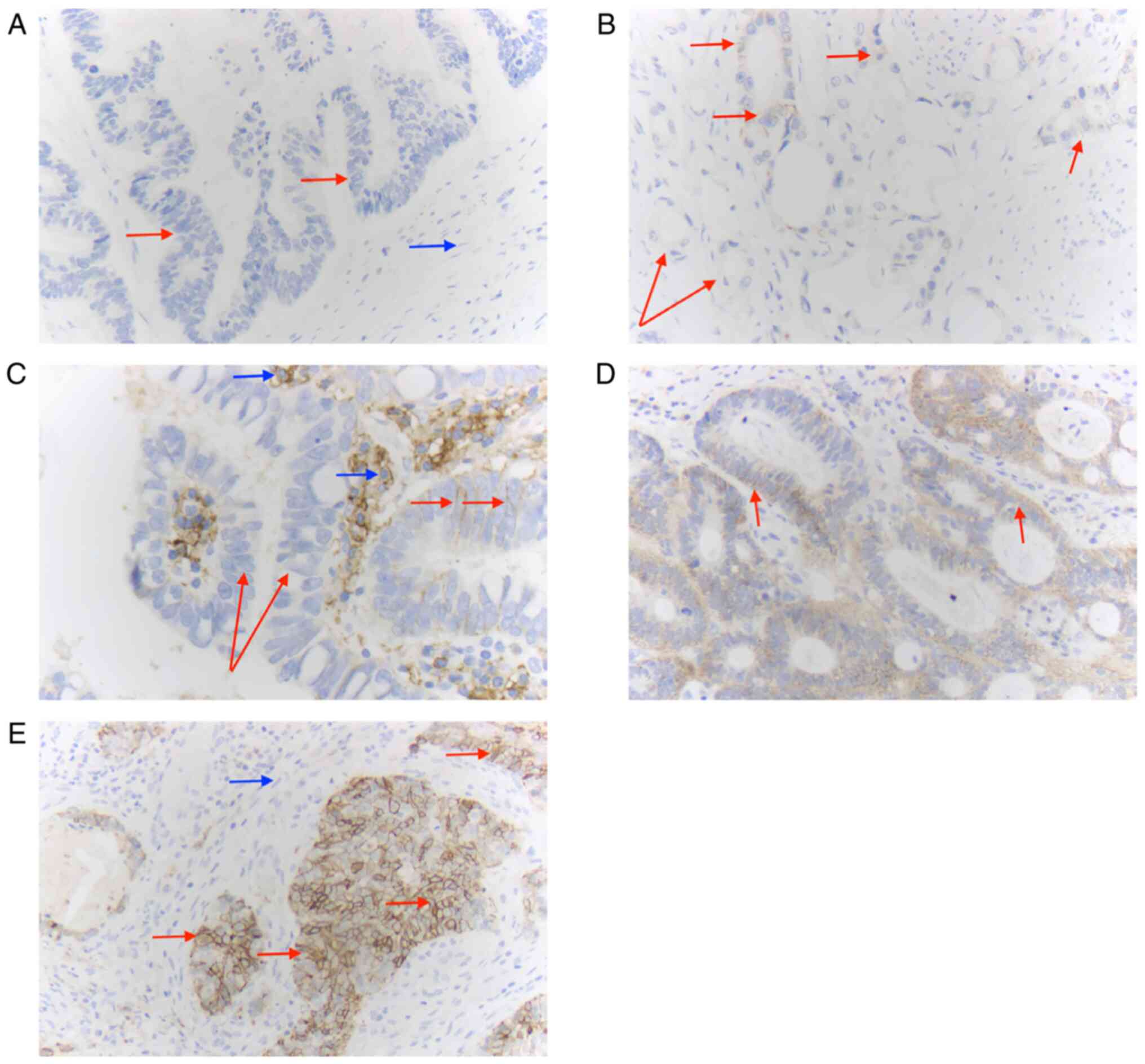
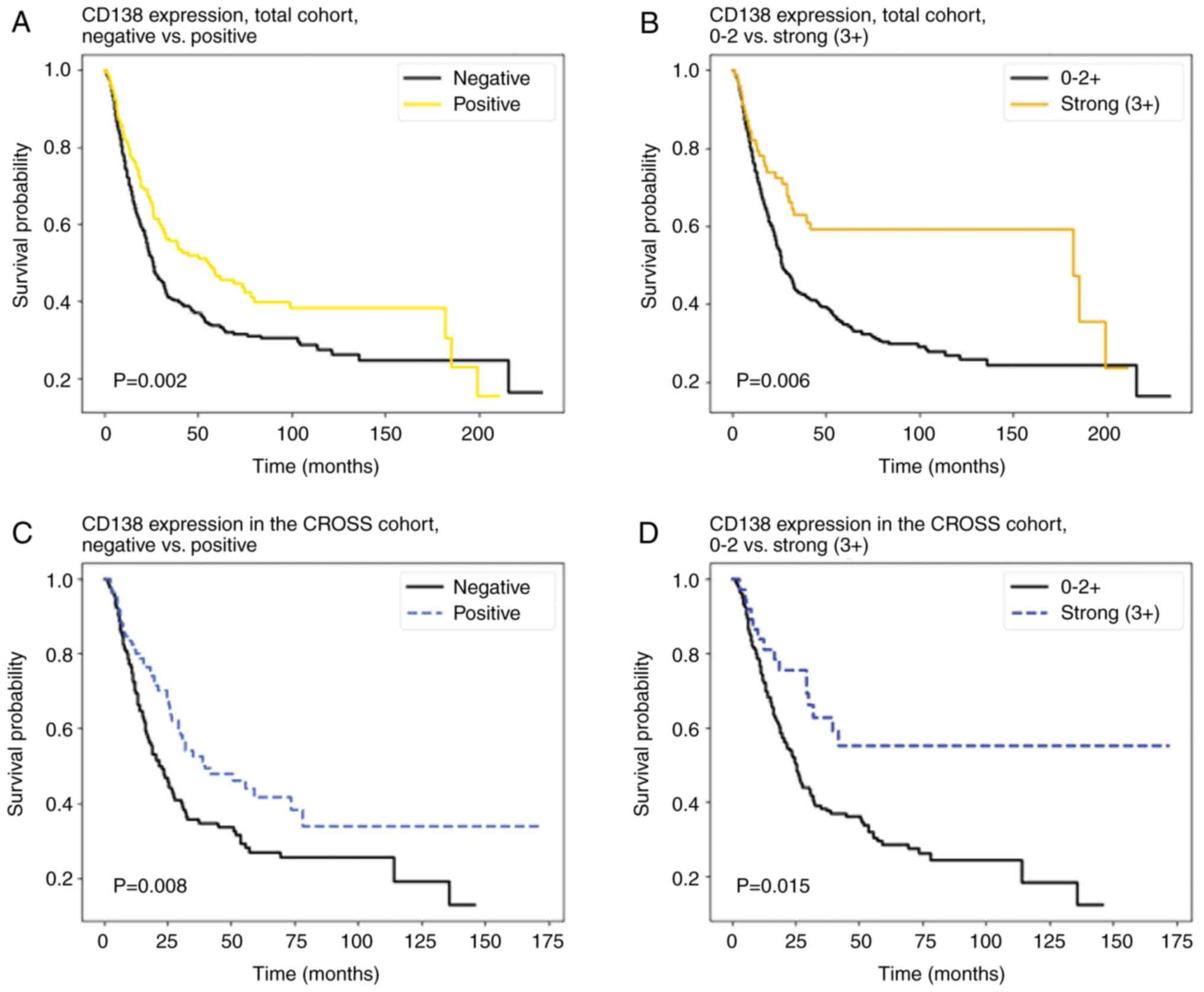
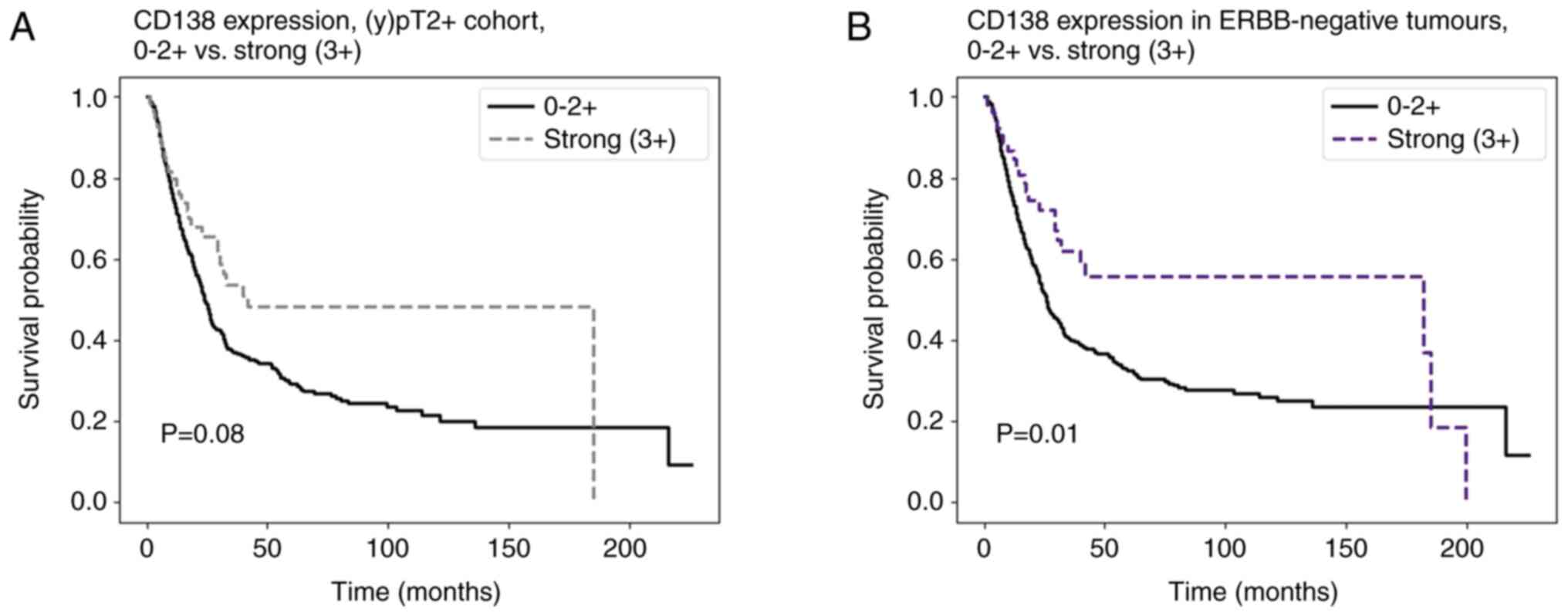
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pennathur A, Gibson MK, Jobe BA and
Luketich JD: Oesophageal carcinoma. Lancet. 381:400–412. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lepage C, Rachet B, Jooste V, Faivre J and
Coleman MP: Continuing rapid increase in esophageal adenocarcinoma
in England and Wales. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:2694–2699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tustumi F, Kimura CM, Takeda FR, Uema RH,
Salum RA, Ribeiro-Junior U and Cecconello I: Prognostic factors and
survival analysis in esophageal carcinoma. Arq Bras Cir Dig.
29:138–141. 2016.(In English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He H, Chen N, Hou Y, Wang Z, Zhang Y,
Zhang G and Fu J: Trends in the incidence and survival of patients
with esophageal cancer: A SEER database analysis. Thorac Cancer.
11:1121–1128. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lagergren J and Lagergren P: Oesophageal
cancer. BMJ. 341:c62802010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Surgical resection with or without
preoperative chemotherapy in oesophageal cancer, . A randomised
controlled trial. Lancet. 359:1727–1733. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gebski V, Burmeister B, Smithers BM, Foo
K, Zalcberg J and Simes J; Australasian Gastro-Intestinal Trials
Group, : Survival benefits from neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy or
chemotherapy in oesophageal carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Lancet
Oncol. 8:226–234. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bang YJ, Van Cutsem E, Feyereislova A,
Chung HC, Shen L, Sawaki A, Lordick F, Ohtsu A, Omuro Y, Satoh T,
et al: Trastuzumab in combination with chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for treatment of HER2-positive advanced gastric
or gastro-oesophageal junction cancer (ToGA): A phase 3,
open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 376:687–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Doi T, Piha–Paul SA, Jalal SI, Mai–Dang H,
Saraf S, Csiki MK and Bennouna J: Updated results for the advanced
esophageal carcinoma cohort of the phase 1b KEYNOTE-028 study of
pembrolizumab. J Clin Oncol. 34 (Suppl 15):S4046. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Piro G, Carbone C, Santoro R, Tortora G
and Melisi D: Predictive biomarkers for the treatment of resectable
esophageal and esophago-gastric junction adenocarcinoma: From
hypothesis generation to clinical validation. Expert Rev Mol Diagn.
18:357–370. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bernfield M, Götte M, Park PW, Reizes O,
Fitzgerald ML, Lincecum J and Zako M: Functions of cell surface
heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Annu Rev Biochem. 68:729–777. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Czarnowski D: Syndecans in cancer: A
review of function, expression, prognostic value, and therapeutic
significance. Cancer Treat Res Commun. 27:1003122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Palaiologou M, Delladetsima I and Tiniakos
D: CD138 (syndecan-1) expression in health and disease. Histol
Histopathol. 29:177–189. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nikolova V, Koo CY, Ibrahim SA, Wang Z,
Spillmann D, Dreier R, Kelsch R, Fischgräbe J, Smollich M, Rossi
LH, et al: Differential roles for membrane-bound and soluble
syndecan-1 (CD138) in breast cancer progression. Carcinogenesis.
30:397–407. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hassan H, Greve B, Pavao MS, Kiesel L,
Ibrahim SA and Götte M: Syndecan-1 modulates β-integrin-dependent
and interleukin-6-dependent functions in breast cancer cell
adhesion, migration, and resistance to irradiation. FEBS J.
280:2216–2227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fears CY and Woods A: The role of
syndecans in disease and wound healing. Matrix Biol. 25:443–456.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dhodapkar MV, Abe E, Theus A, Lacy M,
Langford JK, Barlogie B and Sanderson RD: Syndecan-1 is a
multifunctional regulator of myeloma pathobiology: Control of tumor
cell survival, growth, and bone cell differentiation. Blood.
91:2679–2688. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schönfeld K, Zuber C, Pinkas J, Häder T,
Bernöster K and Uherek C: Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062)
combination treatment in multiple myeloma: Pre-clinical studies. J
Hematol Oncol. 10:132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kelly KR, Chanan–Khan A, Heffner LT, Somlo
G, Siegel DS, Zimmerman T, Karnad A, Munshi NC, Jagannath S,
Greenberg AL, et al: Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062) in combination
with lenalidomide and low-dose dexamethasone in patients with
relapsed and/or refractory multiple myeloma: Clinical activity in
patients already exposed to lenalidomide and bortezomib. Blood.
124:47362014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Koster KL, Huober J and Joerger M: New
antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) in breast cancer-an overview of
ADCs recently approved and in later stages of development. Explor
Target Antitumor Ther. 3:27–36. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rugo HS, Tolaney SM, Loirat D, Punie K,
Bardia A, Hurvitz SA, O'Shaughnessy J, Cortés J, Diéras V, Carey
LA, et al: Safety analyses from the phase 3 ASCENT trial of
sacituzumab govitecan in metastatic triple-negative breast cancer.
NPJ Breast Cancer. 8:982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hoppe S, Meder L, Gebauer F, Ullrich RT,
Zander T, Hillmer AM, Buettner R, Plum P, Puppe J, Malter W and
Quaas A: Trophoblast cell surface Antigen 2 (TROP2) as a predictive
bio-marker for the therapeutic efficacy of sacituzumab govitecan in
adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Cancers (Basel). 14:47892022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ibrahim SA, Hassan H, Vilardo L, Kumar SK,
Kumar AV, Kelsch R, Schneider C, Kiesel L, Eich HT, Zucchi I, et
al: Syndecan-1 (CD138) modulates triple-negative breast cancer stem
cell properties via regulation of LRP-6 and IL-6-mediated STAT3
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e857372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schönfeld K, Herbener P, Zuber C, Häder T,
Bernöster K, Uherek C and Schüttrumpf J: Activity of indatuximab
ravtansine against triple-negative breast cancer in preclinical
tumor models. Pharm Res. 35:1182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu T, Chaganty B, Lin L, Xing L,
Ramakrishnan B, Wen K, Hsieh PA, Wollacott A, Viswanathan K, Adari
H, et al: VIS832, a novel CD138-targeting monoclonal antibody,
potently induces killing of human multiple myeloma and further
synergizes with IMiDs or bortezomib in vitro and in vivo. Blood
Cancer J. 10:1102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brierley JD, Gospodarowicz MK and
Wittekind C: TNM classification of malignant tumours. John Wiley
& Sons; 2017
|
|
28
|
Kind S, Merenkow C, Büscheck F, Möller K,
Dum D, Chirico V, Luebke AM, Höflmayer D, Hinsch A, Jacobsen F, et
al: Prevalence of Syndecan-1 (CD138) expression in different kinds
of human tumors and normal tissues. Dis Markers. 2019:49283152019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Simon R, Mirlacher M and Sauter G:
Immunohistochemical analysis of tissue microarrays. Methods Mol
Biol. 664:113–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Plum PS, Gebauer F, Krämer M, Alakus H,
Berlth F, Chon SH, Schiffmann L, Zander T, Büttner R, Hölscher AH,
et al: HER2/neu (ERBB2) expression and gene amplification
correlates with better survival in esophageal adenocarcinoma. BMC
Cancer. 19:382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chilosi M, Adami F, Lestani M, Montagna L,
Cimarosto L, Semenzato G, Pizzolo G and Menestrina F:
CD138/syndecan-1: A useful immunohistochemical marker of normal and
neoplastic plasma cells on routine trephine bone marrow biopsies.
Mod Pathol. 12:1101–1106. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Szatmári T, Ötvös R, Hjerpe A and Dobra K:
Syndecan-1 in cancer: Implications for cell signaling,
differentiation, and prognostication. Dis Markers. 2015:7960522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kusumoto T, Kodama J, Seki N, Nakamura K,
Hongo A and Hiramatsu Y: Clinical significance of syndecan-1 and
versican expression in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep.
23:917–925. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zellweger T, Ninck C, Mirlacher M,
Annefeld M, Glass AG, Gasser TC, Mihatsch MJ, Gelmann EP and
Bubendorf L: Tissue microarray analysis reveals prognostic
significance of syndecan-1 expression in prostate cancer. Prostate.
55:20–29. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lendorf ME, Manon-Jensen T, Kronqvist P,
Multhaupt HA and Couchman JR: Syndecan-1 and syndecan-4 are
independent indicators in breast carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem.
59:615–629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mikami S, Ohashi K, Usui Y, Nemoto T,
Katsube K, Yanagishita M, Nakajima M, Nakamura K and Koike M: Loss
of syndecan-1 and increased expression of heparanase in invasive
esophageal carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res. 92:1062–1073. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Szumilo J, Burdan F, Zinkiewicz K, Dudka
J, Klepacz R, Dabrowski A and Korobowicz E: Expression of
syndecan-1 and cathepsins D and K in advanced esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. Folia Histochem Cytobiol. 47:571–578.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Horiba MN, Casak SJ, Mishra-Kalyani PS,
Roy P, Beaver JA, Pazdur R, Kluetz PG, Lemery SJ and Fashoyin-Aje
LA: FDA approval summary: Nivolumab for the adjuvant treatment of
adults with completely resected esophageal/gastroesophageal
junction cancer and residual pathologic disease. Clin Cancer Res.
28:5244–5248. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ikeda H, Hideshima T, Fulciniti M, Lutz
RJ, Yasui H, Okawa Y, Kiziltepe T, Vallet S, Pozzi S, Santo L, et
al: The monoclonal antibody nBT062 conjugated to cytotoxic
Maytansinoids has selective cytotoxicity against CD138-positive
multiple myeloma cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res.
15:4028–4037. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Jagannath S, Heffner LT Jr, Ailawadhi S,
Munshi NC, Zimmerman TM, Rosenblatt J, Lonial S, Chanan-Khan A,
Ruehle M, Rharbaoui F, et al: Indatuximab ravtansine (BT062)
monotherapy in patients with relapsed and/or refractory multiple
myeloma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 19:372–380. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schönfeld K, Herbener P, Zuber C, Häder T,
Bernöster K, Uherek C and Schüttrumpf J: Activity of indatuximab
ravtansine against triple-negative breast cancer in preclinical
tumor models. Pharm Res. 35:1182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kelly KR, Ailawadhi S, Siegel DS, Heffner
LT, Somlo G, Jagannath S, Zimmerman TM, Munshi NC, Madan S,
Chanan-Khan A, et al: Indatuximab ravtansine plus dexamethasone
with lenalidomide or pomalidomide in relapsed or refractory
multiple myeloma: A multicentre, phase 1/2a study. Lancet Haematol.
8:e794–e807. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|