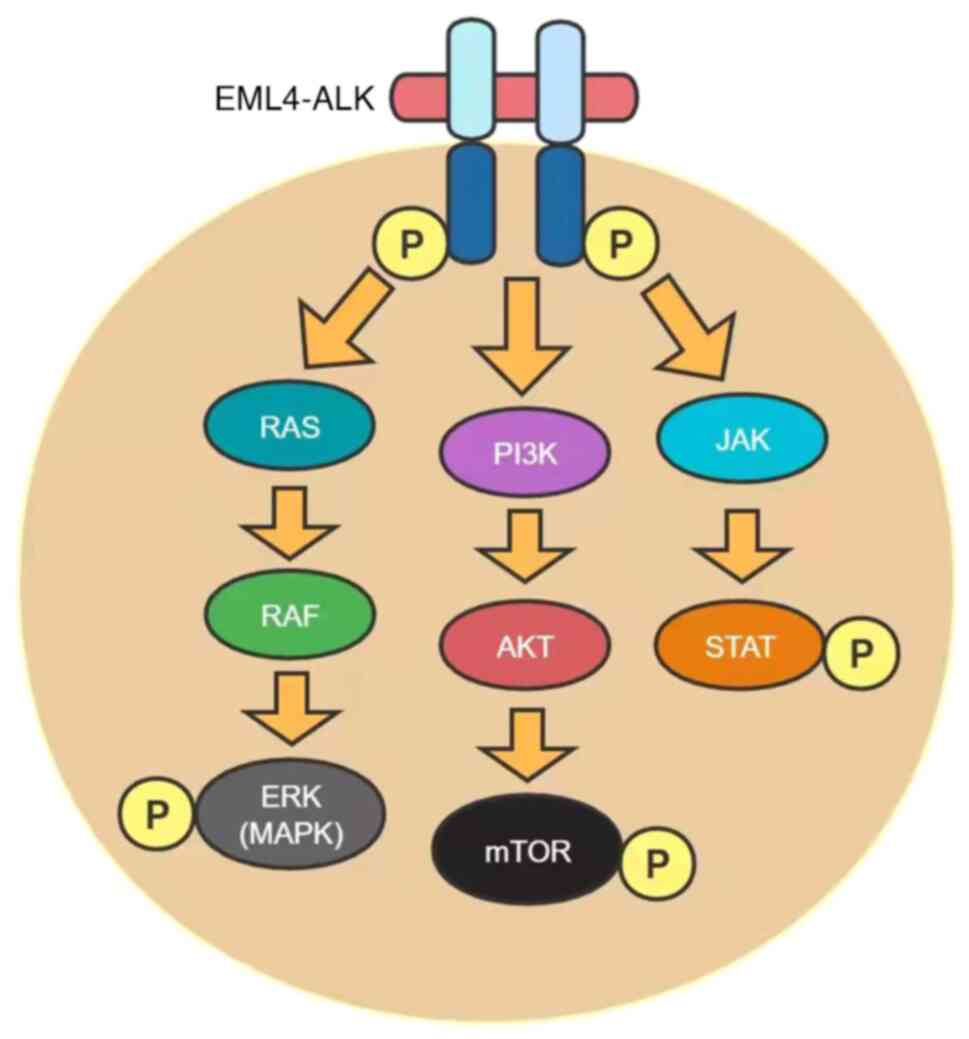
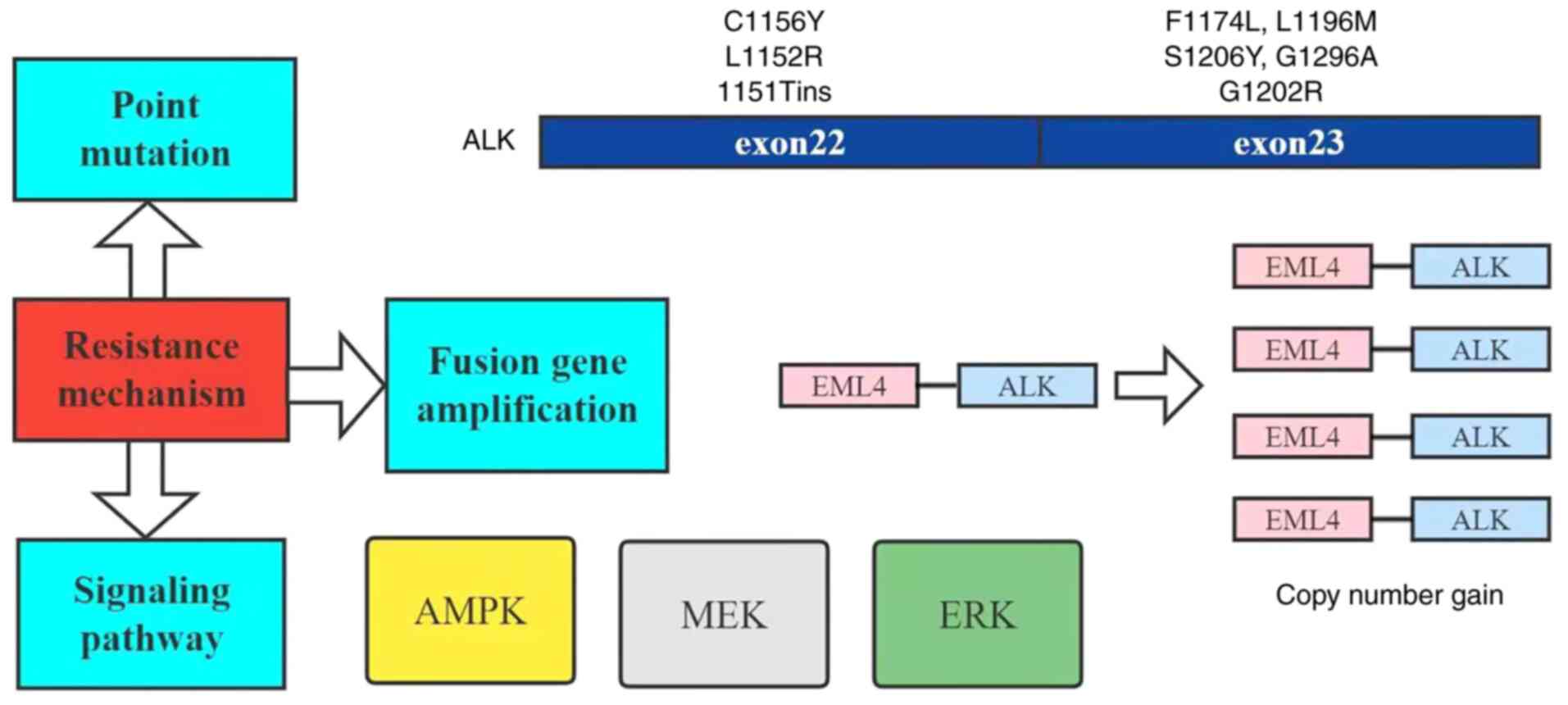
|
1
|
Rotow J and Bivona TG: Understanding and
targeting resistance mechanisms in NSCLC. Nat Rev Cancer.
17:637–658. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ye Z, Huang Y, Ke J, Zhu X, Leng S and Luo
H: Breakthrough in targeted therapy for non-small cell lung cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 133:1110792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang L, Li N, Wang M, Zhang YH, Yan LD,
Zhou W, Yu ZQ, Peng XC and Cai J: Tumorigenic effect of TERT and
its potential therapeutic target in NSCLC (Review). Oncol Rep.
46:1822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Brueckl WM, Ficker JH and Zeitler G:
Clinically relevant prognostic and predictive markers for
immune-checkpoint-inhibitor (ICI) therapy in non-small cell lung
cancer (NSCLC). BMC Cancer. 20:11852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Imyanitov EN, Iyevleva AG and Levchenko
EV: Molecular testing and targeted therapy for non-small cell lung
cancer: Current status and perspectives. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
157:1031942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Li D, Luo H and Zhu X: Circular
RNAs: The star molecules in cancer. Mol Aspects Med. 70:141–152.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Guo B, Li D, Du L and Zhu X: piRNAs:
Biogenesis and their potential roles in cancer. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 39:567–575. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gerlinger M: Targeted drugs ramp up cancer
mutability. Science. 366:1452–1453. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liang G, Fan W, Luo H and Zhu X: The
emerging roles of artificial intelligence in cancer drug
development and precision therapy. Biomed Pharmacother.
128:1102552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li S, Zhang Z, Lai WF, Cui L and Zhu X:
How to overcome the side effects of tumor immunotherapy. Biomed
Pharmacother. 130:1106392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ceccon M, Mologni L, Bisson W, Scapozza L
and Gambacorti-Passerini C: Crizotinib-resistant NPM-ALK mutants
confer differential sensitivity to unrelated Alk inhibitors. Mol
Cancer Res. 11:122–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Toyokawa G, Hirai F, Inamasu E, Yoshida T,
Nosaki K, Takenaka T, Yamaguchi M, Seto T, Takenoyama M and
Ichinose Y: Secondary mutations at I1171 in the ALK gene confer
resistance to both Crizotinib and Alectinib. J Thorac Oncol.
9:e86–e87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gainor JF, Dardaei L, Yoda S, Friboulet L,
Leshchiner I, Katayama R, Dagogo-Jack I, Gadgeel S, Schultz K,
Singh M, et al: Molecular mechanisms of resistance to first- and
second-generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer.
Cancer Discov. 6:1118–1133. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Toyokawa G and Seto T: Updated evidence on
the mechanisms of resistance to ALKInhibitors and strategies to
overcome such resistance: Clinical and preclinical data. Oncol Res
Treat. 38:291–298. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Costa DB: Clinical development and
approval of second generation ALK inhibitors for ALKrearranged lung
cancer. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 3:373–375. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Roskoski R Jr: ROS1 protein-tyrosine
kinase inhibitors in the treatment of ROS1 fusion protein-driven
non-small cell lung cancers. Pharmacol Res. 121:202–212. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shaw AT, Kim DW, Mehra R, Tan DS, Felip E,
Chow LQ, Camidge DR, Vansteenkiste J, Sharma S, De Pas T, et al:
Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J
Med. 370:1189–1197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rothschild SI: New treatment options for
ALK+ advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Critical appraisal of
ceritinib. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 12:735–741. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rossi A: Alectinib for ALK-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 9:1005–1013.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kong X, Pan P, Sun H, Xia H, Wang X, Li Y
and Hou T: Drug discovery targeting anaplastic lymphoma kinase
(ALK). J Med Chem. 62:10927–10954. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Qian M, Zhu B, Wang X and Liebman M: Drug
resistance in ALK-positiveNon-small cell lungcancer patients. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 64:150–157. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, Takada S,
Yamashita Y, Ishikawa S, Fujiwara S, Watanabe H, Kurashina K,
Hatanaka H, et al: Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK
fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature. 448:561–566.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Katayama R, Lovly CM and Shaw AT:
Therapeutic targeting of anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer:
A paradigm for precision cancer medicine. Clin Cancer Res.
21:2227–2235. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Morales La Madrid A, Campbell N, Smith S,
Cohn SL and Salgia R: Targeting ALK: A promising strategy for the
treatment of non-small cell lung cancer, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma,
and neuroblastoma. Target Oncol. 7:199–210. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shaw AT and Solomon B: Targeting
anaplastic lymphoma kinase in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
17:2081–2086. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Z, Sasaki T, Tan X, Carretero J,
Shimamura T, Li D, Xu C, Wang Y, Adelmant GO, Capelletti M, et al:
Inhibition of ALK, PI3K/MEK, and HSP90 in murine lung
adenocarcinoma induced by EML4-ALK fusion oncogene. Cancer Res.
70:9827–9836. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pyo KH, Lim SM, Kim HR, Sung YH, Yun MR,
Kim SM, Kim H, Kang HN, Lee JM, Kim SG, et al: Establishment of a
conditional transgenic mouse model recapitulating EML4-ALK-positive
human non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 12:491–500. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takeuchi K, Choi YL, Soda M, Inamura K,
Togashi Y, Hatano S, Enomoto M, Takada S, Yamashita Y, Satoh Y, et
al: Multiplex reverse transcription-PCR screening for
EML4-ALKfusion transcripts. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6618–6624. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sharma GG, Mota I, Mologni L, Patrucco E,
Gambacorti-Passerini C and Chiarle R: Tumor resistance against
ALKTargeted therapy-where it comes from and where it goes. Cancers
(Basel). 10:622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maddalo D, Manchado E, Concepcion CP,
Bonetti C, Vidigal JA, Han YC, Ogrodowski P, Crippa A, Rekhtman N,
de Stanchina E, et al: In vivo engineering of oncogenic chromosomal
rearrangements with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. Nature. 516:423–427.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rodig SJ, Mino-Kenudson M, Dacic S, Yeap
BY, Shaw A, Barletta JA, Stubbs H, Law K, Lindeman N, Mark E, et
al: Unique clinicopathologic features characterize ALK-rearranged
lung adenocarcinoma in the western population. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5216–5223. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gristina V, La Mantia M, Iacono F, Galvano
A, Russo A and Bazan V: The emerging therapeutic landscape of ALK
inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
13:4742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Du X, Shao Y, Qin HF, Tai YH and Gao HJ:
ALK-rearrangement in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac
Cancer. 9:423–430. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Camidge DR, Bang YJ, Kwak EL, Iafrate AJ,
Varella-Garcia M, Fox SB, Riely GJ, Solomon B, Ou SH, Kim DW, et
al: Activity and safety of crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer: Updated results from a phase 1 study.
Lancet Oncol. 13:1011–1019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Blackhall F, Ross Camidge D, Shaw AT,
Soria JC, Solomon BJ, Mok T, Hirsh V, Jänne PA, Shi Y, Yang PC, et
al: Final results of the large-scale multinational trial PROFILE
1005: Efficacy and safety of crizotinib in previously treated
patients with advanced/metastatic ALK-positive non-small-cell lung
cancer. ESMO Open. 2:e0002192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nishio M, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K,
Solomon BJ, Shaw AT, Hashigaki S, Ohki E, Usari T, Paolini J, et
al: Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in Asian patients with
ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res Treat.
50:691–700. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Solomon BJ, Kim DW, Wu YL, Nakagawa K,
Mekhail T, Felip E, Cappuzzo F, Paolini J, Usari T, Tang Y, et al:
Final overall survival analysis from a study comparing first-line
crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-mutation-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:2251–2258. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim DW, Mehra R, Tan DSW, Felip E, Chow
LQM, Camidge DR, Vansteenkiste J, Sharma S, De Pas T, Riely GJ, et
al: Activity and safety of ceritinib in patients with
ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-1): Updated
results from the multicentre, open-label, phase 1 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 17:452–463. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Crinò L, Ahn MJ, De Marinis F, Groen HJ,
Wakelee H, Hida T, Mok T, Spigel D, Felip E, Nishio M, et al:
Multicenter phase ii study of whole-body and intracranial activity
with ceritinib in patients With ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung
cancer previously treated with chemotherapy and crizotinib: Results
from ASCEND-2. J Clin Oncol. 34:2866–2873. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Soria JC, Tan DSW, Chiari R, Wu YL,
Paz-Ares L, Wolf J, Geater SL, Orlov S, Cortinovis D, Yu CJ, et al:
First-line ceritinib versus platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced
ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer (ASCEND-4): A randomised,
open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 389:917–929. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hida T, Nokihara H, Kondo M, Kim YH, Azuma
K, Seto T, Takiguchi Y, Nishio M, Yoshioka H, Imamura F, et al:
Alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer (J-ALEX): An open-label, randomised
phase 3 trial. Lancet. 390:29–39. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pérol M, Pavlakis N, Levchenko E, Platania
M, Oliveira J, Novello S, Chiari R, Moran T, Mitry E, Nüesch E, et
al: Patient-reported outcomes from the randomized phase III ALEX
study of alectinib versus crizotinib in patients with ALK-positive
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 138:79–87. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Camidge DR, Dziadziuszko R, Peters S, Mok
T, Noe J, Nowicka M, Gadgeel SM, Cheema P, Pavlakis N, de Marinis
F, et al: Updated efficacy and safety data and impact of the
EML4-ALK fusion variant on the efficacy of alectinib in untreated
ALK-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer in the global
phase III ALEX study. J Thorac Oncol. 14:1233–1243. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Camidge DR, Kim HR, Ahn MJ, Yang JCH, Han
JY, Hochmair MJ, Lee KH, Delmonte A, García Campelo MR, Kim DW, et
al: Brigatinib versus crizotinib in advanced ALK inhibitor-naive
ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: Second interim analysis of
the phase III ALTA-1L Trial. J Clin Oncol. 38:3592–3603. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Solomon BJ, Besse B, Bauer TM, Felip E,
Soo RA, Camidge DR, Chiari R, Bearz A, Lin CC, Gadgeel SM, et al:
Lorlatinib in patients with ALK-positive non-small-cell lung
cancer: Results from a global phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol.
19:1654–1667. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Friboulet L, Li N, Katayama R, Lee CC,
Gainor JF, Crystal AS, Michellys PY, Awad MM, Yanagitani N, Kim S,
et al: The ALK inhibitor ceritinib overcomes crizotinib resistance
in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 4:662–673. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xia B, Nagasaka M, Zhu VW, Ou SI and Soo
RA: How to select the best upfront therapy for metastatic disease?
Focus on ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Transl
Lung Cancer Res. 9:2521–2534. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Werner MT, Zhao C, Zhang Q and Wasik MA:
Nucleophosmin-anaplastic lymphoma kinase: The ultimate oncogene and
therapeutic target. Blood. 129:823–831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Tse BC, Said BI, Fan ZJ, Hueniken K, Patel
D, Gill G, Liang M, Razooqi M, Brown MC, Sacher AG, et al:
Longitudinal health utilities, symptoms and toxicities in patients
with ALK-rearranged lung cancer treated with tyrosine kinase
inhibitors: A prospective real-world assessment. Curr Oncol.
27:e552–e559. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Castellanos EH and Horn L: Re-Evaluating
progression in an era of progress: A review of first- and
second-line treatment options in anaplastic lymphoma
kinase-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Oncologist. 21:755–761.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Herbst RS, Giaccone G, de Marinis F,
Reinmuth N, Vergnenegre A, Barrios CH, Morise M, Felip E, Andric Z,
Geater S, et al: Atezolizumab for first-line treatment of
PD-L1-selected patients with NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 383:1328–1339.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hallberg B and Palmer RH: The role of the
ALK receptor in cancer biology. Ann Oncol. 27 (Suppl 3):iii4–iii15.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Choi YL, Soda M, Yamashita Y, Ueno T,
Takashima J, Nakajima T, Yatabe Y, Takeuchi K, Hamada T, Haruta H,
et al: EML4-ALK mutations in lung cancer that confer resistance to
ALK inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 363:1734–1739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Azam M, Seeliger MA, Gray NS, Kuriyan J
and Daley GQ: Activation of tyrosine kinases by mutation of the
gatekeeper threonine. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 15:1109–1118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Heuckmann JM, Hölzel M, Sos ML, Heynck S,
Balke-Want H, Koker M, Peifer M, Weiss J, Lovly CM, Grütter C, et
al: ALK mutations conferring differential resistance to
structurally diverse ALK inhibitors. Clin Cancer Res. 17:7394–7401.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sasaki T, Koivunen J, Ogino A, Yanagita M,
Nikiforow S, Zheng W, Lathan C, Marcoux JP, Du J, Okuda K, et al: A
novel ALK secondary mutation and EGFR signaling cause resistance to
ALK kinase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 71:6051–6060. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Katayama R, Friboulet L, Koike S,
Lockerman EL, Khan TM, Gainor JF, Iafrate AJ, Takeuchi K, Taiji M,
Okuno Y, et al: Two novel ALK mutations mediate acquired resistance
to the next-generation ALK inhibitor alectinib. Clin Cancer Res.
20:5686–5696. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Isozaki H, Hotta K, Ichihara E, Takigawa
N, Ohashi K, Kubo T, Ninomiya T, Ninomiya K, Oda N, Yoshioka H, et
al: Protocol design for the bench to bed trial in
alectinib-refractory non-small-cell lung cancer patients harboring
the EML4-ALK fusion gene (ALRIGHT/OLCSG1405). Clin Lung Cancer.
17:602–605. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sequist LV, Waltman BA, Dias-Santagata D,
Digumarthy S, Turke AB, Fidias P, Bergethon K, Shaw AT, Gettinger
S, Cosper AK, et al: Genotypic and histological evolution of lung
cancers acquiring resistance to EGFR inhibitors. Sci Transl Med.
3:75ra262011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zou HY, Friboulet L, Kodack DP, Engstrom
LD, Li Q, West M, Tang RW, Wang H, Tsaparikos K, Wang J, et al:
PF-06463922, an ALK/ROS1 inhibitor, overcomes resistance to first
and second generation ALK inhibitors in preclinical models. Cancer
Cell. 28:70–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Shaw AT, Friboulet L, Leshchiner I, Gainor
JF, Bergqvist S, Brooun A, Burke BJ, Deng YL, Liu W, Dardaei L, et
al: Resensitization to crizotinib by the lorlatinib ALK resistance
mutation L1198F. N Engl J Med. 374:54–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wu YL, Lu S, Lu Y, Zhou J, Shi YK,
Sriuranpong V, Ho JCM, Ong CK, Tsai CM, Chung CH, et al: Results of
PROFILE 1029, a phase iii comparison of first-line crizotinib
versus chemotherapy in East Asian patients with ALK-positive
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 13:1539–1548.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Krishnamurthy N, Goodman AM, Barkauskas DA
and Kurzrock R: STK11 alterations in the pan-cancer setting:
Prognostic and therapeutic implications. Eur J Cancer. 148:215–229.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wohlhieter CA, Richards AL, Uddin F,
Hulton CH, Quintanal-Villalonga À, Martin A, de Stanchina E, Bhanot
U, Asher M, Shah NS, et al: Concurrent mutations in STK11 and KEAP1
promote ferroptosis protection and SCD1 dependence in lung cancer.
Cell Rep. 33:1084442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Skoulidis F, Goldberg ME, Greenawalt DM,
Hellmann MD, Awad MM, Gainor JF, Schrock AB, Hartmaier RJ, Trabucco
SE, Gay L, et al: STK11/LKB1 mutations and PD-1 inhibitor
resistance in KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov.
8:822–835. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gowans GJ, Hawley SA, Ross FA and Hardie
DG: AMP is a true physiological regulator of AMP-activated protein
kinase by both allosteric activation and enhancing net
phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 18:556–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hemminki A, Markie D, Tomlinson I,
Avizienyte E, Roth S, Loukola A, Bignell G, Warren W, Aminoff M,
Höglund P, et al: A serine/threonine kinase gene defective in
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Nature. 391:184–187. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Mahoney CL, Choudhury B, Davies H, Edkins
S, Greenman C, Haaften G, Mironenko T, Santarius T, Stevens C,
Stratton MR and Futreal PA: LKB1/KRAS mutant lung cancers
constitute a genetic subset of NSCLC with increased sensitivity to
MAPK and mTOR signalling inhibition. Br J Cancer. 100:370–375.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Parachoniak CA, Rankin A, Gaffney B,
Hartmaier R, Spritz D, Erlich RL, Miller VA, Morosini D, Stephens
P, Ross JS, et al: Exceptional durable response to everolimus in a
patient with biphenotypic breast cancer harboring an STK11variant.
Cold Spring Harb Mol Case Stud. 3:a0007782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Sanchez-Cespedes M, Parrella P, Esteller
M, Nomoto S, Trink B, Engles JM, Westra WH, Herman JG and Sidransky
D: Inactivation of LKB1/STK11 is a common event in adenocarcinomas
of the lung. Cancer Res. 62:3659–3662. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hezel AF, Gurumurthy S, Granot Z, Swisa A,
Chu GC, Bailey G, Dor Y, Bardeesy N and Depinho RA: Pancreatic LKB1
deletion leads to acinar polarity defects and cystic neoplasms. Mol
Cell Biol. 28:2414–2425. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wingo SN, Gallardo TD, Akbay EA, Liang MC,
Contreras CM, Boren T, Shimamura T, Miller DS, Sharpless NE,
Bardeesy N, et al: Somatic LKB1 mutations promote cervical cancer
progression. PLoS One. 4:e51372009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gill RK, Yang SH, Meerzaman D, Mechanic
LE, Bowman ED, Jeon HS, Roy Chowdhuri S, Shakoori A, Dracheva T,
Hong KM, et al: Frequent homozygous deletion of the LKB1/STK11gene
in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 30:3784–3791. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lee SM, Choi JE, Na YK, Lee EJ, Lee WK,
Choi YY, Yoon GS, Jeon HS, Kim DS and Park JY: Genetic and
epigenetic alterations of the LKB1 gene and their associations with
mutations in TP53 and EGFR pathway genes in Korean non-small cell
lung cancers. Lung Cancer. 81:194–199. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tanwar PS, Mohapatra G, Chiang S, Engler
DA, Zhang L, Kaneko-Tarui T, Ohguchi Y, Birrer MJ and Teixeira JM:
Loss of LKB1 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes in the ovarian surface
epithelium induces papillary serous ovarian cancer. Carcinogenesis.
35:546–553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Li J, Liu J, Li P, Mao X, Li W, Yang J and
Liu P: Loss of LKB1 disrupts breast epithelial cell polarity and
promotes breast cancer metastasis and invasion. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 33:702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yang JY, Jiang SH, Liu DJ, Yang XM, Huo
YM, Li J, Hua R, Zhang ZG and Sun YW: Decreased LKB1 predicts poor
prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep.
5:105752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang W, Yin L, Song G, Han X, Yin Z and
Luo D: LKB1 loss cooperating with BRAFV600E promotes melanoma cell
invasion and migration by up-regulation MMP-2 via PI3K/Akt/mTOR
pathway. Oncotarget. 8:113847–113857. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Matsumoto S, Iwakawa R, Takahashi K, Kohno
T, Nakanishi Y, Matsuno Y, Suzuki K, Nakamoto M, Shimizu E, Minna
JD and Yokota J: Prevalence and specificity of LKB1 genetic
alterations in lung cancers. Oncogene. 26:5911–5918. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fang R, Zheng C, Sun Y, Han X, Gao B, Li
C, Liu H, Wong KK, Liu XY, Chen H and Ji H: Integrative genomic
analysis reveals a high frequency of LKB1 genetic alteration in
Chinese lung adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Oncol. 9:254–258. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ji H, Ramsey MR, Hayes DN, Fan C, McNamara
K, Kozlowski P, Torrice C, Wu MC, Shimamura T, Perera SA, et al:
LKB1 modulates lung cancer differentiation and metastasis. Nature.
448:807–810. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liang J and Mills GB: AMPK: A contextual
oncogene or tumor suppressor? Cancer Res. 73:2929–2935. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature.
511:543–550. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Imielinski M, Berger AH, Hammerman PS,
Hernandez B, Pugh TJ, Hodis E, Cho J, Suh J, Capelletti M,
Sivachenko A, et al: Mapping the hallmarks of lung adenocarcinoma
with massively parallel sequencing. Cell. 150:1107–1120. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Baas AF, Smit L and Clevers H: LKB1 tumor
suppressor protein: PARtaker in cell polarity. Trends Cell Biol.
14:312–319. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Forcet C, Etienne-Manneville S, Gaude H,
Fournier L, Debilly S, Salmi M, Baas A, Olschwang S, Clevers H and
Billaud M: Functional analysis of Peutz-Jeghers mutations reveals
that the LKB1 C-terminal region exerts a crucial role in regulating
both the AMPK pathway and the cell polarity. Hum Mol Genet.
14:1283–1292. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Galan-Cobo A, Sitthideatphaiboon P, Qu X,
Poteete A, Pisegna MA, Tong P, Chen PH, Boroughs LK, Rodriguez MLM,
Zhang W, et al: LKB1 and KEAP1/NRF2 pathways cooperatively promote
metabolic reprogramming with enhanced glutamine dependence in
KRAS-mutant lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 79:3251–3267. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Koyama S, Akbay EA, Li YY, Aref AR,
Skoulidis F, Herter-Sprie GS, Buczkowski KA, Liu Y, Awad MM,
Denning WL, et al: STK11/LKB1 deficiency promotes neutrophil
recruitment and proinflammatory cytokine production to suppress
T-cell activity in the lung tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res.
76:999–1008. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shackelford DB and Shaw RJ: The LKB1-AMPK
pathway: Metabolism and growth control in tumour suppression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:563–575. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Shen Z, Wen XF, Lan F, Shen ZZ and Shao
ZM: The tumor suppressor gene LKB1 is associated with prognosis in
human breast carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 8:2085–2090.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Liu W, Monahan KB, Pfefferle AD, Shimamura
T, Sorrentino J, Chan KT, Roadcap DW, Ollila DW, Thomas NE,
Castrillon DH, et al: LKB1/STK11 inactivation leads to expansion of
a prometastatic tumor subpopulation in melanoma. Cancer Cell.
21:751–764. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Sanchez-Cespedes M: A role for LKB1 gene
in human cancer beyond the Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Oncogene.
26:7825–7832. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Schabath MB, Welsh EA, Fulp WJ, Chen L,
Teer JK, Thompson ZJ, Engel BE, Xie M, Berglund AE, Creelan BC, et
al: Differential association of STK11 and TP53 with
KRASmutation-associated gene expression, proliferation and immune
surveillance in lung adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 35:3209–3216. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Lamberti G, Sisi M, Andrini E, Palladini
A, Giunchi F, Lollini PL, Ardizzoni A and Gelsomino F: The
mechanisms of PD-L1 regulation in non-small-cell lung cancer
(NSCLC): Which are the involved players? Cancers (Basel).
12:31292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Jordan EJ, Kim HR, Arcila ME, Barron D,
Chakravarty D, Gao J, Chang MT, Ni A, Kundra R, Jonsson P, et al:
Prospective comprehensive molecular characterization of lung
adenocarcinomas for efficient patient matching to approved and
emerging therapies. Cancer Discov. 7:596–609. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Roosan MR, Mambetsariev I, Pharaon R,
Fricke J, Husain H, Reckamp KL, Koczywas M, Massarelli E, Bild AH
and Salgia R: Usefulness of circulating tumor DNA in identifying
somatic mutations and tracking tumor evolution in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 160:1095–1107. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Dahmani R, Just PA, Delay A, Canal F,
Finzi L, Prip-Buus C, Lambert M, Sujobert P, Buchet-Poyau K, Miller
E, et al: A novel LKB1 isoform enhances AMPK metabolic activity and
displays oncogenic properties. Oncogene. 34:2337–2346. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Bouchekioua-Bouzaghou K, Poulard C,
Rambaud J, Lavergne E, Hussein N, Billaud M, Bachelot T, Chabaud S,
Mader S, Dayan G, et al: LKB1 when associated with methylatedERα is
a marker of bad prognosis in breast cancer. Int J Cancer.
135:1307–1318. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Koivunen JP, Kim J, Lee J, Rogers AM, Park
JO, Zhao X, Naoki K, Okamoto I, Nakagawa K, Yeap BY, et al:
Mutations in the LKB1 tumour suppressor are frequently detected in
tumours from Caucasian but not Asian lung cancer patients. Br J
Cancer. 99:245–252. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Roy BC, Kohno T, Iwakawa R, Moriguchi T,
Kiyono T, Morishita K, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Akiyama T and Yokota J:
Involvement of LKB1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of
human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 70:136–145. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Yao YH, Cui Y, Qiu XN, Zhang LZ, Zhang W,
Li H and Yu JM: Attenuated LKB1-SIK1 signaling promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and radioresistance of non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Chin J Cancer. 35:502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Momcilovic M and Shackelford DB: Targeting
LKB1 in cancer-exposing and exploiting vulnerabilities. Br J
Cancer. 113:574–584. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Shackelford DB, Abt E, Gerken L, Vasquez
DS, Seki A, Leblanc M, Wei L, Fishbein MC, Czernin J, Mischel PS,
et al: LKB1 inactivation dictates therapeutic response of non-small
cell lung cancer to the metabolism drug phenformin. Cancer Cell.
23:143–158. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Dobashi Y, Watanabe Y, Miwa C, Suzuki S
and Koyama S: Mammalian target of rapamycin: A central node of
complex signaling cascades. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 4:476–495.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Saxton RA and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
in growth, metabolism, and disease. Cell. 168:960–976. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Engelman JA: Targeting PI3K signalling in
cancer: Opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer.
9:550–562. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Chen B, Tan Z, Gao J, Wu W, Liu L, Jin W,
Cao Y, Zhao S, Zhang W, Qiu Z, et al: Hyperphosphorylation of
ribosomal protein S6 predicts unfavorable clinical survival in
non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1262015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Krencz I, Sebestyén A, Fábián K, Márk Á,
Moldvay J, Khoor A, Kopper L and Pápay J: Expression of
mTORC1/2-related proteins in primary and brain metastatic lung
adenocarcinoma. Hum Pathol. 62:66–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Seki N, Takasu T, Mandai K, Nakata M,
Saeki H, Heike Y, Takata I, Segawa Y, Hanafusa T and Eguchi K:
Expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E in atypical
adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma of the human peripheral
lung. Clin Cancer Res. 8:3046–3053. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Yoshizawa A, Fukuoka J, Shimizu S, Shilo
K, Franks TJ, Hewitt SM, Fujii T, Cordon-Cardo C, Jen J and Travis
WD: Overexpression of phospho-eIF4E is associated with survival
through AKT pathway in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
16:240–248. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Jeon SM, Chandel NS and Hay N: AMPK
regulates NADPH homeostasis to promote tumour cell survival during
energy stress. Nature. 485:661–665. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Joo MS, Kim WD, Lee KY, Kim JH, Koo JH and
Kim SG: AMPK facilitates nuclear accumulation of Nrf2 by
phosphorylating at serine 550. Mol Cell Biol. 36:1931–1942. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Ciccarese F, Zulato E and Indraccolo S:
LKB1/AMPK pathway and drug response in cancer: A therapeutic
perspective. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019:87308162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Singh A, Daemen A, Nickles D, Jeon SM,
Foreman O, Sudini K, Gnad F, Lajoie S, Gour N, Mitzner W, et al:
NRF2 activation promotes aggressive lung cancer and associates with
poor clinical outcomes. Clin Cancer Res. 27:877–888. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Trapp EK, Majunke L, Zill B, Sommer H,
Andergassen U, Koch J, Harbeck N, Mahner S, Friedl TWP, Janni W, et
al: LKB1 pro-oncogenic activity triggers cell survival in
circulating tumor cells. Mol Oncol. 11:1508–1526. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Shaw RJ, Kosmatka M, Bardeesy N, Hurley
RL, Witters LA, DePinho RA and Cantley LC: The tumor suppressor
LKB1 kinase directly activates AMP-activated kinase and regulates
apoptosis in response to energy stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:3329–3335. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Deng L, Yao P, Li L, Ji F, Zhao S, Xu C,
Lan X and Jiang P: p53-mediated control of aspartate-asparagine
homeostasis dictates LKB1 activity and modulates cell survival. Nat
Commun. 11:17552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Goodman AM, Kato S, Bazhenova L, Patel SP,
Frampton GM, Miller V, Stephens PJ, Daniels GA and Kurzrock R:
Tumor mutational burden as an independent predictor of response to
immunotherapy in diverse cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:2598–2608.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Goodman AM, Piccioni D, Kato S, Boichard
A, Wang HY, Frampton G, Lippman SM, Connelly C, Fabrizio D, Miller
V, et al: Prevalence of PDL1 amplification and preliminary response
to immune checkpoint blockade in solid Tumors. JAMA Oncol.
4:1237–1244. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Frampton GM, Fichtenholtz A, Otto GA, Wang
K, Downing SR, He J, Schnall-Levin M, White J, Sanford EM, An P, et
al: Development and validation of a clinical cancer genomic
profiling test based on massively parallel DNA sequencing. Nat
Biotechnol. 31:1023–1031. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Kobayashi A, Kang MI, Okawa H, Ohtsuji M,
Zenke Y, Chiba T, Igarashi K and Yamamoto M: Oxidative stress
sensor Keap1 functions as an adaptor for Cul3-based E3 ligase to
regulate proteasomal degradation of Nrf2. Mol Cell Biol.
24:7130–7139. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Donnelly LL, Hogan TC, Lenahan SM,
Nandagopal G, Eaton JG, Lebeau MA, McCann CL, Sarausky HM, Hampel
KJ, Armstrong JD, et al: Functional assessment of somatic
STK11variants identified in primary human non-small cell lung
cancers. Carcinogenesis. 42:1428–1438. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Gill CM, Loewenstern J, Rutland JW, Arib
H, Pain M, Umphlett M, Kinoshita Y, McBride RB, Bederson J, Donovan
M, et al: STK11 mutation status is associated with decreased
survival in meningiomas. Neurol Sci. 41:2585–2589. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Facchinetti F, Bluthgen MV,
Tergemina-Clain G, Faivre L, Pignon JP, Planchard D, Remon J, Soria
JC, Lacroix L and Besse B: LKB1/STK11 mutations in non-small cell
lung cancer patients: Descriptive analysis and prognostic value.
Lung Cancer. 112:62–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Rittmeyer A, Barlesi F, Waterkamp D, Park
K, Ciardiello F, von Pawel J, Gadgeel SM, Hida T, Kowalski DM, Dols
MC, et al: Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with
previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3,
open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
389:255–265. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Herbst RS, Baas P, Perez-Gracia JL, Felip
E, Kim DW, Han JY, Molina JR, Kim JH, Dubos Arvis C, Ahn MJ, et al:
Use of archival versus newly collected tumor samples for assessing
PD-L1 expression and overall survival: An updated analysis of
KEYNOTE-010 trial. Ann Oncol. 30:281–289. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Zugazagoitia J, Molina-Pinelo S,
Lopez-Rios F and Paz-Ares L: Biological therapies in nonsmall cell
lung cancer. Eur Respir J. 49:16015202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Shire NJ, Klein AB, Golozar A, Collins JM,
Fraeman KH, Nordstrom BL, McEwen R, Hembrough T and Rizvi NA: STK11
(LKB1) mutations in metastatic NSCLC: Prognostic value in the real
world. PLoS One. 15:e02383582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Mograbi B, Heeke S and Hofman P: The
Importance of STK11/LKB1 assessment in non-small cell lung
carcinomas. Diagnostics (Basel). 11:1962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Herter-Sprie GS, Korideck H, Christensen
CL, Herter JM, Rhee K, Berbeco RI, Bennett DG, Akbay EA, Kozono D,
Mak RH, et al: Image-guided radiotherapy platform using single
nodule conditional lung cancer mouse models. Nat Commun.
5:58702014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
He Q, Li J, Dong F, Cai C and Zou X: LKB1
promotes radioresistance in esophageal cancer cells exposed to
radiation, by suppression of apoptosis and activation of autophagy
via the AMPK pathway. Mol Med Rep. 16:2205–2210. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Wang Y, Li N, Jiang W, Deng W, Ye R, Xu C,
Qiao Y, Sharma A, Zhang M, Hung MC, et al: Mutant LKB1 confers
enhanced radiosensitization in combination with trametinib in
KRAS-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
24:5744–5756. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|