabine
resistance by attenuating beclin1-mediated autophagy in the MG63
human osteosarcoma cell line. Mol Med Rep. 16:1701–1706. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ying H, Qu D, Liu C, Ying T, Lv J, Jin S
and Xu H: Chemoresistance is associated with Beclin-1 and PTEN
expression in epithelial ovarian cancers. Oncol Lett. 9:1759–1763.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu Y, Zhao L, Ju Y, Li W, Zhang M, Jiao
Y, Zhang J, Wang S, Wang Y, Zhao M, et al: A novel androstenedione
derivative induces ROS-mediated autophagy and attenuates drug
resistance in osteosarcoma by inhibiting macrophage migration
inhibitory factor (MIF). Cell Death Dis. 5:e13612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Eum KH and Lee M: Targeting the autophagy
pathway using ectopic expression of beclin 1 in combination with
rapamycin in drug-resistant v-Ha-ras-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Mol
Cells. 31:231–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu MY, Fu J, Xu J, O'Malley BW and Wu RC:
Steroid receptor coactivator 3 regulates autophagy in breast cancer
cells through macrophage migration inhibitory factor. Cell Res.
22:1003–1021. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pietrocola F, Pol J, Vacchelli E, Baracco
EE, Levesque S, Castoldi F, Maiuri MC, Madeo F and Kroemer G:
Autophagy induction for the treatment of cancer. Autophagy.
12:1962–1964. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chude CI and Amaravadi RK: Targeting
autophagy in cancer: Update on clinical trials and novel
inhibitors. Int J Mol Sci. 18:12792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pellegrini P, Strambi A, Zipoli C,
Hägg-Olofsson M, Buoncervello M, Linder S and Milito AD: Acidic
extracellular pH neutralizes the autophagy-inhibiting activity of
chloroquine: Implications for cancer therapies. Autophagy.
10:562–571. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Fung C, Chen X, Grandis JR and Duvvuri U:
EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibition induces autophagy in cancer cells.
Cancer Biol Ther. 13:1417–1424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Gorzalczany Y, Gilad Y, Amihai D, Hammel
I, Sagi-Eisenberg R and Merimsky O: Combining an EGFR directed
tyrosine kinase inhibitor with autophagy-inducing drugs: A
beneficial strategy to combat non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer
Lett. 310:207–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pan B, Chen Y, Song H, Xu Y, Wang R and
Chen L: Mir-24-3p downregulation contributes to VP16-DDP resistance
in small-cell lung cancer by targeting ATG4A. Oncotarget.
6:317–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhu J, Li Y, Tian Z, Hua X, Gu J, Li J,
Liu C, Jin H, Wang Y, Jiang G, et al: ATG7 overexpression is
crucial for tumorigenic growth of bladder cancer in vitro and in
vivo by targeting the ETS2/miRNA196b/FOXO1/p27 axis. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 7:299–313. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen J, Zhang L, Zhou H, Wang W, Luo Y,
Yang H and Yi H: Inhibition of autophagy promotes cisplatin-induced
apoptotic cell death through Atg5 and beclin 1 in A549 human lung
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 17:6859–6865. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wu J, Li W, Ning J, Yu W, Rao T and Cheng
F: Long noncoding RNA UCA1 targets miR-582-5p and contributes to
the progression and drug resistance of bladder cancer cells through
ATG7-mediated autophagy inhibition. Onco Targets Ther. 12:495–508.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wu Z, Cai L, Lu J, Wang CD, Guan J, Chen
X, Wu J, Zheng W, Wu Z, Li Q and Su Z: MicroRNA-93 mediates
cabergoline-resistance by targeting ATG7 in prolactinoma. J
Endocrinol. Sep 1–2018.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
55
|
Lemmon MA and Schlessinger J: Cell
signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell. 141:1117–1134. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Botti J, Djavaheri-Mergny M, Pilatte Y and
Codogno P: Autophagy signaling and the cogwheels of cancer.
Autophagy. 2:67–73. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kim MJ, Woo SJ, Yoon CH, Lee JS, An S,
Choi YH, Hwang SG, Yoon G and Lee SJ: Involvement of autophagy in
oncogenic K-ras-induced malignant cell transformation. J Biol Chem.
286:12924–12932. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Elgendy M, Sheridan C, Brumatti G and
Martin SJ: Oncogenic ras-induced expression of noxa and beclin-1
promotes autophagic cell death and limits clonogenic survival. Mol
Cell. 42:23–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ge J, Liu Y, Li Q, Guo X, Gu L, Ma ZG and
Zhu YP: Resveratrol induces apoptosis and autophagy in T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia cells by inhibiting Akt/mTOR and activating
p38-MAPK. Biomed Environ Sci. 26:902–911. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Alers S, Löffler AS, Wesselborg S and
Stork B: Role of AMPK-mTOR-Ulk1/2 in the regulation of autophagy:
Cross talk, shortcuts, and feedbacks. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2–11. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim J, Kundu M, Viollet B and Guan KL:
AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of
Ulk1. Nat Cell Biol. 13:132–141. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Schmukler E, Kloog Y and Pinkas-Kramarski
R: Ras and autophagy in cancer development and therapy. Oncotarget.
5:577–586. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kim YM, Jung CH, Seo M, Kim EK, Park JM,
Bae SS and Kim DH: mTORC1 phosphorylates UVRAG to negatively
regulate autophagosome and endosome maturation. Mol Cell.
57:207–218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wu SY, Lan SH, Cheng DE, Chen WK, Shen CH,
Lee YR, Zuchini R and Liu HS: Ras-related tumorigenesis is
suppressed by BNIP3-mediated autophagy through inhibition of cell
proliferation. Neoplasia. 13:1171–1182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Byun JY, Yoon CH, An S, Park IC, Kang CM,
Kim MJ and Lee SJ: The Rac1/MKK7/JNK pathway signals upregulation
of Atg5 and subsequent autophagic cell death in response to
oncogenic ras. Carcinogenesis. 30:1880–1888. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Liu D, Lin J, Su J, Chen X, Jiang P and
Huang K: Glutamine deficiency promotes PCV2 infection through
induction of autophagy via activation of ROS-mediated JAK2/STAT3
signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 66:11757–11766. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Quesnelle KM, Boehm AL and Grandis JR:
STAT-mediated EGFR signaling in cancer. J Cell Biochem.
102:311–319. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Rouschop KMA, van den Beucken T, Dubois L,
Niessen H, Bussink J, Savelkouls K, Keulers T, Mujcic H, Landuyt W,
Voncken JW, et al: The unfolded protein response protects human
tumor cells during hypoxia through regulation of the autophagy
genes MAP1LC3B and ATG5. J Clin Invest. 120:127–141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shen S, Niso-Santano M, Adjemian S,
Takehara T, Malik SA, Minoux H, Souquere S, Mariño G, Lachkar S,
Senovilla L, et al: Cytoplasmic STAT3 represses autophagy by
inhibiting PKR activity. Mol Cell. 48:667–680. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Eimer S, Belaud-Rotureau MA, Airiau K,
Jeanneteau M, Laharanne E, Véron N, Vital A, Loiseau H, Merlio JP
and Belloc F: Autophagy inhibition cooperates with erlotinib to
induce glioblastoma cell death. Cancer Biol Ther. 11:1017–1027.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wang L, Meng Y and Zhang QZ: LAPTM4B is a
novel diagnostic and prognostic marker for lung adenocarcinoma and
associated with mutant EGFR. BMC Cancer. 19:2932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Tian M, Chen Y, Tian D, Qiao X, Ma Z and
Li J: Beclin1 antagonizes LAPTM4B-mediated EGFR overactivation in
gastric cancer cells. Gene. 626:48–53. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|