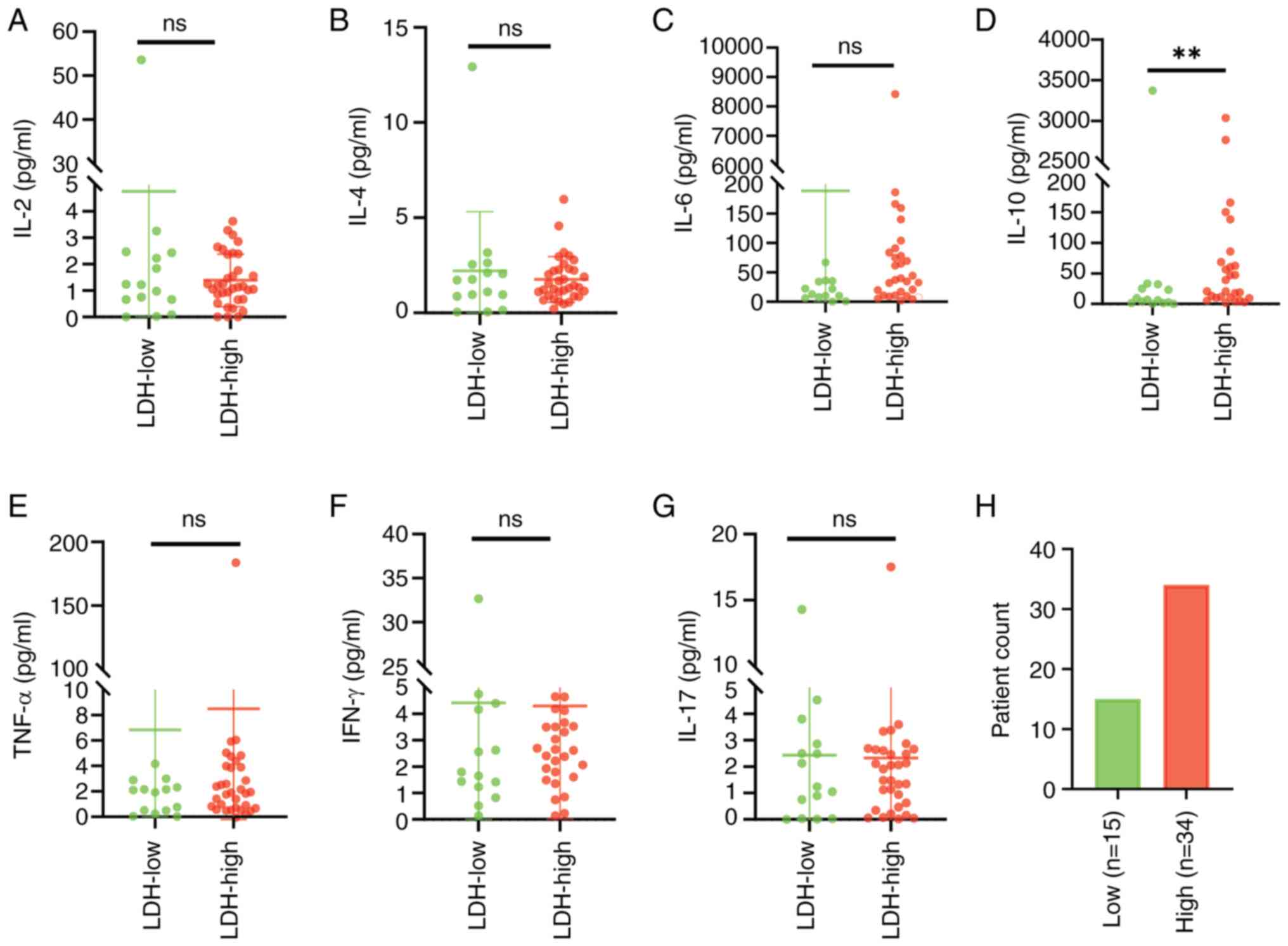
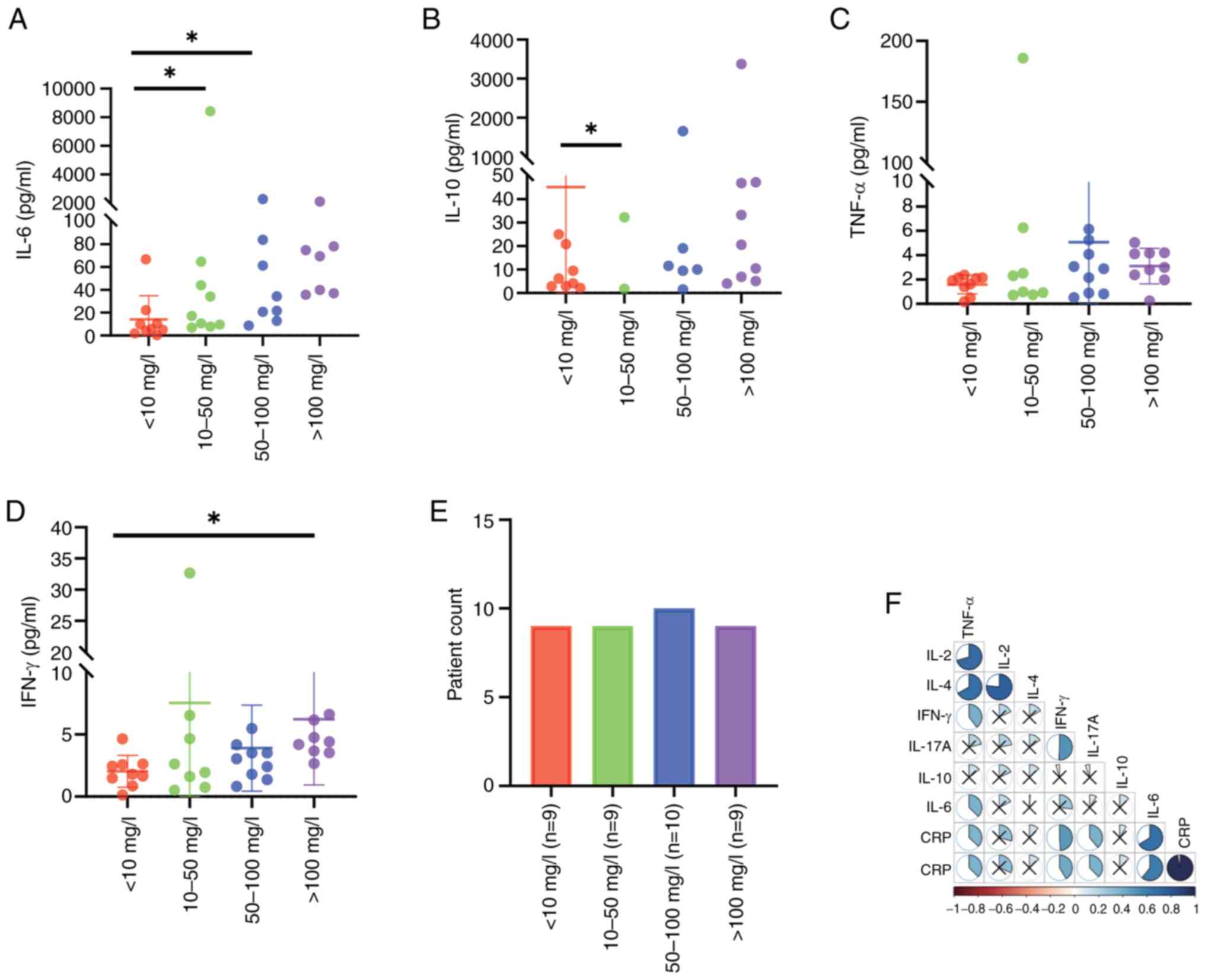
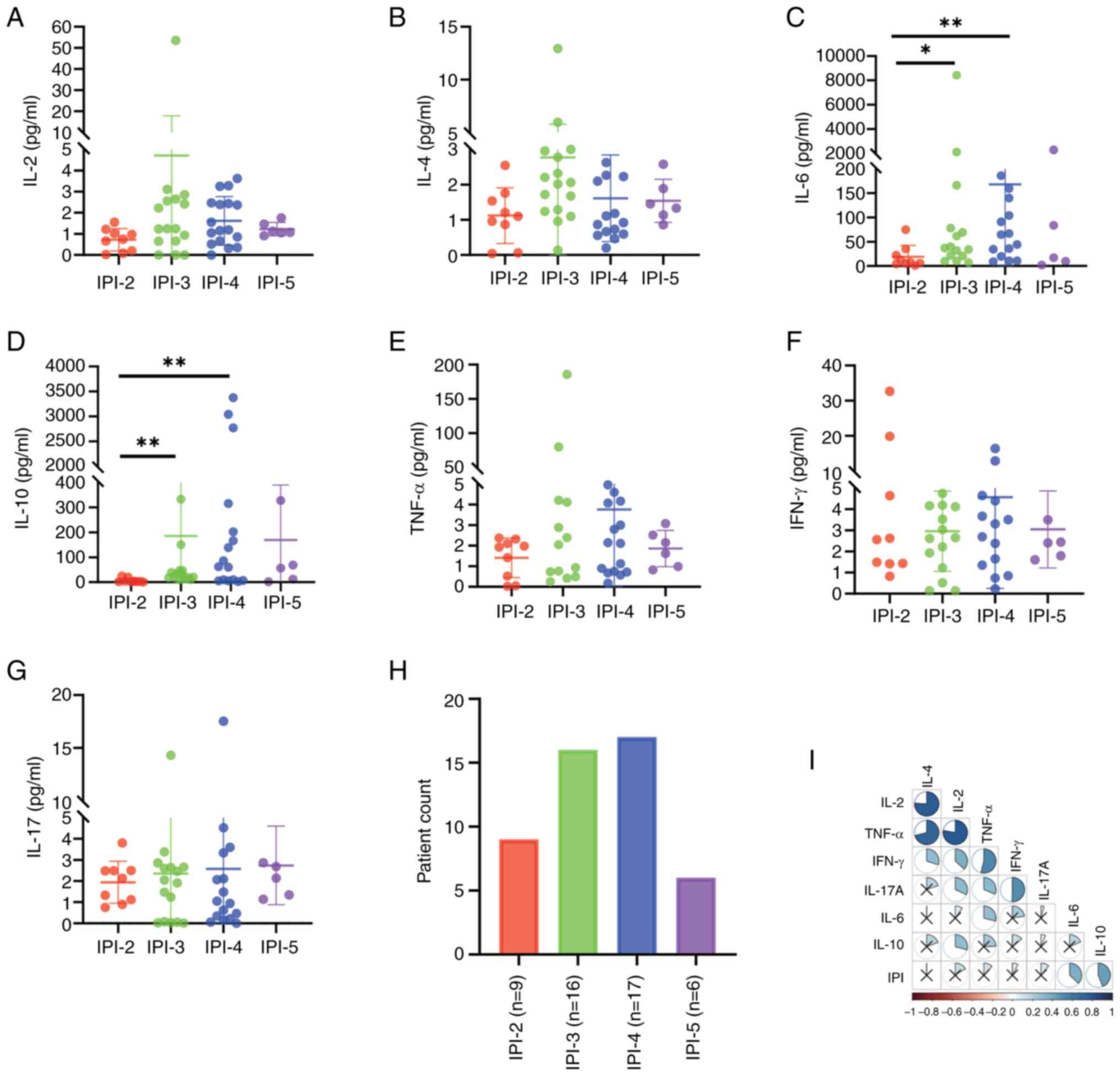
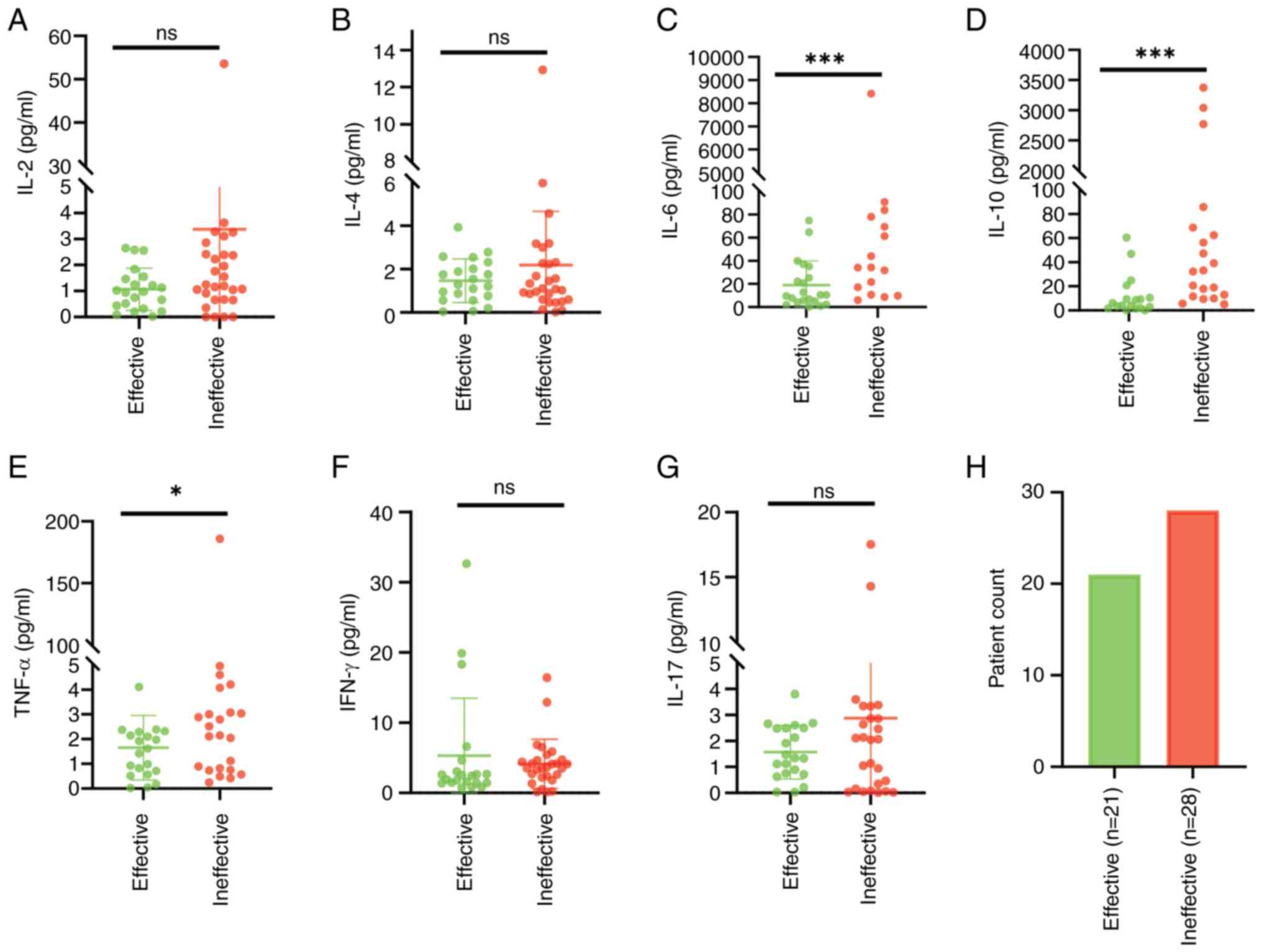
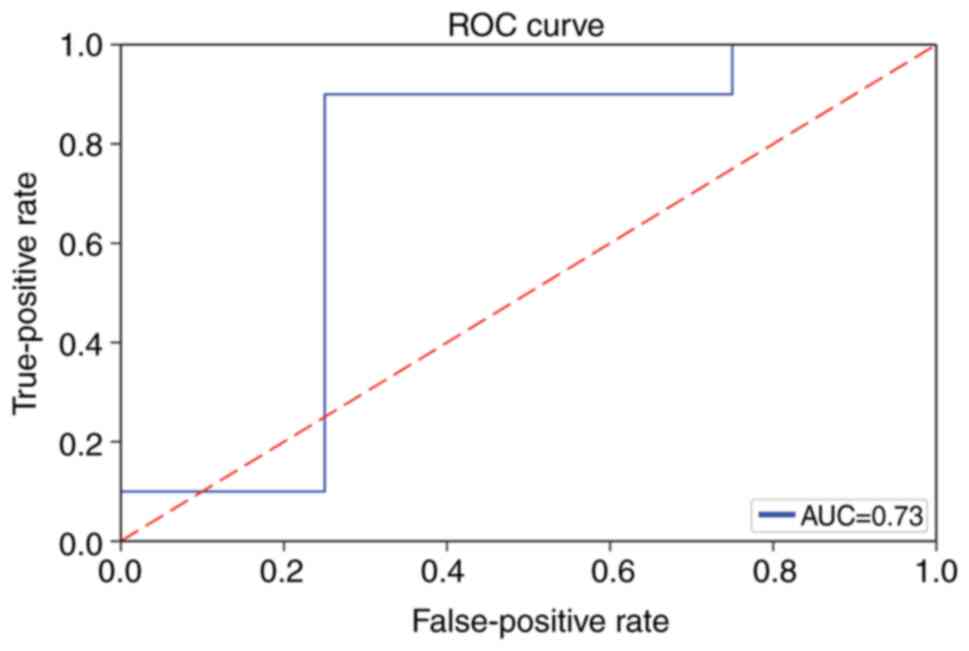
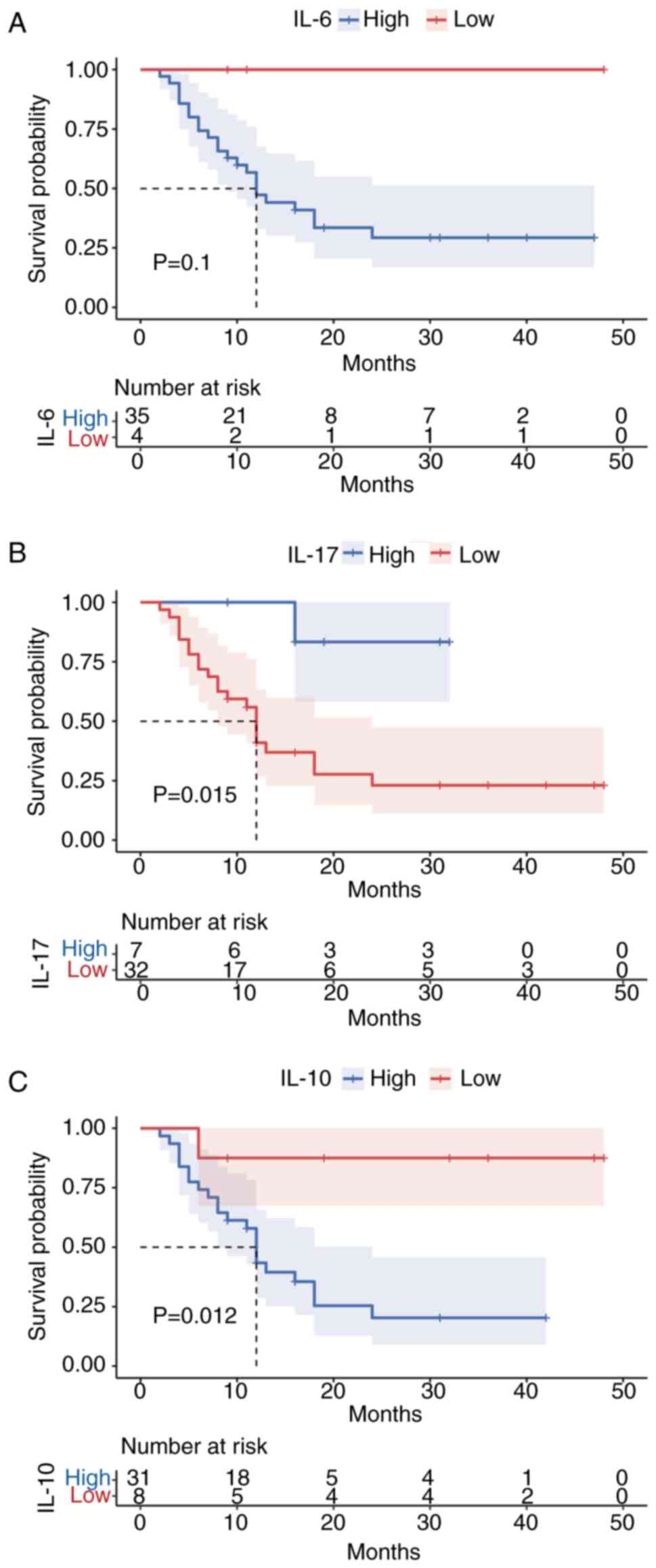
|
1
|
Tout M, Casasnovas O, Meignan M, Lamy T,
Morschhauser F, Salles G, Gyan E, Haioun C, Mercier M, Feugier P,
et al: Rituximab exposure is influenced by baseline metabolic tumor
volume and predicts outcome of DLBCL patients: A lymphoma study
association report. Blood. 129:2616–2623. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tárnok A, Hambsch J, Chen R and Varro R:
Cytometric bead array to measure six cytokines in twenty-five
microliters of serum. Clin Chem. 49:1000–1002. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Malaponte G, Hafsi S, Polesel J,
Castellano G, Spessotto P, Guarneri C, Canevari S, Signorelli SS,
McCubrey JA and Libra M: Tumor microenvironment in diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma: Matrixmetalloproteinases activation is mediated by
osteopontin overexpression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1863:483–489.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lim SH, Woo SY, Kim S, Ko YH, Kim WS and
Kim SJ: Cross-sectional Study of Patients with Diffuse Large B-Cell
Lymphoma: Assessing the effect of host status, tumor burden, and
inflammatory activity on venous thromboembolism. Cancer Res Treat.
48:312–321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Falduto A, Cimino F, Speciale A, Musolino
C, Gangemi S, Saija A and Allegra A: How gene polymorphisms can
influence clinical response and toxicity following R-CHOP therapy
in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Blood Rev.
31:235–249. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou Z, Sehn LH, Rademaker AW, Gordon LI,
Lacasce AS, Crosby-Thompson A, Vanderplas A, Zelenetz AD, Abel GA,
Rodriguez MA, et al: An enhanced International Prognostic Index
(NCCN-IPI) for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated
in the rituximab era. Blood. 123:837–842. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dlouhy I, Filella X, Rovira J, Magnano L,
Rivas-Delgado A, Baumann T, Martínez-Trillos A, Balagué O, Martínez
A, González-Farre B, et al: High serum levels of soluble
interleukin-2 receptor (sIL2-R), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor
necrosis factor alpha (TNF) are associated with adverse clinical
features and predict poor outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Leuk Res. 59:20–25. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhong W, Xu X, Zhu Z, Du Q, Du H, Yang L,
Ling Y, Xiong H and Li Q: Increased expression of IRF8 in tumor
cells inhibits the generation of Th17 cells and predicts
unfavorable survival of diffuse large B cell lymphoma patients.
Oncotarget. 8:49757–49772. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hashwah H, Bertram K, Stirm K, Stelling A,
Wu CT, Kasser S, Manz MG, Theocharides AP, Tzankov A and Müller A:
The IL-6 signaling complex is a critical driver, negative
prognostic factor, and therapeutic target in diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma. EMBO Mol Med. 11:e105762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheson BD, Fisher RI, Barrington SF,
Cavalli F, Schwartz LH, Zucca E, Lister TA; Alliance, Australasian
and Leukaemia Lymphoma Group; Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group, ;
et al: Recommendations for initial evaluation, staging, and
response assessment of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The Lugano
classification. J Clin Oncol. 32:3059–3068. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ruppert AS, Dixon JG, Salles G, Wall A,
Cunningham D, Poeschel V, Haioun C, Tilly H, Ghesquieres H, Ziepert
M, et al: International prognostic indices in diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma: A comparison of IPI, R-IPI, and NCCN-IPI. Blood.
135:2041–2048. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zelenetz AD, Gordon LI, Abramson JS,
Advani RH, Bartlett NL, Caimi PF, Chang JE, Chavez JC, Christian B,
Fayad LE, et al: NCCN Guidelines Insights: B-Cell Lymphomas,
Version 3.2019. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 17:650–661. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhao S, Dong X, Shen W, Ye Z and Xiang R:
Machine learning-based classification of diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma patients by eight gene expression profiles. Cancer Med.
5:837–852. 2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen H, Zhang J, Sun X, Wang Y and Qian Y:
Mitophagy-mediated molecular subtypes depict the hallmarks of the
tumour metabolism and guide precision chemotherapy in pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:9012072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Martelli M, Ferreri AJ, Agostinelli C, Di
Rocco A, Pfreundschuh M and Pileri SA: Diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 87:146–171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nagai H, Miyaki D, Matsui T, Kanayama M,
Higami K, Momiyama K, Ikehara T, Watanabe M, Sumino Y and Miki K:
Th1/Th2 balance: An important indicator of efficacy for
intra-arterial chemotherapy. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
62:959–963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng X, Shi J, Sun W, Ruan X, Guo Y, Zhao
L, Wang J and Li B: Genetic polymorphisms of IL-6 promoter in
cancer susceptibility and prognosis: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget.
9:12351–12364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Narazaki M, Tanaka T and Kishimoto T: The
role and therapeutic targeting of IL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis.
Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 13:535–551. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xiu B, Lin Y, Grote DM, Ziesmer SC,
Gustafson MP, Maas ML, Zhang Z, Dietz AB, Porrata LF, Novak AJ, et
al: IL-10 induces the development of immunosuppressive
CD14(+)HLA-DR(low/-) monocytes in B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
Blood Cancer J. 5:e3282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Purdue MP, Lan Q, Kricker A, Grulich AE,
Vajdic CM, Turner J, Whitby D, Chanock S, Rothman N and Armstrong
BK: Polymorphisms in immune function genes and risk of non-Hodgkin
lymphoma: Findings from the New South Wales non-Hodgkin Lymphoma
Study. Carcinogenesis. 28:704–712. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park YH, Sohn SK, Kim JG, Lee MH, Song HS,
Kim MK, Jung JS, Lee JJ, Kim HJ and Kim DH: Interaction between
BCL2 and interleukin-10 gene polymorphisms alter outcomes of
diffuse large B-cell lymphoma following rituximab plus CHOP
chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2107–2115. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nakamura N, Goto N, Tsurumi H, Takemura M,
Kanemura N, Kasahara S, Hara T, Yasuda I, Shimizu M, Sawada M, et
al: Serum level of soluble tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 is
associated with the outcome of patients with diffuse large B-cell
lymphoma treated with the R-CHOP regimen. Eur J Haematol.
91:322–331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nakayama S, Yokote T, Hirata Y, Akioka T,
Miyoshi T, Hiraoka N, Iwaki K, Takayama A, Nishiwaki U, Masuda Y,
et al: TNF-α expression in tumor cells as a novel prognostic marker
for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified. Am J
Surg Pathol. 38:228–234. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cruceriu D, Baldasici O, Balacescu O and
Berindan-Neagoe I: The dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha
(TNF-α) in breast cancer: Molecular insights and therapeutic
approaches. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 43:1–8. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qu Y, Wang X, Bai S, Niu L, Zhao G, Yao Y,
Li B and Li H: The effects of TNF-α/TNFR2 in regulatory T cells on
the microenvironment and progression of gastric cancer. Int J
Cancer. 150:1373–1391. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Camicia R, Bachmann SB, Winkler HC, Beer
M, Tinguely M, Haralambieva E and Hassa PO: BAL1/ARTD9 represses
the anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic IFNү-STAT1-IRF1-p53 axis
in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Cell Sci. 126((Pt 9)):
1969–1980. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ,
Locksley RM and Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an
inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of
IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 24:179–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fayad L, Keating MJ, Reuben JM, O'Brien S,
Lee BN, Lerner S and Kurzrock R: Interleukin-6 and interleukin-10
levels in chronic lymphocytic leukemia: Correlation with phenotypic
characteristics and outcome. Blood. 97:256–263. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nacinovic-Duletic A, Stifter S, Dvornik S,
Skunca Z and Jonjic N: Correlation of serum IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10
levels with clinicopathological features and prognosis in patients
with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Int J Lab Hematol. 30:230–239.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aydin F, Yilmaz M, Ozdemir F, Kavgaci H,
Yavuz MN and Yavuz AA: Correlation of serum IL-2, IL-6 and IL-10
levels with International Prognostic Index in patients with
aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Am J Clin Oncol. 25:570–572.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guney N, Soydinc HO, Basaran M, Bavbek S,
Derin D, Camlica H, Yasasever V and Topuz E: Serum levels of
interleukin-6 and interleukin-10 in Turkish patients with
aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
10:669–674. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Niitsu N, Okamato M, Nakamine H, Yoshino
T, Tamaru J, Nakamura S, Higashihara M and Hirano M: Simultaneous
elevation of the serum concentrations of vascular endothelial
growth factor and interleukin-6 as independent predictors of
prognosis in aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Eur J Haematol.
68:912002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cortes J and Kurzrock R: Interleukin-10 in
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma. 26:251–259. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
D'Mello KP, Zhao L, Kaser EC, Zhu Z, Xiao
H, Wakefield MR, Bai Q and Fang Y: The role of interleukins and the
widely studied TNF-α in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Med Oncol.
38:562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Uskudar Teke H, Gunduz E, Akay OM, Bal C
and Gulbas Z: Are the high serum interleukin-6 and vascular
endothelial growth factor levels useful prognostic markers in
aggressive non-hodgkin lymphoma patients? Turk J Haematol.
32:21–28. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|