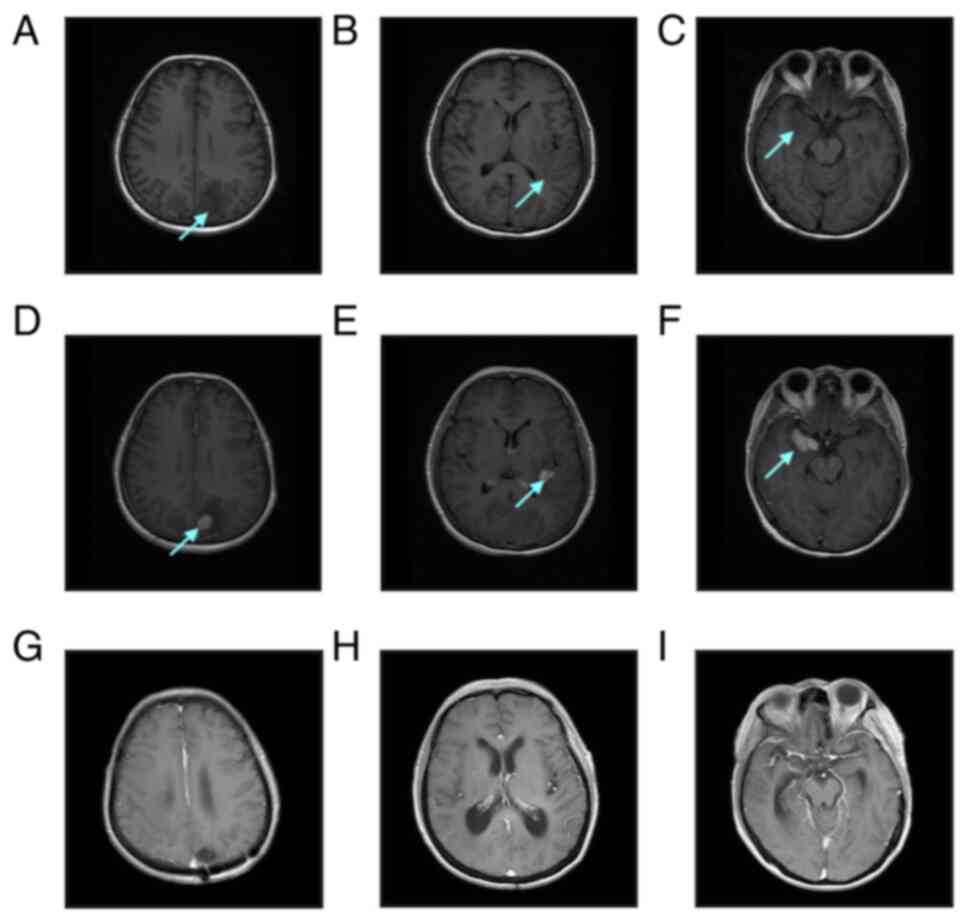
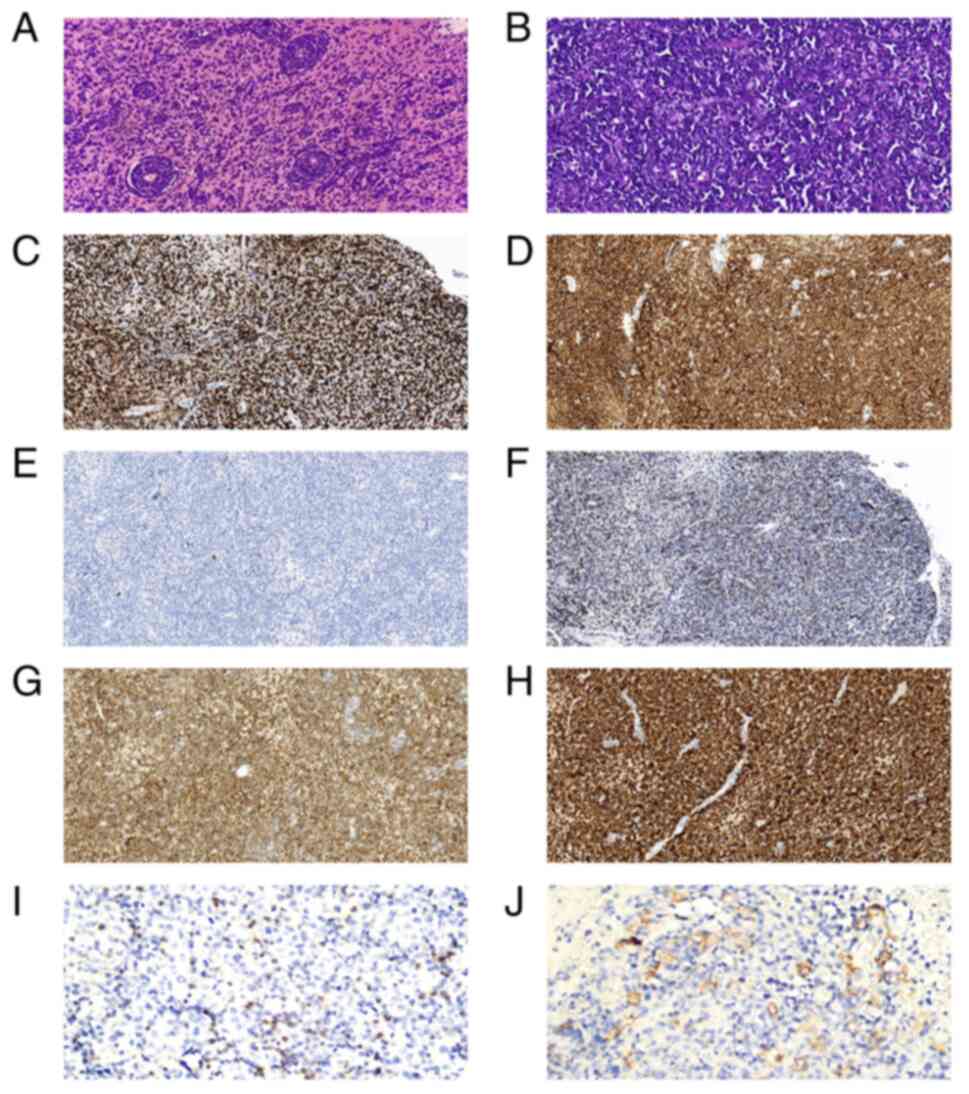
|
1
|
Devi K, Ali N and Ahmed A: Case report of
primary CD20 negative diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Oxf Med Case
Reports. 2021:omab1142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qunaj L, Castillo JJ and Olszewski AJ:
CD20-negative large B-cell lymphomas: Analysis of the National
cancer database. Blood. 128:42262016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Katchi T and Liu D: Diagnosis and
treatment of CD20 negative B cell lymphomas. Biomark Res. 5:52017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tomita A: Genetic and epigenetic
modulation of CD20 Expression in B-Cell Malignancies: Molecular
mechanisms and significance to rituximab resistance. J Clin Exp
Hematop. 56:89–99. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chihara D and Dunleavy K: Primary central
nervous system lymphoma: Evolving biologic insights and recent
therapeutic advances. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 21:73–79. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gamonet C, Bole-Richard E, Delherme A,
Aubin F, Toussirot E, Garnache-Ottou F, Godet Y, Ysebaert L,
Tournilhac O, Caroline D, et al: New CD20 alternative splice
variants: Molecular identification and differential expression
within hematological B cell malignancies. Exp Hematol Oncol.
5:72016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pavlasova G and Mraz M: The regulation and
function of CD20: An ‘enigma’ of B-cell biology and targeted
therapy. Haematologica. 105:1494–1506. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rushton CK, Arthur SE, Alcaide M, Cheung
M, Jiang A, Coyle KM, Cleary KLS, Thomas N, Hilton LK, Michaud N,
et al: Genetic and evolutionary patterns of treatment resistance in
relapsed B-cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 4:2886–2898. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Terui Y, Mishima Y, Sugimura N, Kojima K,
Sakurai T, Mishima Y, Kuniyoshi R, Taniyama A, Yokoyama M, Sakajiri
S, et al: Identification of CD20 C-terminal deletion mutations
associated with loss of CD20 expression in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:2523–2530. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Goldwirt L, Beccaria K, Ple A, Sauvageon H
and Mourah S: Ibrutinib brain distribution: A preclinical study.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 81:783–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lionakis MS, Dunleavy K, Roschewski M,
Widemann BC, Butman JA, Schmitz R, Yang Y, Cole DE, Melani C,
Higham CS, et al: Inhibition of B cell receptor signaling by
ibrutinib in primary CNS lymphoma. Cancer Cell. 31:833–843.e5.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Li Y, Zhuang Z, Wang W, Wei C,
Zhao D, Zhou D and Zhang W: Preliminary evaluation of
zanubrutinib-containing regimens in DLBCL and the cerebrospinal
fluid distribution of zanubrutinib: A 13-case series. Front Oncol.
11:7604052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou S, Xie J, Huang Z, Deng L, Wu L, Yu J
and Meng X: Anti-PD-(L)1 immunotherapy for brain metastases in
non-small cell lung cancer: Mechanisms, advances, and challenges.
Cancer Lett. 502:166–179. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Soussain C, Choquet S, Blonski M, Leclercq
D, Houillier C, Rezai K, Bijou F, Houot R, Boyle E, Gressin R, et
al: Ibrutinib monotherapy for relapse or refractory primary CNS
lymphoma and primary vitreoretinal lymphoma: Final analysis of the
phase II ‘proof-of-concept’ iLOC study by the Lymphoma study
association (LYSA) and the French oculo-cerebral lymphoma (LOC)
network. Eur J Cancer. 117:121–130. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rubenstein JL: Biology of CNS lymphoma and
the potential of novel agents. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ
Program. 2017:556–564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Grommes C, Pastore A, Palaskas N, Tang SS,
Campos C, Schartz D, Codega P, Nichol D, Clark O, Hsieh WY, et al:
Ibrutinib unmasks critical role of bruton tyrosine kinase in
primary CNS lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 7:1018–1029. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taylor MH, Betts CB, Maloney L, Nadler E,
Algazi A, Guarino MJ, Nemunaitis J, Jimeno A, Patel P,
Munugalavadla V, et al: Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in
combination with acalabrutinib in advanced head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma: Phase 2 Proof-of-Concept Study. Clin Cancer Res.
28:903–914. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Overman M, Javle M, Davis RE, Vats P,
Kumar-Sinha C, Xiao L, Mettu NB, Parra ER, Benson AB, Lopez CD, et
al: Randomized phase II study of the Bruton tyrosine kinase
inhibitor acalabrutinib, alone or with pembrolizumab in patients
with advanced pancreatic cancer. J Immunother Cancer.
8:e0005872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang T, Harrison MR, O'Donnell PH, Alva
AS, Hahn NM, Appleman LJ, Cetnar J, Burke JM, Fleming MT, Milowsky
MI, et al: A randomized phase 2 trial of pembrolizumab versus
pembrolizumab and acalabrutinib in patients with platinum-resistant
metastatic urothelial cancer. Cancer. 126:4485–4497. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kim KH, Cho J, Ku BM, Koh J, Sun JM, Lee
SH, Ahn JS, Cheon J, Min YJ, Park SH, et al: The First-week
proliferative response of peripheral blood PD-1+CD8+ T
cells predicts the response to Anti-PD-1 therapy in solid tumors.
Clin Cancer Res. 25:2144–2154. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Taggart D, Andreou T, Scott KJ, Williams
J, Rippaus N, Brownlie RJ, Ilett EJ, Salmond RJ, Melcher A and
Lorger M: Anti-PD-1/anti-CTLA-4 efficacy in melanoma brain
metastases depends on extracranial disease and augmentation of
CD8+ T cell trafficking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:E1540–E1549. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Eguren-Santamaria I, Sanmamed MF, Goldberg
SB, Kluger HM, Idoate MA, Lu BY, Corral J, Schalper KA, Herbst RS
and Gil-Bazo I: PD-1/PD-L1 Blockers in NSCLC brain metastases:
Challenging paradigms and clinical practice. Clin Cancer Res.
26:4186–4197. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lesokhin AM, Ansell SM, Armand P, Scott
EC, Halwani A, Gutierrez M, Millenson MM, Cohen AD, Schuster SJ,
Lebovic D, et al: Nivolumab in patients with relapsed or refractory
hematologic malignancy: Preliminary results of a phase Ib study. J
Clin Oncol. 34:2698–2704. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ansell SM, Minnema MC, Johnson P,
Timmerman JM, Armand P, Shipp MA, Rodig SJ, Ligon AH, Roemer MGM,
Reddy N, et al: Nivolumab for relapsed/refractory diffuse large
B-Cell lymphoma in patients ineligible for or having failed
autologous transplantation: A single-arm, phase II study. J Clin
Oncol. 37:481–489. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nayak L, Iwamoto FM, LaCasce A, Mukundan
S, Roemer MGM, Chapuy B, Armand P, Rodig SJ and Shipp MA: PD-1
blockade with nivolumab in relapsed/refractory primary central
nervous system and testicular lymphoma. Blood. 129:3071–3073. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hanna BS, Yazdanparast H, Demerdash Y,
Roessner PM, Schulz R, Lichter P, Stilgenbauer S and Seiffert M:
Combining ibrutinib and checkpoint blockade improves
CD8+ T-cell function and control of chronic lymphocytic
leukemia in Em-TCL1 mice. Haematologica. 106:968–977. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sagiv-Barfi I, Kohrt HE, Czerwinski DK, Ng
PP, Chang BY and Levy R: Therapeutic antitumor immunity by
checkpoint blockade is enhanced by ibrutinib, an inhibitor of both
BTK and ITK. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:E966–E972. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qorraj M, Bruns H, Böttcher M, Weigand L,
Saul D, Mackensen A, Jitschin R and Mougiakakos D: The PD-1/PD-L1
axis contributes to immune metabolic dysfunctions of monocytes in
chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia. 31:470–478. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chang CH, Qiu J, O'Sullivan D, Buck MD,
Noguchi T, Curtis JD, Chen Q, Gindin M, Gubin MM, van der Windt GJ,
et al: Metabolic competition in the tumor microenvironment is a
driver of cancer progression. Cell. 162:1229–1241. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu JJ, Wang WH, Dong M, Ma SS, Zhang XD,
Zhu LN, Niu ST, Ding MJ, Zhang JM, Zhang L, et al:
Orelabrutinib-bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor-based regimens in
the treatment of central nervous system lymphoma: A retrospective
study. Invest New Drugs. 40:650–659. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Wang W, Zhao DQ, Zhang W and Zhou
DB: Preliminary results of a phase II study of orelabrutinib in
combination with anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody in refractory or
relapsed primary CNS lymphoma. Proceedings of the EHA2022. EHA
Library; pp. S2242022
|