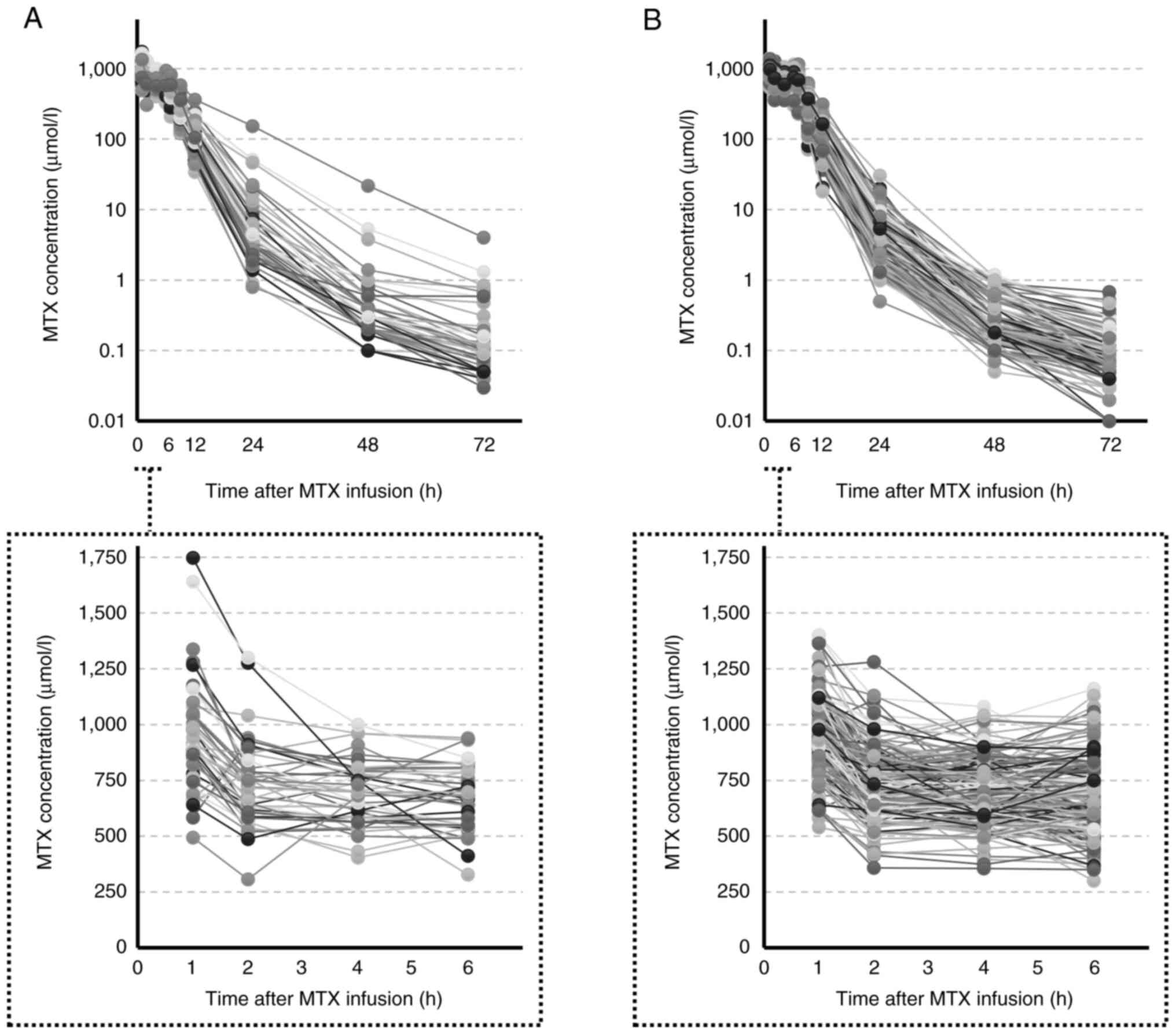
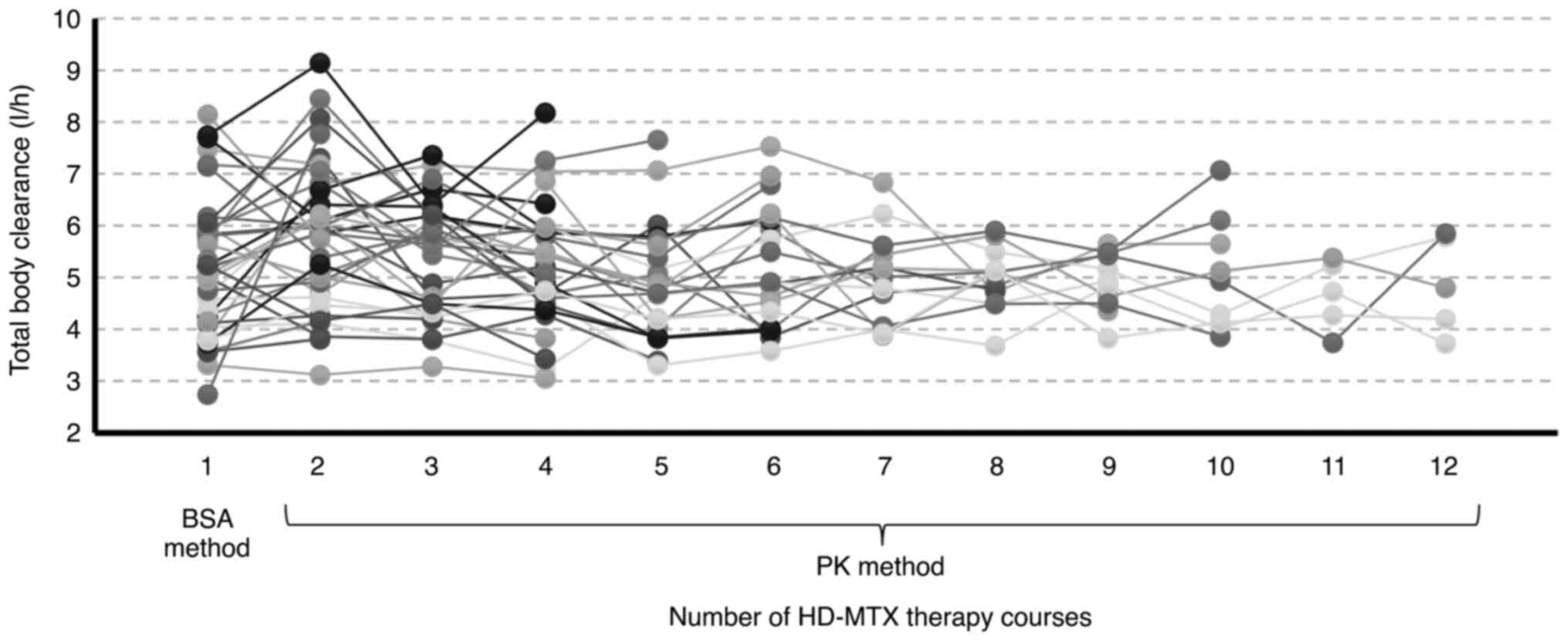
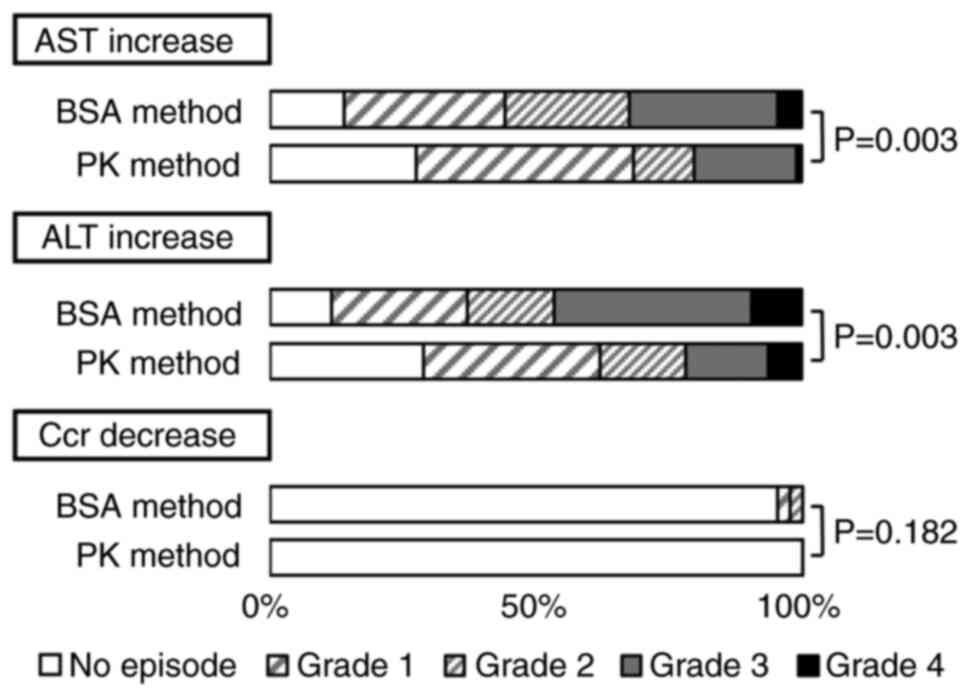
|
1
|
Widemann BC and Adamson PC: Understanding
and managing methotrexate nephrotoxicity. Oncologist. 11:694–703.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rizvi SAA, Shahzad Y, Saleh AM and
Muhammad N: Dose issues in cancer chemotherapy. Oncology.
98:520–527. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tishler M, Caspi D, Fishel B and Yaron M:
The effects of leucovorin (folinic acid) on methotrexate therapy in
rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Rheum. 31:906–908. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jaffe N and Gorlick R: High-dose
methotrexate in osteosarcoma: Let the questions surcease-time for
final acceptance. J Clin Oncol. 26:4365–4366. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shea B, Swinden MV, Ghogomu ET, Ortiz Z,
Katchamart W, Rader T, Bombardier C, Wells GA and Tugwell P: Folic
acid and folinic acid for reducing side effects in patients
receiving methotrexate for rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol.
41:1049–1060. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang R, Mei S and Zhao Z: Leucovorin
(folinic acid) rescue for high-dose methotrexate: A review. J Clin
Pharm Ther. 47:1452–1460. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wilmanns W, Sauer H and Schalhorn A:
Biochemical control of high-dose methotrexate/leucovorin rescue
therapy. Recent Results Cancer Res. 74:42–49. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Visentin M, Zhao R and Goldman ID: The
antifolates. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 26629–648. (ix)2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Meyers PA, Gorlick R, Heller G, Casper E,
Lane J, Huvos AG and Healey JH: Intensification of preoperative
chemotherapy for osteogenic sarcoma: Results of the memorial
sloan-kettering (T12) protocol. J Clin Oncol. 16:2452–2458. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Crews KR, Liu T, Rodriguez-Galindo C, Tan
M, Meyer WH, Panetta JC, Link MP and Daw NC: High-dose methotrexate
pharmacokinetics and outcome of children and young adults with
osteosarcoma. Cancer. 100:1724–1733. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Anninga JK, Gelderblom H, Fiocco M, Kroep
JR, Taminiau AHM, Hogendoorn PCW and Egeler RM: Chemotherapeutic
adjuvant treatment for osteosarcoma: Where do we stand? Eur J
Cancer. 47:2431–2445. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang B and Zhang Y, Li R, Li J, Lu X and
Zhang Y: The efficacy and safety comparison of first-line
chemotherapeutic agents (high-dose methotrexate, doxorubicin,
cisplatin, and ifosfamide) for osteosarcoma: A network
meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 15:512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rathore R and Van Tine BA: Pathogenesis
and current treatment of osteosarcoma: Perspectives for future
therapies. J Clin Med. 10:11822021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rajeswari B, Guruprasad CS, Nair M,
Prasanth VR, Sugath BS and Thankamony P: High dose methotrexate
containing regimen in pediatric non-metastatic extremity
osteosarcoma patients: Experience from a tertiary cancer center in
India. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 39:225–232. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pinedo HM and Chabner BA: Role of drug
concentration, duration of exposure, and endogenous metabolites in
determining methotrexate cytotoxicity. Cancer Treat Rep.
61:709–715. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ferrari S, Sassoli V, Orlandi M, Strazzari
S, Puggioli C, Battistini A and Bacci G: Serum methotrexate (MTX)
concentrations and prognosis in patients with osteosarcoma of the
extremities treated with a multidrug neoadjuvant regimen. J
Chemother. 5:135–141. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Graf N, Winkler K, Betlemovic M, Fuchs N
and Bode U: Methotrexate pharmacokinetics and prognosis in
osteosarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 12:1443–1451. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Delepine N, Delepine G, Cornille H, Brion
F, Arnaud P and Desbois JC: Dose escalation with pharmacokinetics
monitoring in methotrexate chemotherapy of osteosarcoma. Anticancer
Res. 15:489–494. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bacci G, Ferrari S, Picci P, Zolezzi C,
Gherlinzoni F, Iantorno D and Cazzola A: Methotrexate serum
concentration and histological response to multiagent primary
chemotherapy for osteosarcoma of the limbs. J Chemother. 8:472–478.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bacci G, Ferrari S, Delepine N, Bertoni F,
Picci P, Mercuri M, Bacchini P, Brach del Prever A, Tienghi A,
Comandone A and Campanacci M: Predictive factors of histologic
response to primary chemotherapy in osteosarcoma of the extremity:
Study of 272 patients preoperatively treated with high-dose
methotrexate, doxorubicin, and cisplatin. J Clin Oncol. 16:658–663.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lin F, Juan Y, Zheng SE, Shen Z, Tang LN,
Zhao H and Yao Y: Relationship of serum methotrexate concentration
in high-dose methotrexate chemotherapy to prognosis and
tolerability: A prospective cohort study in Chinese adults with
osteosarcoma. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 70:150–160. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zelcer S, Kellick M, Wexler LH, Shi W,
Sankaran M, Lo S, Healey J, Huvos AG, Meyers PA and Gorlick R:
Methotrexate levels and outcome in osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood
Cancer. 44:638–642. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang B, Yao H, Xie X, Yin J, Zou C, Huang
G and Shen J: Relationship of peak serum methotrexate concentration
to prognosis and drug tolerance in non-metastatic extremity
osteosarcomas. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 82:221–227. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kawakatsu S, Nikanjam M, Lin M, Le S,
Saunders I, Kuo DJ and Capparelli EV: Population pharmacokinetic
analysis of high-dose methotrexate in pediatric and adult oncology
patients. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 84:1339–1348. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Arshad U, Taubert M, Seeger-Nukpezah T,
Ullah S, Spindeldreier KC, Jaehde U, Hallek M, Fuhr U, Vehreschild
JJ and Jakob C: Evaluation of body-surface-area adjusted dosing of
high-dose methotrexate by population pharmacokinetics in a large
cohort of cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 21:7192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Stoller RG, Hande KR, Jacobs SA, Rosenberg
SA and Chabner BA: Use of plasma pharmacokinetics to predict and
prevent methotrexate toxicity. N Engl J Med. 297:630–634. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Perez C, Wang YM, Sutow WW and Herson J:
Significance of the 48-h plasma level in high-dose methotrexate
regimens. Cancer Clin Trials. 1:107–111. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hegyi M, Gulácsi A, Cságoly E, Csordás K,
Eipel OT, Erdélyi DJ, Müller J, Nemes K, Lautner-Csorba O and
Kovács GT: Clinical relations of methotrexate pharmacokinetics in
the treatment for pediatric osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
138:1697–1702. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park JA and Shin HY: Influence of genetic
polymorphisms in the folate pathway on toxicity after high-dose
methotrexate treatment in pediatric osteosarcoma. Blood Res.
51:50–57. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Howard SC, McCormick J, Pui CH, Buddington
RK and Harvey RD: Preventing and managing toxicities of high-dose
methotrexate. Oncologist. 21:1471–1482. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Traivaree C, Likasitthananon N,
Monsereenusorn C and Rujkijyanont P: The effect of intravenous
hydration strategy on plasma methotrexate clearance during
intravenous high-dose methotrexate administration in pediatric
oncology patients. Cancer Manag Res. 10:4471–4478. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bielack SS, Blattmann C, Borkhardt A,
Csóka M, Hassenpflug W, Kabíčková E, Kager L, Kessler T, Kratz C,
Kühne T, et al: Osteosarcoma and causes of death: A report of 1520
deceased patients from the cooperative osteosarcoma study group
(COSS). Eur J Cancer. 176:50–57. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shaikh AB, Li F, Li M, He B, He X, Chen G,
Guo B, Li D, Jiang F, Dang L, et al: Present advances and future
perspectives of molecular targeted therapy for osteosarcoma. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:5062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rathore R, Caldwell KE, Schutt C,
Brashears CB, Prudner BC, Ehrhardt WR, Leung CH, Lin H, Daw NC,
Beird HC, et al: Metabolic compensation activates pro-survival
mTORC1 signaling upon 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase inhibition
in osteosarcoma. Cell Rep. 34:1086782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwong DL, Ha SY, Chau KY, Choi PH, Chan
GC, Kwong PW and Lau YL: Multidisciplinary management of
osteosarcoma: Experience in Hong Kong. Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
15:229–236. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Watanabe M, Fukuoka N, Takeuchi T,
Yamaguchi K, Motoki T, Tanaka H, Kosaka S and Houchi H: Developing
population pharmacokinetic parameters for high-dose methotrexate
therapy: Implication of correlations among developed parameters for
individual parameter estimation using the bayesian least-squares
method. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:916–921. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fukuhara K, Ikawa K, Morikawa N and
Kumagai K: Population pharmacokinetics of high-dose methotrexate in
Japanese adult patients with malignancies: A concurrent analysis of
the serum and urine concentration data. J Clin Pharm Ther.
33:677–684. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wippel B, Gundle KR, Dang T, Paxton J,
Bubalo J, Stork L, Fu R, Ryan CW and Davis LE: Safety and efficacy
of high-dose methotrexate for osteosarcoma in adolescents compared
with young adults. Cancer Med. 8:111–116. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Young EP, Cheng WS, Bernhardt MB, Wang LL,
Rainusso N and Foster JH: Risk factors associated with delayed
methotrexate clearance and increased toxicity in pediatric patients
with osteosarcoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 67:e281232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Abe K, Maeda-Minami A, Ishizu T, Iwata S,
Kobayashi E, Shimoi T, Kawano Y, Hashimoto H, Yamaguchi M, Furukawa
T, et al: Risk factors for hepatic toxicity of high-dose
methotrexate in patients with osteosarcoma. Anticancer Res.
42:1043–1050. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Porta-Oltra B and Merino-Sanjuán M:
Personalized pharmacotherapy in oncology: Application of
pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic criteria. Farm Hosp. 45:45–55.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fujita Y, Nakamura T, Aomori T, Nishiba H,
Shinozaki T, Yanagawa T, Takagishi K, Watanabe H, Okada Y, Nakamura
K, et al: Pharmacokinetic individualization of high-dose
methotrexate chemotherapy for the treatment of localized
osteosarcoma. J Chemother. 22:186–190. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yamaoka K, Tanigawara K, Nakagawa T and
Uno T: A pharmacokinetic analysis program (multi) for
microcomputer. J Pharmacobiodyn. 4:879–885. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Misaka KO, Suga Y, Staub Y, Tsubata A,
Shimada T, Sai Y and Matsushita R: Risk factors for delayed
elimination of methotrexate in children, adolescents and young
adults with osteosarcoma. In Vivo. 34:3459–3465. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pauley JL, Panetta JC, Crews KR, Pei D,
Cheng C, McCormick J, Howard SC, Sandlund JT, Jeha S, Ribeiro R, et
al: Between-course targeting of methotrexate exposure using
pharmacokinetically guided dosage adjustments. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 72:369–378. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Foster JH, Thompson PA, Bernhardt MB,
Margolin JF, Hilsenbeck SG, Jo E, Marquez-Do DA, Scheurer ME and
Schafer ES: A prospective study of a simple algorithm to
individually dose high-dose methotrexate for children with leukemia
at risk for methotrexate toxicities. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
83:349–360. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shen YQ, Wang ZJ, Wu XY, Li K, Wang ZJ, Xu
WF, Zhou F and Jin RM: Dose-individualization efficiently maintains
sufficient exposure to methotrexate without additional toxicity in
high-dose methotrexate regimens for pediatric acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Curr Med Sci. 42:769–777. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dupuis C, Mercier C, Yang C,
Monjanel-Mouterde S, Ciccolini J, Fanciullino R, Pourroy B, Deville
JL, Duffaud F, Bagarry-Liegey D, et al: High-dose methotrexate in
adults with osteosarcoma: A population pharmacokinetics study and
validation of a new limited sampling strategy. Anti Cancer Drugs.
19:267–273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lui G, Treluyer JM, Fresneau B,
Piperno-Neumann S, Gaspar N, Corradini N, Gentet JC, Marec Berard
P, Laurence V, Schneider P, et al: A pharmacokinetic and
pharmacogenetic analysis of osteosarcoma patients treated with
high-dose methotrexate: Data from the OS2006/sarcoma-09 trial. J
Clin Pharmacol. 58:1541–1549. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|