|
1
|
Rock KL, Gramm C, Rothstein L, Clark K,
Stein R, Dick L, Hwang D and Goldberg AL: Inhibitors of the
proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the
generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell.
78:761–771. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kwon YT and Ciechanover A: The ubiquitin
code in the ubiquitin-proteasome system and autophagy. Trends
Biochem Sci. 42:873–886. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dikic I: Proteasomal and autophagic
degradation systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 86:193–224. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ronai ZA: Monoubiquitination in
proteasomal degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:8894–8896.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martinez-Fonts K, Davis C, Tomita T,
Elsasser S, Nager AR, Shi Y, Finley D and Matouschek A: The
proteasome 19S cap and its ubiquitin receptors provide a versatile
recognition platform for substrates. Nat Commun. 11:4772020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Varshavsky A: The ubiquitin system, an
immense realm. Annu Rev Biochem. 81:167–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Husnjak K and Dikic I: Ubiquitin-binding
proteins: Decoders of ubiquitin-mediated cellular functions. Annu
Rev Biochem. 81:291–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yau R and Rape M: The increasing
complexity of the ubiquitin code. Nat Cell Biol. 18:579–586. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Swatek KN and Komander D: Ubiquitin
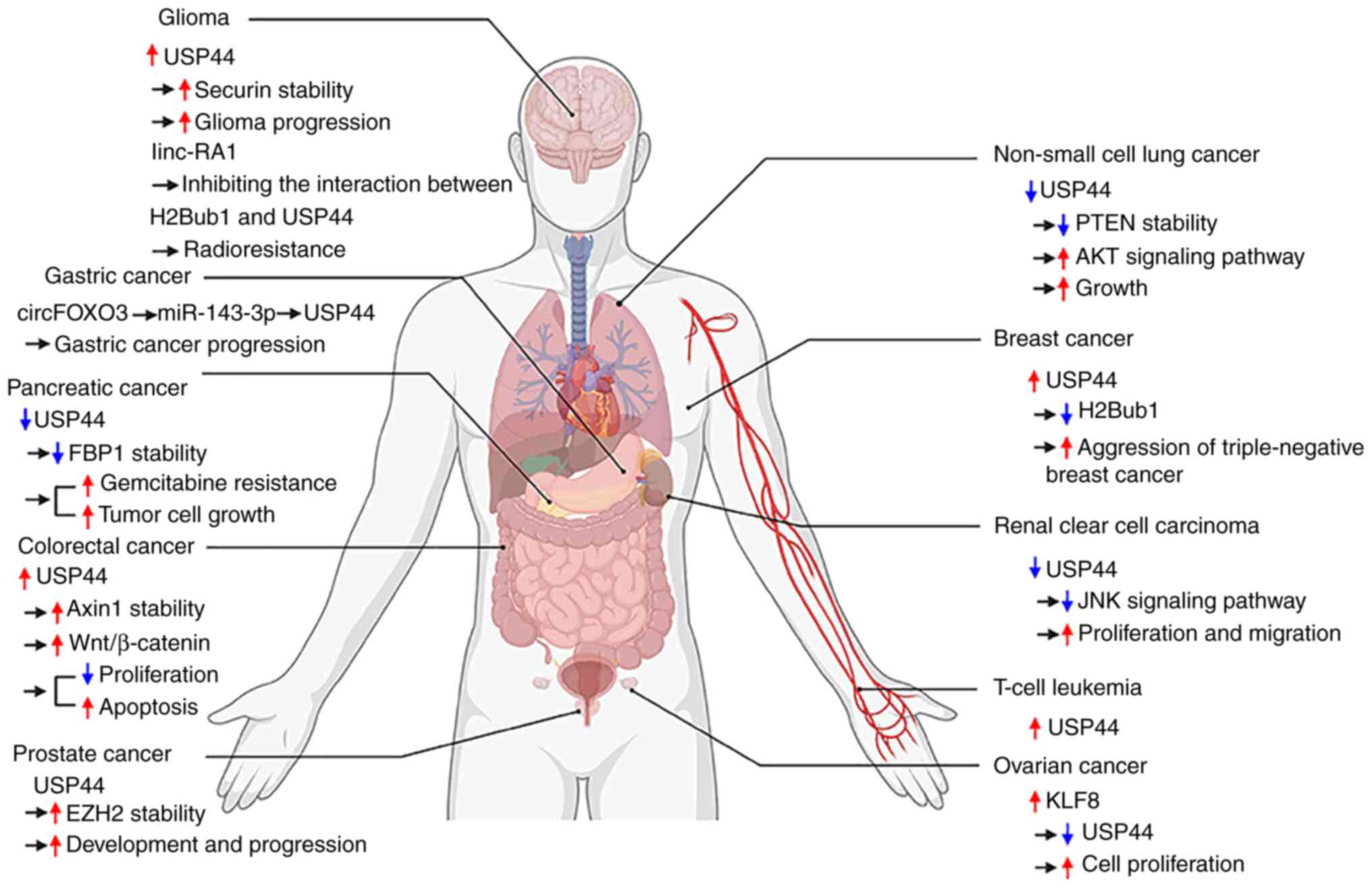
modifications. Cell Res. 26:399–422. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mevissen TET and Komander D: Mechanisms of
deubiquitinase specificity and regulation. Annu Rev Biochem.
86:159–192. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Komander D and Rape M: The ubiquitin code.
Annu Rev Biochem. 81:203–229. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim W, Bennett EJ, Huttlin EL, Guo A, Li
J, Possemato A, Sowa ME, Rad R, Rush J, Comb MJ, et al: Systematic
and quantitative assessment of the ubiquitin-modified proteome. Mol
Cell. 44:325–340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Morreale FE and Walden H: Types of
ubiquitin ligases. Cell. 165:248–248.e1. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Heride C, Urbé S and Clague MJ: Ubiquitin
code assembly and disassembly. Curr Biol. 24:R215–R220. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Quesada V, Díaz-Perales A,
Gutiérrez-Fernández A, Garabaya C, Cal S and López-Otín C: Cloning
and enzymatic analysis of 22 novel human ubiquitin-specific
proteases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 314:54–62. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stegmeier F, Rape M, Draviam VM, Nalepa G,
Sowa ME, Ang XL, McDonald ER III, Li MZ, Hannon GJ, Sorger PK, et
al: Anaphase initiation is regulated by antagonistic ubiquitination
and deubiquitination activities. Nature. 446:876–881. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fuchs G, Shema E, Vesterman R, Kotler E,
Wolchinsky Z, Wilder S, Golomb L, Pribluda A, Zhang F, Haj-Yahya M,
et al: RNF20 and USP44 regulate stem cell differentiation by
modulating H2B monoubiquitylation. Mol Cell. 46:662–673. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang YK, Tian WZ, Zhang RS, Zhang YJ and
Ma HT: Ubiquitin-specific protease 44 inhibits cell growth by
suppressing AKT signaling in non-small cell lung cancer. Kaohsiung
J Med Sci. 35:535–541. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Komander D, Clague MJ and Urbe S: Breaking
the chains: Structure and function of the deubiquitinases. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 10:550–563. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Belle JI and Nijnik A: H2A-DUBbing the
mammalian epigenome: Expanding frontiers for histone H2A
deubiquitinating enzymes in cell biology and physiology. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 50:161–174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu M, Li P, Li M, Li W, Yao T, Wu JW, Gu
W, Cohen RE and Shi Y: Crystal structure of a UBP-family
deubiquitinating enzyme in isolation and in complex with ubiquitin
aldehyde. Cell. 111:1041–1054. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wilkinson KD: Regulation of
ubiquitin-dependent processes by deubiquitinating enzymes. FASEB J.
11:1245–1256. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Amerik A, Swaminathan S, Krantz BA,
Wilkinson KD and Hochstrasser M: In vivo disassembly of free
polyubiquitin chains by yeast Ubp14 modulates rates of protein
degradation by the proteasome. EMBO J. 16:4826–4838. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
D'Andrea A and Pellman D: Deubiquitinating
enzymes: A new class of biological regulators. Crit Rev Biochem Mol
Biol. 33:337–352. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chung CH and Baek SH: Deubiquitinating
enzymes: Their diversity and emerging roles. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 266:633–640. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang Y, Foreman O, Wigle DA, Kosari F,
Vasmatzis G, Salisbury JL, van Deursen J and Galardy PJ: USP44
regulates centrosome positioning to prevent aneuploidy and suppress
tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 122:4362–4374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lan X, Atanassov BS, Li W, Zhang Y,
Florens L, Mohan RD, Galardy PJ, Washburn MP, Workman JL and Dent
SYR: USP44 is an integral component of N-CoR that contributes to
gene repression by deubiquitinating histone H2B. Cell Rep.
17:2382–2393. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mosbech A, Lukas C, Bekker-Jensen S and
Mailand N: The deubiquitylating enzyme USP44 counteracts the DNA
double-strand break response mediated by the RNF8 and RNF168
ubiquitin ligases. J Biol Chem. 288:16579–16587. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Suresh B, Ramakrishna S, Lee HJ, Choi JH,
Kim JY, Ahn WS and Baek KH: K48- and K63-linked polyubiquitination
of deubiquitinating enzyme USP44. Cell Biol Int. 34:799–808. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang HY, Liao BW, Xu ZS, Ran Y, Wang DP,
Yang Y, Luo WW and Wang YY: USP44 positively regulates innate
immune response to DNA viruses through deubiquitinating MITA. PLoS
Pathog. 16:e10081782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lang G, Bonnet J, Umlauf D, Karmodiya K,
Koffler J, Stierle M, Devys D and Tora L: The tightly controlled
deubiquitination activity of the human SAGA complex differentially
modifies distinct gene regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol.
31:3734–3744. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Z, Jones A, Joo HY, Zhou D, Cao Y,
Chen S, Erdjument-Bromage H, Renfrow M, He H, Tempst P, et al:
USP49 deubiquitinates histone H2B and regulates cotranscriptional
pre-mRNA splicing. Genes Dev. 27:1581–1595. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harrigan JA, Jacq X, Martin NM and Jackson
SP: Deubiquitylating enzymes and drug discovery: Emerging
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 17:57–78. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cheng J, Guo J, North BJ, Wang B, Cui CP,
Li H, Tao K, Zhang L and Wei W: Functional analysis of
deubiquitylating enzymes in tumorigenesis and development. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1872:1883122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin YH, Forster M, Liang Y, Yu M, Wang H,
Robert F, Langlais D, Pelletier J, Clare S and Nijnik A: USP44 is
dispensable for normal hematopoietic stem cell function, lymphocyte
development, and B-cell-mediated immune response in a mouse model.
Exp Hematol. 72:1–8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu H: Regulation of APC-Cdc20 by the
spindle checkpoint. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 14:706–714. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sudakin V, Chan GK and Yen TJ: Checkpoint
inhibition of the APC/C in HeLa cells is mediated by a complex of
BUBR1, BUB3, CDC20, and MAD2. J Cell Biol. 154:925–936. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Garnett MJ, Mansfeld J, Godwin C,
Matsusaka T, Wu J, Russell P, Pines J and Venkitaraman AR: UBE2S
elongates ubiquitin chains on APC/C substrates to promote mitotic
exit. Nat Cell Biol. 11:1363–1369. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wickliffe KE, Lorenz S, Wemmer DE, Kuriyan
J and Rape M: The mechanism of linkage-specific ubiquitin chain
elongation by a single-subunit E2. Cell. 144:769–781. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Williamson A, Banerjee S, Zhu X, Philipp
I, Iavarone AT and Rape M: Regulation of ubiquitin chain initiation
to control the timing of substrate degradation. Mol Cell.
42:744–757. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chang L, Zhang Z, Yang J, McLaughlin SH
and Barford D: Atomic structure of the APC/C and its mechanism of
protein ubiquitination. Nature. 522:450–454. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ciechanover A: Proteolysis: From the
lysosome to ubiquitin and the proteasome. Nat Rev Mol. 6:79–87.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meyer HJ and Rape M: Processive ubiquitin
chain formation by the anaphase-promoting complex. Semin Cell Dev
Biol. 22:544–550. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Primorac I and Musacchio A: Panta rhei:
The APC/C at steady state. J Cell Biol. 201:177–189. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Reddy SK, Rape M, Margansky WA and
Kirschner MW: Ubiquitination by the anaphase-promoting complex
drives spindle checkpoint inactivation. Nature. 446:921–925. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Izawa D and Pines J: The mitotic
checkpoint complex binds a second CDC20 to inhibit active APC/C.
Nature. 517:631–634. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Alfieri C, Chang L, Zhang Z, Yang J,
Maslen S, Skehel M and Barford D: Molecular basis of APC/C
regulation by the spindle assembly checkpoint. Nature. 536:431–436.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ciccia A and Elledge SJ: The DNA damage
response: Making it safe to play with knives. Mol Cell. 40:179–204.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bekker-Jensen S and Mailand N: Assembly
and function of DNA double-strand break repair foci in mammalian
cells. DNA Repair (Amst). 9:1219–1228. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lukas J, Lukas C and Bartek J: More than
just a focus: The chromatin response to DNA damage and its role in
genome integrity maintenance. Nat Cell Biol. 13:1161–1169. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen Y, Zhao Y, Yang X, Ren X, Huang S,
Gong S, Tan X, Li J, He S, Li Y, et al: USP44 regulates
irradiation-induced DNA double-strand break repair and suppresses
tumorigenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Nat Commun. 13:5012022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kamileri I, Karakasilioti I and Garinis
GA: Nucleotide excision repair: New tricks with old bricks. Trends
Genet. 28:566–573. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Marteijn JA, Lans H, Vermeulen W and
Hoeijmakers JH: Understanding nucleotide excision repair and its
roles in cancer and ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 15:465–481.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang Y, Mandemaker IK, Matsumoto S,
Foreman O, Holland CP, Lloyd WR, Sugasawa K, Vermeulen W, Marteijn
JA and Galardy PJ: USP44 stabilizes DDB2 to facilitate nucleotide
excision repair and prevent tumors. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6634112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sakaguchi S, Yamaguchi T, Nomura T and Ono
M: Regulatory T cells and immune tolerance. Cell. 133:775–787.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang J, Wei P, Barbi J, Huang Q, Yang E,
Bai Y, Nie J, Gao Y, Tao J, Lu Y, et al: The deubiquitinase USP44
promotes Treg function during inflammation by preventing FOXP3
degradation. EMBO Rep. 21:e503082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Luo WW and Shu HB: Delicate regulation of
the cGAS-MITA-mediated innate immune response. Cell Mol Immunol.
15:666–675. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Chen S, Li J, Wang DL and Sun FL: Histone
H2B lysine 120 monoubiquitination is required for embryonic stem
cell differentiation. Cell Res. 22:1402–1405. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Karpiuk O, Najafova Z, Kramer F, Hennion
M, Galonska C, König A, Snaidero N, Vogel T, Shchebet A,
Begus-Nahrmann Y, et al: The histone H2B monoubiquitination
regulatory pathway is required for differentiation of multipotent
stem cells. Mol Cell. 46:705–713. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy: From phenomenology
to molecular understanding in less than a decade. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 8:931–937. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen S, Jing Y, Kang X, Yang L, Wang DL,
Zhang W, Zhang L, Chen P, Chang JF, Yang XM and Sun FL: Histone H2B
monoubiquitination is a critical epigenetic switch for the
regulation of autophagy. Nucleic Acids Res. 45:1144–1158.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zheng J, Wang B, Zheng R, Zhang J, Huang
C, Zheng R, Huang Z, Qiu W, Liu M, Yang K, et al: Linc-RA1 inhibits
autophagy and promotes radioresistance by preventing H2Bub1/USP44
combination in glioma cells. Cell Death Dis. 11:7582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Targa A and Rancati G: Cancer: A CINful
evolution. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 52:136–144. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gordon DJ, Resio B and Pellman D: Causes
and consequences of aneuploidy in cancer. Nat Rev Genet.
13:189–203. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Simonetti G, Bruno S, Padella A, Tenti E
and Martinelli G: Aneuploidy: Cancer strength or vulnerability? Int
J Cancer. 144:8–25. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Nishimura S, Oki E, Ando K, Iimori M,
Nakaji Y, Nakashima Y, Saeki H, Oda Y and Maehara Y: High
ubiquitin-specific protease 44 expression induces DNA aneuploidy
and provides independent prognostic information in gastric cancer.
Cancer Med. 6:1453–1464. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang Y, van Deursen J and Galardy PJ:
Overexpression of ubiquitin specific protease 44 (USP44) induces
chromosomal instability and is frequently observed in human T-cell
leukemia. PLoS One. 6:e233892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yuan T, Yan F, Ying M, Cao J, He Q, Zhu H
and Yang B: Inhibition of ubiquitin-specific proteases as a novel
anticancer therapeutic strategy. Front Pharmacol. 9:10802018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Timson DJ: Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase:
Getting the message across. Biosci Rep. 39:BSR201901242019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Yang C, Zhu S, Yang H, Deng S, Fan P, Li M
and Jin X: USP44 suppresses pancreatic cancer progression and
overcomes gemcitabine resistance by deubiquitinating FBP1. Am J
Cancer Res. 9:1722–1733. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jin X, Pan Y, Wang L, Ma T, Zhang L, Tang
AH, Billadeau DD, Wu H and Huang H: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
inhibits ERK activation and bypasses gemcitabine resistance in
pancreatic cancer by blocking IQGAP1-MAPK interaction. Cancer Res.
77:4328–4341. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Teodoridis JM, Strathdee G and Brown R:
Epigenetic silencing mediated by CpG island methylation: Potential
as a therapeutic target and as a biomarker. Drug Resist Updat.
7:267–278. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sloane MA, Wong JW, Perera D, Nunez AC,
Pimanda JE, Hawkins NJ, Sieber OM, Bourke MJ, Hesson LB and Ward
RL: Epigenetic inactivation of the candidate tumor suppressor USP44
is a frequent and early event in colorectal neoplasia. Epigenetics.
9:1092–1100. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Huang T, Zhang Q, Ren W, Yan B, Yi L, Tang
T, Lin H and Zhang Y: USP44 suppresses proliferation and enhances
apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by inactivating the
Wnt/β-catenin pathway via Axin1 deubiquitination. Cell Biol Int.
44:1651–1659. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhou J, Wang T, Qiu T, Chen Z, Ma X, Zhang
L and Zou J: Ubiquitin-specific protease-44 inhibits the
proliferation and migration of cells via inhibition of JNK pathway
in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 20:2142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Tang W, Cao Y and Ma X: Novel prognostic
prediction model constructed through machine learning on the basis
of methylation-driven genes in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.
Biosci Rep. 40:BSR202016042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xu D, Tian W, Jiang C, Huang Z and Zheng
S: The anthelmintic agent oxfendazole inhibits cell growth in
non-small cell lung cancer by suppressing c-Src activation. Mol Med
Rep. 19:2921–2926. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Liu T, Sun B, Zhao X, Li Y, Zhao X, Liu Y,
Yao Z, Gu Q, Dong X, Shao B, et al: USP44+ cancer stem cell
subclones contribute to breast cancer aggressiveness by promoting
vasculogenic mimicry. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:2121–2131. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sun B, Zhang S, Zhang D, Du J, Guo H, Zhao
X, Zhang W and Hao X: Vasculogenic mimicry is associated with high
tumor grade, invasion and metastasis, and short survival in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 16:693–698.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Sun T, Sun BC, Zhao XL, Zhao N, Dong XY,
Che N, Yao Z, Ma YM, Gu Q, Zong WK and Liu ZY: Promotion of tumor
cell metastasis and vasculogenic mimicry by way of transcription
coactivation by Bcl-2 and Twist1: A study of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 54:1690–1706. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Luo F, Yang K, Liu RL, Meng C, Dang RF and
Xu Y: Formation of vasculogenic mimicry in bone metastasis of
prostate cancer: Correlation with cell apoptosis and senescence
regulation pathways. Pathol Res Pract. 210:291–295. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Chen X, Wu X and Lei W: USP44
hypermethylation promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in
breast cancer. Future Oncol. 17:279–289. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tarcic O, Granit RZ, Pateras IS, Masury H,
Maly B, Zwang Y, Yarden Y, Gorgoulis VG, Pikarsky E, Ben-Porath I
and Oren M: RNF20 and histone H2B ubiquitylation exert opposing
effects in Basal-Like versus luminal breast cancer. Cell Death
Differ. 24:694–704. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zou Y, Qiu G, Jiang L, Cai Z, Sun W, Hu H,
Lu C, Jin W and Hu G: Overexpression of ubiquitin specific
proteases 44 promotes the malignancy of glioma by stabilizing
tumor-promoter securin. Oncotarget. 8:58231–58246. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Duan R, Du W and Guo W: EZH2: A novel
target for cancer treatment. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1042020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Nutt SL, Keenan C, Chopin M and Allan RS:
EZH2 function in immune cell development. Biol Chem. 401:933–943.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yao Y, Hu H, Yang Y, Zhou G, Shang Z, Yang
X, Sun K, Zhan S, Yu Z, Li P, et al: Downregulation of enhancer of
zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is essential for the induction of autophagy
and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. Genes (Basel). 7:832016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ito T, Teo YV, Evans SA, Neretti N and
Sedivy JM: Regulation of cellular senescence by polycomb chromatin
modifiers through distinct DNA damage- and histone
methylation-dependent pathways. Cell Rep. 22:3480–3492. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Park JM, Lee JE, Park CM and Kim JH: USP44
promotes the tumorigenesis of prostate cancer cells through EZH2
protein stabilization. Mol Cells. 42:17–27. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Xiang T, Jiang HS, Zhang BT and Liu G:
CircFOXO3 functions as a molecular sponge for miR-143-3p to promote
the progression of gastric carcinoma via upregulating USP44. Gene.
753:1447982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Wang Z, Oron E, Nelson B, Razis S and
Ivanova N: Distinct lineage specification roles for NANOG, OCT4,
and SOX2 in human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 10:440–454.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Yu J, Vodyanik MA, Smuga-Otto K,
Antosiewicz-Bourget J, Frane JL, Tian S, Nie J, Jonsdottir GA,
Ruotti V, Stewart R, et al: Induced pluripotent stem cell lines
derived from human somatic cells. Science. 318:1917–1920. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Boyer LA, Lee TI, Cole MF, Johnstone SE,
Levine SS, Zucker JP, Guenther MG, Kumar RM, Murray HL, Jenner RG,
et al: Core transcriptional regulatory circuitry in human embryonic
stem cells. Cell. 122:947–956. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Jung M, Peterson H, Chavez L, Kahlem P,
Lehrach H, Vilo J and Adjaye J: A data integration approach to
mapping OCT4 gene regulatory networks operative in embryonic stem
cells and embryonal carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 5:e107092010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Tropel P, Jung L, André C, Ndandougou A
and Viville S: CpG island methylation correlates with the use of
alternative promoters for USP44 gene expression in human
pluripotent stem cells and testes. Stem Cells Dev. 26:1100–1110.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Mocciaro A and Rape M: Emerging regulatory
mechanisms in ubiquitin-dependent cell cycle control. J Cell Sci.
125:255–263. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Kernan J, Bonacci T and Emanuele MJ: Who
guards the guardian? Mechanisms that restrain APC/C during the cell
cycle. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1865:1924–1933. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Petroski MD and Deshaies RJ: Function and
regulation of cullin-RING ubiquitin ligases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
6:9–20. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Visconti R, Palazzo L, Della Monica R and
Grieco D: Fcp1-dependent dephosphorylation is required for
M-phase-promoting factor inactivation at mitosis exit. Nat Commun.
3:8942012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Berdasco M and Esteller M: Aberrant
epigenetic landscape in cancer: How cellular identity goes awry.
Dev Cell. 19:698–711. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Esteller M: Epigenetic gene silencing in
cancer: The DNA hypermethylome. Hum Mol Genet. 16:R50–R59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Jung J, Kim Y, Song J, Yoon YJ, Kim DE,
Kim JA, Jin Y, Lee YJ, Kim S, Kwon BM and Han DC: KRIBB53 binds to
OCT4 and enhances its degradation through the proteasome, causing
apoptotic cell death of OCT4-positive testicular germ cell tumors.
Carcinogenesis. 39:838–849. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|