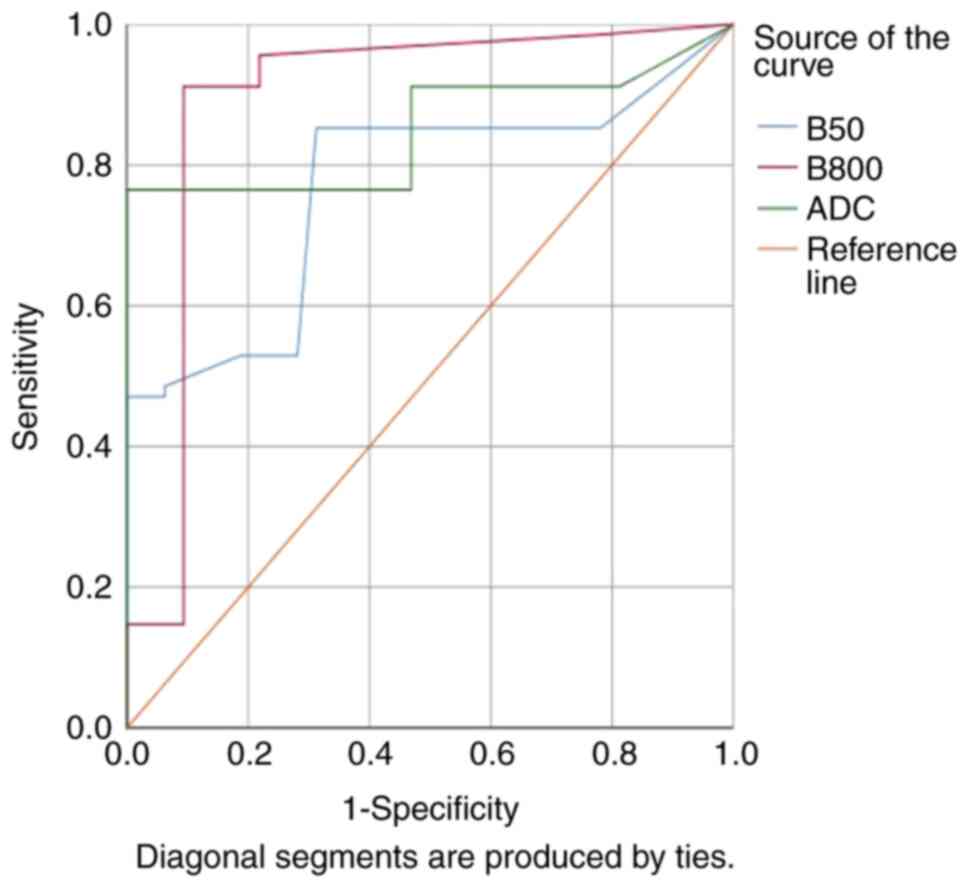
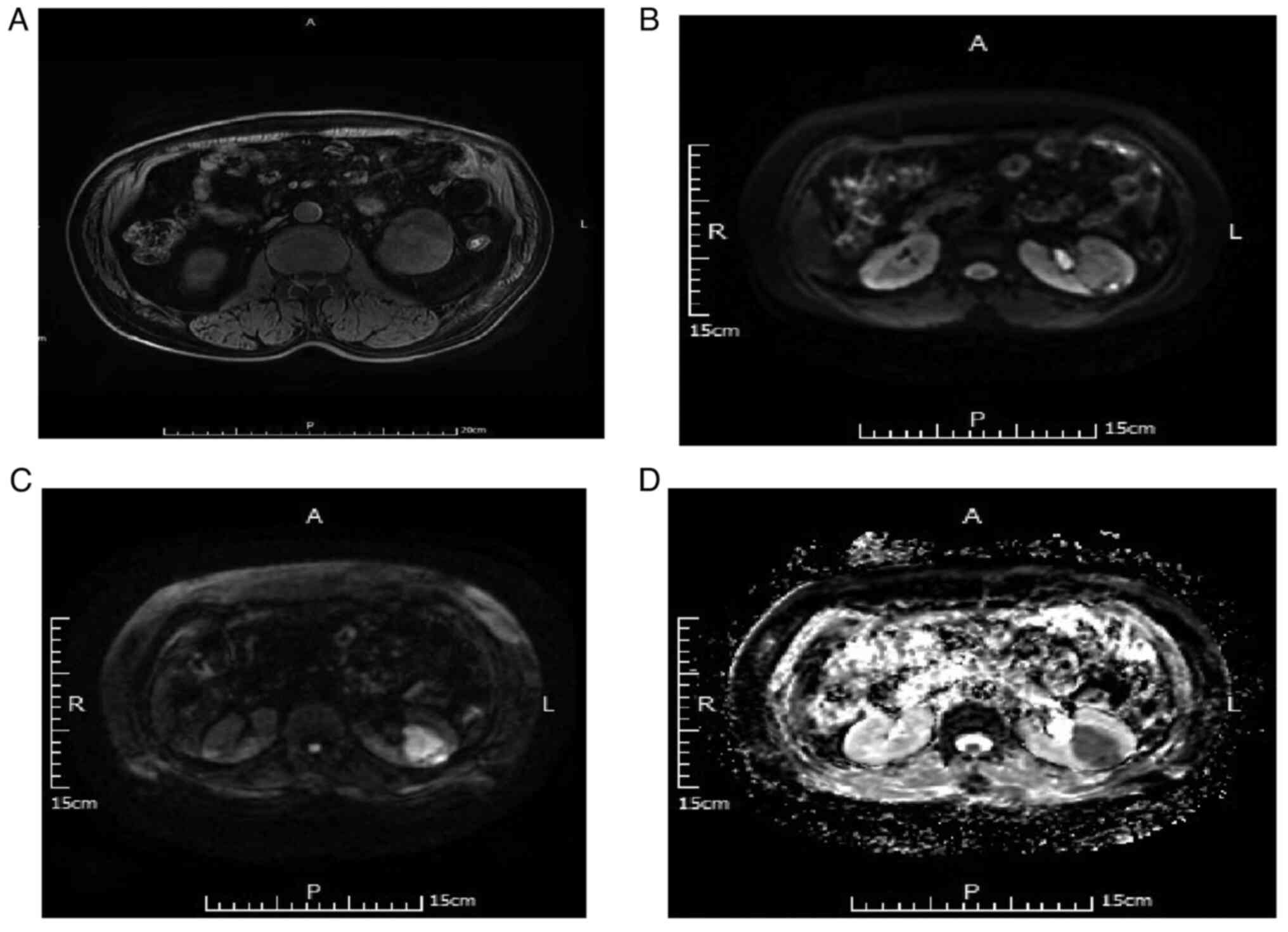
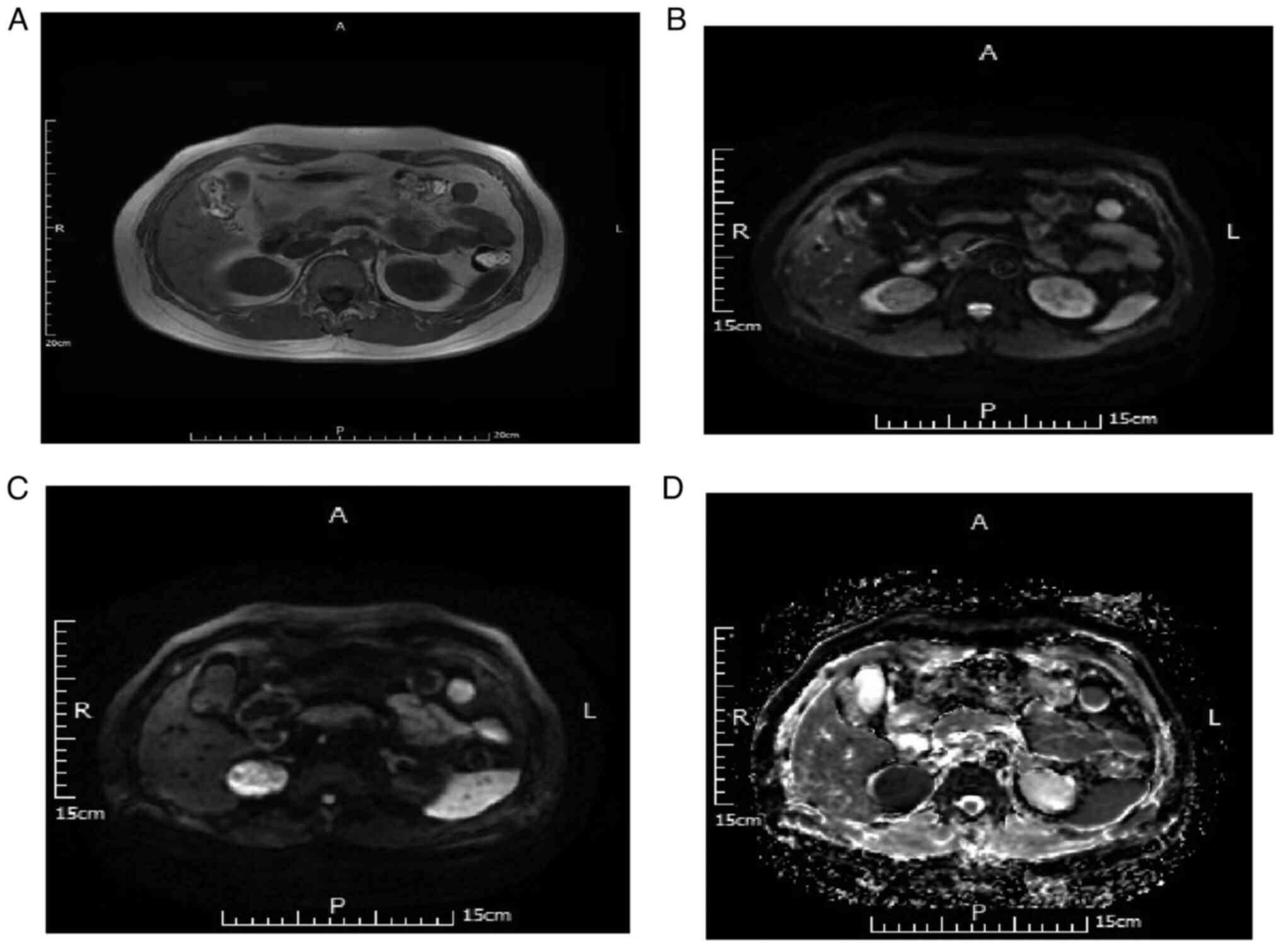
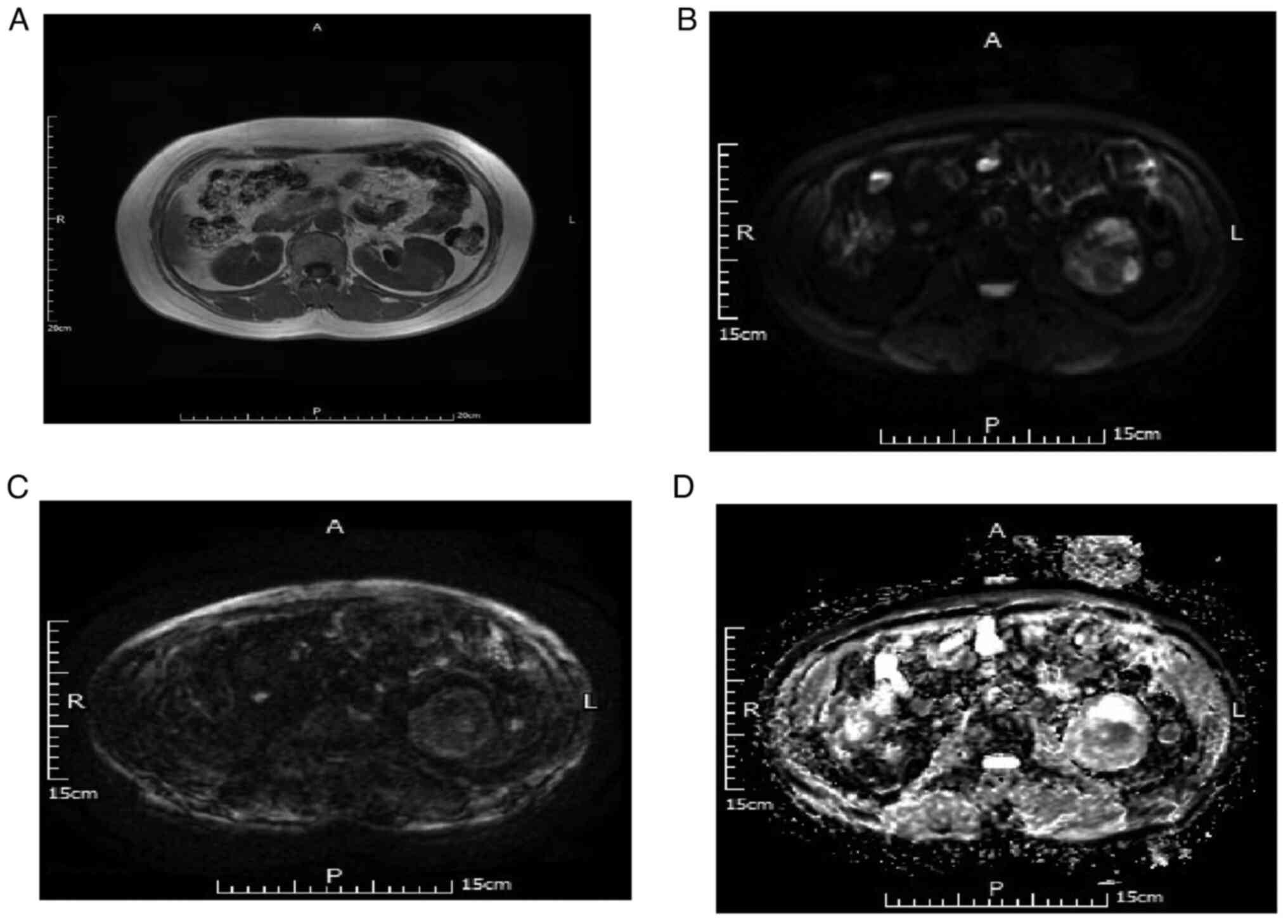
|
1
|
Wang H, Cheng L, Zhang X, Wang D, Guo A,
Gao Y and Ye H: Renal cell carcinoma: Diffusion-weighted MR imaging
for subtype differentiation at 3.0 T. Radiology. 257:135–143. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chowdhury S and Choueiri TK: Recent
advances in the systemic treatment of metastatic papillary renal
cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 9:373–379. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Erbay G, Koc Z, Karadeli E, Kuzgunbay B,
Goren MR and Bal N: Evaluation of malignant and benign renal
lesions using diffusion-weighted MRI with multiple b values. Acta
Radiol. 3:359–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dale BM, Braithwaite AC, Boll DT and
Merkle EM: Field strength and diffusion encoding technique affect
the apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in
diffusion-weighted imaging of the abdomen. Invest Radiol.
45:104–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Srinivasan A, Dvorak R, Perni K, Rohrer S
and Mukherji SK: Differentiation of benign and malignant pathology
in the head and neck using 3T apparent diffusion coefficient
values: Early experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 29:40–44. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Manenti G, Di Roma M, Mancino S,
Bartolucci DA, Palmieri G, Mastrangeli R, Miano R, Squillaci E and
Simonetti G: Malignant renal neoplasms: Correlation between ADC
values and cellularity in diffusion weighted magnetic resonance
imaging at 3 T. Radiol Med. 113:199–213. 2008.(In English,
Italian). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen J, Sun J, Xing W, Ding J, Chen T, Dai
Y, Sun J and Hu J: Prediction of nuclear grade of clear cell renal
cell carcinoma with MRI: Intratumoral susceptibility signal
intensity versus necrosis. Acta Radiol. 55:378–384. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hartman DS, Davis CJ Jr, Johns T and
Goldman SM: Cystic renal cell carcinoma. Urology. 28:145–153. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parienty RA, Pradel J and Parienty I:
Cystic renal cancers: CT characteristics. Radiology. 157:741–744.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Özgök Y, Ateş M, Hoşcan MB, İstanbulluoğlu
O, Başal Ş and Zor M: Renal cell carcinoma dwelling upon a renal
cyst wall and laparoscopic management. Urol J. 10:1165–1167.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bielsa O, Lloreta J and Gelabert-Mas A:
Cystic renal cell carcinoma: Pathological features, survival and
implications for treatment. Br J Urol. 82:16–20. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huan L: Comparison of CT and MRI in the
diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma of different pathological
subtypes. Contemp Med. 19:139–140. 2021.
|
|
13
|
Robbin ML, Lockhart ME and Barr RG: Renal
imaging with ultrasound contrast: Current status. Radiol Clin North
Am. 41:963–978. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Israel GM, Hindman N and Bosniak MA:
Evaluation of cystic renal masses: Comparison of CT and MR imaging
by using the Bosniak classification system. Radiology. 231:365–371.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park BK, Kim B, Kim SH, Ko K, Lee HM and
Choi HY: Assessment of cystic renal masses based on Bosniak
classification: Comparison of CT and contrast-enhanced US. Eur J
Radiol. 61:310–314. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Y, Wu N, Xue T, Hao Y and Dai J:
Comparison of contrast-enhanced sonography with MRI in the
diagnosis of complex cystic renal masses. J Clin Ultrasound.
43:203–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mühlfeld AS, Lange C, Kroll G, Floege J,
Krombach GA, Kuhl C, Eitner F and Schrading S: Pilot study of
non-contrast-enhanced MRI vs ultrasound in renal transplant
recipients with acquired cystic kidney disease: A prospective
intra-individual comparison. Clin Transplant. 27:694–701. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|