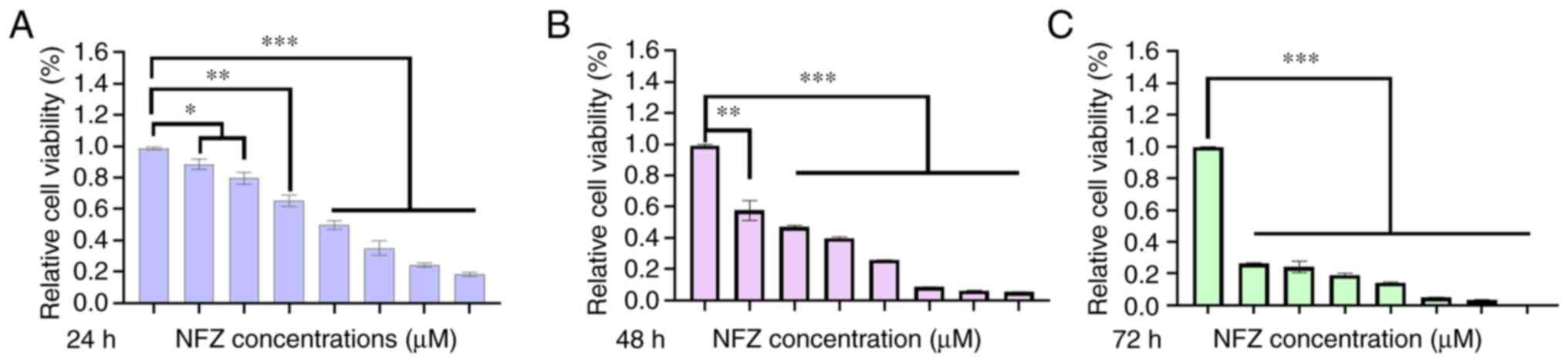
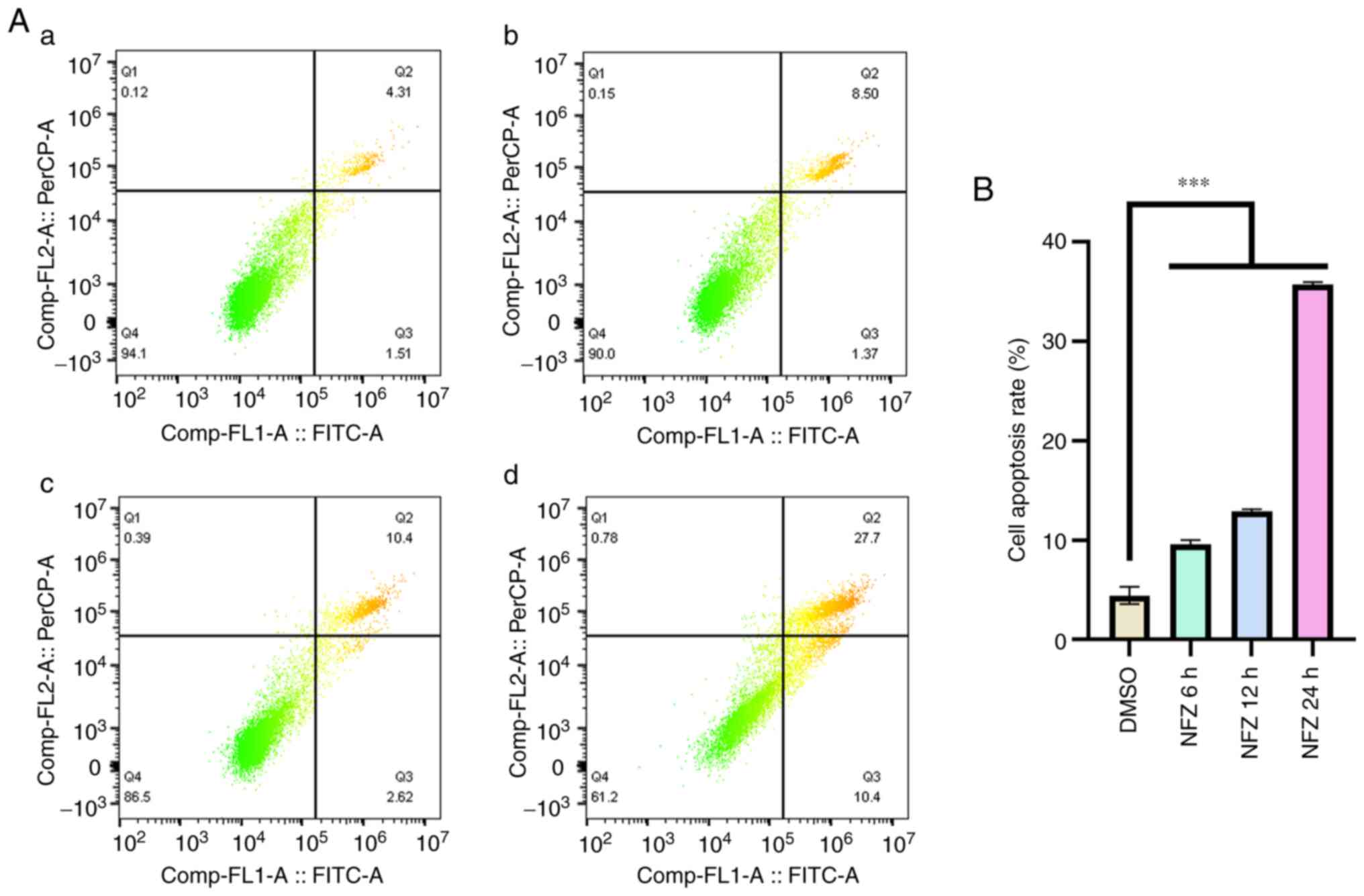
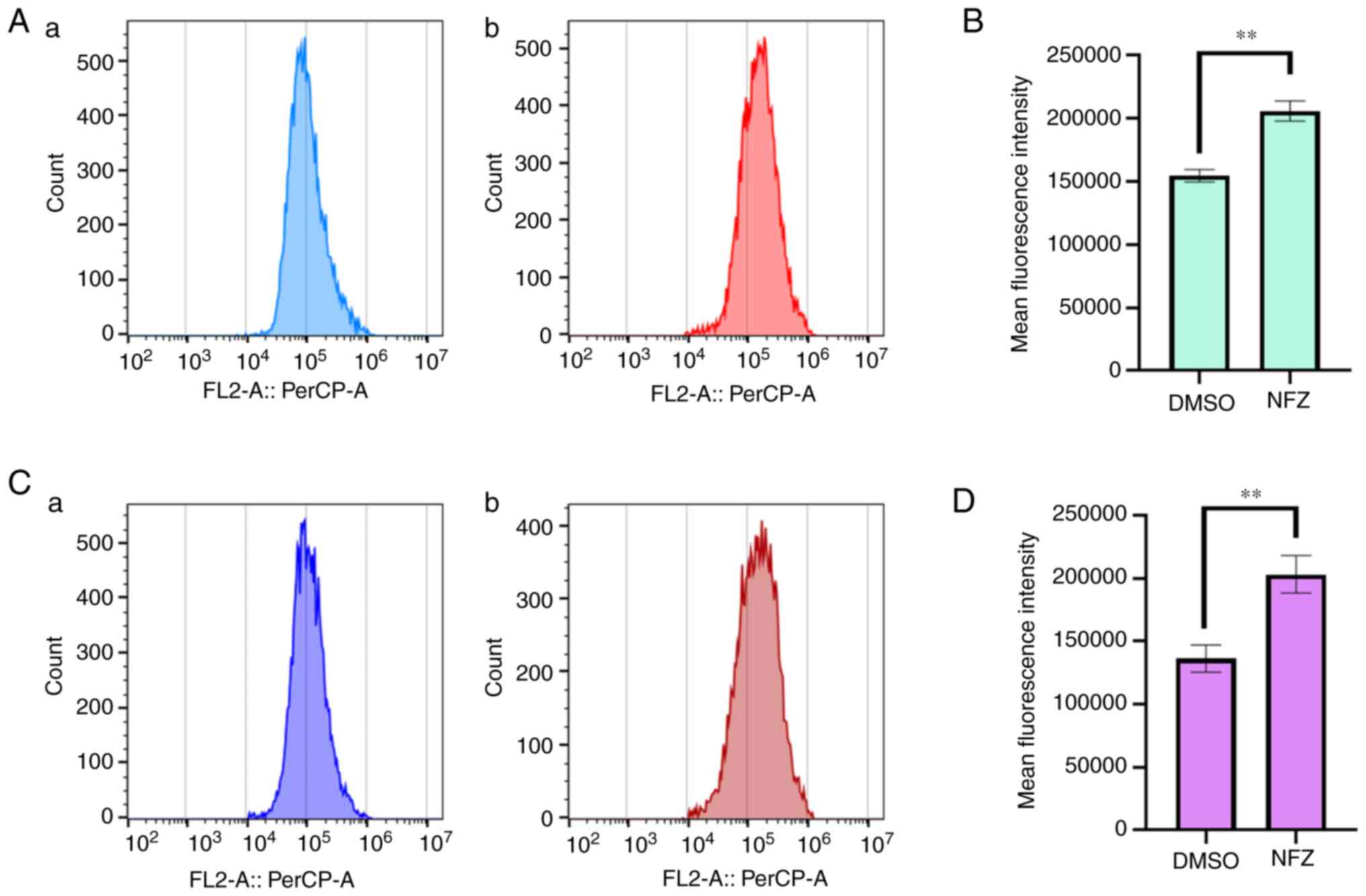
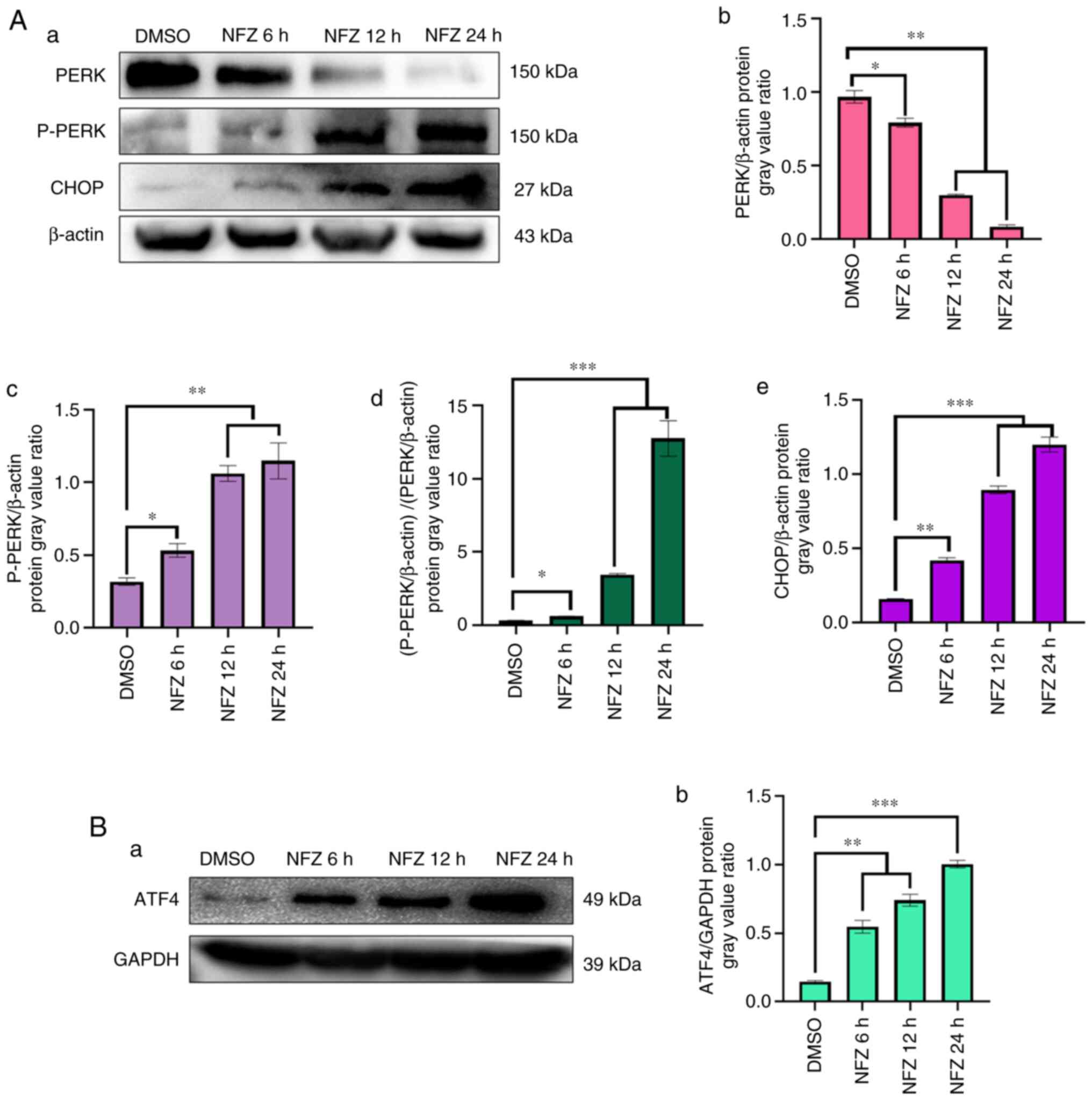
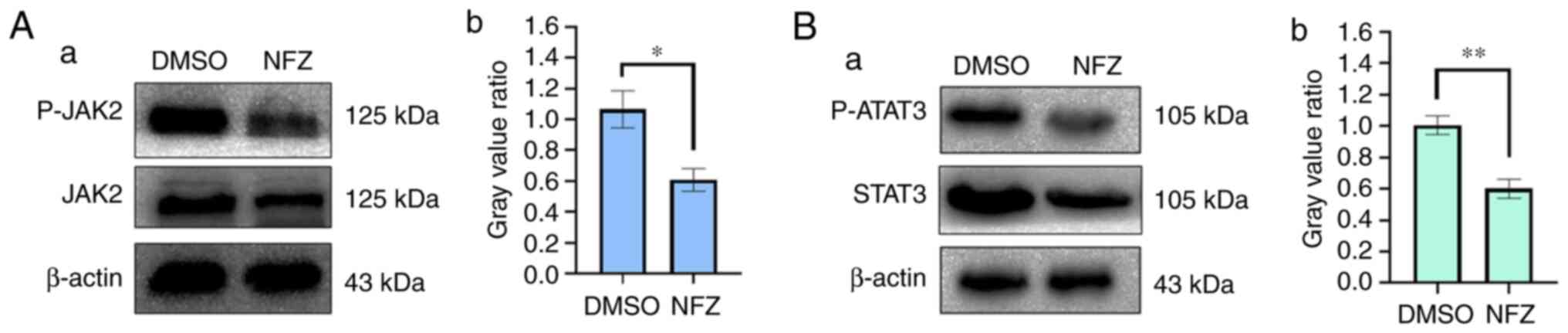
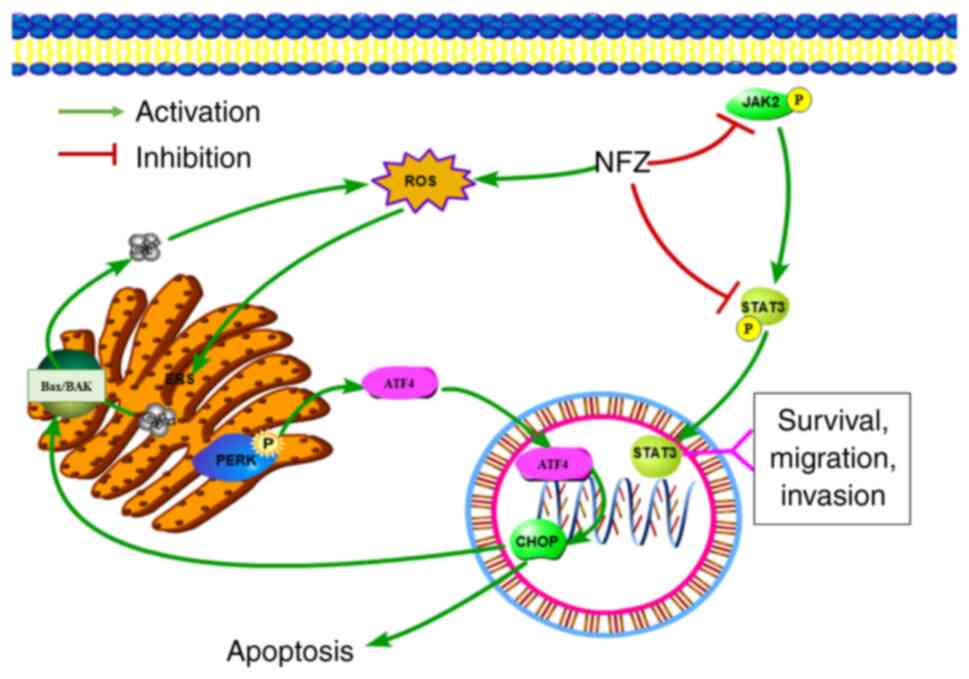
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD, Schild SE
and Adjei AA: Non-small cell lung cancer: Epidemiology, risk
factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc. 83:584–594.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Basumallik N and Agarwal M: Small cell
lung cancer. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure
Island, FL: 2022
|
|
4
|
Jurisic V, Vukovic V, Obradovic J,
Gulyaeva LF, Kushlinskii NE and Djordjević N: EGFR polymorphism and
survival of NSCLC patients treated with TKIs: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. J Oncol. 2020:19732412020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jurišić V, Obradovic J, Pavlović S and
Djordjevic N: Epidermal growth factor receptor gene in
non-small-cell lung cancer: The importance of promoter polymorphism
investigation. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2018:61921872018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma SV, Bell DW, Settleman J and Haber
DA: Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations in lung cancer. Nat
Rev Cancer. 7:169–181. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pushpakom S, Iorio F, Eyers PA, Escott KJ,
Hopper S, Wells A, Doig A, Guilliams T, Latimer J, McNamee C, et
al: Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat
Rev Drug Discov. 18:41–58. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ward WC and Dodd MC: A comparative study
of the in vitro bacteriostatic action of some simple derivatives of
furan, thiophene, and pyrrole. J Bacteriol. 56:649–652. 1948.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
CarronMCE, . Antibacterial
Nitrofurfuryldene Derivatives and Methods of Using Same. US Patent
US3290213A, Filed July 9 1975; issued. December 6–1966.
|
|
10
|
Masunari A and Tavares LC: A new class of
nifuroxazide analogues: Synthesis of 5-nitrothiophene derivatives
with antimicrobial activity against multidrug-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus. Bioorg Med Chem. 15:4229–4236. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Said E, Zaitone SA, Eldosoky M and
Elsherbiny NM: Nifuroxazide, a STAT3 inhibitor, mitigates
inflammatory burden and protects against diabetes-induced
nephropathy in rats. Chem Biol Interact. 281:111–120. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhao T, Jia H, Cheng Q, Xiao Y, Li M, Ren
W, Li C, Feng Y, Feng Z, Wang H and Zheng J: Nifuroxazide prompts
antitumor immune response of TCL-loaded DC in mice with
orthotopically-implanted hepatocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 37:3405–3414.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gan C, Zhang Q, Liu H, Wang G, Wang L, Li
Y, Tan Z, Yin W, Yao Y, Xie Y, et al: Nifuroxazide ameliorates
pulmonary fibrosis by blocking myofibroblast genesis: A drug
repurposing study. Respir Res. 23:322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saber S, Nasr M, Kaddah MMY,
Mostafa-Hedeab G, Cavalu S, Mourad AAE, Gaafar AGA, Zaghlool SS,
Saleh S, Hafez MM, et al: Nifuroxazide-loaded cubosomes exhibit an
advancement in pulmonary delivery and attenuate bleomycin-induced
lung fibrosis by regulating the STAT3 and NF-κB signaling: A new
challenge for unmet therapeutic needs. Biomed Pharmacother.
148:1127312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu JY, Zhang YC, Song LN, Zhang L, Yang
FY, Zhu XR, Cheng ZQ, Cao X and Yang JK: Nifuroxazide ameliorates
lipid and glucose metabolism in palmitate-induced HepG2 cells. RSC
Adv. 9:39394–39404. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Caballano-Infantes E, Terron-Bautista J,
Beltrán-Povea A, Cahuana GM, Soria B, Nabil H, Bedoya FJ and Tejedo
JR: Regulation of mitochondrial function and endoplasmic reticulum
stress by nitric oxide in pluripotent stem cells. World J Stem
Cells. 9:26–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cao S, Tang J, Huang Y, Li G, Li Z, Cai W,
Yuan Y, Liu J, Huang X and Zhang H: The road of solid tumor
survival: From drug-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress to drug
resistance. Front Mol Biosci. 8:6205142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
da Costa MOL, Pavani TFA, Lima AN, Scott
AL, Ramos DFV, Lazarini M and Rando DGG: Nifuroxazide as JAK2
inhibitor: A binding mode proposal and Hel cell proliferation
assay. Eur J Pharm Sci. 162:1058222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luo Y, Zeng A, Fang A, Song L, Fan C, Zeng
C, Ye T, Chen H, Tu C and Xie Y: Nifuroxazide induces apoptosis,
inhibits cell migration and invasion in osteosarcoma. Invest New
Drugs. 37:1006–1013. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nelson EA, Walker SR, Kepich A, Gashin LB,
Hideshima T, Ikeda H, Chauhan D, Anderson KC and Frank DA:
Nifuroxazide inhibits survival of multiple myeloma cells by
directly inhibiting STAT3. Blood. 112:5095–5102. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang F, Hu M, Lei Q, Xia Y, Zhu Y, Song X,
Li Y, Jie H, Liu C, Xiong Y, et al: Nifuroxazide induces apoptosis
and impairs pulmonary metastasis in breast cancer model. Cell Death
Dis. 6:e17012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ye TH, Yang FF, Zhu YX, Li YL, Lei Q, Song
XJ, Xia Y, Xiong Y, Zhang LD, Wang NY, et al: Inhibition of Stat3
signaling pathway by nifuroxazide improves antitumor immunity and
impairs colorectal carcinoma metastasis. Cell Death Dis.
8:e25342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
El-Sherbiny M, El-Sayed RM, Helal MA,
Ibrahiem AT, Elmahdi HS, Eladl MA, Bilay SE, Alshahrani AM, Tawfik
MK, Hamed ZE, et al: Nifuroxazide mitigates angiogenesis in
Ehlrich's solid carcinoma: Molecular docking, bioinformatic and
experimental studies on inhibition of Il-6/Jak2/Stat3 signaling.
Molecules. 26:68582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu Y, Ye T, Yu X, Lei Q, Yang F, Xia Y,
Song X, Liu L, Deng H, Gao T, et al: Nifuroxazide exerts potent
anti-tumor and anti-metastasis activity in melanoma. Sci Rep.
6:202532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sies H: Oxidative stress: Oxidants and
antioxidants. Exp Physiol. 82:291–295. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu L, Sun X, Guo Y and Ge K: Evodiamine
induces ROS-Dependent cytotoxicity in human gastric cancer cells
via TRPV1/Ca2+ pathway. Chem Biol Interact.
351:1097562022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun Y, St Clair DK, Xu Y, Crooks PA and St
Clair WH: A NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signaling pathway
mediates the selective radiosensitization effect of parthenolide in
prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:2880–2890. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiao B, Liu C, Liu BT, Zhang X, Liu RR and
Zhang XW: TTF1-NPs Induce ERS-Mediated apoptosis and inhibit human
hepatoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Oncol Res. 23:311–320.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Limia CM, Sauzay C, Urra H, Hetz C, Chevet
E and Avril T: Emerging roles of the endoplasmic reticulum
associated unfolded protein response in cancer cell migration and
invasion. Cancers (Basel). 11:6312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oakes SA: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
signaling in cancer cells. Am J Pathol. 190:934–946. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rozpedek W, Pytel D, Mucha B, Leszczynska
H, Diehl JA and Majsterek I: The role of the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP
signaling pathway in tumor progression during endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Curr Mol Med. 16:533–544. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen D, Fan Z, Rauh M, Buchfelder M,
Eyupoglu IY and Savaskan N: ATF4 promotes angiogenesis and neuronal
cell death and confers ferroptosis in a xCT-dependent manner.
Oncogene. 36:5593–5608. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kania E, Pająk B and Orzechowski A:
Calcium homeostasis and ER stress in control of autophagy in cancer
cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3527942015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oyadomri S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guo FJ, Liu Y, Zhou J, Luo S, Zhao W, Li X
and Liu C: XBP1S protects cells from ER stress-induced apoptosis
through Erk1/2 signaling pathway involving CHOP. Histochem Cell
Biol. 138:447–460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Colovic N, Jurisic V, Terzic T, Atkinson
HD and Colovic M: Immunochemotherapy for Bcl-2 and MUM-negative
aggressive primary cutaneous B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Arch
Dermatol Res. 301:689–692. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Popović B, Jekić B, Novaković I, Luković
LJ, Tepavcević Z, Jurisić V, Vukadinović M and Milasin J: Bcl-2
expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1095:19–25. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Karan-Djurasevic T, Palibrk V, Zukic B,
Spasovski V, Glumac I, Colovic M, Colovic N, Jurisic V, Scorilas A,
Pavlovic S and Tosic N: Expression of Bcl2L12 in chronic
lymphocytic leukemia patients: Association with clinical and
molecular prognostic markers. Med Oncol. 30:4052013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiao B, Lin D and Zhang X, Zhang M and
Zhang X: TTF1, in the form of nanoparticles, inhibits angiogenesis,
cell migration and cell invasion in vitro and in vivo in human
hepatoma through STAT3 regulation. Molecules. 21:15072016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|