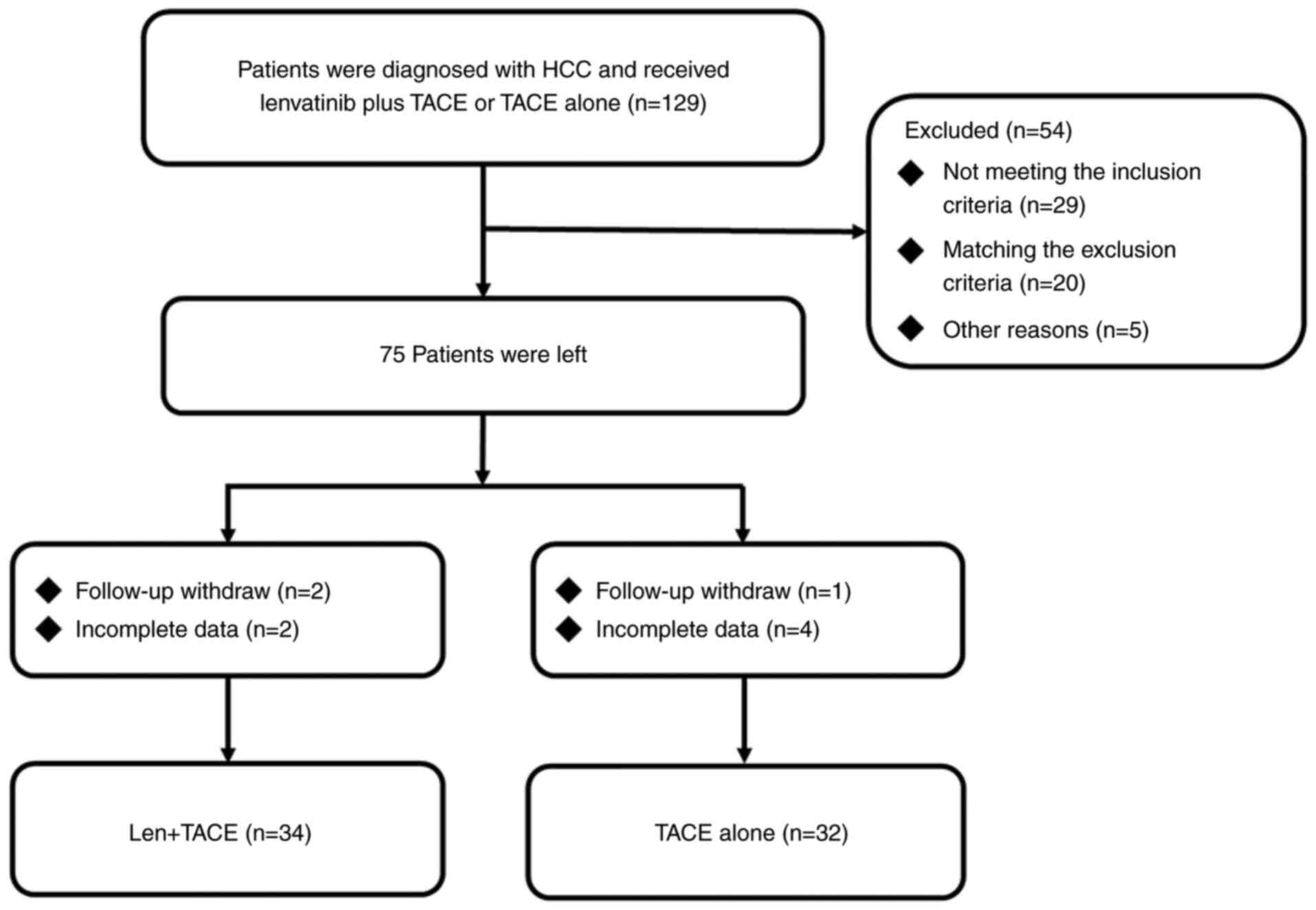
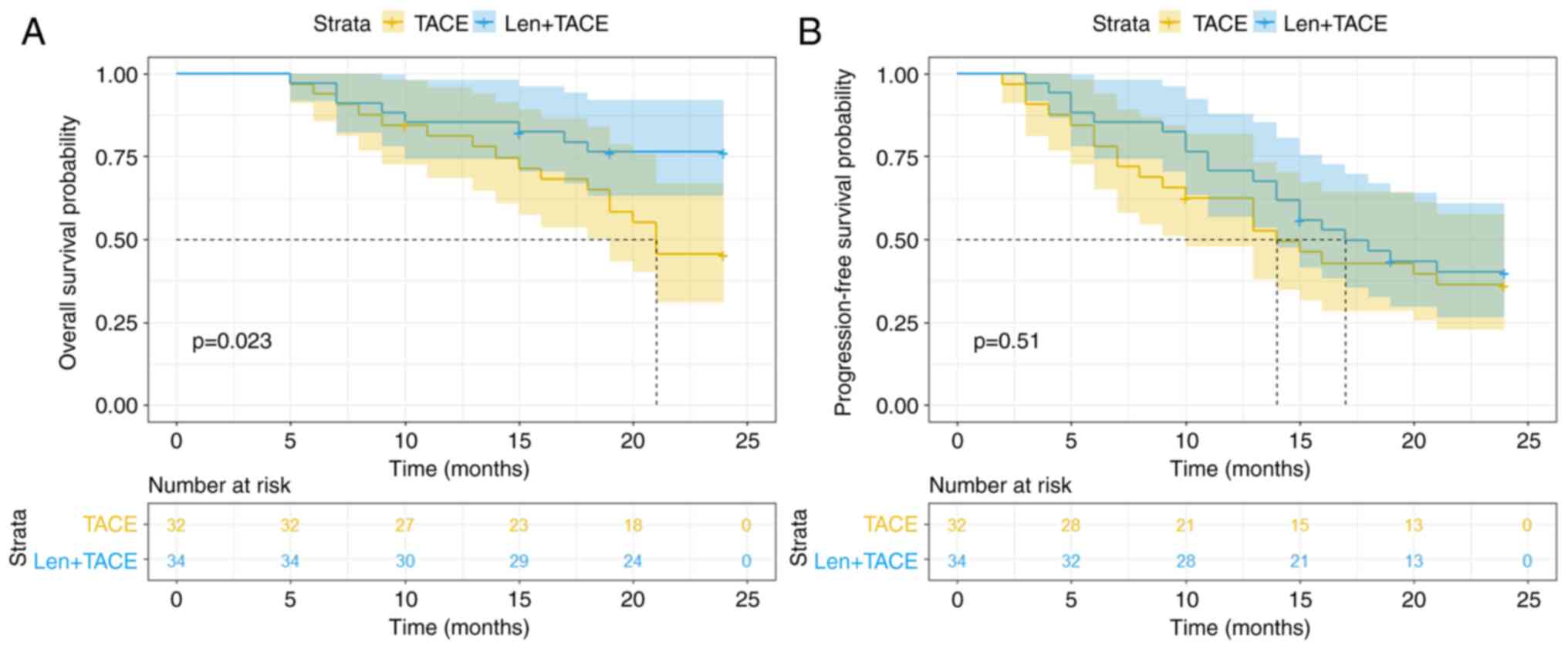
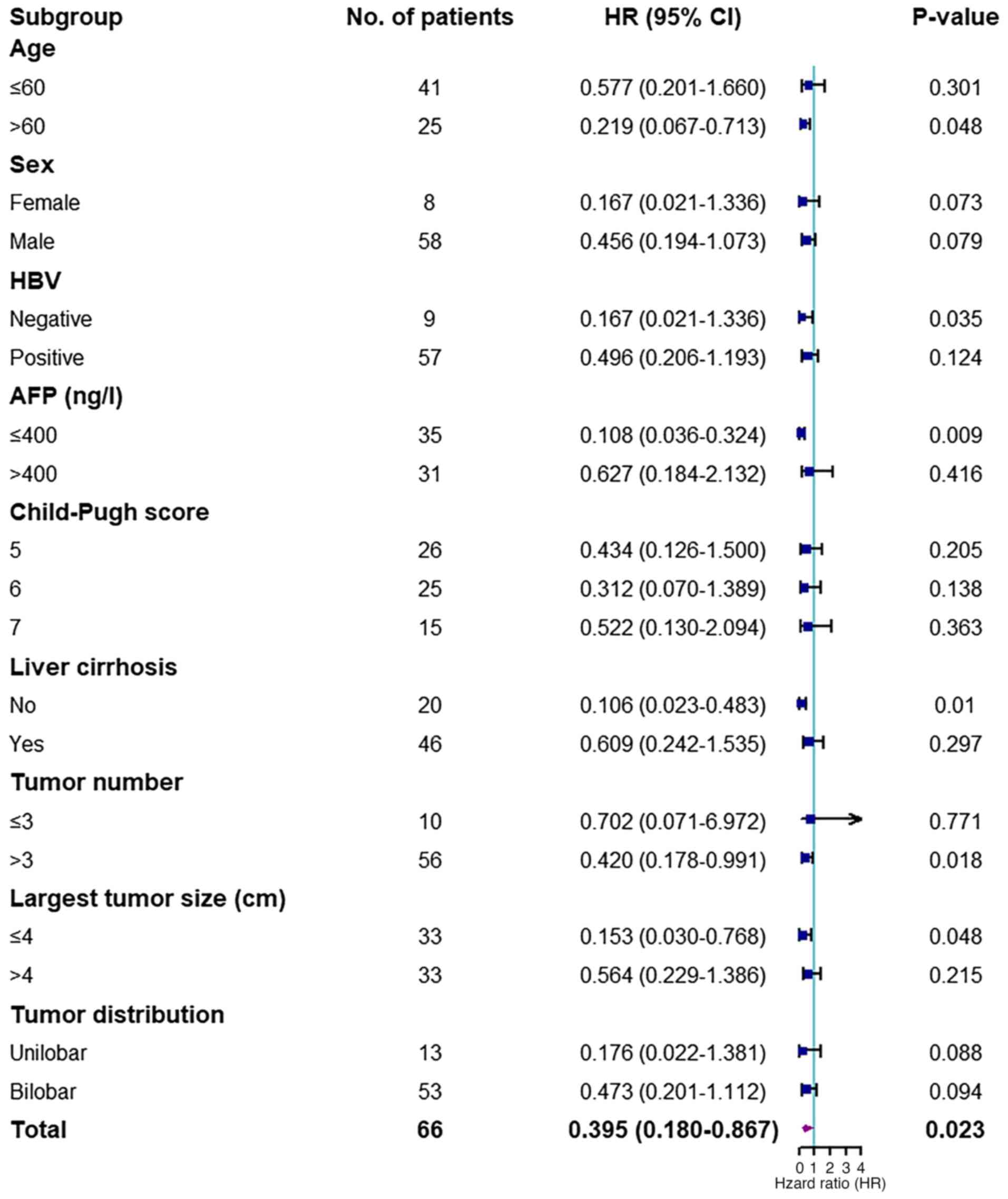
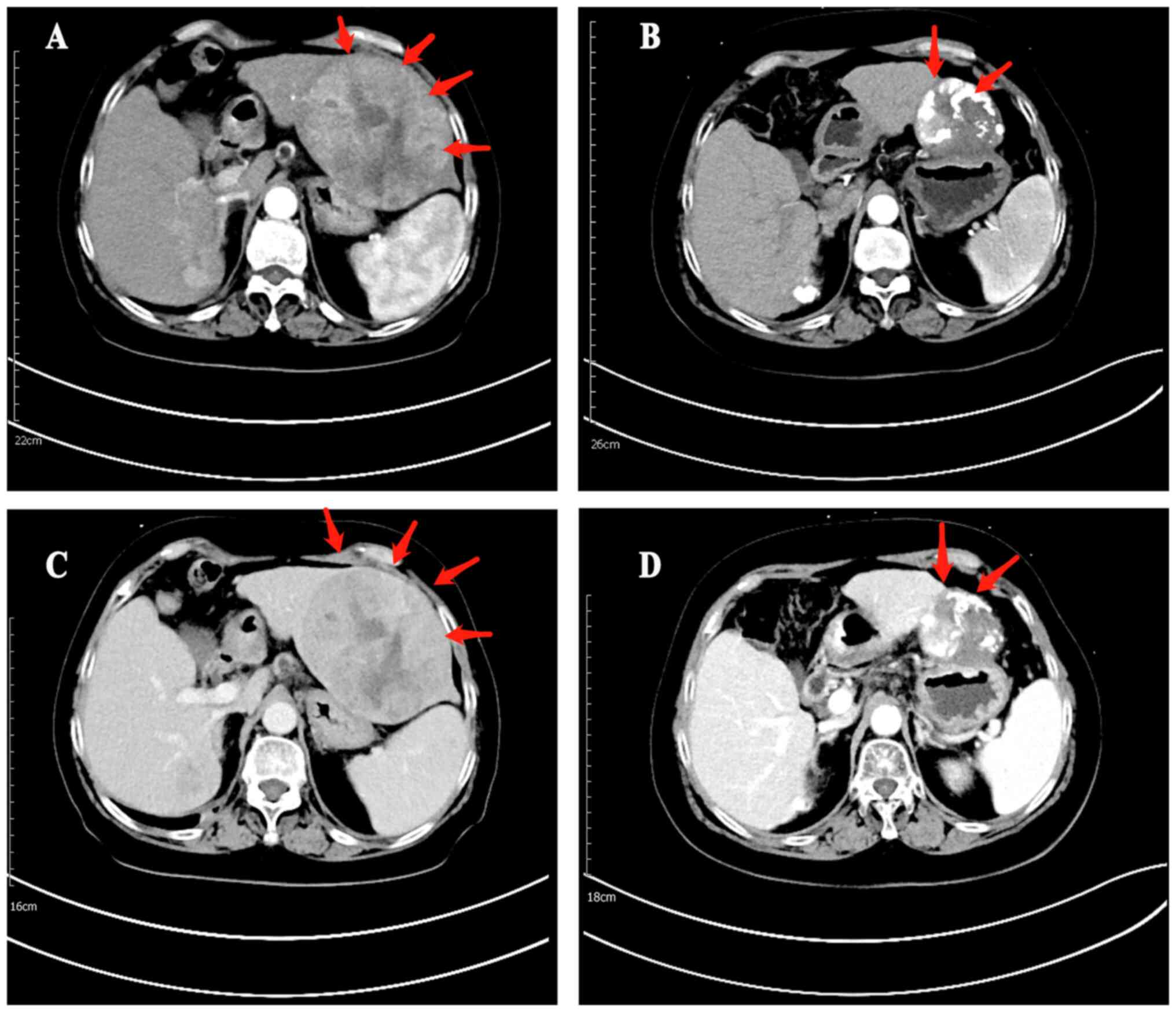
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qiu H, Cao S and Xu R: Cancer incidence,
mortality, and burden in China: A time-trend analysis and
comparison with the United States and United Kingdom based on the
global epidemiological data released in 2020. Cancer Commun (Lond).
41:1037–1048. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grandhi MS, Kim AK, Ronnekleiv-Kelly SM,
Kamel IR, Ghasebeh MA and Pawlik TM: Hepatocellular carcinoma: From
diagnosis to treatment. Surg Oncol. 25:74–85. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moon H, Choi JE, Lee IJ, Kim TH, Kim SH,
Ko YH, Kim HB, Nam BH and Park JW: All-treatment array of
hepatocellular carcinoma from initial diagnosis to death
Observation of cumulative treatments. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
143:2327–2339. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega
J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Kelley RK, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V,
Salem R, et al: BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and
treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 76:681–693.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bolondi L, Burroughs A, Dufour JF, Galle
PR, Mazzaferro V, Piscaglia F, Raoul JL and Sangro B: Heterogeneity
of patients with intermediate (BCLC B) Hepatocellular Carcinoma:
proposal for a subclassification to facilitate treatment decisions.
Semin Liver Dis. 32:348–359. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yi PS, Wang H and Li JS: Evolution and
current status of the subclassification of intermediate
hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Surg. 12:85–92.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kudo M, Arizumi T, Ueshima K, Sakurai T,
Kitano M and Nishida N: Subclassification of BCLC B stage
hepatocellular carcinoma and treatment strategies: Proposal of
modified bolondi's subclassification (Kinki Criteria). Dig Dis.
33:751–758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kudo M: Extremely High Objective Response
Rate of Lenvatinib: Its Clinical Relevance and Changing the
Treatment Paradigm in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver cancer.
7:215–224. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li X, Feng GS, Zheng CS, Zhuo CK and Liu
X: Influence of transarterial chemoembolization on angiogenesis and
expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic
fibroblast growth factor in rat with Walker-256 transplanted
hepatoma: An experimental study. World J Gastroenterol.
9:2445–2449. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shim JH, Park JW, Kim JH, An M, Kong SY,
Nam BH, Choi JI, Kim HB, Lee WJ and Kim CM: Association between
increment of serum VEGF level and prognosis after transcatheter
arterial chemoembolization in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
Cancer Sci. 99:2037–2044. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, Pivetta
G, Ragazzi R, Baldan A, Girardi L, Cillo U, Burra P, Giacomin A and
Farinati F: Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): The role of angiogenesis and
invasiveness. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:914–921. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kalbasi A and Ribas A: Tumour-intrinsic
resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Nat Rev Immunol.
20:25–39. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rahma OE and Hodi FS: The intersection
between tumor angiogenesis and immune suppression. Clin Cancer Res.
25:5449–5457. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kudo M, Ueshima K, Ikeda M, Torimura T,
Tanabe N, Aikata H, Izumi N, Yamasaki T, Nojiri S, Hino K, et al:
Randomised, multicentre prospective trial of transarterial
chemoembolisation (TACE) plus sorafenib as compared with TACE alone
in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: TACTICS trial. Gut.
69:1492–1501. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park JW, Kim YJ, Kim DY, Bae SH, Paik SW,
Lee YJ, Kim HY, Lee HC, Han SY, Cheong JY, et al: Sorafenib with or
without concurrent transarterial chemoembolization in patients with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: The phase III STAH trial. J
Hepatol. 70:684–691. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li H, Li S, Geng J, Zhao S, Tan K, Yang Z,
Feng D and Liu L: Efficacy evaluation of the combination therapy of
sorafenib and transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable HCC:
A systematic review and meta-analysis of comparative studies. Ann
Transl Med. 8:5402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang Z, Wang E, Bai W, Xia D, Ding R, Li
J, Wang Q, Liu L, Sun J, Mu W, et al: Exploratory analysis to
identify candidates benefitting from combination therapy of
transarterial chemoembolization and sorafenib for first-line
treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter
retrospective observational study. Liver Cancer. 9:308–325. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Okamoto K, Ikemori-Kawada M, Jestel A, von
König K, Funahashi Y, Matsushima T, Tsuruoka A, Inoue A and Matsui
J: Distinct binding mode of multikinase inhibitor lenvatinib
revealed by biochemical characterization. ACS Med Chem Lett.
6:89–94. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kudo M, Finn RS, Qin S, Han KH, Ikeda K,
Piscaglia F, Baron A, Park JW, Han G, Jassem J, et al: Lenvatinib
versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3
non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 391:1163–1173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vogel A, Qin S, Kudo M, Su Y, Hudgens S,
Yamashita T, Yoon JH, Fartoux L, Simon K, López C, et al:
Lenvatinib versus sorafenib for first-line treatment of
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: Patient-reported outcomes
from a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial.
Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:649–658. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Facciorusso A, Tartaglia N, Villani R,
Serviddio G, Ramai D, Mohan BP, Chandan S, Abd El Aziz MA,
Evangelista J, Cotsoglou C and Ambrosi A: Lenvatinib versus
sorafenib as first-line therapy of advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Transl Res.
13:2379–2387. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu JN, Li JJ, Yan S, Zhang GN and Yi PS:
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with lenvatinib versus
transarterial chemoembolization combined with sorafenib for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 13:10747932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kudo M, Ueshima K, Chan S, Minami T,
Chishina H, Aoki T, Takita M, Hagiwara S, Minami Y, Ida H, et al:
Lenvatinib as an initial treatment in patients with
intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma beyond Up-To-Seven
Criteria and Child-Pugh A Liver Function: A Proof-Of-Concept Study.
Cancers (Basel). 11:10842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen YX, Zhang JX, Zhou CG, Liu J, Liu S,
Shi HB and Zu QQ: Comparison of the efficacy and safety of
transarterial chemoembolization with or without lenvatinib for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A retrospective propensity
score-matched analysis. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 9:685–694. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fu Z, Li X, Zhong J, Chen X, Cao K, Ding
N, Liu L, Zhang X, Zhai J and Qu Z: Lenvatinib in combination with
transarterial chemoembolization for treatment of unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma (uHCC): A retrospective controlled study.
Hepatol Int. 15:663–675. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kudo M, Matsui O, Izumi N, Kadoya M,
Okusaka T, Miyayama S, Yamakado K, Tsuchiya K, Ueshima K, Hiraoka
A, et al: Transarterial chemoembolization failure/refractoriness:
JSH-LCSGJ criteria 2014 update. Oncology. 87 (Suppl 1):S22–S31.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lee JS, Kim BK, Kim SU, Park JY, Ahn SH,
Seong JS, Han KH and Kim DY: A survey on transarterial
chemoembolization refractoriness and a real-world treatment pattern
for hepatocellular carcinoma in Korea. Clin Mol Hepatol. 26:24–32.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lencioni R and Llovet JM: Modified RECIST
(mRECIST) assessment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis.
30:52–60. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
National Cancer Institute (NCI), . Common
terminology criteria for adverse events (CTCAE) version 5.0. NCI;
Bethesda, MD: 2017
|
|
31
|
Hsu C, Po-Ching-Liang, Morita S, Hu FC and
Cheng AL: Perspectives on the design of clinical trials combining
transarterial chemoembolization and molecular targeted therapy.
Liver Cancer. 1:168–176. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kudo M, Ueshima K, Ikeda M, Torimura T,
Tanabe N, Aikata H, Izumi N, Yamasaki T, Nojiri S, Hino K, et al:
Final Results of TACTICS: A randomized, prospective trial comparing
transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib to transarterial
chemoembolization alone in patients with unresectable
hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Cancer. 11:354–367. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mir IH, Guha S, Behera J and
Thirunavukkarasu C: Targeting molecular signal transduction
pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma and its implications for
cancer therapy. Cell Biol Int. 45:2161–2177. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schicho A, Hellerbrand C, Krüger K, Beyer
LP, Wohlgemuth W, Niessen C, Hohenstein E, Stroszczynski C, Pereira
PL and Wiggermann P: Impact of different embolic agents for
transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) procedures on systemic
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) levels. J Clin Transl
Hepatol. 4:288–292. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qu XD, Chen CS, Wang JH, Yan ZP, Chen JM,
Gong GQ, Liu QX, Luo JJ, Liu LX, Liu R and Qian S: The efficacy of
TACE combined sorafenib in advanced stages hepatocellullar
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 12:2632012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xie Y, Tian H, Xiang B, Zhang Y, Liu J,
Cai Z and Xiang H: Transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib
versus sorafenib for intermediate-advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma: A meta-analysis comparing clinical outcomes. Medicine
(Baltimore). 100:e269582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xue M, Wu Y, Zhu B, Zou X, Fan W and Li J:
Advanced hepatocellular carcinoma treated by transcatheter arterial
chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads plus lenvatinib versus
sorafenib, a propensity score matching retrospective study. Am J
Cancer Res. 11:6107–6118. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Matsuki M, Hoshi T, Yamamoto Y,
Ikemori-Kawada M, Minoshima Y, Funahashi Y and Matsui J: Lenvatinib
inhibits angiogenesis and tumor fibroblast growth factor signaling
pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma models. Cancer Med.
7:2641–2653. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yamamoto Y, Matsui J, Matsushima T,
Obaishi H, Miyazaki K, Nakamura K, Tohyama O, Semba T, Yamaguchi A,
Hoshi SS, et al: Lenvatinib, an angiogenesis inhibitor targeting
VEGFR/FGFR, shows broad antitumor activity in human tumor xenograft
models associated with microvessel density and pericyte coverage.
Vasc Cell. 6:182014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hoshi T, Watanabe Miyano S, Watanabe H,
Sonobe RMK, Seki Y, Ohta E, Nomoto K, Matsui J and Funahashi Y:
Lenvatinib induces death of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
harboring an activated FGF signaling pathway through inhibition of
FGFR-MAPK cascades. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 513:1–7. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
He X, Hikiba Y, Suzuki Y, Nakamori Y,
Kanemaru Y, Sugimori M, Sato T, Nozaki A, Chuma M and Maeda S: EGFR
inhibition reverses resistance to lenvatinib in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Sci Rep. 12:80072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Romei C, Ciampi R and Elisei R: A
comprehensive overview of the role of the RET proto-oncogene in
thyroid carcinoma. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 12:192–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim JY, Sinn DH, Gwak GY, Choi GS, Saleh
AM, Joh JW, Cho SK, Shin SW, Carriere KC, Ahn JH, et al:
Transarterial chemoembolization versus resection for
intermediate-stage (BCLC B) hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol
Hepatol. 22:250–258. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kudo M: A new treatment option for
intermediate-stage hepatocellular carcinoma with high tumor Burden:
Initial lenvatinib therapy with subsequent selective TACE. Liver
Cancer. 8:299–311. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Arizumi T, Minami T, Chishina H, Kono M,
Takita M, Yada N, Hagiwara S, Minami Y, Ida H, Ueshima K, et al:
Impact of tumor factors on survival in patients with hepatocellular
carcinoma classified based on kinki criteria stage B2. Dig Dis.
35:583–588. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang Z, Wu Y, Zheng T, Chen X, Chen G,
Chen H, Guo X, Zheng S, Xie X and Zhang B: Efficacy of
transarterial chemoembolization combined with molecular targeted
agents for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A network
meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). 14:37102022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hu HT, Kim JH, Lee LS, Kim KA, Ko GY, Yoon
HK, Sung KB, Gwon DI, Shin JH and Song HY: Chemoembolization for
hepatocellular carcinoma: Multivariate analysis of predicting
factors for tumor response and survival in a 362-patient cohort. J
Vasc Interv Radiol. 22:917–923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Takayasu K, Arii S, Ikai I, Omata M, Okita
K, Ichida T, Matsuyama Y, Nakanuma Y, Kojiro M, Makuuchi M, et al:
Prospective cohort study of transarterial chemoembolization for
unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in 8510 patients.
Gastroenterology. 131:461–469. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Miyayama S, Kikuchi Y, Yoshida M,
Yamashiro M, Sugimori N, Ikeda R, Okimura K, Sakuragawa N, Ueda T,
Sanada T, et al: Outcomes of conventional transarterial
chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma ≥10 cm. Hepatol Res.
49:787–798. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mosconi C, Gramenzi A, Biselli M, Cappelli
A, Bruno A, De Benedittis C, Cucchetti A, Modestino F, Peta G,
Bianchi G, et al: Survival and Tolerability of Transarterial
Chemoembolization in Greater Versus less than 70 Years of Age
Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Propensity
Score Analysis. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 43:1015–1024. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Di Costanzo GG, Tortora R, De Luca M,
Galeota Lanza A, Lampasi F, Tartaglione MT, Picciotto FP, Imparato
M, Mattera S, Cordone G and Ascione A: Impact of age on toxicity
and efficacy of sorafenib-targeted therapy in cirrhotic patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma. Med Oncol. 30:4462013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Abou-Alfa GK, Meyer T, Cheng AL,
El-Khoueiry AB, Rimassa L, Ryoo BY, Cicin I, Merle P, Chen Y, Park
JW, et al: Cabozantinib in patients with advanced and progressing
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 379:54–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang
YH, Bodoky G, Pracht M, Yokosuka O, Rosmorduc O, Breder V, et al:
Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who
progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 389:56–66.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang X, El-Serag HB and Thrift AP: Sex
and race disparities in the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma
in the united states examined through age-period-cohort analysis.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 29:88–94. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhang JX, Chen YX, Zhou CG, Liu J, Liu S,
Shi HB and Zu QQ: Transarterial chemoembolization combined with
lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization combined with
sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A comparative
retrospective study. Hepatol Res. 52:794–803. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang B, Jie L, Yang T, Chen M, Gao Y,
Zhang T, Zhang Y, Wu H and Liao Z: TACE plus lenvatinib versus TACE
plus sorafenib for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma with
portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective cohort study. Front
Oncol. 11:8215992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ding X, Sun W, Li W, Shen Y, Guo X, Teng
Y, Liu X, Zheng L, Li W and Chen J: Transarterial chemoembolization
plus lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization plus
sorafenib as first-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with
portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective randomized study. Cancer.
127:3782–3793. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|