Introduction
The bones are the primary metastatic site in 46% of
patients with breast cancer (BC), and bone metastases (BMs) have
been reported to occur in 71% of metastatic BC cases (1). In patients with BC and BMs, although
the main treatment strategy is systemic therapy, palliative
radiotherapy (RT) for BMs is often used for pain relief. In
general, the majority of patients who need palliative RT for BMs
cannot expect long-term survival. Therefore, hypofractionated
low-dose RT (e.g. a single fraction of 8 Gy) for pain relief is
often performed for BMs. However, the prognosis of patients with
BMs is heterogeneous, and the prognosis of patients with BMs from
BC is considered to be favorable (2,3).
Therefore, to select the appropriate RT methods for BMs from BC,
precise prediction of life expectancy is crucial in patients with
BC and BMs.
Svensson et al (2) reported that the 1-year survival rate
after the diagnosis of BMs was lowest in patients with lung cancer
(10%) and highest in patients with BC (51%), and that 1 in 10
patients with BMs from BC survived for 5 years. In Katagiri's
prognostic scoring system for patients with BMs from various cancer
types, BC was classified as a comparatively favorable cancer type
(3). In addition, BC has individual
features; unlike other cancer types, the prognoses of patients with
BC are affected by positive hormone receptor expression, human
epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression and
histological grade (4,5). Furthermore, the majority of patients
with BC who receive RT for BMs have already received systemic
therapy, including chemotherapy and/or hormonal therapy. After
systemic therapy, there is a possibility that the features of the
BC cells have changed from those at the initial presentation
(6). Although generalized
prognostic assessment systems for patients with BM, such as the
Katagiri score (3) and Tokuhashi
score (7), have been proposed,
there are few prognostic assessment systems that are specialized
for patients with BMs from BC. Considering the high incidence of
BMs from BC and the individual features of BC, prognostic
assessments specific to BMs from BC are needed. For individualized
RT, prognostic factors specific to patients who received RT for BMs
from BC were therefore assessed in the present study.
Materials and methods
Ethical considerations
All procedures performed in the present study were
in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional
and/or National Research Committee and the 1964 Helsinki
Declaration and its later amendments. Informed consent for the use
of clinical data was obtained by opt-out methods. This
retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the
National Hospital Organization Shikoku Cancer Center (Matsuyama,
Japan; approval no. RIN2021-71).
Study population
The cases of 167 consecutive female patients who
received first-time RT for BMs from BC between January 2007 and
June 2018 in the National Hospital Organization Shikoku Cancer
Center were retrospectively reviewed. A total of 24 patients were
excluded for the following reasons: i) No computed tomography (CT)
of the chest and abdomen within 3 months of beginning RT (n=14);
ii) discontinuation of RT (n=2); iii) synchronous and/or sequential
double cancer (n=5); and iv) follow-up duration of <6 months
despite survival (n=3). Thus, 143 patients were included for
analysis. Among the 143 patients, 117 patients (82%) had died and
26 patients (18%) were alive at the last follow-up day of clinical
examination.
BMs were detected with CT, bone scintigraphy and/or
18F fluorodeoxyglucose positron-emission tomography/CT
(FDG-PET/CT). Visceral metastases were evaluated with CT and/or
FDG-PET/CT within 3 months of the beginning of first-time RT to
BMs. Patients who had not undergone contrast-enhanced magnetic
resonance imaging (MRI) were classified in a no brain metastases
cohort. Performance status (PS) was evaluated according to the
Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group scale (8).
Radiotherapy
Patients received three-dimensional conformal RT. RT
was delivered using 4- or 10-MV photons with a linear accelerator
(Clinac 21-EX; Varian Medical Systems, Inc.).
Statistical analysis
The primary endpoint was overall survival (OS) time,
which was defined as the time from the beginning of the first-time
RT for BMs to death. OS was calculated using the Kaplan-Meier
method, and statistical differences in OS were evaluated by the
log-rank test. The Cox proportional hazard model was used for
univariate and multivariate analyses. Factors, including age, PS,
estrogen receptor status, progesterone receptor status, HER2
overexpression, triple-negative BC type, nuclear grade (NG)
(9), the timing of the appearance
of metastases (relapse vs. de novo), previous systemic
therapy, number of BMs (single vs. multiple) and sites of
synchronous metastases (lung, liver and brain), were analyzed using
univariate analysis. Factors that had P-values of <0.05 on
univariate analysis were subjected to multivariate analysis.
P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference. All statistical analyses were performed using EZR
(Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University), which is a
graphical user interface for R (The R Foundation for Statistical
Computing; version 3.5.0) (10).
More precisely, it is a modified version of R commander (2.5-1),
designed to incorporate statistical functions frequently used in
biostatistics.
Results
Clinical characteristics
A total of 128 patients (90%) had multiple BMs (only
vertebral, 7 patients; only non-vertebral, 5 patients; both
vertebral and non-vertebral, 116 patients) and 15 patients (10%)
had a single bone metastasis (vertebral, 11 patients;
non-vertebral, 4 patients). Overall, 98 patients (69%) had
undergone previous systemic therapy, including chemotherapy,
hormone therapy and/or anti-HER2 agent therapy for >3 months
before RT. A total of 58 patients (41%) underwent FDG-PET/CT before
the RT. In addition, 39 patients (27%) underwent contrast-enhanced
T1-weighted MRI (CE-MRI) within 3 months of the beginning of the RT
or during RT, and brain metastases were detected in 14 patients
(10%).
The majority of patients received 30 Gy in 10
fractions. Overall, 130 patients (91%) received at least 30 Gy in
10 fractions and 13 patients (9%) received hypofractionated
low-dose RT. A total of 108 patients (76%) received RT to the
vertebral bone and 29 patients (20%) received RT to the pelvic
bone. Patient characteristics are listed in Table I.
 | Table I.Patient characteristics. |
Table I.
Patient characteristics.
| Characteristic | Value |
|---|
| Median age (range),
years | 61 (33–88) |
| PS, n (%) |
|
| 0 | 9 (6.3) |
| 1 | 66 (46.2) |
| 2 | 35 (24.5) |
| 3 | 19 (13.3) |
| 4 | 12 (8.4) |
|
Unknown | 2 (1.4) |
| Timing of appearance
of metastases, n (%) |
|
|
Relapse | 97 (67.8) |
| de
novo | 46 (32.2) |
| ER, n (%) |
|
|
Positive | 117 (81.8) |
|
Negative | 19 (13.3) |
|
Unknown | 7 (4.9) |
| PgR, n (%) |
|
|
Positive | 95 (66.4) |
|
Negative | 41 (28.7) |
|
Unknown | 7 (4.9) |
| HER2 overexpression,
n (%) |
|
| Yes | 20 (14.0) |
| No | 110 (76.9) |
|
Unknown | 13 (9.1) |
| TN type, n (%) |
|
| Yes | 9 (6.3) |
| No | 124 (86.7) |
|
Unknown | 10 (7.0) |
| NG, n (%) |
|
| 1 | 20 (14.0) |
| 2 | 24 (16.8) |
| 3 | 56 (39.2) |
|
Unknown | 43 (30.1) |
| Previous systemic
therapy, n (%) |
|
| Yes | 98 (68.5) |
| No | 45 (31.5) |
| Number of bone
metastases, n (%) |
|
|
Single | 15 (10.5) |
|
Multiple | 128 (89.5) |
| RT sites, n (%) |
|
|
Vertebral | 108 (75.5) |
|
Pelvis | 29 (20.3) |
|
Other | 6 (4.2) |
| Brain metastases |
|
| Yes | 14 (9.8) |
| No | 25 (17.5) |
| Not
examined | 104 (72.8) |
| Liver metastases |
|
| Yes | 55 (38.5) |
| No | 88 (61.5) |
| Lung metastases |
|
| Yes | 56 (39.2) |
| No | 87 (60.8) |
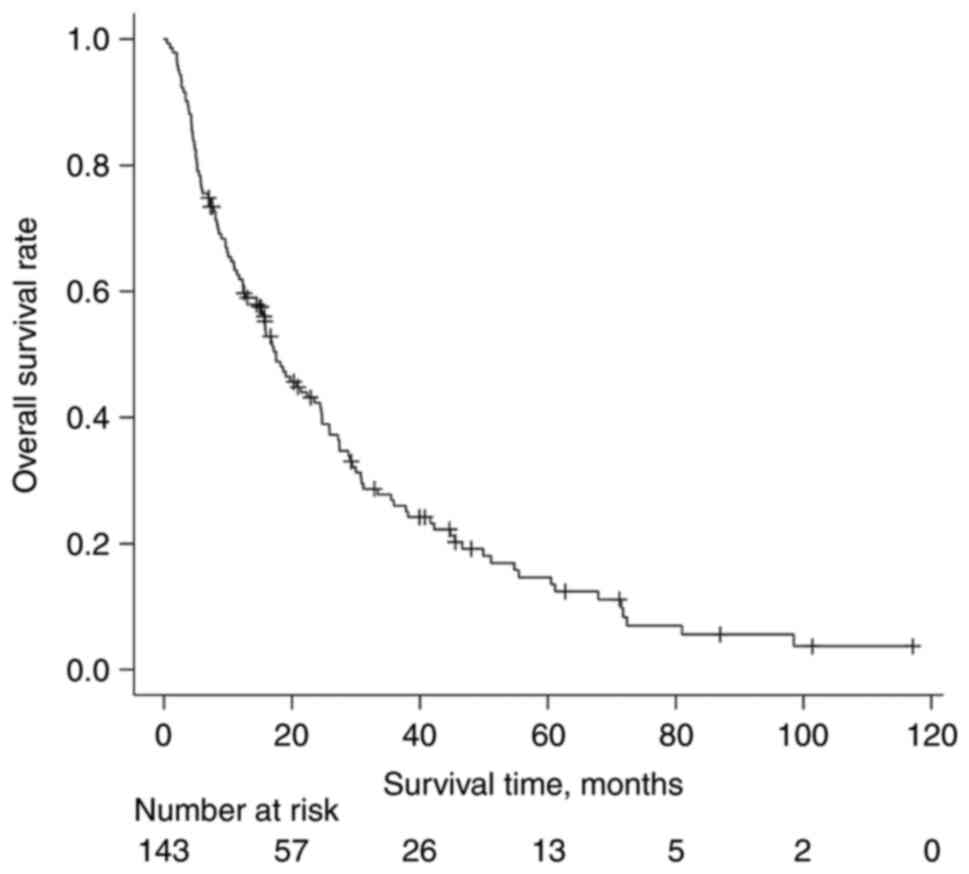
The median follow-up duration of survival was 22
months (range, 7–117 months) from first-time RT for BMs. The median
OS time was 17.5 months. The OS curve is shown in Fig. 1.
Prognostic factors for patients who
received first-time RT for BMs from BC
Upon univariate analysis, PS ≥2 (P=0.021), NG 3
(P<0.001), previous systemic therapy (P=0.003), synchronous
brain metastases (P<0.001), synchronous liver metastases
(P<0.001) and synchronous lung metastases (P=0.006) were
significantly associated with poor OS after first-time RT for BMs
(Table II). There were no
significant differences in OS between PS 0–1 and unknown PS
(P=0.260), and between NG 1–2 and unknown NG (P=0.956).
 | Table II.Univariate analysis for overall
survival. |
Table II.
Univariate analysis for overall
survival.
| Characteristic | 1-year OS rate,
% | P-value | HR (95% CI) |
|---|
| Age, years (<60
vs. ≥61) | 62.4 vs. 61.4 | 0.943 | 1.01 (0.70-1.46) |
| PS (0, 1 vs. ≥2) | 76.8 vs. 45.5 | 0.021 | 1.55 (1.07-2.24) |
| Timing of appearance
of metastases (relapse vs. de novo) | 59.2 vs. 67.4 | 0.182 | 0.77 (0.52-1.13) |
| ER (positive vs.
negative) | 63.8 vs. 53.1 | 0.141 | 1.49 (0.88-2.55) |
| PgR (positive vs.
negative) | 62.0 vs. 61.9 | 0.630 | 1.11 (0.73-1.68) |
| HER2 overexpression
(positive vs. negative) | 65.0 vs. 61.4 | 0.441 | 1.24
(0.72-2.15) |
| TN type (yes vs.
no) | 40.0 vs. 63.6 | 0.311 | 0.68
(0.33-1.40) |
| NG (1, 2 vs.
3) | 74.9 vs. 43.5 | <0.001 | 2.30
(1.46-3.60) |
| Previous systemic
therapy (no vs. yes) | 73.3 vs. 56.6 | 0.003 | 1.84
(1.22-2.76) |
| Number of bone
metastases (single vs. multiple | 60.0 vs. 62.1 | 0.774 | 1.10
(0.59-2.05) |
| RT sites (vertebral
vs. non-vertebral) | 64.6 vs. 53.3 | 0.093 | 1.42
(0.94-2.14) |
| Brain metastases
(no vs. yes) | 65.8 vs. 23.1 | <0.001 | 3.06
(1.67-5.62) |
| Liver metastases
(no vs. yes) | 71.4 vs. 46.5 | <0.001 | 2.20
(1.51-3.20) |
| Lung metastases (no
vs. yes) | 70.1 vs. 48.4 | 0.006 | 1.73
(1.17-2.54) |
The 1-year OS rate was as follows: PS 0–1 vs. PS
2–4, 76.8 vs. 45.5%; NG 1–2 vs. NG 3, 74.9 vs. 43.5%; previous
chemotherapy yes vs. no, 56.6 vs. 73.3%; synchronous brain
metastases yes vs. no, 23.1 vs. 65.8%; synchronous liver metastases
yes vs. no, 46.5 vs. 71.4%; and synchronous lung metastases yes vs.
no, 48.4 vs. 70.1% (Table II).
Upon multivariate analysis, the significant
prognostic factors after first-time RT for BMs were NG 3 [hazard
ratio, 2.18; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.34-3.53; P=0.002],
synchronous brain metastases (hazard ratio, 1.96; 95% CI,
1.01-3.81; P=0.046), synchronous liver metastases (hazard ratio,
1.75; 95% CI, 1.17-2.63; P=0.006), PS (hazard ratio, 1.63; 95% CI,
1.10-2.41; P=0.016) and previous systemic therapy (hazard ratio,
1.58; 95% CI, 1.03-2.42; P=0.038). Age, the timing of the
appearance of metastases, hormone-receptor status, HER2 status,
number of bone metastases (single vs. multiple) and synchronous
lung metastases were not significant factors.
Comprehensive prognostic assessment
based on regression coefficients in patients who received
first-time RT for BMs from BC
A comprehensive prognostic assessment using
regression coefficients of significant prognostic factors in
multivariate analysis (Table III)
was performed. Points according to risk levels of each significant
prognostic factor [unfavorable points (UFPs)] were assigned to each
prognostic factor as follows: 1.5 points for NG 3 and synchronous
brain metastases, and 1 point for PS ≥2, previous systemic therapy
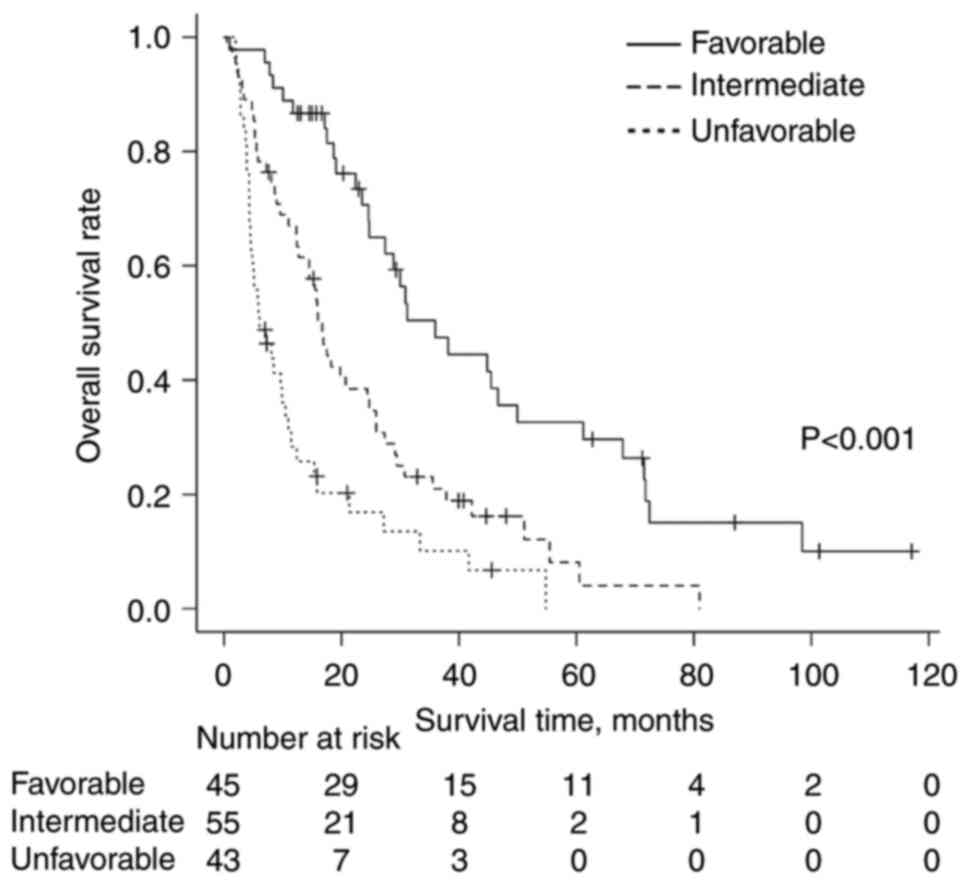
and synchronous liver metastases (Table IV). Patients with BMs from BC were
classified into three groups stratified by their total UFPs as
follows: i) Favorable group with total UFPs of ≤1 (n=45); ii)
intermediate group with total UFPs of 1.5–3 (n=55); and iii)
unfavorable group with total UFPs of ≥3.5 (n=43). The median OS
time was 36 months for the favorable group, 17 months for the
intermediate group and 6 months for the unfavorable group. There
were statistically significant differences in OS time between the
three groups (P<0.001). The OS curves are shown in Fig. 2.
 | Table III.Multivariate analysis for overall
survival. |
Table III.
Multivariate analysis for overall
survival.
| Characteristic | Regression
coefficient | P-value | HR (95% CI) |
|---|
| PS (≥2 vs.
0–1) | 0.4860 | 0.016 | 1.63
(1.10–2.41) |
| NG (3 vs. 1–2) | 0.7776 | 0.002 | 2.18
(1.34–3.53) |
| Previous systemic
therapy (yes vs. no) | 0.4543 | 0.038 | 1.58
(1.03–2.42) |
| Brain metastases
(yes vs. no) | 0.6747 | 0.046 | 1.96
(1.01–3.81) |
| Liver metastases
(yes vs. no) | 0.5621 | 0.006 | 1.75
(1.17–2.63) |
| Lung metastases
(yes vs. no) | 0.1131 | 0.627 | 1.12
(0.71–1.77) |
 | Table IV.UFPs for significant prognostic
factors. |
Table IV.
UFPs for significant prognostic
factors.
| Factor | UFPs |
|---|
| PS |
|
| ≥2 | 1 |
|
0–1 | 0 |
| NG |
|
| 3 | 1.5 |
|
1–2 | 0 |
| Previous systemic
therapy |
|
|
Yes | 1 |
| No | 0 |
| Brain
metastases |
|
|
Yes | 1.5 |
| No | 0 |
| Liver
metastases |
|
|
Yes | 1 |
| No | 0 |
Discussion
For individualization of RT to BMs from BC,
prognostic factors for patients who received first-time RT to BMs
from BC were investigated in the present study. Based on the
multivariate analysis, NG 3, synchronous brain metastases,
synchronous liver metastases, PS ≥2 and previous systemic therapy
were the statistically significant unfavorable prognostic factors
for OS in patients who received first-time RT for BMs from BC. By
contrast, hormone receptor status, HER2 status, the timing of
appearance of metastases (relapse vs. de novo), number of
BMs (single vs. multiple) and synchronous lung metastases were not
significant factors. In addition, a comprehensive prognostic
assessment using total UFPs according to risk levels of each
unfavorable factor seemed to be useful to predict OS after
first-time RT for BMs. OS was significantly poorer in patients
whose total UFPs were higher.
In clinical practice, RT with variable
dose-fractionation schedules (e.g. single fraction RT of 8 Gy,
traditional RT with 30 Gy in 10 fractions and stereotactic body RT)
is administered to BMs. According to a meta-analysis,
single-fraction RT was not inferior to multiple-fraction RT
regarding pain relief from BMs (11). However, re-irradiation was more
frequent for single-fraction RT (11). Differences in local control
according to dose-fractionation schedules have been reported in
several studies regarding metastatic spinal cord compression (MSCC)
(12,13). Rades et al (12) reported that RT of 30 Gy in ≥10
fractions was superior to 20 Gy in ≤5 fractions in local control
for all patients with MSCC (median OS time of assessed patients was
13 months). However, the same group also found that there were no
significant differences in local progression-free survival time
between 30 Gy in 10 fractions and 20 Gy in 5 fractions when limited
to patients with poor or intermediate prognosis (median OS time of
assessed patients was 3.2 months) (13). Considering these results,
hypofractionated low-dose RT is likely to be inadequate for
long-term survivors. Highly precise RT using stereotactic body RT
or intensity-modulated RT can now be performed if necessary. The
prediction of prognosis is more important for BMs from BC compared
with BMs from other primary sites.
Histological grade or NG has been one of the most
often used major prognostic factors for operable BC, along with
lymph node metastases and tumor size (14,15).
From the results of the present study, NG 3 was an independent
unfavorable prognostic factor also for patients with BMs from
BC.
Synchronous metastases in other organs also affect
the prognoses of patients with BMs from BC. According to previous
reports regarding patients with BMs from BC, patients who have
synchronous metastases in other organs showed shorter median OS
times (median OS time, 9–17 months) compared with patients with
bone-only metastases (median OS time, 31–33 months) (4,5). Chen
et al (4) reported that
brain, liver and lung metastases were significantly associated with
poor OS in patients with metastatic BC. In addition, prognoses of
patients with brain metastases and patients with multiple site
metastases had the poorest prognosis. Largillier et al
(5) reported that brain metastases
and liver metastases were significant unfavorable factors for
survival in metastatic BC, regardless of hormone receptor status.
In addition, Gerratana et al (16) reported that liver metastasis was an
independent predictor for poor OS in patients who had received
anticancer therapy for metastatic BC. From the results of these
studies, brain metastases and liver metastases seemed to be
especially unfavorable factors in patients with metastatic BC. In
the present study, regarding patients who had BMs and synchronous
metastases at other organs, the prognosis was unfavorable in the
order of brain, liver and then lung metastasis.
Based on the results from multivariate analysis,
previous systemic therapy was also a significantly unfavorable
prognostic factor in the present study. Previous systemic therapy
has the potential to induce resistance to systemic therapy and is
likely to lead to an unfavorable prognosis.
In the present study, hormone-receptor status and
HER2 status were not significant factors. There was a possibility
that the hormone-receptor status and HER2 status at the initial
presentation had changed after previous systemic therapy. Features
of tumor cells in metastatic lesions sometimes differ from those in
primary lesions (17).
Approximately 70% of the present study patients had received
previous systemic therapy. This may be one of the possible
explanations that the hormone-receptor/HER2 status and TN type were
not significant factors for OS in patients who received first-time
RT to BMs in the study. Furthermore, the number of BMs (single vs.
multiple) also was not a significant factor. Previous systemic
therapy may also contribute to this result.
Comprehensive prognostic assessment using the
designated UFPs seemed to be useful for the prediction of the
prognoses of patients with BMs from BC. The median survival time of
the favorable group (total UFPs ≤1) was >3 years.
Well-fractionated higher-dose RTs are likely to be suitable for
these patients. By contrast, single fraction RT of 8 Gy is suitable
for the unfavorable group (total UFPs ≥3.5). Prognostic assessment
using total UFPs was helpful to determine the appropriate
dose-fractionation schedules for patients with BMs from BC.
The present study has several limitations, including
its retrospective nature. First, due to the lack of laboratory data
in numerous cases, the prognostic assessment using UFPs cannot be
compared to Katagiri's prognostic scoring system (3), which is very detailed. However,
clinically, a number of cases do not have the laboratory data used
in Katagiri's prognostic scoring system. The present prognostic
assessment using UFPs does not require these data and can therefore
be used in such cases. Second, the quality of life of patients with
BC and BMs after palliative RT could not be assessed, which is an
important factor in palliative treatment; moreover, the medical
records did not provide sufficient data for evaluating these
factors. Third, the sample size was small and insufficient to
validate the prognostic scoring system more precisely. Therefore,
large-scale prospective studies are required in the future for
validating this prognostic system.
In conclusion, PS ≥2, NG 3, previous systemic
therapy, synchronous brain metastases and synchronous liver
metastases were significantly associated with poor OS time for
patients with BMs from BC. A comprehensive prognostic assessment
using UFPs based on these factors seemed to be useful to select
patients who needed comparatively well-fractionated high-dose RT
for BMs from BC.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the present
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
KM, HK and YH designed the study concepts. KM, HK,
YH, KN, MK, SO and TK collected patient data, and analyzed and
interpreted the data. KM, HK and YH confirm the authenticity of all
the raw data. KM, HK, YH, KN, MK, SO and TK collaborated in the
discussion. KM, HK and YH prepared the manuscript, and KN, MK, SH
and TK revised it critically for important intellectual content.
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The present study was approved by the Ethics
Committee of the National Hospital Organization Shikoku Cancer
Center (Matsuyama, Japan; approval no. RIN2021-71). The opt-out
method was applied with regard to consent for this study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
SO received honorarium from AstraZeneca plc. All
other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
|
1
|
Solomayer EF, Diel IJ, Meyberg GC, Gollan
C and Bastert G: Metastatic breast cancer: Clinical course,
prognosis and therapy related to the first site of metastasis.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 59:271–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Svensson E, Christiansen CF, Ulrichsen SP,
Rorth MR and Sorensen HT: Survival after bone metastasis by primary
cancer type: A Danish population-based cohort study. BMJ Open.
7:e0160222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Katagiri H, Okada R, Takagi T, Takahashi
M, Murata H, Harada H, Nishimura T, Asakura H and Ogawa H: New
prognostic factors and scoring system for patients with skeletal
metastasis. Cancer Med. 3:1359–1367. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen MT, Sun HF, Zhao Y, Fu WY, Yang LP,
Gao SP, Li LD, Jiang HL and Jin W: Comparison of patterns and
prognosis among distant metastatic breast cancer patients by age
groups: A SEER population-based analysis. Sci Rep. 7:92542017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Largillier R, Ferrero JM, Doyen J,
Barriere J, Namer M, Mari V, Courdi A, Hannoun-Levi JM, Ettore F,
Birtwisle-Peyrottes I, et al: Prognostic factors in 1,038 women
with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 19:2012–2019. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Morales-Vasquez F and
Hortobagyi GN: Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in
patients with breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 608:1–22. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tokuhashi Y, Matsuzaki H, Toriyama S,
Kawano H and Ohsaka S: Scoring system for the preoperative
evaluation of metastatic spine tumor prognosis. Spine. (Phila Pa
1976). 15:1110–1113. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Black MM, Barclay TH and Hankey BF:
Prognosis in breast cancer utilizing histologic characteristics of
the primary tumor. Cancer. 36:2048–2055. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chow R, Hoskin P, Schild SE, Raman S, Im
J, Zhang D, Chan S, Chiu N, Chiu L, Lam H, et al: Single vs
multiple fraction palliative radiation therapy for bone metastases:
Cumulative meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 141:56–61. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rades D, Lange M, Veninga T, Stalpers LJ,
Bajrovic A, Adamietz IA, Rudat V and Schild SE: Final results of a
prospective study comparing the local control of short-course and
long-course radiotherapy for metastatic spinal cord compression.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:524–530. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rades D, Segedin B, Conde-Moreno AJ,
Garcia R, Perpar A, Metz M, Badakhshi H, Schreiber A, Nitsche M,
Hipp P, et al: Radiotherapy with 4 Gy × 5 versus 3 Gy × 10 for
metastatic epidural spinal cord compression: Final results of the
SCORE-2 trial (ARO 2009/01). J Clin Oncol. 34:597–602. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Q, Mori I, Sakurai T, Yoshimura G,
Suzuma T, Nakamura Y, Nakamura M, Taniguchi E, Tamaki T, Umemura T
and Kakudo K: Correlation between nuclear grade and biological
prognostic variables in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer.
8:105–110. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Lee AH, Elston CW,
Grainge MJ, Hodi Z, Blamey RW and Ellis IO: Prognostic significance
of Nottingham histologic grade in invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 26:3153–3158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gerratana L, Fanotto V, Bonotto M,
Bolzonello S, Minisini AM, Fasola G and Puglisi F: Pattern of
metastasis and outcome in patients with breast cancer. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 32:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Curigliano G, Bagnardi V, Viale G,
Fumagalli L, Rotmensz N, Aurilio G, Locatelli M, Pruneri G, Giudici
S, Bellomi M, et al: Should liver metastases of breast cancer be
biopsied to improve treatment choice? Ann Oncol. 22:2227–2233.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|