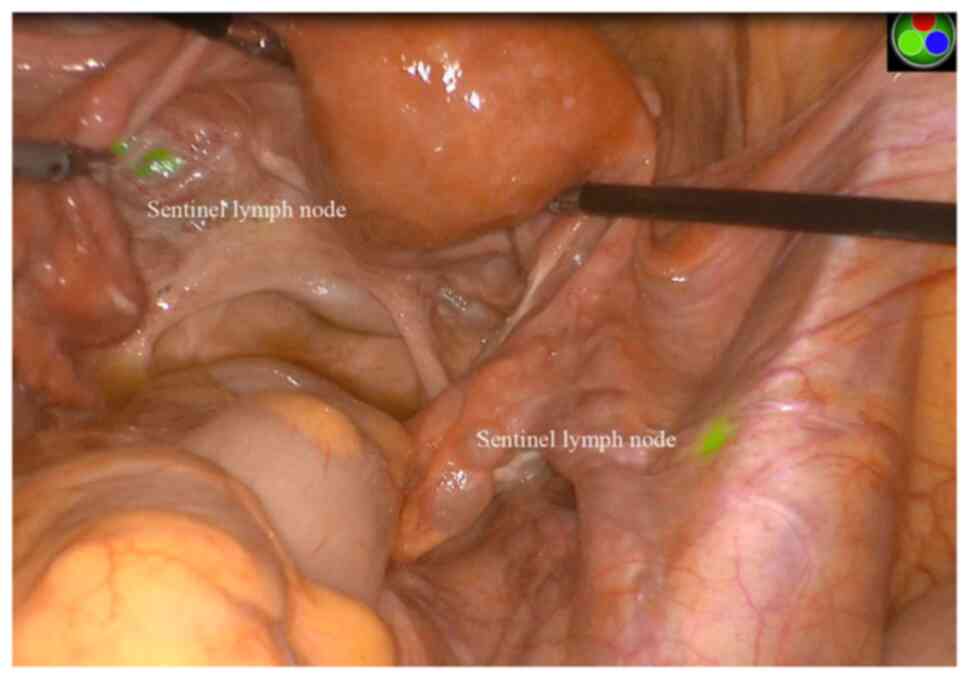
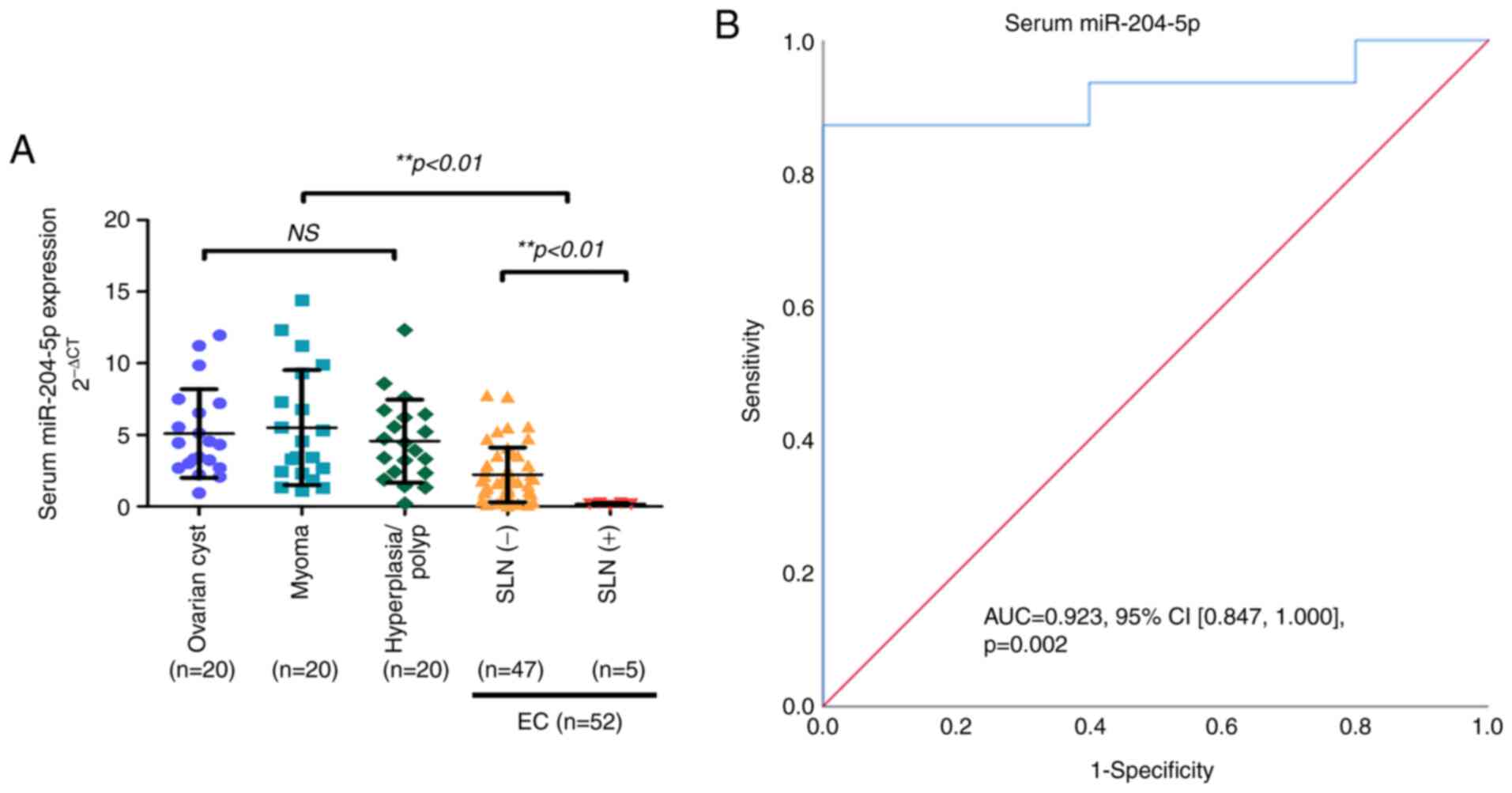
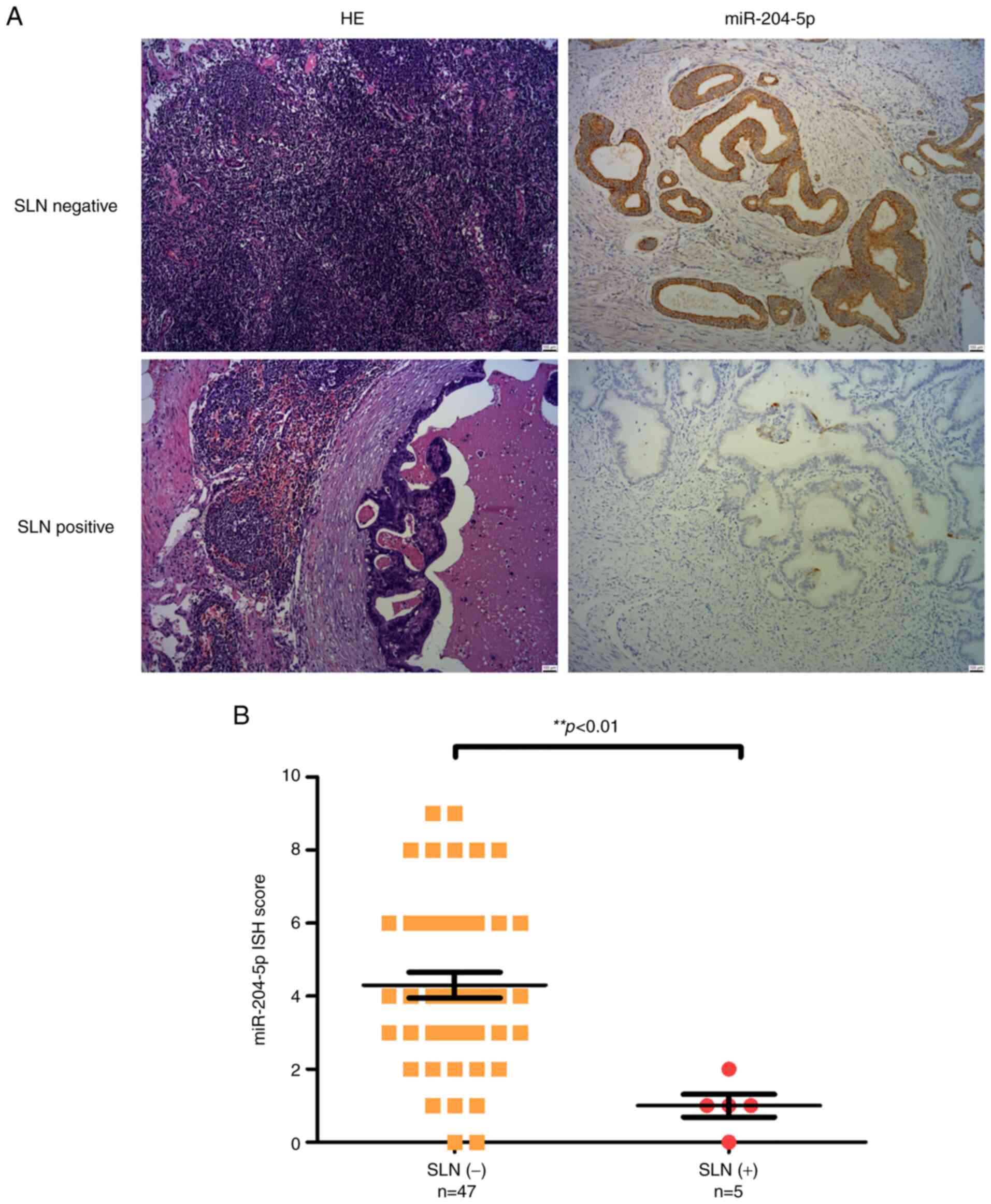
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Buldukoglu OC, Turker A, Usubutun A and
Salman MC: Relationship of lymph node status with survival and
recurrence among women with endometrial cancer. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 151:267–271. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li Y, Cong P, Wang P, Peng C, Liu M and
Sun G: Risk factors for pelvic lymph node metastasis in endometrial
cancer. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 300:1007–1013. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Suchetha S, Mathew AP, Rema P and Thomas
S: Pattern of lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer: A single
institution experience. Indian J Surg Oncol. 12:73–77. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Frost JA, Webster KE, Bryant A and
Morrison J: Lymphadenectomy for the management of endometrial
cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 10:CD0075852017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Accorsi GS, Paiva LL, Schmidt R, Vieira M,
Reis R and Andrade C: Sentinel lymph node mapping vs systematic
lymphadenectomy for endometrial cancer: Surgical morbidity and
lymphatic complications. J Minim Invasive Gynecol. 27:938–945.e2.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Latif N, Oh J, Brensinger C, Morgan M, Lin
LL, Cory L and Ko EM: Lymphadenectomy is associated with an
increased risk of postoperative venous thromboembolism in early
stage endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 161:130–134. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Colombo N, Creutzberg C, Amant F, Bosse T,
González-Martín A, Ledermann J, Marth C, Nout R, Querleu D, Mirza
MR, et al: ESMO-ESGO-ESTRO consensus conference on endometrial
cancer: Diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 27:16–41.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Koh WJ, Abu-Rustum NR, Bean S, Bradley K,
Campos SM, Cho KR, Chon HS, Chu C, Cohn D, Crispens MA, et al:
Uterine neoplasms, version 1.2018, NCCN clinical practice
guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 16:170–199. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Smith AJB, Fader AN and Tanner EJ:
Sentinel lymph node assessment in endometrial cancer: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 216:459–476.e10.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tanner EJ, Sinno AK, Stone RL, Levinson
KL, Long KC and Fader AN: Factors associated with successful
bilateral sentinel lymph node mapping in endometrial cancer.
Gynecol Oncol. 138:542–547. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kataoka F, Susumu N, Yamagami W, Kuwahata
M, Takigawa A, Nomura H, Takeuchi H, Nakahara T, Kameyama K and
Aoki D: The importance of para-aortic lymph nodes in sentinel lymph
node mapping for endometrial cancer by using hysteroscopic
radio-isotope tracer injection combined with subserosal dye
injection: Prospective study. Gynecol Oncol. 140:400–404. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang H, Tan Z, Hu H, Liu H, Wu T, Zheng C,
Wang X, Luo Z, Wang J, Liu S, et al: MicroRNA-21 promotes breast
cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting LZTFL1. BMC
Cancer. 19:7382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bao W, Wang HH, Tian FJ, He XY, Qiu MT,
Wang JY, Zhang HJ, Wang LH and Wan XP: A TrkB-STAT3-miR-204-5p
regulatory circuitry controls proliferation and invasion of
endometrial carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 12:1552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Creasman W: Revised FIGO staging for
carcinoma of the endometrium. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 105:1092009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang Y, Bao W, Liu Y, Wang S, Xu S, Li X,
Li Y and Wu S: miR-98-5p contributes to cisplatin resistance in
epithelial ovarian cancer by suppressing miR-152 biogenesis via
targeting Dicer1. Cell Death Dis. 9:4472018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cabanas RM: An approach for the treatment
of penile carcinoma. Cancer. 39:456–466. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burke TW, Levenback C, Tornos C, Morris M,
Wharton JT and Gershenson DM: Intraabdominal lymphatic mapping to
direct selective pelvic and paraaortic lymphadenectomy in women
with high-risk endometrial cancer: Results of a pilot study.
Gynecol Oncol. 62:169–173. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Slama J, Dundr P, Dusek L and Cibula D:
High false negative rate of frozen section examination of sentinel
lymph nodes in patients with cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
129:384–388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sonoda K, Yahata H, Okugawa K, Kaneki E,
Ohgami T, Yasunaga M, Baba S, Oda Y, Honda H and Kato K: Value of
intraoperative cytological and pathological sentinel lymph node
diagnosis in fertility-sparing trachelectomy for early-stage
cervical cancer. Oncology. 94:92–98. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Holloway RW, Ahmad S, Kendrick JE, Bigsby
GE, Brudie LA, Ghurani GB, Stavitzski NM, Gise JL, Ingersoll SB and
Pepe JW: A prospective cohort study comparing colorimetric and
fluorescent imaging for sentinel lymph node mapping in endometrial
cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 24:1972–1979. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Nagai T, Niikura H, Okamoto S, Nakabayashi
K, Matoda M, Utsunomiya H, Nagase S, Watanabe M, Takeshima N and
Yaegashi N: A new diagnostic method for rapid detection of lymph
node metastases using a one-step nucleic acid amplification (OSNA)
assay in endometrial cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:980–986. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Liu T, Zou XZ, Huang N, Ge XY, Yao MZ, Liu
H, Zhang Z and Hu CP: Down-regulation of miR-204 attenuates
endothelial-mesenchymal transition by enhancing autophagy in
hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension. Eur J Pharmacol.
863:1726732019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Du F, Zhang Y, Xu Q, Teng Y, Tao M, Chen
AF and Jiang R: Preeclampsia serum increases CAV1 expression and
cell permeability of human renal glomerular endothelial cells via
down-regulating miR-199a-5p, miR-199b-5p, miR-204. Placenta.
99:141–151. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Courboulin A, Paulin R, Giguère NJ,
Saksouk N, Perreault T, Meloche J, Paquet ER, Biardel S, Provencher
S, Côté J, et al: Role for miR-204 in human pulmonary arterial
hypertension. J Exp Med. 208:534–548. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang M, Cao M, Kong L, Liu J, Wang Y,
Song C, Chen X, Lai M, Fang X, Chen H and Zhang C: miR-204-5p
promotes lipid synthesis in mammary epithelial cells by targeting
SIRT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 533:1490–1496. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He H, Chen K, Wang F, Zhao L, Wan X, Wang
L and Mo Z: miR-204-5p promotes the adipogenic differentiation of
human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by modulating DVL3
expression and suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Int J Mol Med.
35:1587–1595. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu G, Chen J, Jing G and Shalev A:
Thioredoxin-interacting protein regulates insulin transcription
through microRNA-204. Nat Med. 19:1141–1146. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zanette DL, Rivadavia F, Molfetta GA,
Barbuzano FG, Proto-Siqueira R, Silva WA Jr, Falcao RP and Zago MA:
miRNA expression profiles in chronic lymphocytic and acute
lymphocytic leukemia. Braz J Med Biol Res. 40:1435–1440. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yuan X, Wang S, Liu M, Lu Z, Zhan Y, Wang
W and Xu AM: Histological and pathological assessment of miR-204
and SOX4 levels in gastric cancer patients. Biomed Res Int.
2017:68946752017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Chen R, Li Z, Cheng H, Li X, Li T
and Zhu C: MiR-204 negatively regulates cell growth and metastasis
by targeting ROBO4 in human bladder cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
12:8515–8524. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Xing L, Xu H, Wang K, She J, Shi
F, Wu H, Sun Y, Gao J and He S: miR-204-5p suppress lymph node
metastasis via regulating CXCL12 and CXCR4 in gastric cancer. J
Cancer. 11:3199–3206. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shimomura A, Shiino S, Kawauchi J,
Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, Matsuzaki J, Ono M, Takeshita F, Niida S,
Shimizu C, et al: Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting
breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 107:326–334. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zou Y, Jing C, Liu L and Wang T: Serum
microRNA-135a as a diagnostic biomarker in non-small cell lung
cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e178142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Schneider R, McKeever P, Kim T, Graff C,
van Swieten JC, Karydas A, Boxer A, Rosen H, Miller BL, Laforce R
Jr, et al: Downregulation of exosomal miR-204-5p and miR-632 as a
biomarker for FTD: A GENFI study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
89:851–858. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|