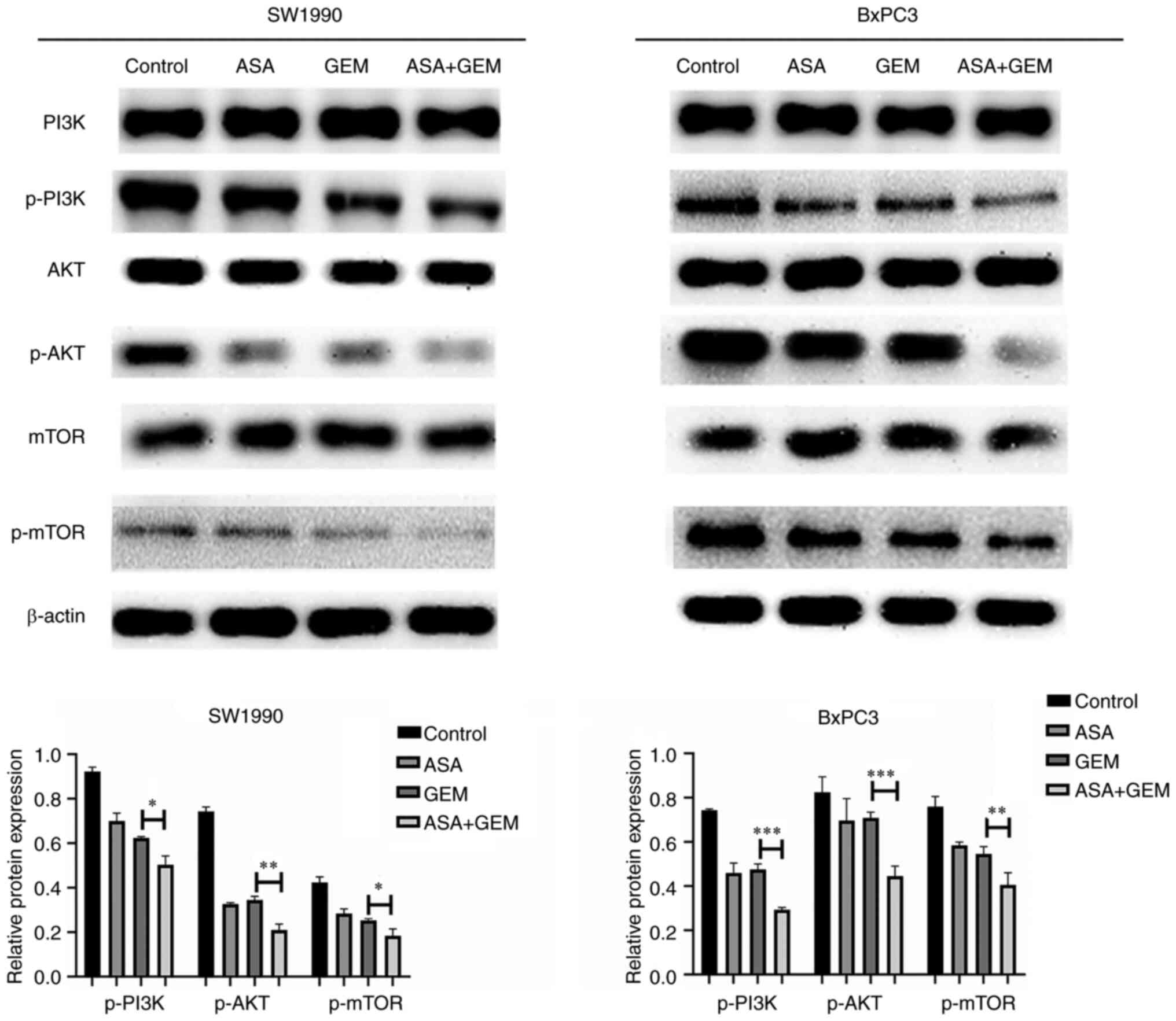
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tuveson DA and Neoptolemos JP:
Understanding metastasis in pancreatic cancer: A call for new
clinical approaches. Cell. 148:21–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mann KM, Ying H, Juan J, Jenkins NA and
Copeland NG: KRAS-related proteins in pancreatic cancer. Pharmacol
Ther. 168:29–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Song M, Bode AM, Dong Z and Lee MH: AKT as
a therapeutic target for cancer. Cancer Res. 79:1019–1031. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang Y, Kwok-Shing Ng P, Kucherlapati M,
Chen F, Liu Y, Tsang YH, de Velasco G, Jeong KJ, Akbani R,
Hadjipanayis A, et al: A pan-cancer proteogenomic atlas of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway alterations. Cancer Cell. 31:820–832.
e8232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Juanpere N, Agell L, Lorenzo M, de Muga S,
López-Vilaró L, Murillo R, Mojal S, Serrano S, Lorente JA, Lloreta
J and Hernández S: Mutations in FGFR3 and PIK3CA, singly or
combined with RAS and AKT1, are associated with AKT but not with
MAPK pathway activation in urothelial bladder cancer. Hum Pathol.
43:1573–1582. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Coussy F, El Botty R, Lavigne M, Gu C,
Fuhrmann L, Briaux A, de Koning L, Dahmani A, Montaudon E, Morisset
L, et al: Combination of PI3K and MEK inhibitors yields durable
remission in PDX models of PIK3CA-mutated metaplastic breast
cancers. J Hematol Oncol. 13:132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Candido S, Salemi R, Piccinin S, Falzone L
and Libra M: The PIK3CA H1047R Mutation confers resistance to BRAF
and MEK inhibitors in A375 melanoma cells through the
cross-activation of MAPK and PI3K-Akt pathways. Pharmaceutics.
14:5902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Feng M, Xiong G, Cao Z, Yang G, Zheng S,
Qiu J, You L, Zheng L, Zhang T and Zhao Y: LAT2 regulates
glutamine-dependent mTOR activation to promote glycolysis and
chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37:2742018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou P, Li B, Liu F, Zhang M, Wang Q, Liu
Y, Yao Y and Li D: The epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
and cancer stem cells: Implication for treatment resistance in
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 16:522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Marais R, Sellers W, Livingston D and
Mihich E: Twenty-fourth annual Pezcoller symposium: Molecular basis
for resistance to targeted agents. Cancer Res. 73:1046–1049. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
De Craene B, Gilbert B, Stove C, Bruyneel
E, van Roy F and Berx G: The transcription factor snail induces
tumor cell invasion through modulation of the epithelial cell
differentiation program. Cancer Res. 65:6237–6244. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chaw SY, Majeed AA, Dalley AJ, Chan A,
Stein S and Farah CS: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)
biomarkers-E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and Vimentin-in oral
squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol.
48:997–1006. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Luo T, Wang L, Wu P, Gong W, Chen W, Zhao
H and Zheng Z: Downregulated vimentin and upregulated E-cadherin in
T1 stage non-small-cell lung cancer: Does it suggest a
mesenchymal-epithelial transition? Neoplasma. 64:693–699. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang W, Wang L, Mizokami A, Shi J, Zou C,
Dai J, Keller ET, Lu Y and Zhang J: Down-regulation of E-cadherin
enhances prostate cancer chemoresistance via Notch signaling. Chin
J Cancer. 36:352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mallini P, Lennard T, Kirby J and Meeson
A: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: What is the impact on
breast cancer stem cells and drug resistance. Cancer Treat Rev.
40:341–348. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tempero MA, Malafa MP, Al-Hawary M,
Behrman SW, Benson AB, Cardin DB, Chiorean EG, Chung V, Czito B,
Chiaro MD, et al: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, version 2.2021, NCCN
clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
19:439–457. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Springfeld C, Jager D, Buchler MW, Strobel
O, Hackert T, Palmer DH and Neoptolemos JP: Chemotherapy for
pancreatic cancer. Presse Med. 48:e159–e174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Falzone L, Salomone S and Libra M:
Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the
third millennium. Front Pharmacol. 9:13002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Conroy T, Hammel P, Hebbar M, Abdelghani
MB, Wei AC, Raoul JL, Choné L, Francois E, Artru P, Biagi JJ, et
al: FOLFIRINOX or gemcitabine as adjuvant therapy for pancreatic
cancer. New Engl J Med. 379:2395–2406. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Khorana AA, McKernin SE, Berlin J, Hong
TS, Maitra A, Moravek C, Mumber M, Schulick R, Zeh HJ and Katz MHG:
Potentially curable pancreatic adenocarcinoma: ASCO clinical
practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 37:2082–2088. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tempero MA: NCCN Guidelines updates:
Pancreatic cancer. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 17:603–605.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zelenay S, van der Veen AG, Bottcher JP,
Snelgrove KJ, Rogers N, Acton SE, Chakravarty P, Girotti MR, Marais
R, Quezada SA, et al: Cyclooxygenase-dependent tumor growth through
evasion of immunity. Cell. 162:1257–1270. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ulrich CM, Bigler J and Potter JD:
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention:
Promise, perils and pharmacogenetics. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:130–140.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rothwell PM, Fowkes FG, Belch JF, Ogawa H,
Warlow CP and Meade TW: Effect of daily aspirin on long-term risk
of death due to cancer: Analysis of individual patient data from
randomised trials. Lancet. 377:31–41. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan XL, Lombardo KM, Bamlet WR, Oberg AL,
Robinson DP, Anderson KE and Petersen GM: Aspirin, nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen, and pancreatic cancer risk:
A clinic-based case-control study. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
4:1835–1841. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang P, Lan TH, Zhou YM, Deng JP, Wei CZ,
Wang GH and Tian L: Risk factor analysis of perioperative
complications in patients with radical gastrectomy for gastric
cancer. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 22:736–741. 2019.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yue W, Yang CS, DiPaola RS and Tan XL:
Repurposing of metformin and aspirin by targeting AMPK-mTOR and
inflammation for pancreatic cancer prevention and treatment. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 7:388–397. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Simon TG, Ma Y, Ludvigsson JF, Chong DQ,
Giovannucci EL, Fuchs CS, Meyerhardt JA, Corey KE, Chung RT, Zhang
X and Chan AT: Association between aspirin use and risk of
hepatocellular carcinoma. JAMA Oncol. 4:1683–1690. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kehm RD, Hopper JL, John EM, Phillips KA,
MacInnis RJ, Dite GS, Milne RL, Liao Y, Zeinomar N, Knight JA, et
al: Regular use of aspirin and other non-steroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs and breast cancer risk for women at
familial or genetic risk: A cohort study. Breast Cancer Res.
21:522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ou YQ, Zhu W, Li Y, Qiu PX, Huang YJ, Xie
J, He SM, Zheng XK, Leng TD, Xu D and Yan GM: Aspirin inhibits
proliferation of gemcitabine-resistant human pancreatic cancer
cells and augments gemcitabine-induced cytotoxicity. Acta Pharm
Sin. 31:73–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yue W, Zheng X, Lin Y, Yang CS, Xu Q,
Carpizo D, Huang H, DiPaola RS and Tan XL: Metformin combined with
aspirin significantly inhibit pancreatic cancer cell growth in
vitro and in vivo by suppressing anti-apoptotic proteins Mcl-1 and
Bcl-2. Oncotarget. 6:21208–21224. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Baron JA, Cole BF, Sandler RS, Haile RW,
Ahnen D, Bresalier R, McKeown-Eyssen G, Summers RW, Rothstein R,
Burke CA, et al: A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent
colorectal adenomas. N Engl J Med. 348:891–899. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sandler RS, Halabi S, Baron JA, Budinger
S, Paskett E, Keresztes R, Petrelli N, Pipas JM, Karp DD, Loprinzi
CL, et al: A randomized trial of aspirin to prevent colorectal
adenomas in patients with previous colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
348:883–890. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cao Y, Nishihara R, Wu K, Wang M, Ogino S,
Willett WC, Spiegelman D, Fuchs CS, Giovannucci EL and Chan AT:
Population-wide impact of long-term use of aspirin and the risk for
cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2:762–769. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fraser DM, Sullivan FM, Thompson AM and
McCowan C: Aspirin use and survival after the diagnosis of breast
cancer: A population-based cohort study. Br J Cancer. 111:623–627.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qorri B, Mokhtari RB, Harless WW and
Szewczuk MR: Next generation of cancer drug repurposing:
therapeutic combination of aspirin and oseltamivir phosphate
potentiates gemcitabine to disable key survival pathways critical
for pancreatic cancer progression. Cancers (Basel). 14:13742022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zinger A, Koren L, Adir O, Poley M, Alyan
M, Yaari Z, Noor N, Krinsky N, Simon A, Gibori H, et al:
Collagenase nanoparticles enhance the penetration of drugs into
pancreatic tumors. ACS Nano. 13:11008–11021. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang G, Zhou Z, Zhao Z, Li Q, Wu Y, Yan S,
Shen Y and Huang P: Enzyme-triggered transcytosis of dendrimer-drug
conjugate for deep penetration into pancreatic tumors. ACS Nano.
14:4890–4904. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu F, Kai J, Chen L, Wu M, Dong J, Wang Q
and Zeng LH: Akt inhibitor perifosine prevents epileptogenesis in a
rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Bull. 34:283–290.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Fournier KF,
Wang H, Marquis L, Abbruzzese JL, Gallick GE, Logsdon CD, McConkey
DJ and Choi W: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to
drug resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 69:5820–5828.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Thorpe LM, Yuzugullu H and Zhao JJ: PI3K
in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and
therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:7–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Quan C, Sun J, Lin Z, Jin T, Dong B, Meng
Z and Piao J: Ezrin promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation
and invasion through activating the Akt/mTOR pathway and inducing
YAP translocation. Cancer Manag Res. 11:6553–6566. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Samuel EL, Marcano DC, Berka V, Bitner BR,
Wu G, Potter A, Fabian RH, Pautler RG, Kent TA, Tsai AL and Tour
JM: Highly efficient conversion of superoxide to oxygen using
hydrophilic carbon clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 112:2343–2348.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Trachootham D, Lu W, Ogasawara MA, Nilsa
RD and Huang P: Redox regulation of cell survival. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 10:1343–1374. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
He K, Wu L, Ding Q, Haider F, Yu H, Wang H
and Xiang G: Apatinib promotes apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells
through downregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and
increased levels of reactive oxygen species. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:51520722019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zou P, Zhang J, Xia Y, Kanchana K, Guo G,
Chen W, Huang Y, Wang Z, Yang S and Liang G: ROS generation
mediates the anti-cancer effects of WZ35 via activating JNK and ER
stress apoptotic pathways in gastric cancer. Oncotarget.
6:5860–5876. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang F, Wang Q, Zhou ZW, Yu SN, Pan ST, He
ZX, Zhang X, Wang D, Yang YX, Yang T, et al: Plumbagin induces cell
cycle arrest and autophagy and suppresses epithelial to mesenchymal
transition involving PI3K/Akt/mTOR-mediated pathway in human
pancreatic cancer cells. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:537–560.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gu WJ and Liu HL: Induction of pancreatic
cancer cell apoptosis, invasion, migration, and enhancement of
chemotherapy sensitivity of gemcitabine, 5-FU, and oxaliplatin by
hnRNP A2/B1 siRNA. Anticancer Drugs. 24:566–576. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin S, Pan Y and Xu C: Effects of aspirin
on pancreatic cancer cells PANC-1 and its potential molecular
mechanism. J BUON. 25:2449–2455. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Drew DA, Cao Y and Chan AT: Aspirin and
colorectal cancer: The promise of precision chemoprevention. Nat
Rev Cancer. 16:173–186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|