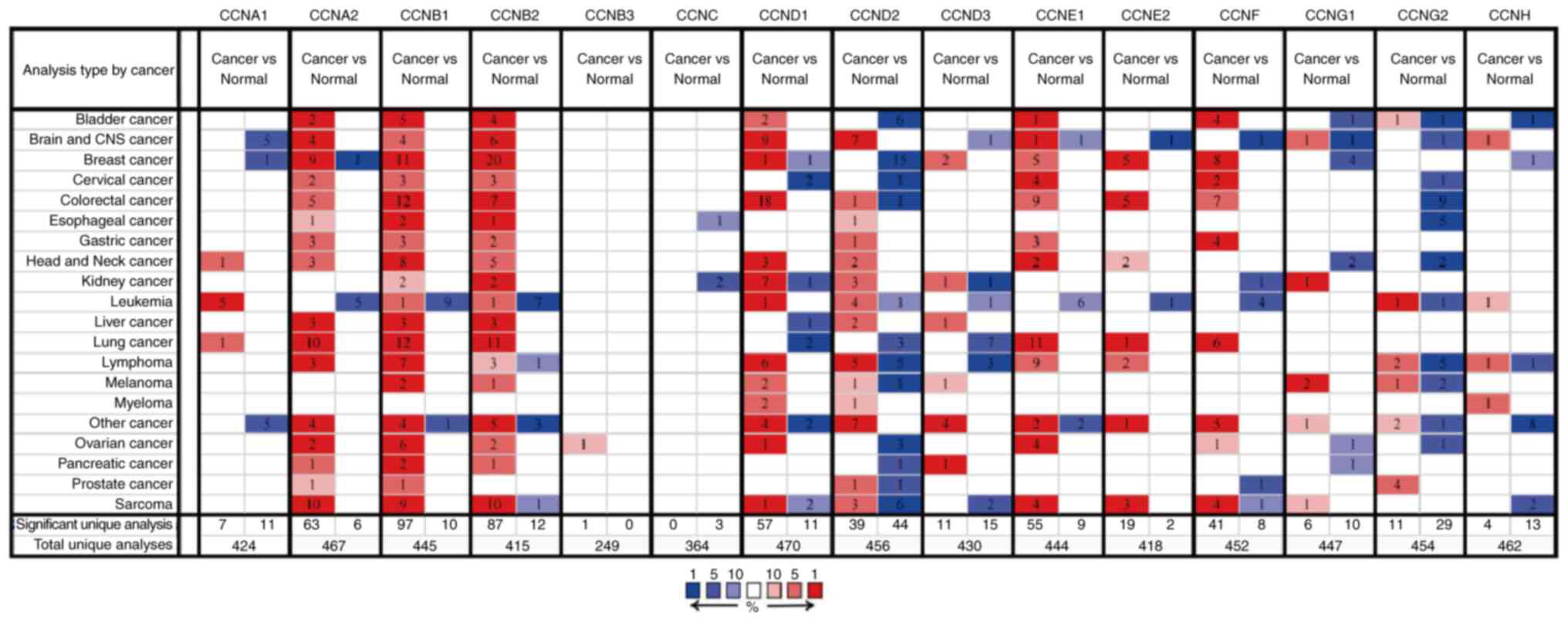
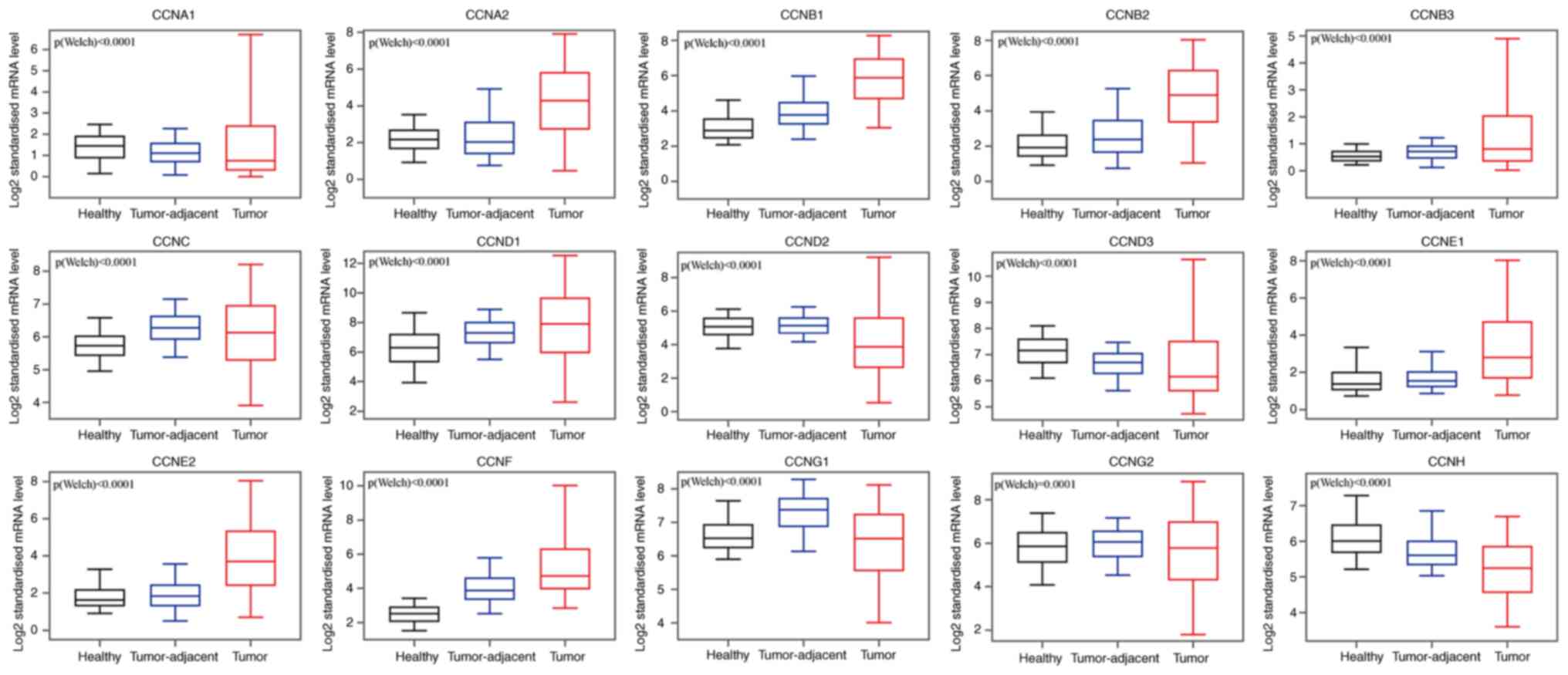
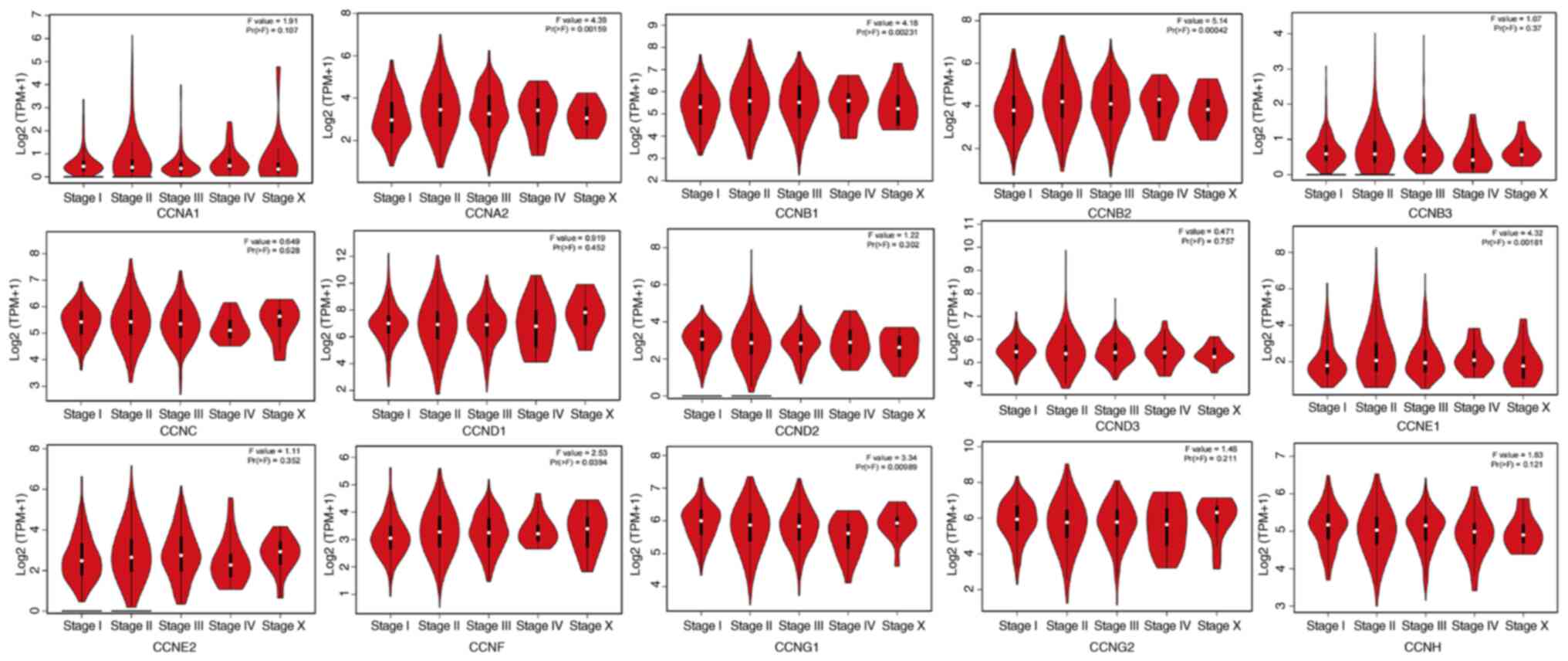
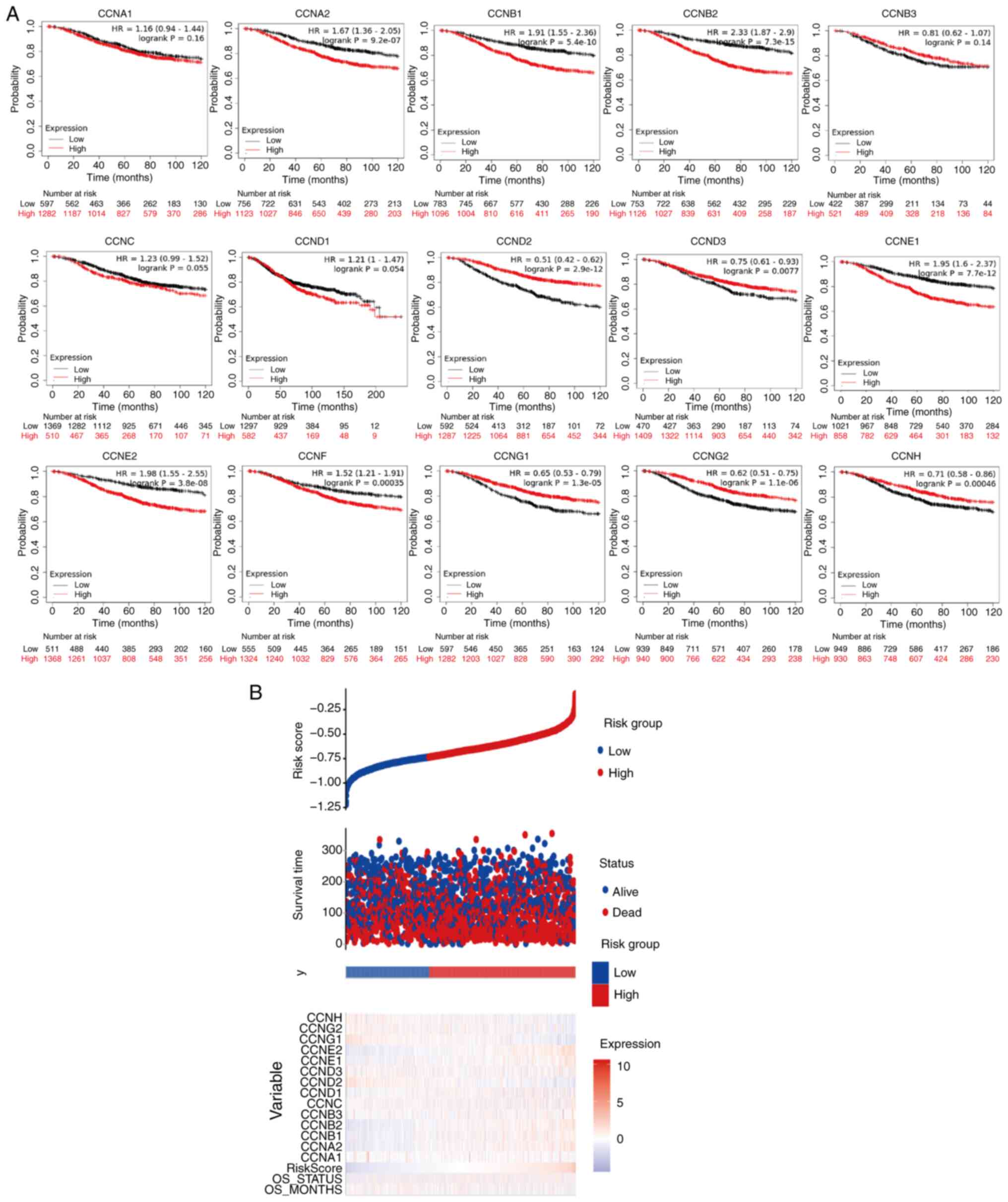
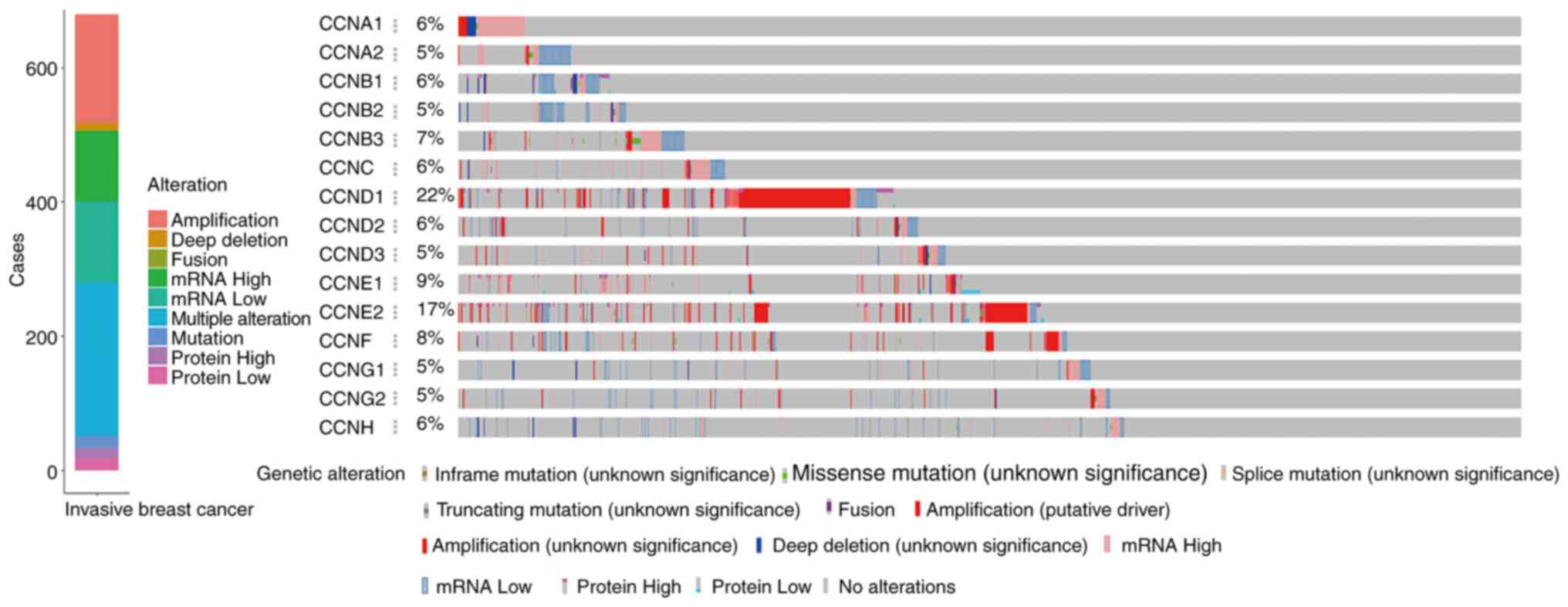
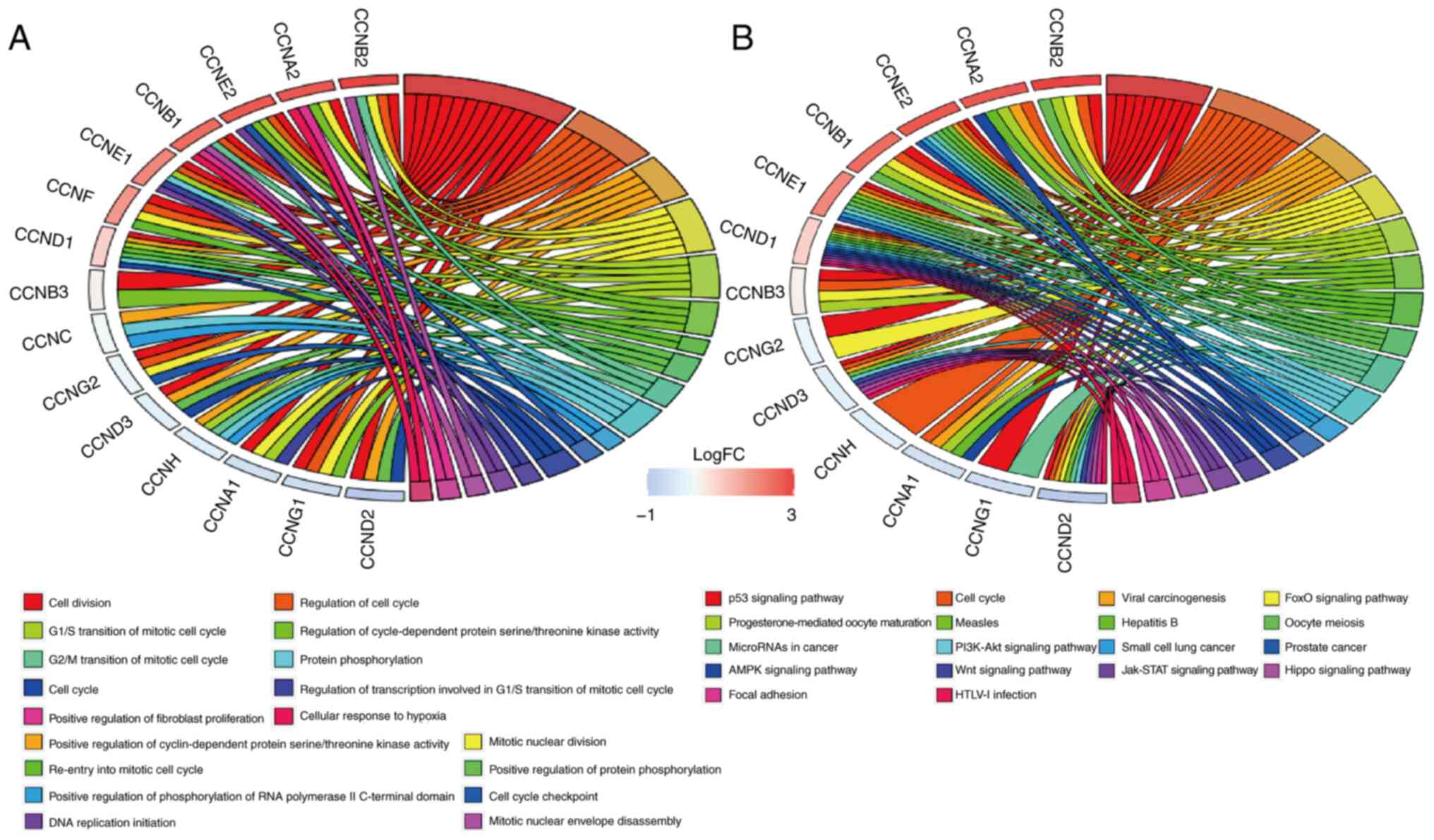
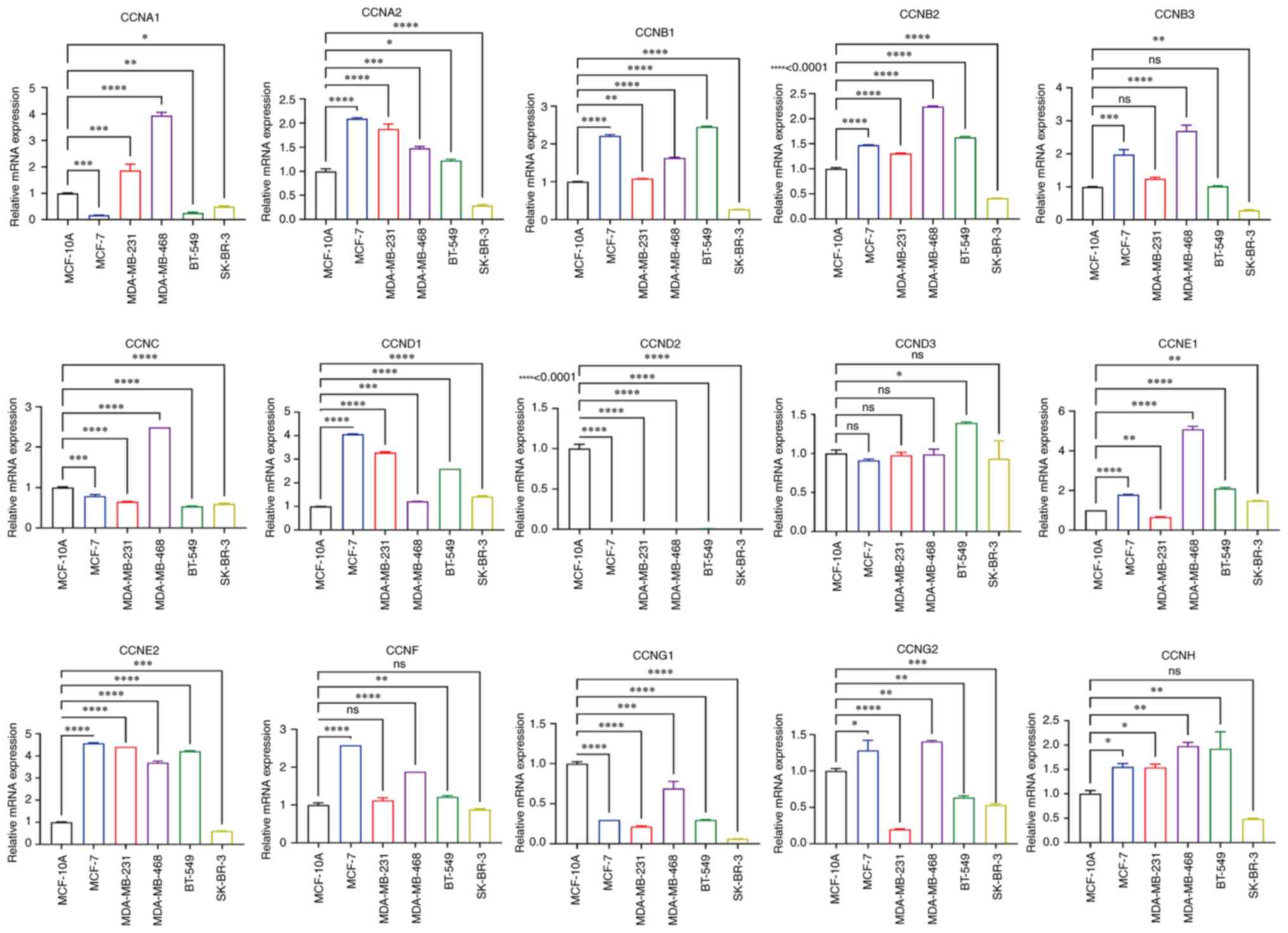
|
1
|
Cai Z and Liu Q: Cell cycle regulation in
treatment of breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1026:251–270. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Steeg PS and Zhou Q: Cyclins and breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 52:17–28. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bai C, Richman R and Elledge SJ: Human
cyclin F. EMBO J. 13:6087–6098. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ye C, Wang J, Wu P, Li X and Chai Y:
Prognostic role of cyclin B1 in solid tumors: A meta-analysis.
Oncotarget. 8:2224–2232. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lee YS, Ryu SW, Bae SJ, Park TH, Kwon K,
Noh YH and Kim SY: Cross-platform meta-analysis of multiple gene
expression profiles identifies novel expression signatures in
acquired anthracycline-resistant breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
33:1985–1993. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Miftakhova R, Hedblom A, Semenas J,
Robinson B, Simoulis A, Malm J, Rizvanov A, Heery DM, Mongan NP,
Maitland NJ, et al: Cyclin A1 and P450 aromatase promote metastatic
homing and growth of stem-like prostate cancer cells in the bone
marrow. Cancer Res. 76:2453–2464. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li R, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Wang S, Chen X, Yu
X, Ma J and Huang X: Cyclin B2 overexpression in human
hepatocellular carcinoma is associated with poor prognosis. Arch
Med Res. 50:10–17. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dorn J, Spatz H, Schmieder M, Barth TF,
Blatz A, Henne-Bruns D, Knippschild U and Kramer K: Cyclin H
expression is increased in GIST with very-high risk of malignancy.
BMC Cancer. 10:3502010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Huang KC, Yang J, Ng MC, Ng SK, Welch WR,
Muto MG, Berkowitz RS and Ng SW: Cyclin A1 expression and
paclitaxel resistance in human ovarian cancer cells. Eur J Cancer.
67:152–163. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chujan S, Kitkumthorn N, Siriangkul S and
Mutirangura A: CCNA1 promoter methylation: A potential marker for
grading Papanicolaou smear cervical squamous intraepithelial
lesions. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:7971–7975. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takashima S, Saito H, Takahashi N, Imai K,
Kudo S, Atari M, Saito Y, Motoyama S and Minamiya Y: Strong
expression of cyclin B2 mRNA correlates with a poor prognosis in
patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Tumour Biol.
35:4257–4265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wiseman M: The second world cancer
research fund/American institute for cancer research expert report.
Food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: A
global perspective. Proc Nutr Soc. 67:253–256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Harbeck N and Gnant M: Breast cancer.
Lancet. 389:1134–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zeng X, Liu C, Yao J, Wan H, Wan G, Li Y
and Chen N: Breast cancer stem cells, heterogeneity, targeting
therapies and therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Res.
163:1053202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ochsenreither S, Majeti R, Schmitt T,
Stirewalt D, Keilholz U, Loeb KR, Wood B, Choi YE, Bleakley M,
Warren EH, et al: Cyclin-A1 represents a new immunogenic targetable
antigen expressed in acute myeloid leukemia stem cells with
characteristics of a cancer-testis antigen. Blood. 119:5492–5501.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang R, Nakamaki T, Lübbert M, Said J,
Sakashita A, Freyaldenhoven BS, Spira S, Huynh V, Müller C and
Koeffler HP: Cyclin A1 expression in leukemia and normal
hematopoietic cells. Blood. 93:2067–2074. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao T, Han Y, Yu L, Ao S, Li Z and Ji J:
CCNA2 is a prognostic biomarker for ER+ breast cancer and tamoxifen
resistance. PLoS One. 9:e917712014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hein JB and Nilsson J: Interphase
APC/C-Cdc20 inhibition by cyclin A2-Cdk2 ensures efficient mitotic
entry. Nat Commun. 7:109752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pei J, Zhang J, Yang X, Wu Z, Sun C, Wang
Z and Wang B: NEK5 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation
through up-regulation of cyclin A2. Mol Carcinog. 58:933–943. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ding K, Li W, Zou Z, Zou X and Wang C:
CCNB1 is a prognostic biomarker for ER+ breast cancer. Med
Hypotheses. 83:359–564. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu HY, Liu YY, Yang F, Zhang L, Zhang FL,
Hu X, Shao ZM and Li DQ: Acetylation of MORC2 by NAT10 regulates
cell-cycle checkpoint control and resistance to DNA-damaging
chemotherapy and radiotherapy in breast cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
48:3638–3656. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu AQ, Wang ZX, Wu W, Chen KY, Yan SR and
Mao ZB: Circular RNA CircCCNB1 sponges micro RNA-449a to inhibit
cellular senescence by targeting CCNE2. Aging (Albany NY).
11:10220–10241. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shubbar E, Kovács A, Hajizadeh S, Parris
TZ, Nemes S, Gunnarsdóttir K, Einbeigi Z, Karlsson P and Helou K:
Elevated cyclin B2 expression in invasive breast carcinoma is
associated with unfavorable clinical outcome. BMC Cancer. 13:12013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qian X, Song X, He Y, Yang Z, Sun T, Wang
J, Zhu G, Xing W and You C: CCNB2 overexpression is a poor
prognostic biomarker in Chinese NSCLC patients. Biomed
Pharmacother. 74:222–227. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gao Z, Man X, Li Z, Bi J, Liu X, Li Z, Zhu
Y, Zhang Z and Kong C: Expression profiles analysis identifies the
values of carcinogenesis and the prognostic prediction of three
genes in adrenocortical carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 41:2440–2452.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lozano JC, Perret E, Schatt P, Arnould C,
Peaucellier G and Picard A: Molecular cloning, gene localization,
and structure of human cyclin B3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
291:406–413. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Han H, Bertrand KC, Patel KR, Fisher KE,
Roy A, Muscal JA and Venkatramani R: BCOR-CCNB3 fusion-positive
clear cell sarcoma of the kidney. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
67:e281512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoshida A, Arai Y, Hama N, Chikuta H,
Bando Y, Nakano S, Kobayashi E, Shibahara J, Fukuhara H, Komiyama
M, et al: Expanding the clinicopathologic and molecular spectrum of
BCOR-associated sarcomas in adults. Histopathology. 76:509–520.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shibayama T, Okamoto T, Nakashima Y, Kato
T, Sakurai T, Minamiguchi S, Kataoka TR, Shibuya S, Yoshizawa A,
Toguchida J and Haga H: Screening of BCOR-CCNB3 sarcoma using
immunohistochemistry for CCNB3: A clinicopathological report of
three pediatric cases. Pathol Int. 65:410–414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ren S and Rollins BJ: Cyclin C/cdk3
promotes Rb-dependent G0 exit. Cell. 117:239–251. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Miyata Y, Liu Y, Jankovic V, Sashida G,
Lee JM, Shieh JH, Naoe T, Moore M and Nimer SD: Cyclin C regulates
human hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell quiescence. Stem Cells.
28:308–317. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu W and Ji JY: Dysregulation of CDK8 and
cyclin C in tumorigenesis. J Genet Genomics. 38:439–452. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yu YN, Yip GW, Tan PH, Thike AA, Matsumoto
K, Tsujimoto M and Bay BH: Y-box binding protein 1 is up-regulated
in proliferative breast cancer and its inhibition deregulates the
cell cycle. Int J Oncol. 37:483–492. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roy PG and Thompson AM: Cyclin D1 and
breast cancer. Breast. 15:718–127. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Elsheikh S, Green AR, Aleskandarany MA,
Grainge M, Paish CE, Lambros MB, Reis-Filho JS and Ellis IO: CCND1
amplification and cyclin D1 expression in breast cancer and their
relation with proteomic subgroups and patient outcome. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 109:325–335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
He Q, Wu J, Liu XL, Ma YH, Wu XT, Wang WY
and An HX: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
cyclin D1 amplification in patients with breast cancer: A
meta-analysis. J BUON. 22:1209–1216. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Villegas SL, Darb-Esfahani S, von
Minckwitz G, Huober J, Weber K, Marmé F, Furlanetto J, Schem C,
Pfitzner BM, Lederer B, et al: Expression of cyclin D1 protein in
residual tumor after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 168:179–187. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Shi Q, Li Y, Li S, Jin L, Lai H, Wu Y, Cai
Z, Zhu M, Li Q, Li Y, et al: LncRNA DILA1 inhibits cyclin D1
degradation and contributes to tamoxifen resistance in breast
cancer. Nat Commun. 11:55132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pors J, Naso J, Berg K and Churg A: Cyclin
D1 immunohistochemical staining to separate benign from malignant
mesothelial proliferations. Mod Pathol. 33:312–318. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kwapisz D: Cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6
inhibitors in breast cancer: Palbociclib, ribociclib, and
abemaciclib. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 166:41–54. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hung CS, Wang SC, Yen YT, Lee TH, Wen WC
and Lin RK: Hypermethylation of CCND2 in lung and breast cancer is
a potential biomarker and drug target. Int J Mol Sci. 19:30962018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Callahan CL, Wang Y, Marian C, Weng DY,
Eng KH, Tao MH, Ambrosone CB, Nie J, Trevisan M, Smiraglia D, et
al: DNA methylation and breast tumor clinicopathological features:
The western New York exposures and breast cancer (WEB) study.
Epigenetics. 11:643–652. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ding ZY, Li R, Zhang QJ, Wang Y, Jiang Y,
Meng QY, Xi QL and Wu GH: Prognostic role of cyclin D2/D3 in
multiple human malignant neoplasms: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 8:2717–2729. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luhtala S, Staff S, Tanner M and Isola J:
Cyclin E amplification, over-expression, and relapse-free survival
in HER-2-positive primary breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:9813–9823.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Keyomarsi K, Tucker SL, Buchholz TA,
Callister M, Ding Y, Hortobagyi GN, Bedrosian I, Knickerbocker C,
Toyofuku W, Lowe M, et al: Cyclin E and survival in patients with
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 347:1566–1575. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee C, Fernandez KJ, Alexandrou S, Sergio
CM, Deng N, Rogers S, Burgess A and Caldon CE: Cyclin E2 promotes
whole genome doubling in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel).
12:22682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Peek GW and Tollefsbol TO: Combinatorial
PX-866 and raloxifene decrease Rb phosphorylation, cyclin E2
transcription, and proliferation of MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J
Cell Biochem. 117:1688–1696. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lindskog C: The potential clinical impact
of the tissue-based map of the human proteome. Expert Rev
Proteomics. 12:213–215. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fu J, Qiu H, Cai M, Pan Y, Cao Y, Liu L,
Yun J and Zhang CZ: Low cyclin F expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma associates with poor differentiation and unfavorable
prognosis. Cancer Sci. 104:508–515. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao L, Jiang L, He L, Wei Q, Bi J, Wang
Y, Yu L, He M, Zhao L and Wei M: Identification of a novel cell
cycle-related gene signature predicting survival in patients with
gastric cancer. J Cell Physiol. 234:6350–6360. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Noh JM, Kim J, Cho DY, Choi DH, Park W and
Huh SJ: Exome sequencing in a breast cancer family without BRCA
mutation. Radiat Oncol J. 33:149–154. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tamura K, Kanaoka Y, Jinno S, Nagata A,
Ogiso Y, Shimizu K, Hayakawa T, Nojima H and Okayama H: Cyclin G: A
new mammalian cyclin with homology to fission yeast Cig1. Oncogene.
8:2113–2118. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zimmermann M, Arachchige-Don AP, Donaldson
MS, Patriarchi T and Horne MC: Cyclin G2 promotes cell cycle arrest
in breast cancer cells responding to fulvestrant and metformin and
correlates with patient survival. Cell Cycle. 15:3278–3295. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wu D, Han B, Guo L and Fan Z: Molecular
mechanisms associated with breast cancer based on integrated gene
expression profiling by bioinformatics analysis. J Obstet Gynaecol.
36:615–621. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Knowles LM and Smith JW: Genome-wide
changes accompanying knockdown of fatty acid synthase in breast
cancer. BMC Genomics. 8:1682007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Miller LD, Smeds J, George J, Vega VB,
Vergara L, Ploner A, Pawitan Y, Hall P, Klaar S, Liu ET and Bergh
J: An expression signature for p53 status in human breast cancer
predicts mutation status, transcriptional effects, and patient
survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:13550–13555. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mao L, Ling X and Chen J: Cyclin H
regulates lung cancer progression as a carcinoma inducer. Comput
Math Methods Med. 2021:66460772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Rhodes DR, Yu J, Shanker K, Deshpande N,
Varambally R, Ghosh D, Barrette T, Pandey A and Chinnaiyan AM:
ONCOMINE: A cancer microarray database and integrated data-mining
platform. Neoplasia. 6:1–6. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C and
Zhang Z: GEPIA: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression
profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 45((W1)):
W98–W102. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Nagy Á, Munkácsy G and Győrffy B:
Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci Rep.
11:60472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Hoadley KA, Yau C, Hinoue T, Wolf DM,
Lazar AJ, Drill E, Shen R, Taylor AM, Cherniack AD, Thorsson V, et
al: Cell-of-origin patterns dominate the molecular classification
of 10,000 tumors from 33 types of cancer. Cell. 173:291–304.e6.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
R Core Team: R: A language and environment
for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing;
Vienna: 2012
|
|
66
|
RStudio Team, . RStudio: Integrated
Development for R. RStudio Inc. Boston, MA: 2015
|
|
67
|
Tang T, Guo C, Xia T, Zhang R, Zen K, Pan
Y and Jin L: LncCCAT1 promotes breast cancer stem cell function
through activating WNT/β-catenin signaling. Theranostics.
9:7384–7402. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shao F, Pang X and Baeg GH: Targeting the
JAK/STAT signaling pathway for breast cancer. Curr Med Chem.
28:5137–5151. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Costa RLB, Han HS and Gradishar WJ:
Targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in triple-negative breast
cancer: A review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 169:397–406. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li X, Zeng Z, Wang J, Wu Y, Chen W, Zheng
L, Xi T, Wang A and Lu Y: MicroRNA-9 and breast cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 122:1096872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Qiao K, Ning S, Wan L, Wu H, Wang Q, Zhang
X, Xu S and Pang D: LINC00673 is activated by YY1 and promotes the
proliferation of breast cancer cells via the miR-515-5p/MARK4/Hippo
signaling pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:4182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lee MG, Kwon YS, Nam KS, Kim SY, Hwang IH,
Kim S and Jang H: Chaga mushroom extract induces autophagy via the
AMPK-mTOR signaling pathway in breast cancer cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 274:1140812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Woo SH, Seo SK, An S, Choe TB, Hong SI,
Lee YH and Park IC: Implications of caspase-dependent proteolytic
cleavage of cyclin A1 in DNA damage-induced cell death. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 453:438–442. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Klajic J, Busato F, Edvardsen H, Touleimat
N, Fleischer T, Bukholm I, Børresen-Dale AL, Lønning PE, Tost J and
Kristensen VN: DNA methylation status of key cell-cycle regulators
such as CDKNA2/p16 and CCNA1 correlates with treatment response to
doxorubicin and 5-fluorouracil in locally advanced breast tumors.
Clin Cancer Res. 20:6357–6366. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Deng JL, Xu YH and Wang G: Identification
of potential crucial genes and key pathways in breast cancer using
bioinformatic analysis. Front Genet. 10:6952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tang J, Kong D, Cui Q, Wang K, Zhang D,
Gong Y and Wu G: Prognostic genes of breast cancer identified by
gene co-expression network analysis. Front Oncol. 8:3742018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Jayanthi VSPKSA, Das AB and Saxena U:
Grade-specific diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in breast
cancer. Genomics. 112:388–396. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Zhou H, Lv Q and Guo Z: Transcriptomic
signature predicts the distant relapse in patients with ER+ breast
cancer treated with tamoxifen for five years. Mol Med Rep.
17:3152–3157. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Li N, Fassl A, Chick J, Inuzuka H, Li X,
Mansour MR, Liu L, Wang H, King B, Shaik S, et al: Cyclin C is a
haploinsufficient tumour suppressor. Nat Cell Biol. 16:1080–1091.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bozickovic O, Hoang T, Fenne IS, Helland
T, Skartveit L, Ouchida M, Mellgren G and Sagen JV: Cyclin C
interacts with steroid receptor coactivator 2 and upregulates cell
cycle genes in MCF-7 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1853:2383–2391.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Kurebayashi J, Otsuki T, Kunisue H, Tanaka
K, Yamamoto S and Sonoo H: Expression levels of estrogen
receptor-alpha, estrogen receptor-beta, coactivators, and
corepressors in breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 6:512–518.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Butt AJ, McNeil CM, Musgrove EA and
Sutherland RL: Downstream targets of growth factor and oestrogen
signalling and endocrine resistance: The potential roles of c-Myc,
cyclin D1 and cyclin E. Endocr Relat Cancer. 12 (Suppl 1):S47–S59.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Filipits M, Dafni U, Gnant M,
Polydoropoulou V, Hills M, Kiermaier A, de Azambuja E, Larsimont D,
Rojo F, Viale G, et al: Association of p27 and cyclin D1 expression
and benefit from adjuvant trastuzumab treatment in HER2-positive
early breast cancer: A TransHERA study. Clin Cancer Res.
24:3079–3086. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tobin NP, Sims AH, Lundgren KL, Lehn S and
Landberg G: Cyclin D1, Id1 and EMT in breast cancer. BMC Cancer.
11:4172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Fischer H, Chen J, Skoog L and Lindblom A:
Cyclin D2 expression in familial and sporadic breast cancer. Oncol
Rep. 9:1157–1161. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Li Z, Heng J, Yan J, Guo X, Tang L, Chen
M, Peng L, Wu Y, Wang S, Xiao Z, et al: Integrated analysis of gene
expression and methylation profiles of 48 candidate genes in breast
cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 160:371–383. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Justenhoven C, Pierl CB, Haas S, Fischer
HP, Hamann U, Baisch C, Harth V, Spickenheuer A, Rabstein S,
Vollmert C, et al: Polymorphic loci of E2F2, CCND1 and CCND3 are
associated with HER2 status of breast tumors. Int J Cancer.
124:2077–2081. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Turner NC, Liu Y, Zhu Z, Loi S, Colleoni
M, Loibl S, DeMichele A, Harbeck N, André F, Bayar MA, et al:
Cyclin E1 expression and palbociclib efficacy in previously treated
hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
37:1169–1178. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Zhao ZM, Yost SE, Hutchinson KE, Li SM,
Yuan YC, Noorbakhsh J, Liu Z, Warden C, Johnson RM, Wu X, et al:
CCNE1 amplification is associated with poor prognosis in patients
with triple negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 19:962019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Meijer-van Gelder
ME, Timmermans M, Trapman AM, Garcia RR, Arnold M, Goedheer AJ, de
Weerd V, Portengen H, et al: Which cyclin E prevails as prognostic
marker for breast cancer? Results from a retrospective study
involving 635 lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:3319–3328. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Seyhan AA, Varadarajan U, Choe S, Liu W
and Ryan TE: A genome-wide RNAi screen identifies novel targets of
neratinib resistance leading to identification of potential drug
resistant genetic markers. Mol Biosyst. 8:1553–1570. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Gupta ED, Pachauri M, Ghosh PC and Rajam
MV: Targeting polyamine biosynthetic pathway through RNAi causes
the abrogation of MCF 7 breast cancer cell line. Tumour Biol.
37:1159–1171. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wang X, Zhang T, Zhang S and Shan J:
Prognostic values of F-box members in breast cancer: An online
database analysis and literature review. Biosci Rep.
39:BSR201809492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Piscopo DM and Hinds PW: A role for the
cyclin box in the ubiquitin-mediated degradation of cyclin G1.
Cancer Res. 68:5581–5590. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liu F, Gao X, Yu H, Yuan D, Zhang J, He Y
and Yue L: Effects of expression of exogenous cyclin G1 on
proliferation of human endometrial carcinoma cells. Chin J Physiol.
56:83–89. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Tian JM, Ran B, Zhang CL, Yan DM and Li
XH: Estrogen and progesterone promote breast cancer cell
proliferation by inducing cyclin G1 expression. Braz J Med Biol
Res. 51:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Shahi RB, De Brakeleer S, Caljon B,
Pauwels I, Bonduelle M, Joris S, Fontaine C, Vanhoeij M, Van Dooren
S, Teugels E and De Grève J: Identification of candidate cancer
predisposing variants by performing whole-exome sequencing on index
patients from BRCA1 and BRCA2-negative breast cancer families. BMC
Cancer. 19:3132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Patel H, Abduljabbar R, Lai CF, Periyasamy
M, Harrod A, Gemma C, Steel JH, Patel N, Busonero C, Jerjees D, et
al: Expression of CDK7, cyclin H, and MAT1 is elevated in breast
cancer and is prognostic in estrogen receptor-positive breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 22:5929–5938. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|