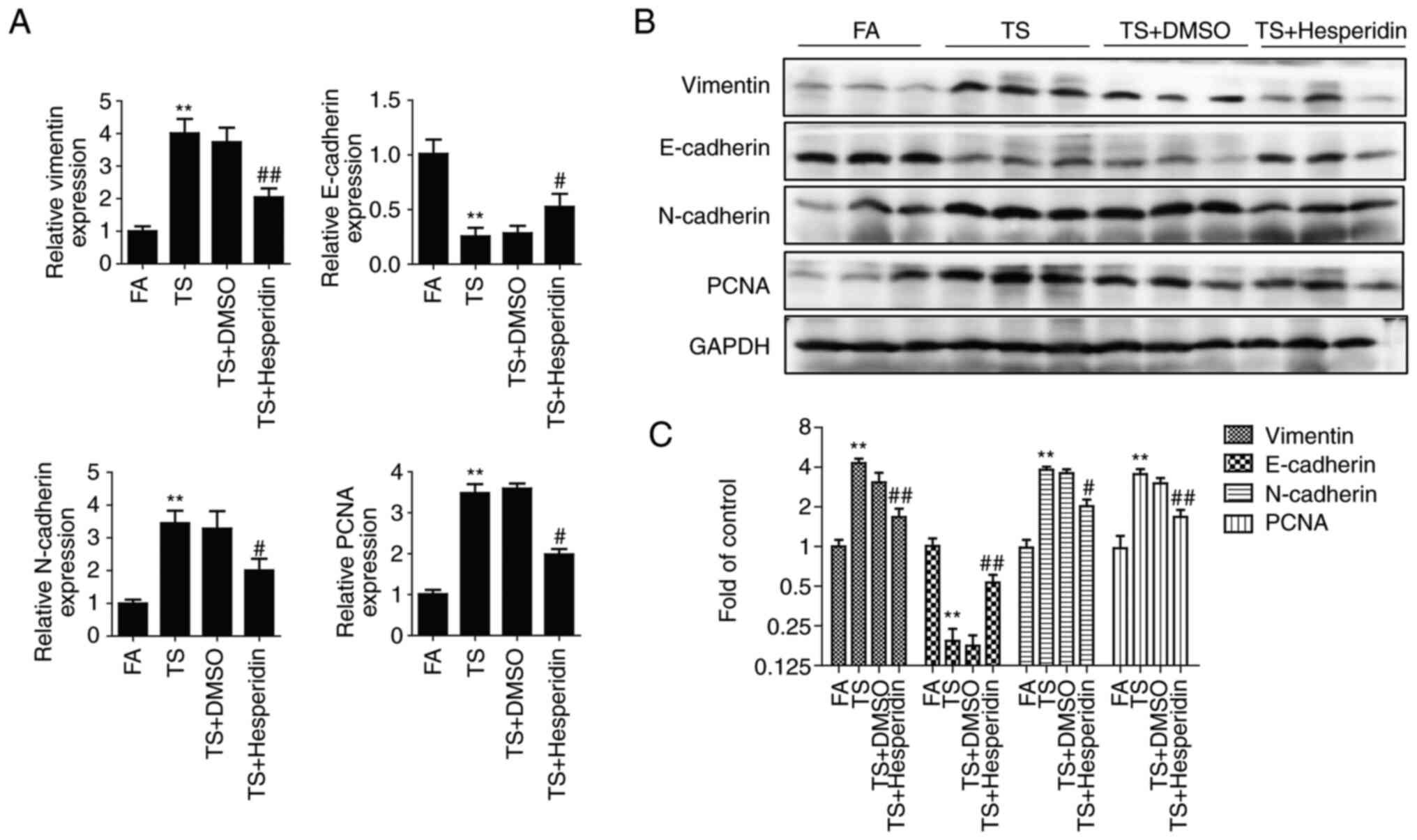
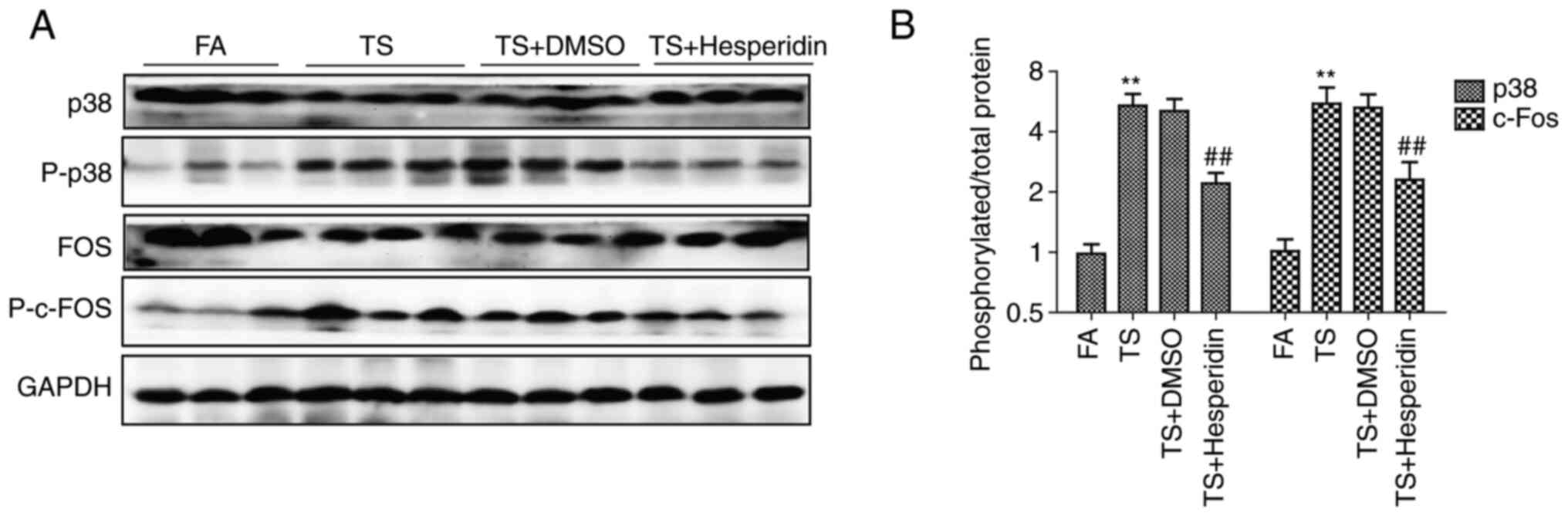
|
1
|
Alexander M, Kim SY and Cheng H: Update
2020: Management of non-small cell lung cancer. Lung. 198:897–907.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang Z, Sun S, Lee M, Maslov AY, Shi M,
Waldman S, Marsh A, Siddiqui T, Dong X, Peter Y, et al: Single-cell
analysis of somatic mutations in human bronchial epithelial cells
in relation to aging and smoking. Nat Genet. 54:492–498. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pfeifer GP: Smoke signals in the DNA of
normal lung cells. Nature. 578:224–226. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nasim F, Sabath BF and Eapen GA: Lung
cancer. Med Clin North Am. 103:463–473. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS: Lung Cancer
2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med.
41:1–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu J, Chen SJ, Hsu SW, Zhang J, Li JM,
Yang DC, Gu S, Pinkerton KE and Chen CH: MARCKS cooperates with
NKAP to activate NF-kB signaling in smoke-related lung cancer.
Theranostics. 11:4122–4136. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wen J, Fu JH, Zhang W and Guo M: Lung
carcinoma signaling pathways activated by smoking. Chin J Cancer.
30:551–558. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang Z, Xie W, Wu R, Geng H, Zhao L, Xie
C, Li X, Huang C, Zhu J, Zhu M, et al: ERK5 negatively regulates
tobacco smoke-induced pulmonary epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Oncotarget. 6:19605–19618. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pastushenko I, Mauri F, Song Y, Cock F,
Meeusen B, Swedlund B, Impens F, Van Haver D, Opitz M, Thery M, et
al: Fat1 deletion promotes hybrid EMT state, tumour stemness and
metastasis. Nature. 589:448–455. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Banerjee P, Xiao GY, Tan X, Zheng VJ, Shi
L, Rabassedas MNB, Guo HF, Liu X, Yu J, Diao L, et al: The EMT
activator ZEB1 accelerates endosomal trafficking to establish a
polarity axis in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Nat Commun.
12:63542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Adachi Y, Ito K, Hayashi Y, Kimura R, Tan
TZ, Yamaguchi R and Ebi H: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is
a cause of both intrinsic and acquired resistance to KRAS G12C
inhibitor in KRAS G12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 26:5962–5973. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chu S, Ma L, Wu Y, Zhao X, Xiao B and Pan
Q: C-EBPβ mediates in cigarette/IL-17A-induced bronchial
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in COPD mice. BMC Pulm Med.
21:3762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen TY, Liu CH, Chen TH, Chen MR, Liu SW,
Lin P and Lin KM: Conditioned media of adipose-derived stem cells
suppresses sidestream cigarette smoke extract induced cell death
and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung epithelial cells. Int
J Mol Sci. 22:120692021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lu L, Chen J, Li M, Tang L, Wu R, Jin L
and Liang Z: β-carotene reverses tobacco smoke-induced gastric EMT
via Notch pathway in vivo. Oncol Rep. 39:1867–1873.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie C, Zhu J, Huang C, Yang X, Wang X,
Meng Y, Geng S, Wu J, Shen H, Hu Z, et al: Interleukin-17A mediates
tobacco smoke-induced lung cancer epithelial-mesenchymal transition
through transcriptional regulation of ΔNp63α on miR-19. Cell Biol
Toxicol. 38:273–289. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xie C, Zhu J, Yang X, Huang C, Zhou L,
Meng Z, Li X and Zhong C: TAp63α is involved in tobacco
smoke-induced lung cancer EMT and the anti-cancer activity of
curcumin via miR-19 transcriptional suppression. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:6454022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Su X, Chen J, Lin X, Chen X, Zhu Z, Wu W,
Lin H, Wang J, Ye J and Zeng Y: FERMT3 mediates cigarette
smoke-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Respir Res. 22:2862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gandhi GR, Antony PJ, Lana MJMP, da Silva
BFX, Oliveira RV, Jothi G, Hariharan G, Mohana T, Gan RY, Gurgel
RQ, et al: Natural products modulating interleukins and other
inflammatory mediators in tumor-bearing animals: A systematic
review. Phytomedicine. 100:1540382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan LTO and Trio-Ranche FKC: Atypical
lymphoid proliferation of the orbit. GMS Ophthalmol Cases.
12:Doc062022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mondal P, Mohapatra S, Bhunia D, Gharai
PK, Mukherjee N, Gupta V and Ghosh S and Ghosh S: Designed hybrid
anticancer nuclear-localized peptide inhibits aggressive cancer
cell proliferation. RSC Med Chem. 13:196–201. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu JY, Chen YJ, Fu XQ, Li JK, Chou JY, Yin
CL, Bai JX, Wu Y, Wang XQ, Li AS, et al: Chrysoeriol suppresses
hyperproliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like
synoviocytes and inhibits JAK2/STAT3 signaling. BMC Complement Med
Ther. 22:732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Irie H, Ozaki M, Chubachi S, Hegab AE,
Tsutsumi A, Kameyama N, Sakurai K, Nakayama S, Kagawa S, Wada S, et
al: Short-term intermittent cigarette smoke exposure enhances
alveolar type 2 cell stemness via fatty acid oxidation. Respir Res.
23:412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gu W, Wang L, Deng G, Gu X, Tang Z, Li S,
Jin W, Yang J, Guo X and Li Q: Knockdown of long noncoding RNA MIAT
attenuates cigarette smoke-induced airway remodeling by
downregulating miR-29c-3p-HIF3A axis. Toxicol Lett. 357:11–19.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Geng H, Zhao L, Liang Z, Zhang Z, Xie D,
Bi L, Wang Y, Zhang T, Cheng L, Yu D and Zhong C: Cigarette smoke
extract-induced proliferation of normal human urothelial cells via
the MAPK/AP-1 pathway. Oncol Lett. 13:469–475. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rovida E and Tusa I: Targeting MAPK in
cancer 2.0. Int J Mol Sci. 23:57022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Caeser R, Hulton C, Costa E, Durani V,
Little M, Chen X, Tischfield SE, Asher M, Kombak FE, Chavan SS, et
al: MAPK pathway activation selectively inhibits ASCL1-driven small
cell lung cancer. iScience. 24:1032242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang B, Zhuang R, Luo X, Yin L, Pang C,
Feng T, You H, Zhai Y, Ren Y, Zhang L, et al: Prevalence of
metabolically healthy obese and metabolically obese but normal
weight in adults worldwide: A meta-analysis. Horm Metab Res.
47:839–845. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Okada T, Sinha S, Esposito I, Schiavon G,
López-Lago MA, Su W, Pratilas CA, Abele C, Hernandez JM, Ohara M,
et al: The Rho GTPase Rnd1 suppresses mammary tumorigenesis and EMT
by restraining Ras-MAPK signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 17:81–94. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kang J, Park JH, Kong JS, Kim MJ, Lee SS,
Park S and Myung JK: PINX1 promotes malignant transformation of
thyroid cancer through the activation of the AKT/MAPK/β-catenin
signaling pathway. Am J Cancer Res. 11:5485–5495. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kumar D, Patel SA, Hassan MK, Mohapatra N,
Pattanaik N and Dixit M: Reduced IQGAP2 expression promotes EMT and
inhibits apoptosis by modulating the MEK-ERK and p38 signaling in
breast cancer irrespective of ER status. Cell Death Dis.
12:3892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhu N, Zhang XJ, Zou H, Zhang YY, Xia JW,
Zhang P, Zhang YZ, Li J, Dong L, Wumaier G and Li SQ: PTPL1
suppresses lung cancer cell migration via inhibiting TGF-β1-induced
activation of p38 MAPK and Smad 2/3 pathways and EMT. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 42:1280–1287. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shu L, Chen S, Lin S, Lin H, Shao Y, Yao
J, Qu L, Zhang Y, Liu X, Du X, et al: The pseudomonas aeruginosa
secreted protein PA3611 promotes bronchial epithelial cell
epithelial-mesenchymal transition via integrin αvβ6-mediated
TGF-β1-induced p38/NF-κB pathway activation. Front Microbiol.
12:7637492022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li S, Wang H, Ma R and Wang L: Schisandrin
B inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness of
large-cell lung cancer cells and tumorigenesis in xenografts via
inhibiting the NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Oncol Rep.
45:1152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liang Z, Wu R, Xie W, Zhu M, Xie C, Li X,
Zhu J, Zhu W, Wu J, Geng S, et al: Curcumin reverses tobacco
smoke-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition by suppressing the
MAPK pathway in the lungs of mice. Mol Med Rep. 17:2019–2025.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Saxena A, Walters MS, Shieh JH, Shen LB,
Gomi K, Downey RJ, Crystal RG and Moore MAS: Extracellular vesicles
from human airway basal cells respond to cigarette smoke extract
and affect vascular endothelial cells. Sci Rep. 11:61042021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lu Q, Lai Y, Zhang H, Ren K, Liu W, An Y,
Yao J and Fan H: Hesperetin inhibits TGF-β1-induced migration and
invasion of triple negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells via
suppressing Fyn/Paxillin/RhoA pathway. Integr Cancer Ther.
21:153473542210869002022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ricci A, Gallorini M, Del Bufalo D,
Cataldi A, D'Agostino I, Carradori S and Zara S: Negative
modulation of the angiogenic cascade induced by allosteric kinesin
Eg5 inhibitors in a gastric adenocarcinoma in vitro model.
Molecules. 27:9572022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang SW, Sheng H, Zheng F and Zhang F:
Hesperetin promotes DOT1L degradation and reduces histone H3K79
methylation to inhibit gastric cancer metastasis. Phytomedicine.
84:1534992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang J, Wu D, Vikash, Song J, Wang J, Yi
J and Dong W: Hesperetin induces the apoptosis of gastric cancer
cells via activating mitochondrial pathway by increasing reactive
oxygen species. Dig Dis Sci. 60:2985–2995. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Semis HS, Kandemir FM, Kaynar O, Dogan T
and Arikan SM: The protective effects of hesperidin against
paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy in rats. Life Sci.
287:1201042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou L, Gu W, Kui F, Gao F, Niu Y, Li W,
Zhang Y, Guo L, Wang J, Guo Z and Du G: The mechanism and candidate
compounds of aged citrus peel (chenpi) preventing chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease and its progression to lung cancer.
Food Nutr Res. 65:2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kong W, Ling X, Chen Y, Wu X, Zhao Z, Wang
W, Wang S, Lai G and Yu Z: Hesperetin reverses
P-glycoprotein-mediated cisplatin resistance in DDP-resistant human
lung cancer cells via modulation of the nuclear factor-κB signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 45:1213–1224. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu G, Cao C, Deng Z, Li J, Zhou X, Huang Z
and Cen C: Effects of matrine in combination with cisplatin on
liver cancer. Oncol Lett. 21:662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang B, Gong A, Shi H, Bie Q, Liang Z, Wu
P, Mao F, Qian H and Xu W: Identification of a novel YAP-14-3-3ζ
negative feedback loop in gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
8:71894–71910. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lu L, Chen J, Tang H, Bai L, Lu C, Wang K,
Li M, Yan Y, Tang L, Wu R, et al: EGCG suppresses ERK5 activation
to reverse tobacco smoke-triggered gastric epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in BALB/c mice. Nutrients. 8:3802016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lu L, Liang Q, Shen S, Feng L, Jin L and
Liang ZF: Tobacco smoke plays an important role in initiation and
development of lung cancer by promoting the characteristics of
cancer stem cells. Cancer Manag Res. 12:9735–9739. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Intlekofer AM and Finley LWS: Metabolic
signatures of cancer cells and stem cells. Nat Metab. 1:177–188.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liang Z, Wu R, Xie W, Xie C, Wu J, Geng S,
Li X, Zhu M, Zhu W, Zhu J, et al: Effects of curcumin on tobacco
smoke-induced hepatic MAPK pathway activation and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in vivo. Phytother Res.
31:1230–1239. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Liang Z, Lu L, Mao J, Li X, Qian H and Xu
W: Curcumin reversed chronic tobacco smoke exposure induced
urocystic EMT and acquisition of cancer stem cells properties via
Wnt/β-catenin. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30662017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Terry S, Savagner P, Ortiz-Cuaran S,
Mahjoubi L, Saintigny P, Thiery JP and Chouaib S: New insights into
the role of EMT in tumor immune escape. Mol Oncol. 11:824–846.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jang HR, Shin SB, Kim CH, Won JY, Xu R,
Kim DE and Yim H: PLK1/vimentin signaling facilitates immune escape
by recruiting Smad2/3 to PD-L1 promoter in metastatic lung
adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 28:2745–2764. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bai X, Wei H, Liu W, Coker OO, Gou H, Liu
C, Zhao L, Li C, Zhou Y, Wang G, et al: Cigarette smoke promotes
colorectal cancer through modulation of gut microbiota and related
metabolites. Gut. 71:2439–2450. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jia Y, Zhang Q, Liu Z, Pan P, Jia Y, Zhu
P, Jiao Y, Kang G and Ma X: The role of α5-nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor/NLRP3 signaling pathway in lung adenocarcinoma cell
proliferation and migration. Toxicology. 469:1531202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Agraval H, Sharma JR, Prakash N and Yadav
UCS: Fisetin suppresses cigarette smoke extract-induced epithelial
to mesenchymal transition of airway epithelial cells through
regulating COX-2/MMPs/β-catenin pathway. Chem Biol Interact.
351:1097712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang J, Chang Y, Xia H, Xu L and Wei X:
HIST1H2BN induced cell proliferation and EMT phenotype in prostate
cancer via NF-κB signal pathway. Genes Genomics. 43:1361–1369.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xueqin T, Jinhong M and Yuping H: Inhibin
subunit beta A promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of breast
cancer through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Bioengineered.
12:11567–11575. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yang M, Jin M, Li K, Liu H, Yang X, Zhang
X, Zhang B, Gong A and Bie Q: TRAF6 promotes gastric cancer cell
self-renewal, proliferation, and migration. Stem Cells Int.
2020:32961922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Drosten M and Barbacid M: Targeting the
MAPK pathway in KRAS-driven tumors. Cancer Cell. 37:543–550. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lee S, Rauch J and Kolch W: Targeting MAPK
signaling in cancer: Mechanisms of drug resistance and sensitivity.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:11022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Arora A, Bhuria V, Singh S, Pathak U,
Mathur S, Hazari PP, Roy BG, Sandhir R, Soni R, Dwarakanath BS and
Bhatt AN: Amifostine analog, DRDE-30, alleviates radiation induced
lung damage by attenuating inflammation and fibrosis. Life Sci.
298:1205182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xie X, Deng T, Duan J, Xie J, Yuan J and
Chen M: Exposure to polystyrene microplastics causes reproductive
toxicity through oxidative stress and activation of the p38 MAPK
signaling pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 190:1101332020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Sanit J, Prompunt E, Adulyaritthikul P,
Nokkaew N, Mongkolpathumrat P, Kongpol K, Kijtawornrat A, Petchdee
S, Barrère-Lemaire S and Kumphune S: Combination of metformin and
p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, reduced myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury in non-obese type 2 diabetic
Goto-Kakizaki rats. Exp Ther Med. 18:1701–1714. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yamamoto S, Lee S, Ariyasu T, Endo S,
Miyata S, Yasuda A, Harashima A, Ohta T, Kumagai-Τakei N, Ito T, et
al: Ingredients such as trehalose and hesperidin taken as
supplements or foods reverse alterations in human T cells, reducing
asbestos exposure-induced antitumor immunity. Int J Oncol.
58:22021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Deng J, Liu L, Li L, Sun J and Yan F:
Hesperidin delays cell cycle progression into the G0/G1 phase via
suspension of MAPK signaling pathway in intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 36:e229812022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|