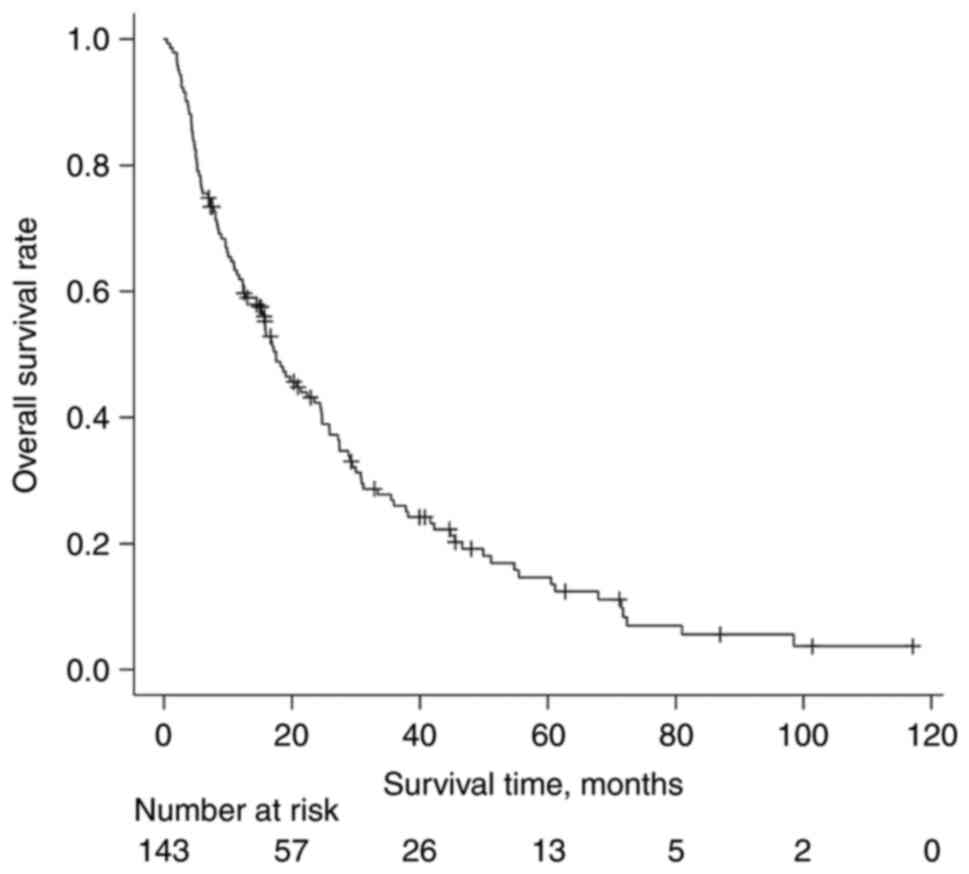
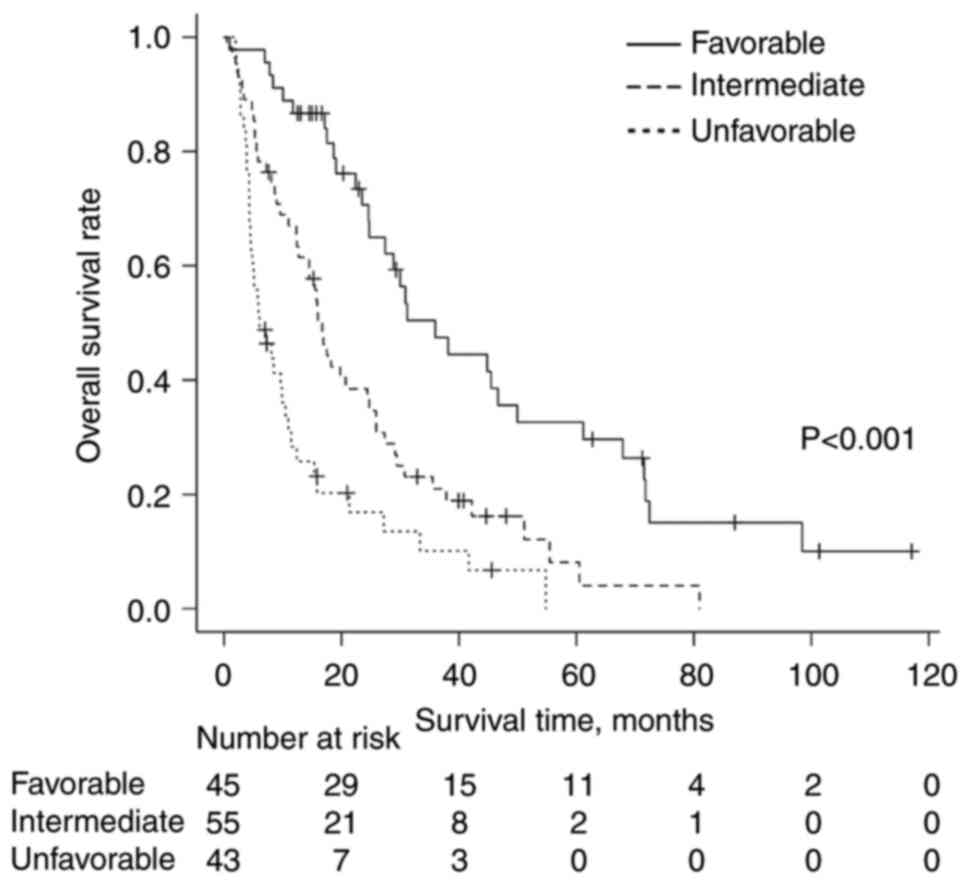
|
1
|
Solomayer EF, Diel IJ, Meyberg GC, Gollan
C and Bastert G: Metastatic breast cancer: Clinical course,
prognosis and therapy related to the first site of metastasis.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 59:271–278. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Svensson E, Christiansen CF, Ulrichsen SP,
Rorth MR and Sorensen HT: Survival after bone metastasis by primary
cancer type: A Danish population-based cohort study. BMJ Open.
7:e0160222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Katagiri H, Okada R, Takagi T, Takahashi
M, Murata H, Harada H, Nishimura T, Asakura H and Ogawa H: New
prognostic factors and scoring system for patients with skeletal
metastasis. Cancer Med. 3:1359–1367. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen MT, Sun HF, Zhao Y, Fu WY, Yang LP,
Gao SP, Li LD, Jiang HL and Jin W: Comparison of patterns and
prognosis among distant metastatic breast cancer patients by age
groups: A SEER population-based analysis. Sci Rep. 7:92542017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Largillier R, Ferrero JM, Doyen J,
Barriere J, Namer M, Mari V, Courdi A, Hannoun-Levi JM, Ettore F,
Birtwisle-Peyrottes I, et al: Prognostic factors in 1,038 women
with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 19:2012–2019. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Morales-Vasquez F and
Hortobagyi GN: Overview of resistance to systemic therapy in
patients with breast cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 608:1–22. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tokuhashi Y, Matsuzaki H, Toriyama S,
Kawano H and Ohsaka S: Scoring system for the preoperative
evaluation of metastatic spine tumor prognosis. Spine. (Phila Pa
1976). 15:1110–1113. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Black MM, Barclay TH and Hankey BF:
Prognosis in breast cancer utilizing histologic characteristics of
the primary tumor. Cancer. 36:2048–2055. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chow R, Hoskin P, Schild SE, Raman S, Im
J, Zhang D, Chan S, Chiu N, Chiu L, Lam H, et al: Single vs
multiple fraction palliative radiation therapy for bone metastases:
Cumulative meta-analysis. Radiother Oncol. 141:56–61. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rades D, Lange M, Veninga T, Stalpers LJ,
Bajrovic A, Adamietz IA, Rudat V and Schild SE: Final results of a
prospective study comparing the local control of short-course and
long-course radiotherapy for metastatic spinal cord compression.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 79:524–530. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rades D, Segedin B, Conde-Moreno AJ,
Garcia R, Perpar A, Metz M, Badakhshi H, Schreiber A, Nitsche M,
Hipp P, et al: Radiotherapy with 4 Gy × 5 versus 3 Gy × 10 for
metastatic epidural spinal cord compression: Final results of the
SCORE-2 trial (ARO 2009/01). J Clin Oncol. 34:597–602. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang Q, Mori I, Sakurai T, Yoshimura G,
Suzuma T, Nakamura Y, Nakamura M, Taniguchi E, Tamaki T, Umemura T
and Kakudo K: Correlation between nuclear grade and biological
prognostic variables in invasive breast cancer. Breast Cancer.
8:105–110. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Lee AH, Elston CW,
Grainge MJ, Hodi Z, Blamey RW and Ellis IO: Prognostic significance
of Nottingham histologic grade in invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin
Oncol. 26:3153–3158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gerratana L, Fanotto V, Bonotto M,
Bolzonello S, Minisini AM, Fasola G and Puglisi F: Pattern of
metastasis and outcome in patients with breast cancer. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 32:125–133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Curigliano G, Bagnardi V, Viale G,
Fumagalli L, Rotmensz N, Aurilio G, Locatelli M, Pruneri G, Giudici
S, Bellomi M, et al: Should liver metastases of breast cancer be
biopsied to improve treatment choice? Ann Oncol. 22:2227–2233.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|