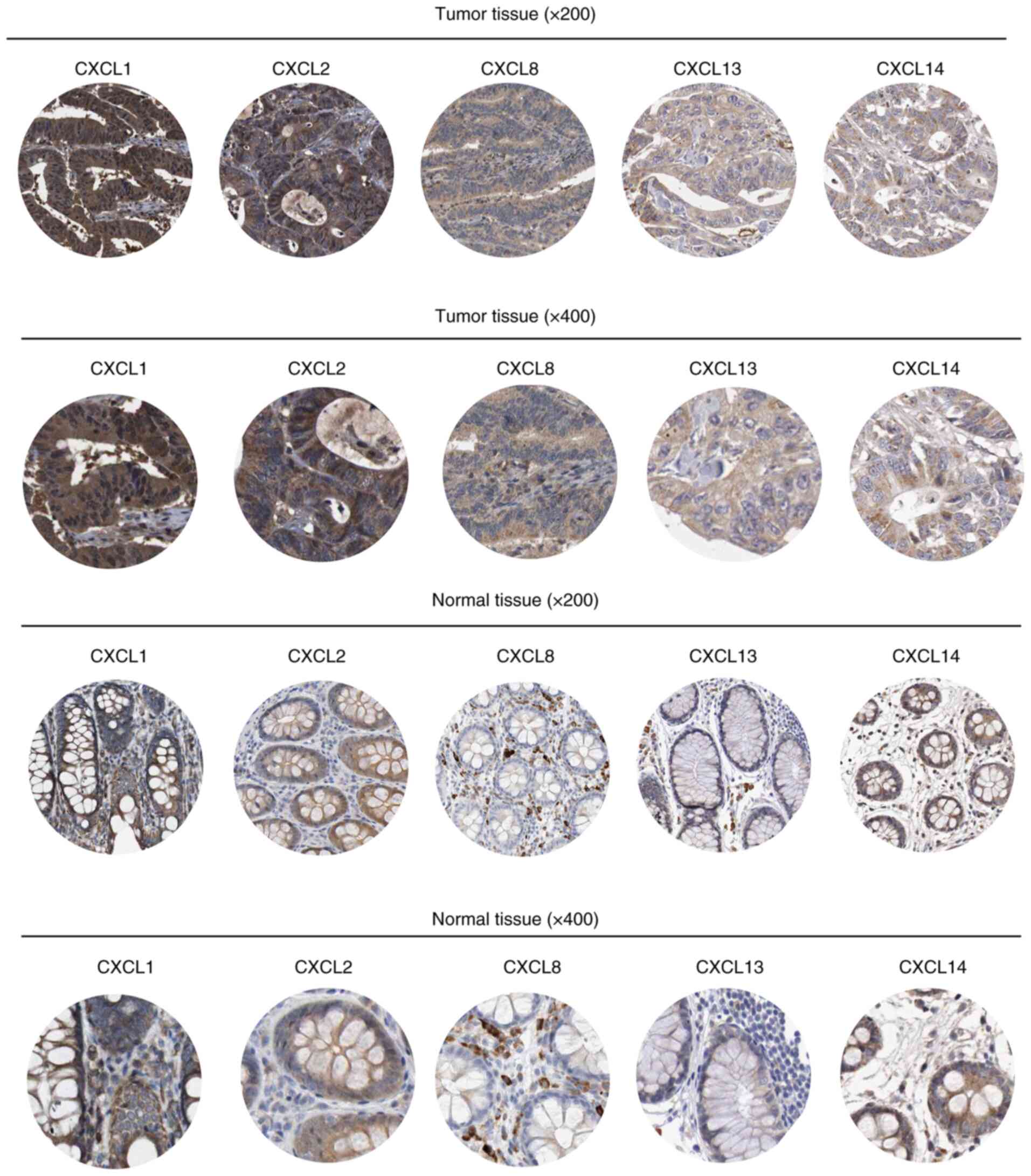
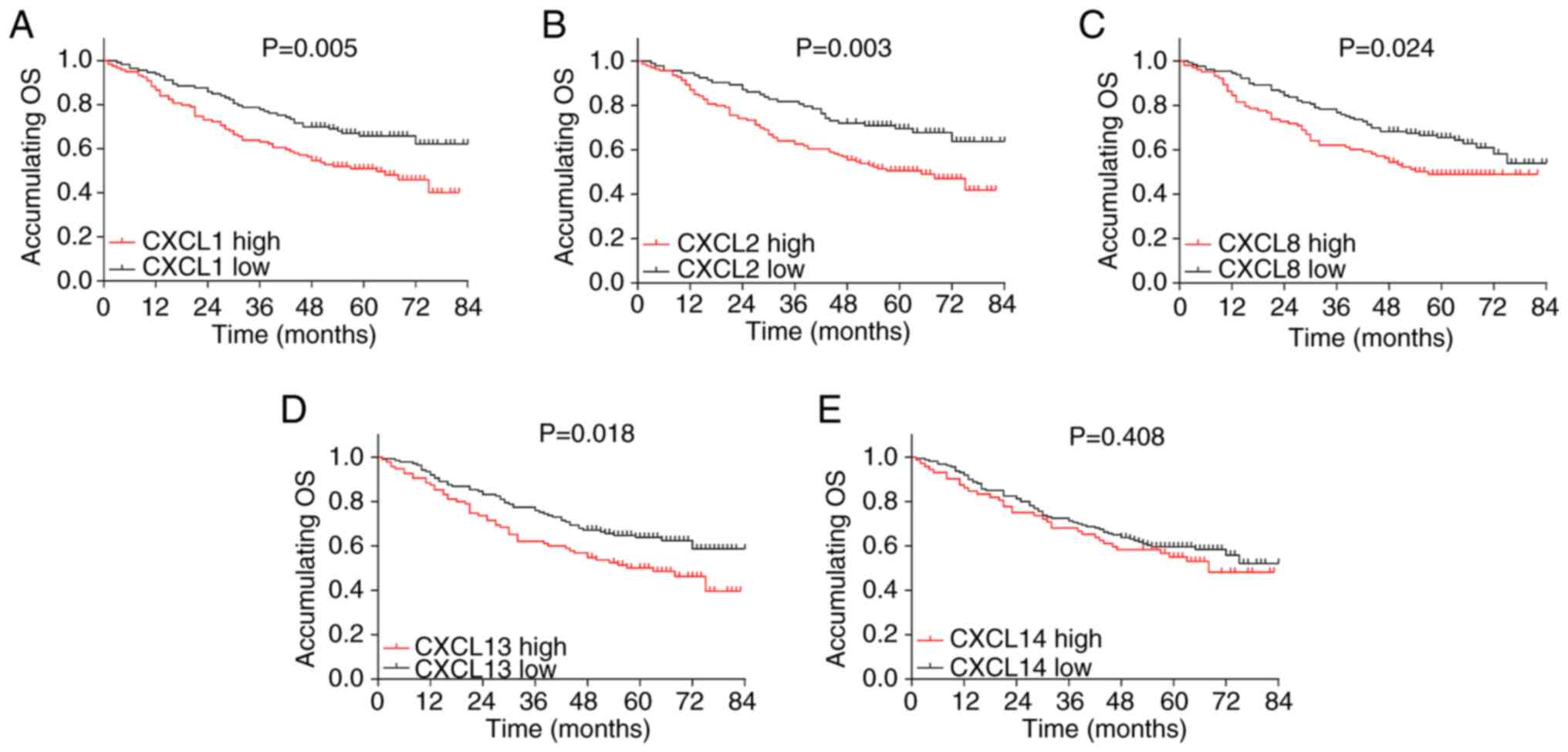
|
1
|
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JL, Kasi PM
and Wallace MB: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 394:1467–1480. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Oh HH and Joo YE: Novel biomarkers for the
diagnosis and prognosis of colorectal cancer. Intest Res.
18:168–183. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cabrero-de Las Heras S and
Martínez-Balibrea E: CXC family of chemokines as prognostic or
predictive biomarkers and possible drug targets in colorectal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 24:4738–4749. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Acharyya S, Oskarsson T, Vanharanta S,
Malladi S, Kim J, Morris PG, Manova-Todorova K, Leversha M, Hogg N,
Seshan VE, et al: A CXCL1 paracrine network links cancer
chemoresistance and metastasis. Cell. 150:165–178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kasashima H, Yashiro M, Nakamae H, Masuda
G, Kinoshita H, Morisaki T, Fukuoka T, Hasegawa T, Nakane T, Hino
M, et al: Clinicopathologic significance of the CXCL1-CXCR2 axis in
the tumor microenvironment of gastric carcinoma. PLoS One.
12:e01786352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu Q, Li A, Tian Y, Wu JD, Liu Y, Li T,
Chen Y, Han X and Wu K: The CXCL8-CXCR1/2 pathways in cancer.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 31:61–71. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zheng Z, Cai Y, Chen H, Chen Z, Zhu D,
Zhong Q and Xie W: CXCL13/CXCR5 axis predicts poor prognosis and
promotes progression through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. 8:6822019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Zhang J, Sun X, Su Q and You C:
Down-regulation of miR-29b in carcinoma associated fibroblasts
promotes cell growth and metastasis of breast cancer. Oncotarget.
8:39559–39570. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kondo T, Ozawa S, Ikoma T, Yang XY,
Kanamori K, Suzuki K, Iwabuchi H, Maehata Y, Miyamoto C, Taguchi T,
et al: Expression of the chemokine CXCL14 and cetuximab-dependent
tumour suppression in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncogenesis. 5:e2402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nagtegaal ID, Odze RD, Klimstra D, Paradis
V, Rugge M, Schirmacher P, Washington KM, Carneiro F and Cree IA;
WHO Classification of Tumours Editorial Board, : The 2019 WHO
classification of tumours of the digestive system. Histopathology.
76:182–188. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tong GJ, Zhang GY, Liu J, Zheng ZZ, Chen
Y, Niu PP and Xu XT: Comparison of the eighth version of the
american joint committee on cancer manual to the seventh version
for colorectal cancer: A retrospective review of our data. World J
Clin Oncol. 9:148–161. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fu H, Jin C, Zhu Q, Liu T, Ke B, Li A and
Zhang T: Dysregulated expressions of PTEN, NF-κB, WWP2, p53 and
c-Myc in different subtypes of B cell lymphoma and reactive
follicular hyperplasia. Am J Transl Res. 11:1092–1101.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ding J, Xu K, Zhang J, Lin B, Wang Y, Yin
S, Xie H, Zhou L and Zheng S: Overexpression of CXCL2 inhibits cell
proliferation and promotes apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
BMB Rep. 51:630–635. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sunaga N, Kaira K, Tomizawa Y, Shimizu K,
Imai H, Takahashi G, Kakegawa S, Ohtaki Y, Nagashima T and Kasahara
N: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of interleukin-8
expression and its relationship to KRAS mutation in lung
adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 110:2047–2053. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Uehara H, Troncoso P, Johnston D, Bucana
CD, Dinney C, Dong Z, Fidler IJ and Pettaway CA: Expression of
interleukin-8 gene in radical prostatectomy specimens is associated
with advanced pathologic stage. Prostate. 64:40–49. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu T, Ruan H, Song Z, Cao Q, Wang K, Bao
L, Liu D, Tong J, Yang H, Chen K and Zhang X: Identification of
CXCL13 as a potential biomarker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
via comprehensive bioinformatics analysis. Biomed Pharmacother.
118:1092642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li C, Kang D, Sun X, Liu Y, Wang J and Gao
P: The effect of C-X-C motif chemokine 13 on hepatocellular
carcinoma associates with Wnt signaling. Biomed Res Int.
2015:3454132015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mishra P, Banerjee D and Ben-Baruch A:
Chemokines at the crossroads of tumor-fibroblast interactions that
promote malignancy. J Leukoc Biol. 89:31–39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Verbeke H, Struyf S, Laureys G and Van
Damme J: The expression and role of CXC chemokines in colorectal
cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:345–358. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ruiz de Porras V, Bystrup S,
Martínez-Cardús A, Pluvinet R, Sumoy L, Howells L, James MI, Iwuji
C, Manzano JL, Layos L, et al: Curcumin mediates
oxaliplatin-acquired resistance reversion in colorectal cancer cell
lines through modulation of CXC-Chemokine/NF-κB signalling pathway.
Sci Rep. 6:246752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li X, He J, Zhou M, Cao Y, Jin Y and Zou
Q: Identification and validation of core genes involved in the
development of papillary thyroid carcinoma via bioinformatics
analysis. Int J Genomics. 2019:58949262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu Z, Zhang X, Guo H, Fu L, Pan G and Sun
Y: CXCL13-CXCR5 axis promotes the growth and invasion of colon
cancer cells via PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 400:287–295.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|