|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Van Cutsem E, Cervantes A, Nordlinger B
and Arnold D; ESMO Guidelines Working Group, : Metastatic
colorectal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 25 (Suppl 3):iii1–iii9. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Biller LH and Schrag D: Diagnosis and
treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: A review. JAMA.
325:669–685. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scheithauer W, Rosen H, Kornek GV, Sebesta
C and Depisch D: Randomised comparison of combination chemotherapy
plus supportive care with supportive care alone in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer. BMJ. 306:752–755. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chae YK, Arya A, Iams W, Cruz MR, Chandra
S, Choi J and Giles F: Current landscape and future of dual
anti-CTLA4 and PD-1/PD-L1 blockade immunotherapy in cancer: Lessons
learned from clinical trials with melanoma and non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). J Immunother Cancer. 6:392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stein A, Moehler M, Trojan J, Goekkurt E
and Vogel A: Immuno-oncology in GI tumours: Clinical evidence and
emerging trials of PD-1/PD-L1 antagonists. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
130:13–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boland CR and Goel A: Microsatellite
instability in colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2073–2087.e3. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jenkins MA, Hayashi S, O'Shea AM, Burgart
LJ, Smyrk TC, Shimizu D, Waring PM, Ruszkiewicz AR, Pollett AF,
Redston M, et al: Pathology features in Bethesda guidelines predict
colorectal cancer microsatellite instability: A population-based
study. Gastroenterology. 133:48–56. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kawakami H, Zaanan A and Sinicrope FA:
Microsatellite instability testing and its role in the management
of colorectal cancer. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 16:302015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Catalano I, Grassi E, Bertotti A and
Trusolino L: Immunogenomics of colorectal tumors: Facts and
hypotheses on an evolving Saga. Trends Cancer. 5:779–788. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marcus L, Lemery SJ, Keegan P and Pazdur
R: FDA approval summary: Pembrolizumab for the treatment of
microsatellite instability-high solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
25:3753–3758. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Overman MJ, Lonardi S, Leone F, McDermott
RS, Morse MA, Wong KYM, Neyns B, Leach JL, Garcia Alfonso P, Lee
JJ, et al: Nivolumab in patients with DNA mismatch repair
deficient/microsatellite instability high metastatic colorectal
cancer: Update from CheckMate 142. J Clin Oncol. 35 (Suppl
4):S5192017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Overman MJ, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, Lenz HJ,
Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, Morse MA, Van Cutsem E, McDermott R, Hill
A, et al: Durable clinical benefit with Nivolumab plus ipilimumab
in DNA mismatch repair-deficient/microsatellite instability-high
metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:773–779. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Overman MJ, Lonardi S, Wong KYM, Lenz HJ,
Gelsomino F, Aglietta M, Morse M, Van Cutsem E, McDermott RS, Hill
AG, et al: Nivolumab (NIVO) + low-dose ipilimumab (IPI) in
previously treated patients (pts) with microsatellite
instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic
colorectal cancer (mCRC): Long-term follow-up. J Clin Oncol. 37
(Suppl 4):S6352019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lenz HJJ, Van Cutsem E, Limon ML, Wong KY,
Hendlisz A, Aglietta M, Garcia-Alfonso P, Neyns B, Luppi G, Cardin
D, et al: Durable clinical benefit with nivolumab (NIVO) plus
low-dose ipilimumab (IPI) as first-line therapy in microsatellite
instability-high/mismatch repair deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic
colorectal cancer (mCRC). Ann Oncol. 29:viii7142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
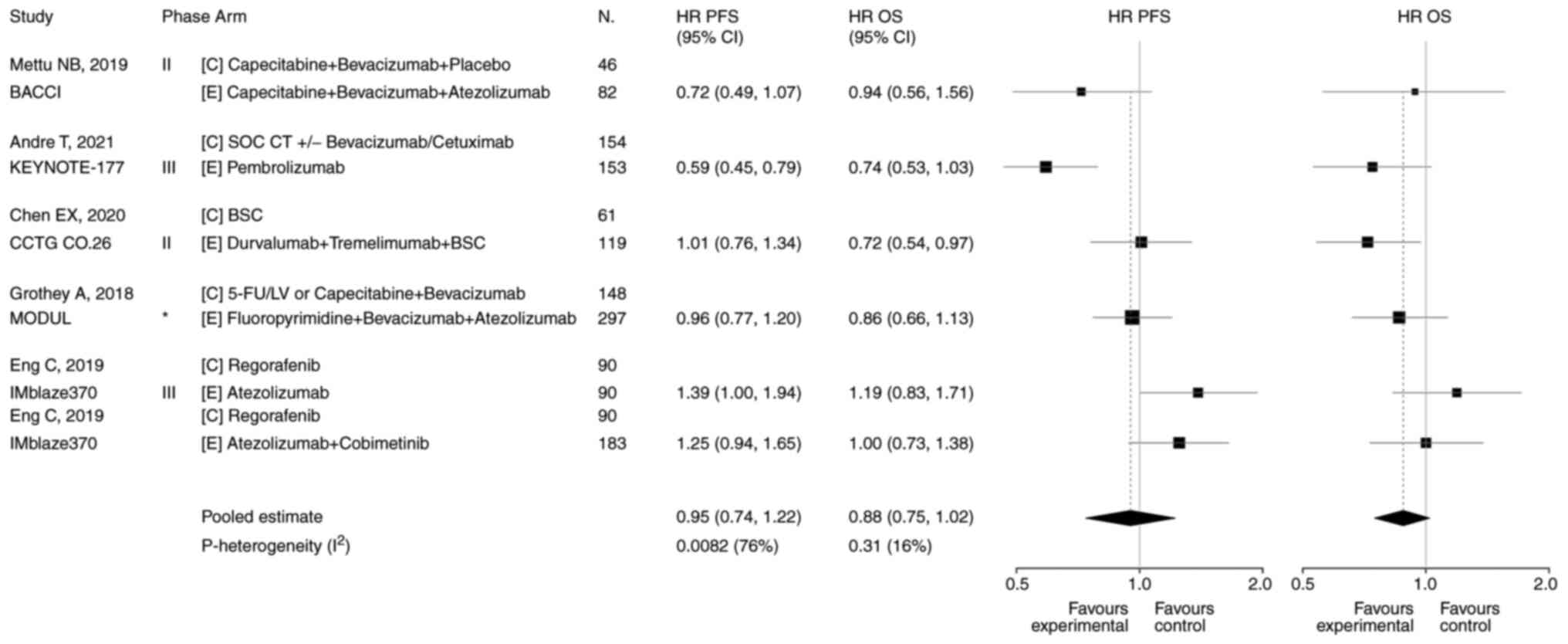
Andre T, Shiu KK, Kim TW, Jensen BV,
Jensen LH, Punt CJA, Smith DM, Garcia-Carbonero R, Alcaide J, Gibbs
P, et al: Final overall survival for the phase III KN177 study:
Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy in microsatellite
instability-high/mismatch repair deficient (MSI-H/dMMR) metastatic
colorectal cancer (mCRC). J Clin Oncol. 39 (Suppl 15):S35002021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
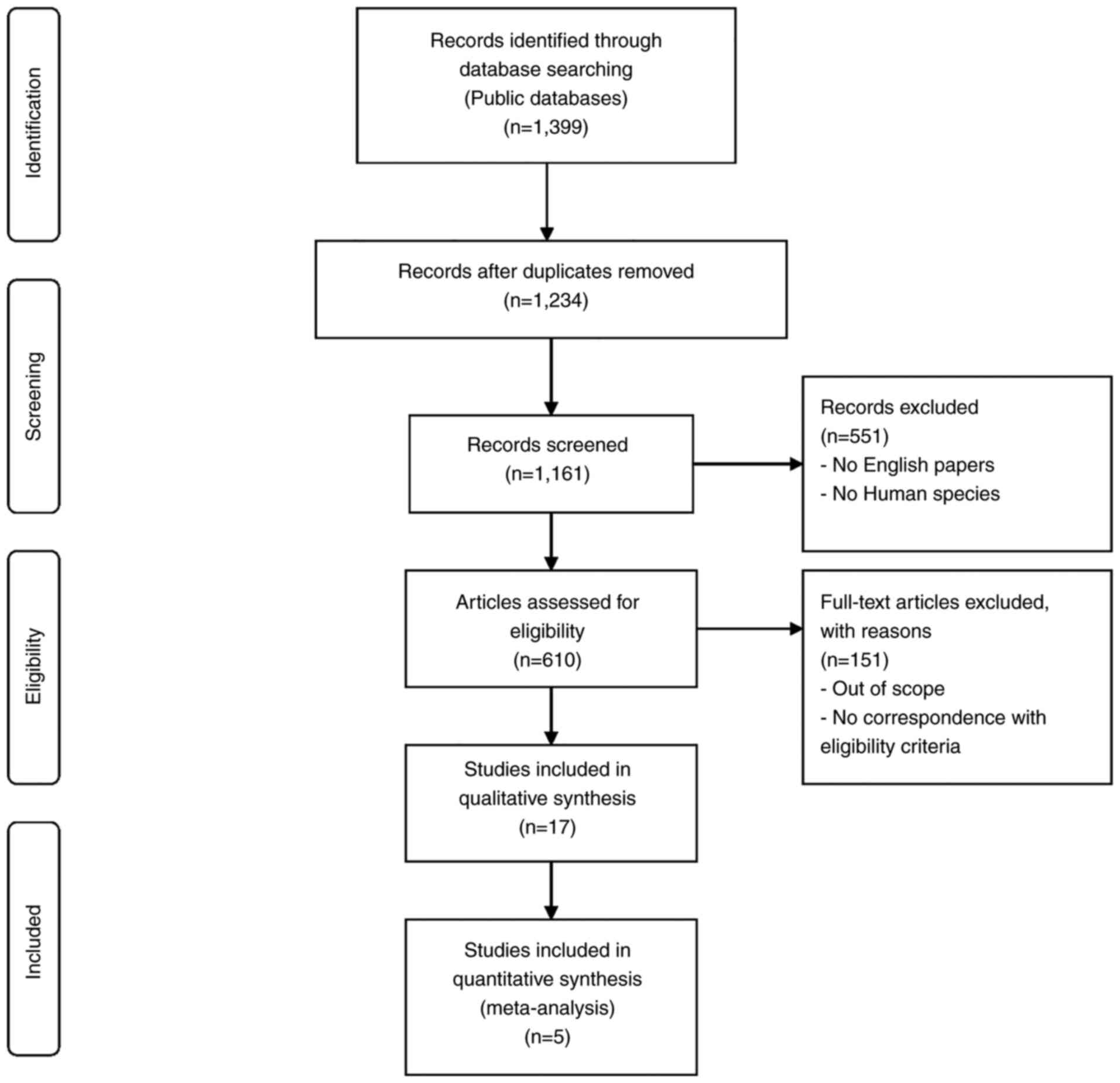
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group, : Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med.
6:e10000972009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rethlefsen ML, Kirtley S, Waffenschmidt S,
Ayala AP, Moher D, Page MJ and Koffel JB; PRISMA-S Group, :
PRISMA-S: An extension to the PRISMA statement for reporting
literature searches in systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 10:392021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Freites-Martinez A, Santana N,
Arias-Santiago S and Viera A: Using the common terminology criteria
for adverse events (CTCAE-Version 5.0) to evaluate the severity of
adverse events of anticancer therapies. Actas Dermosifiliogr (Engl
Ed). 112:90–92. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
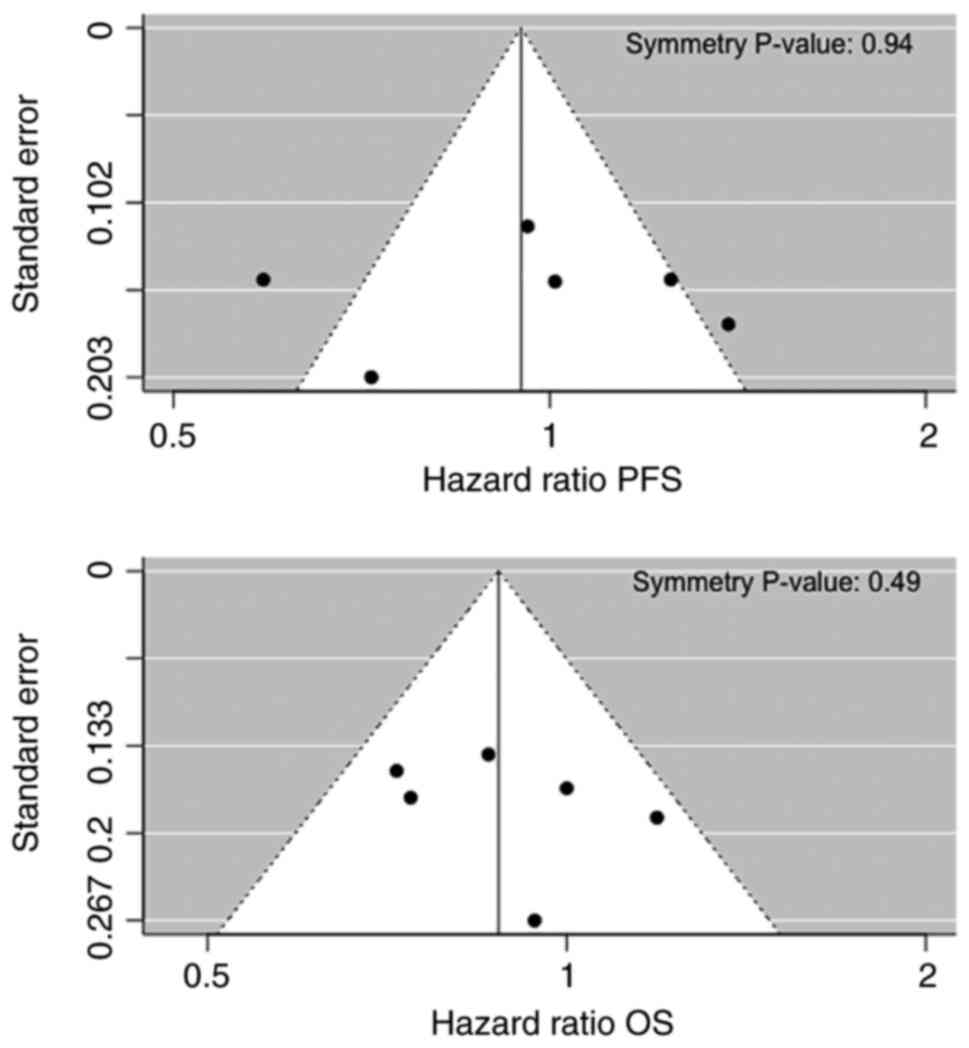
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Viechtbauer W: Conducting meta-analyses in
R with the metafor package. J Stat Softw. 36:1–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
R Core Team R, . A language and
environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical
Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2014.http://www.R-project.org/
|
|
24
|
O'Neil BH, Wallmark JM, Lorente D, Elez E,
Raimbourg J, Gomez-Roca C, Ejadi S, Piha-Paul SA, Stein MN, Abdul
Razak AR, et al: Safety and antitumor activity of the anti-PD-1
antibody pembrolizumab in patients with advanced colorectal
carcinoma. PLoS One. 12:e01898482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee HT, Lee SH and Heo YS: Molecular
interactions of antibody drugs targeting PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 in
immuno-oncology. Molecules. 24:11902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR,
Kemberling H, Eyring AD, Skora AD, Luber BS, Azad NS, Laheru D, et
al: PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl
J Med. 372:2509–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Le DT, Kim TW, Van Cutsem E, Geva R, Jäger
D, Hara H, Burge M, O'Neil B, Kavan P, Yoshino T, et al: Phase II
open-label study of pembrolizumab in treatment-refractory,
microsatellite instability-high/mismatch repair-deficient
metastatic colorectal cancer: KEYNOTE-164. J Clin Oncol. 38:11–19.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shiu KK, Andre T, Kim TW, Jensen BV,
Jensen LH, Punt CJA, Smith DM, Garcia-Carbonero R, Benavides M,
Gibbs P, et al: KEYNOTE-177: Phase III randomized study of
pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for microsatellite
instability-high advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 39
(Suppl 3):S62021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Callahan MK, Odunsi K, Sznol M, Nemunaitis
JJ, Ott PA, Dillon PM, Park AJ, Schwarzenberger P, Ricciardi T,
Macri MJ, et al: Phase 1 study to evaluate the safety and
tolerability of MEDI4736 (durvalumab, DUR) + tremelimumab (TRE) in
patients with advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 35 (Suppl
15):S30692017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chen EX, Jonker DJ, Loree JM, Kennecke HF,
Berry SR, Couture F, Ahmad CE, Goffin JR, Kavan P, Harb M, et al:
Effect of combined immune checkpoint inhibition vs. best supportive
care alone in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: The
Canadian Cancer Trials Group CO.26 study. JAMA Oncol. 6:831–838.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu L, Mayes PA, Eastman S, Shi H,
Yadavilli S, Zhang T, Yang J, Seestaller-Wehr L, Zhang SY, Hopson
C, et al: The BRAF and MEK inhibitors dabrafenib and trametinib:
Effects on immune function and in combination with immunomodulatory
antibodies targeting PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4. Clin Cancer Res.
21:1639–1651. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hellmann MD, Kim TW, Lee CB, Goh BC,
Miller WH Jr, Oh DY, Jamal R, Chee CE, Chow LQM, Gainor JF, et al:
Phase Ib study of atezolizumab combined with cobimetinib in
patients with solid tumors. Ann Oncol. 30:1134–1142. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eng C, Kim TW, Bendell J, Argilés G,
Tebbutt NC, Di Bartolomeo M, Falcone A, Fakih M, Kozloff M, Segal
NH, et al: Atezolizumab with or without cobimetinib versus
regorafenib in previously treated metastatic colorectal cancer
(IMblaze370): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised,
controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 20:849–861. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schmoll HJ, Arnold D, De Gramont A,
Ducreux M, Grothey A, O'Dwyer PJ, Van Cutsem E, Hermann F, Bosanac
I, Bendahmane B, et al: MODUL-a multicenter randomized clinical
trial of biomarker-driven maintenance therapy following first-line
standard induction treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: An
adaptable signal-seeking approach. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
144:1197–1204. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Grothey A, Tabernero J, Arnold D, De
Gramont A, Ducreux MP, O'Dwyer PJ, Van Cutsem E, Bosanac I, Srock
S, Mancao C, et al: Fluoropyrimidine (FP) + bevacizumab (BEV) +
atezolizumab vs. FP/BEV in BRAFwt metastatic colorectal cancer
(mCRC): Findings from Cohort 2 of MODUL-a multicentre, randomized
trial of biomarker-driven maintenance treatment following
first-line induction therapy. Ann Oncol. 29:VIII714–VIII715. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mettu NB, Twohy E, Ou FS, Halfdanarson TR,
Lenz HJ, Breakstone R, Boland PM, Crysler O, Wu C, Grothey A, et
al: BACCI: A phase II randomized, double-blind, multicenter,
placebo-controlled study of capecitabine (C) bevacizumab (B) plus
atezolizumab (A) or placebo (P) in refractory metastatic colorectal
cancer (mCRC): An ACCRU network study. Ann Oncol. 30:v2032019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Messersmith WA: NCCN Guidelines Updates:
Management of metastatic colorectal cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
17:599–601. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Topalian SL, Drake CG and Pardoll DM:
Immune checkpoint blockade: A common denominator approach to cancer
therapy. Cancer Cell. 27:450–461. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kyi C and Postow MA: Immune checkpoint
inhibitor combinations in solid tumors: Opportunities and
challenges. Immunotherapy. 8:821–837. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ganesh K, Stadler ZK, Cercek A, Mendelsohn
RB, Shia J, Segal NH and Diaz LA Jr: Immunotherapy in colorectal
cancer: Rationale, challenges and potential. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 16:361–375. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Overman MJ, Yothers G, Jacobs SA, Sanoff
HK, Cohen DJ, Guthrie KA, Henry NL, Ganz PA, Kopetz S, Lucas PC, et
al: NRG-GI004/SWOG-S1610: Colorectal Cancer Metastatic dMMR
Immuno-Therapy (COMMIT) Study-A randomized phase III study of
atezolizumab (atezo) monotherapy versus mFOLFOX6/bevacizumab/atezo
in the first-line treatment of patients (pts) with deficient DNA
mismatch repair (dMMR) or microsatellite instability high (MSI-H)
metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). J Clin Oncol. 39 (Suppl
3):TPS1582021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Sinicrope FA, Ou FS, Zemla T, Nixon AB,
Mody K, Levasseur A, Dueck AC, Dhanarajan AR, Lieu CH, Cohen DJ, et
al: Randomized trial of standard chemotherapy alone or combined
with atezolizumab as adjuvant therapy for patients with stage III
colon cancer and deficient mismatch repair (ATOMIC, Alliance
A021502). J Clin Oncol. 37 (Suppl 15):e151692019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
He S, Hu D, Feng H, Xue Y, Jin J and Wang
X: Efficacy of immunotherapy with PD-1 inhibitor in colorectal
cancer: A meta-analysis. J Comp Eff Res. 9:1285–1292. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xie YH, Chen YX and Fang JY: Comprehensive
review of targeted therapy for colorectal cancer. Signal Transduct
Target Ther. 5:222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wan L, Wang Z, Xue J, Yang H and Zhu Y:
Tumor mutation burden predicts response and survival to immune
checkpoint inhibitors: A meta-analysis. Transl Cancer Res.
9:5437–5449. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Schrock AB, Ouyang C, Sandhu J, Sokol E,
Jin D, Ross JS, Miller VA, Lim D, Amanam I, Chao J, et al: Tumor
mutational burden is predictive of response to immune checkpoint
inhibitors in MSI-high metastatic colorectal cancer. Ann Oncol.
30:1096–1103. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Llosa NJ, Cruise M, Tam A, Wicks EC,
Hechenbleikner EM, Taube JM, Blosser RL, Fan H, Wang H, Luber BS,
et al: The vigorous immune microenvironment of microsatellite
instable colon cancer is balanced by multiple counter-inhibitory
checkpoints. Cancer Discov. 5:43–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Parikh AR, Clark JW, Wo JYL, Yeap BY,
Allen JN, Blaszkowsky LS, Ryan DP, Giantonio BJ, Weekes CD, Zhu AX,
et al: A phase II study of ipilimumab and nivolumab with radiation
in microsatellite stable (MSS) metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma
(mCRC). J Clin Oncol. 37 (Suppl 15):S35142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lee JJ, Yothers G, George TJ, Fakih M,
Basu Mallick A, Maalouf BN, Krauss JC, Heron DE, Allegra CJ and
Jacobs SA: NSABP FC-9: Phase II study of dual immune checkpoint
blockade (ICB) with durvalumab (D) plus tremelimumab (T) following
palliative hypofractionated radiotherapy (SBRT) in patients (pts)
with microsatellite-stable (MSS) metastatic colorectal cancer
(mCRC) progressing on chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 36 (Suppl
15):e156812018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Monjazeb A, Giobbie-Hurder A, Lako A,
Tesfaye AA, Stroiney A, Gentzler RD, Jabbour S, Alese OB, Rahma OE,
Cleary JM, et al: Analysis of colorectal cancer patients treated on
ETCTN 10021: A multicenter randomized trial of combined PD-L1 and
CTLA-4 inhibition with targeted low-dose or hypofractionated
radiation. J Clin Oncol. 37 (Suppl 8):S492019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
A Phase Ib study to evaluate the safety,
efficacy, pharmacokinetics of cibisatamab in combination with
atezolizumab after pretreatment with obinutuzumab in participants
with previously treated metastatic colorectal adenocarcinoma.
ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier. NCT03866239. Other Study ID Numbers:
CO40939; EudraCT Number: 2018-003198-93. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03866239March
31–2021
|
|
52
|
Martinelli E, Troiani T, Cardone C,
Ciardiello D, Zanaletti N, Borrelli C, Terminiello M, Avallone A,
Falcone A, Maiello E, et al: Phase II study of avelumab in
combination with cetuximab as a rechallenge strategy in pre-treated
RAS wild type metastatic colorectal cancer patients: CAVE
(cetuximab-avelumab) colon. Ann Oncol. 30:v2512019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Stein A, Binder M, Goekkurt E, Lorenzen S,
Riera-Knorrenschild J, Depenbusch R, Ettrich TJ, Doerfel S,
Al-Batran SE, Karthaus M, et al: Avelumab and cetuximab in
combination with FOLFOX in patients with previously untreated
metastatic colorectal cancer (MCRC): Final results of the phase II
AVETUX trial (AIO-KRK-0216). J Clin Oncol. 38 (Suppl 4):S962020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Van Den Eynde M, Huyghe N, De Cuyper A,
Sinapi I, Ferrier M, Gilet M, Van Maanen A, Castella ML, Galon J
and Carrasco J: Interim analysis of the AVETUXIRI Trial: Avelumab
combined with cetuximab and irinotecan for treatment of refractory
microsatellite stable (MSS) metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC)-A
proof of concept, open-label, non-randomized phase IIa study. J
Clin Oncol. 39 (Suppl 3):S802021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Martinelli E, Ciardiello D, Martini G,
Troiani T, Cardone C, Vitiello PP, Normanno N, Rachiglio AM,
Maiello E, Latiano T, et al: Implementing anti-epidermal growth
factor receptor (EGFR) therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer:
Challenges and future perspectives. Ann Oncol. 31:30–40. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Damato A, Berselli A, Iachetta F,
Romagnani A, Larocca M, Garcia Arias A, Antonuzzo L, Nasti G,
Bergamo F and Pinto C: Preliminary safety analysis of phase II
open-label NIVACOR trial (GOIRC-03-2018) in patients with advanced
colorectal cancer RAS or BRAF mutated. J Clin Oncol. 39 (Suppl
3):S372021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Antoniotti C, Borelli B, Rossini D,
Pietrantonio F, Morano F, Salvatore L, Lonardi S, Marmorino F,
Tamberi S, Corallo S, et al: AtezoTRIBE: A randomised phase II
study of FOLFOXIRI plus bevacizumab alone or in combination with
atezolizumab as initial therapy for patients with unresectable
metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 20:6832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cousin S, Bellera CA, Guégan JP,
Gomez-Roca CA, Metges JP, Adenis A, Pernot S, Cantarel C, Kind M,
Toulmonde M, et al: REGOMUNE: A phase II study of regorafenib plus
avelumab in solid tumors-Results of the non-MSI-H metastatic
colorectal cancer (mCRC) cohort. J Clin Oncol. 38 (Suppl
15):S40192020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Siena S, Sartore-Bianchi A, Personeni N,
Pietrantonio F, Germano G, Amatu A, Bonoldi E, Valtorta E, Barault
L, Di Nicolantonio F, et al: Pembrolizumab in MMR-proficient
metastatic colorectal cancer pharmacologically primed to trigger
dynamic hypermutation status: The ARETHUSA trial. J Clin Oncol. 37
(Suppl 15):TPS26592019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab, Temozolomide in
Microsatellite Stable, MGMT Silenced Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
(MAYA). ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier. NCT03832621. Other Study ID
Number: INT202-18. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03832621March
31–2021
|
|
61
|
Basket Combination Study of Inhibitors of
DNA Damage Response, Angiogenesis and Programmed Death Ligand 1 in
Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors (DAPPER). ClinicalTrials.gov
Identifier. NCT03851614. Other Study ID Number: DAPPER-001.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03851614March
31–2021
|
|
62
|
Tintelnot J and Stein A: Immunotherapy in
colorectal cancer: Available clinical evidence, challenges and
novel approaches. World J Gastroenterol. 25:3920–3928. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Huyghe N, Baldin P and Van Den Eynde M:
Immunotherapy with immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal
cancer: What is the future beyond deficient mismatch-repair
tumours? Gastroenterol Rep (Oxf). 8:11–24. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lee WS, Yang H, Chon HJ and Kim C:
Combination of anti-angiogenic therapy and immune checkpoint
blockade normalizes vascular-immune crosstalk to potentiate cancer
immunity. Exp Mol Med. 52:1475–1485. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ganesh S, Shui X, Craig KP, Park J, Wang
W, Brown BD and Abrams MT: RNAi-Mediated beta-catenin inhibition
promotes T cell infiltration and antitumor activity in combination
with immune checkpoint blockade. Mol Ther. 26:2567–2579. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bacac M, Colombetti S, Herter S, Sam J,
Perro M, Chen S, Bianchi R, Richard M, Schoenle A, Nicolini V, et
al: CD20-TCB with obinutuzumab pretreatment as next-generation
treatment of hematologic malignancies. Clin Cancer Res.
24:4785–4797. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Taïeb J, André T, El Hajbi F, Barbier E,
Toullec C, Kim S, Bouche O, Di Fiore F, Chauvenet M, Perrier H, et
al: Avelumab versus standard second line treatment chemotherapy in
metastatic colorectal cancer patients with microsatellite
instability: The SAMCO-PRODIGE 54 randomised phase II trial. Dig
Liver Dis. 53:318–323. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rodriguez-Pascual J, Ayuso-Sacido A and
Belda-Iniesta C: Drug resistance in cancer immunotherapy: New
strategies to improve checkpoint inhibitor therapies. Cancer Drug
Resist. 2:980–993. 2019.
|
|
69
|
Ghiringhelli F and Fumet JD: Is there a
place for immunotherapy for metastatic microsatellite stable
colorectal cancer? Front Immunol. 10:18162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shan T, Chen S, Wu T, Yang Y, Li S and
Chen X: PD-L1 expression in colon cancer and its relationship with
clinical prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 12:1764–1769.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Domingo E, Freeman-Mills L, Rayner E,
Glaire M, Briggs S, Vermeulen L, Fessler E, Medema JP, Boot A,
Morreau H, et al: Somatic POLE proofreading domain mutation, immune
response, and prognosis in colorectal cancer: A retrospective,
pooled biomarker study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1:207–216.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tsantoulis P, Hill LA, Walker SM, Wirapati
P, Graham DM, Wilson RH, Coyle V, Delorenzi M, HarkinD P, Kennedy
RD and Tejpar S: Association of a specific innate immune response
to DNA damage with DNA repair deficient colorectal cancers. J Clin
Oncol. 34:30352016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Sun G, Dong X, Tang X, Qu H, Zhang H and
Zhao E: The prognostic value of immunoscore in patients with
colorectal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer
Med. 8:182–189. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Saito T, Nishikawa H, Wada H, Nagano Y,
Sugiyama D, Atarashi K, Maeda Y, Hamaguchi M, Ohkura N, Sato E, et
al: Two FOXP3(+) CD4(+) T cell subpopulations distinctly control
the prognosis of colorectal cancers. Nat Med. 22:679–684. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Spallanzani A, Gelsomino F, Caputo F,
Santini C, Andrikou K, Orsi G, Rimini M, Pipitone S, Riggi L,
Bardasi C, et al: Immunotherapy in the treatment of colorectal
cancer: A new kid on the block. J Cancer Metastasis Treat.
4:282018. View Article : Google Scholar
|