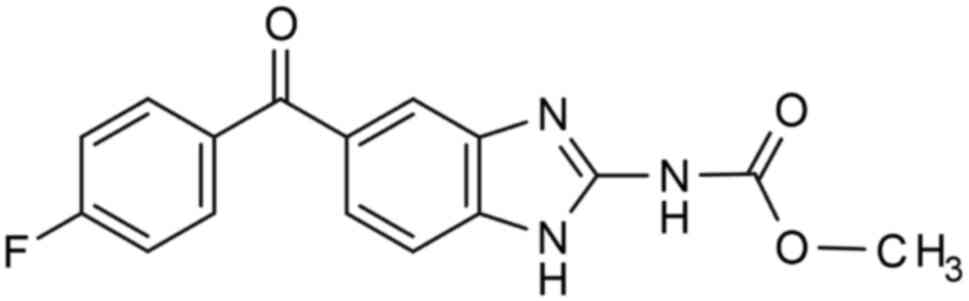
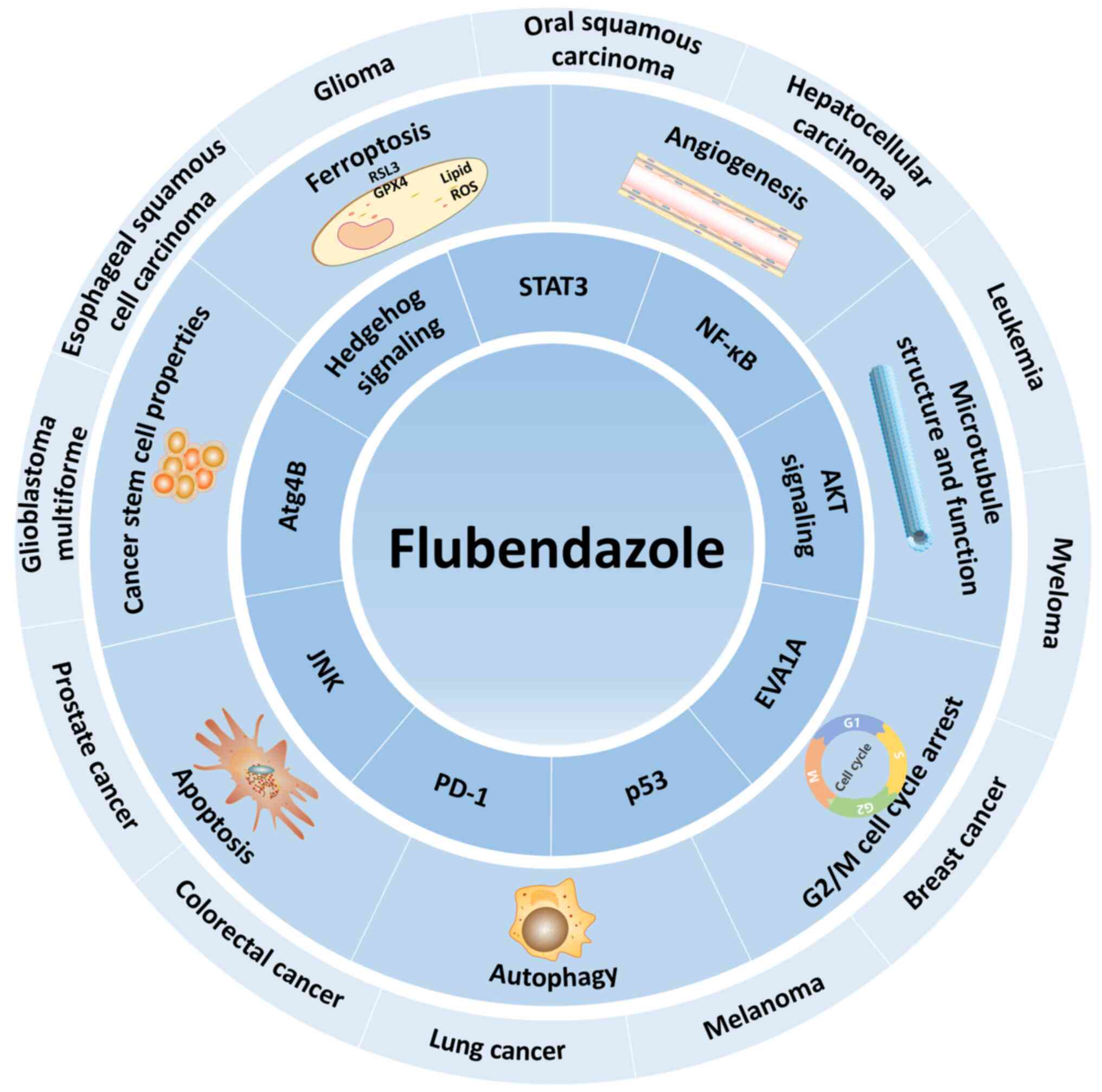
|
1
|
Čáňová K, Rozkydalová L and Rudolf E:
Anthelmintic flubendazole and its potential use in anticancer
therapy. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 60:5–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friedman PA and Platzer EG: Interaction of
anthelmintic benzimidazoles with Ascaris suum embryonic tubulin.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 630:271–278. 1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lacey E: Mode of action of benzimidazoles.
Parasitol Today. 6:112–115. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Venugopal S, Kaur B, Verma A, Wadhwa P,
Magan M, Hudda S and Kakoty V: Recent advances of benzimidazole as
anticancer agents. Chem Biol Drug Des. 102:357–376. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Michiels M, Hendriks R, Heykants J and van
den Bossche H: The pharmacokinetics of mebendazole and flubendazole
in animals and man. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 256:180–191.
1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bossche HV, Thienpont D and Janssens PG:
Chemotherapy of Gastrointestinal Helminths. Springer; Berlin: pp.
p7191985
|
|
7
|
Nath J, Paul R, Ghosh SK, Paul J, Singha B
and Debnath N: Drug repurposing and relabeling for cancer therapy:
Emerging benzimidazole antihelminthics with potent anticancer
effects. Life Sci. 258:1181892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tweats DJ, Johnson GE, Scandale I,
Whitwell J and Evans DB: Genotoxicity of flubendazole and its
metabolites in vitro and the impact of a new formulation on in vivo
aneugenicity. Mutagenesis. 31:309–321. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim J, Bang J, Ryu B, Kim CY and Park JH:
Flubendazole exposure disrupts neural development and function of
zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio). Sci Total Environ. 898:1653762023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moreno L, Alvarez L, Mottier L, Virkel G,
Bruni SS and Lanusse C: Integrated pharmacological assessment of
flubendazole potential for use in sheep: Disposition kinetics,
liver metabolism and parasite diffusion ability. J Vet Pharmacol
Ther. 27:299–308. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Krízová V, Nobilis M, Prusková L, Chládek
J, Szotáková B, Cvilink V, Skálová L and Lamka J: Pharmacokinetics
of flubendazole and its metabolites in lambs and adult sheep (Ovis
aries). J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 32:606–612. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen C, Ding Y, Liu H, Sun M, Wang H and
Wu D: Flubendazole plays an important anti-tumor role in different
types of cancers. Int J Mol Sci. 23:5192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Spagnuolo PA, Hu J, Hurren R, Wang X,
Gronda M, Sukhai MA, Di Meo A, Boss J, Ashali I, Beheshti Zavareh
R, et al: The antihelmintic flubendazole inhibits microtubule
function through a mechanism distinct from Vinca alkaloids and
displays preclinical activity in leukemia and myeloma. Blood.
115:4824–4833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Michaelis M, Agha B, Rothweiler F,
Löschmann N, Voges Y, Mittelbronn M, Starzetz T, Harter PN, Abhari
BA, Fulda S, et al: Identification of flubendazole as potential
anti-neuroblastoma compound in a large cell line screen. Sci Rep.
5:82022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Son DS, Lee ES and Adunyah SE: The
antitumor potentials of benzimidazole anthelmintics as repurposing
drugs. Immune Netw. 20:e292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schipper LJ, Zeverijn LJ, Garnett MJ and
Voest EE: Can Drug repurposing accelerate precision oncology?
Cancer Discov. 12:1634–1641. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hijazi MA, Gessner A and El-Najjar N:
Repurposing of chronically used drugs in cancer therapy: A chance
to grasp. Cancers (Basel). 15:31992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kawczak P, Feszak I, Brzeziński P and
Bączek T: Structure-activity relationships and therapeutic
applications of retinoids in view of potential benefits from drug
repurposing process. Biomedicines. 12:10592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fletcher DA and Mullins RD: Cell mechanics
and the cytoskeleton. Nature. 463:485–492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gudimchuk NB and McIntosh JR: Regulation
of microtubule dynamics, mechanics and function through the growing
tip. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 22:777–795. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jordan MA and Wilson L: Microtubules as a
target for anticancer drugs. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:253–265. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kralova V, Hanušová V, Caltová K, Špaček
P, Hochmalová M, Skálová L and Rudolf E: Flubendazole and
mebendazole impair migration and epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in oral cell lines. Chem Biol Interact. 293:124–132.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hou ZJ, Luo X, Zhang W, Peng F, Cui B, Wu
SJ, Zheng FM, Xu J, Xu LZ, Long ZJ, et al: Flubendazole,
FDA-approved anthelmintic, targets breast cancer stem-like cells.
Oncotarget. 6:6326–6340. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Králová V, Hanušová V, Rudolf E, Čáňová K
and Skálová L: Flubendazole induces mitotic catastrophe and
senescence in colon cancer cells in vitro. J Pharm Pharmacol.
68:208–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Čáňová K, Rozkydalová L, Vokurková D and
Rudolf E: Flubendazole induces mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis in
melanoma cells. Toxicol In Vitro. 46:313–322. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oh E, Kim YJ, An H, Sung D, Cho TM,
Farrand L, Jang S, Seo JH and Kim JY: Flubendazole elicits
anti-metastatic effects in triple-negative breast cancer via STAT3
inhibition. Int J Cancer. 143:1978–1993. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jamasbi E, Hamelian M, Hossain MA and
Varmira K: The cell cycle, cancer development and therapy. Mol Biol
Rep. 49:10875–10883. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rieder CL and Cole R: Microtubule
disassembly delays the G2-M transition in vertebrates. Curr Biol.
10:1067–1070. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim YJ, Sung D, Oh E, Cho Y, Cho TM,
Farrand L, Seo JH and Kim JY: Flubendazole overcomes trastuzumab
resistance by targeting cancer stem-like properties and HER2
signaling in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 412:118–130.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou X, Zou L, Chen W, Yang T, Luo J, Wu
K, Shu F, Tan X, Yang Y, Cen S, et al: Flubendazole, FDA-approved
anthelmintic, elicits valid antitumor effects by targeting P53 and
promoting ferroptosis in castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Pharmacol Res. 164:1053052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rudolf K and Rudolf E: An analysis of
mitotic catastrophe induced cell responses in melanoma cells
exposed to flubendazole. Toxicol In Vitro. 68:1049302020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Králová V, Hanušová V, Staňková P,
Knoppová K, Čáňová K and Skálová L: Antiproliferative effect of
benzimidazole anthelmintics albendazole, ricobendazole, and
flubendazole in intestinal cancer cell lines. Anticancer Drugs.
24:911–919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhou X, Liu J, Zhang J, Wei Y and Li H:
Flubendazole inhibits glioma proliferation by G2/M cell cycle
arrest and pro-apoptosis. Cell Death Discov. 4:182018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ren LW, Li W, Zheng XJ, Liu JY, Yang YH,
Li S, Zhang S, Fu WQ, Xiao B, Wang JH and Du GH: Benzimidazoles
induce concurrent apoptosis and pyroptosis of human glioblastoma
cells via arresting cell cycle. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 43:194–208.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Jin W, Yu J, Su Y, Lin H, Liu T, Chen J,
Ge C, Zhao F, Geng Q, Mao L, et al: Drug repurposing flubendazole
to suppress tumorigenicity via PCSK9-dependent inhibition and
potentiate lenvatinib therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Biol Sci. 19:2270–2288. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Glick D, Barth S and Macleod KF:
Autophagy: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Pathol. 221:3–12.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Debnath J, Gammoh N and Ryan KM: Autophagy
and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
24:560–575. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mizushima N, Noda T, Yoshimori T, Tanaka
Y, Ishii T, George MD, Klionsky DJ, Ohsumi M and Ohsumi Y: A
protein conjugation system essential for autophagy. Nature.
395:395–398. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin S, Yang L, Yao Y, Xu L, Xiang Y, Zhao
H, Wang L, Zuo Z, Huang X and Zhao C: Flubendazole demonstrates
valid antitumor effects by inhibiting STAT3 and activating
autophagy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xie X, Cai X, Tang Y, Jiang C, Zhou F,
Yang L, Liu Z, Wang L, Zhao H, Zhao C and Huang X: Flubendazole
elicits antitumor effects by inhibiting STAT3 and activating
autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6806002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhen Y, Zhao R, Wang M, Jiang X, Gao F, Fu
L, Zhang L and Zhou XL: Flubendazole elicits anti-cancer effects
via targeting EVA1A-modulated autophagy and apoptosis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Theranostics. 10:8080–8097. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhen Y, Yuan Z, Zhang J, Chen Y, Fu Y, Liu
Y, Fu L, Zhang L and Zhou XL: Flubendazole induces mitochondrial
dysfunction and DRP1-mediated mitophagy by targeting EVA1A in
breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 13:3752022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Carneiro BA and El-Deiry WS: Targeting
apoptosis in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:395–417. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen C, Liu J, Lin X, Xiang A, Ye Q, Guo
J, Rui T, Xu J and Hu S: Crosstalk between cancer-associated
fibroblasts and regulated cell death in tumors: Insights into
apoptosis, autophagy, ferroptosis, and pyroptosis. Cell Death
Discov. 10:1892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang B, Yan X and Li Y: Cancer stem cell
for tumor therapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:48142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Borlongan MC, Saha D and Wang H: Tumor
microenvironment: A niche for cancer stem cell immunotherapy. Stem
Cell Rev Rep. 20:3–24. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Conde I, Ribeiro AS and Paredes J: Breast
cancer stem cell membrane biomarkers: Therapy targeting and
clinical implications. Cells. 11:9342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jiang X, Stockwell BR and Conrad M:
Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 22:266–282. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang D:
Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 18:280–296. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Wang S, Guo Q, Zhou L and Xia X:
Ferroptosis: A double-edged sword. Cell Death Discov. 10:2652024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li Y, Acharya G, Elahy M, Xin H and
Khachigian LM: The anthelmintic flubendazole blocks human melanoma
growth and metastasis and suppresses programmed cell death
protein-1 and myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation. Cancer
Lett. 459:268–276. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee H, Jeong AJ and Ye SK: Highlighted
STAT3 as a potential drug target for cancer therapy. BMB Rep.
52:415–423. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Parri E, Kuusanmaki H, van Adrichem AJ,
Kaustio M and Wennerberg K: Identification of novel regulators of
STAT3 activity. PLoS One. 15:e02308192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Carpenter RL and Lo HW: STAT3 target genes
relevant to human cancers. Cancers (Basel). 6:897–925. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tolomeo M and Cascio A: The multifaced
Role of STAT3 in cancer and its implication for anticancer therapy.
Int J Mol Sci. 22:6032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang HF and Lai R: STAT3 in cancer-friend
or foe? Cancers (Basel). 6:1408–1440. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yu H, Lin L, Zhang Z, Zhang H and Hu H:
Targeting NF-κB pathway for the therapy of diseases: Mechanism and
clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:2092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Taniguchi K and Karin M: NF-κB,
inflammation, immunity and cancer: Coming of age. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:309–324. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mirzaei S, Saghari S, Bassiri F, Raesi R,
Zarrabi A, Hushmandi K, Sethi G and Tergaonkar V: NF-κB as a
regulator of cancer metastasis and therapy response: A focus on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Physiol. 237:2770–2795.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hanušová V, Skálová L, Králová V and
Matoušková P: The effect of flubendazole on adhesion and migration
in SW480 and SW620 colon cancer cells. Anticancer Agents Med Chem.
18:837–846. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tao J, Zhao H, Xie X, Luo M, Gao Z, Sun H
and Huang Z: The anthelmintic drug flubendazole induces cell
apoptosis and inhibits NF-κB signaling in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 12:471–478. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Glaviano A, Foo ASC, Lam HY, Yap KCH,
Jacot W, Jones RH, Eng H, Nair MG, Makvandi P, Geoerger B, et al:
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling transduction pathway and targeted therapies
in cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sabbah DA, Hajjo R, Bardaweel SK and Zhong
HA: Targeting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in anticancer
research: A recent update on inhibitor design and clinical trials
(2020–2023). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 34:141–158. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cocco S, Leone A, Roca MS, Lombardi R,
Piezzo M, Caputo R, Ciardiello C, Costantini S, Bruzzese F, Sisalli
MJ, et al: Inhibition of autophagy by chloroquine prevents
resistance to PI3K/AKT inhibitors and potentiates their antitumor
effect in combination with paclitaxel in triple negative breast
cancer models. J Transl Med. 20:2902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Kierans SJ and Taylor CT: Regulation of
glycolysis by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF): Implications for
cellular physiology. J Physiol. 599:23–37. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Zhou Y, Liao M, Li Z, Ye J, Wu L, Mou Y,
Fu L and Zhen Y: Flubendazole enhances the inhibitory effect of
paclitaxel via HIF1α/PI3K/AKT signaling pathways in breast cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:151212023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li Y, Wu B, Hossain MJ, Quagliata L,
O'Meara C, Wilkins MR, Corley S and Khachigian LM: Flubendazole
inhibits PD-1 and suppresses melanoma growth in immunocompetent
mice. J Transl Med. 21:4672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhao H, Liu H, Yang Y and Wang H: The
emerging role of EVA1A in different types of cancers. Int J Mol
Sci. 23:66652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu Y, Su Z, Tavana O and Gu W:
Understanding the complexity of p53 in a new era of tumor
suppression. Cancer Cell. 42:946–967. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tang Q, Chen Y, Li X, Long S, Shi Y, Yu Y,
Wu W, Han L and Wang S: The role of PD-1/PD-L1 and application of
immune-checkpoint inhibitors in human cancers. Front Immunol.
13:9644422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Yi M, Zheng X, Niu M, Zhu S, Ge H and Wu
K: Combination strategies with PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Current
advances and future directions. Mol Cancer. 21:282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wu Q, Wu W, Fu B, Shi L, Wang X and Kuca
K: JNK signaling in cancer cell survival. Med Res Rev.
39:2082–2104. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Abdelrahman KS, Hassan HA, Abdel-Aziz SA,
Marzouk AA, Narumi A, Konno H and Abdel-Aziz M: JNK signaling as a
target for anticancer therapy. Pharmacol Rep. 73:405–434. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yang G, Li Y, Zhao Y, Ouyang L, Chen Y,
Liu B and Liu J: Targeting Atg4B for cancer therapy: Chemical
mediators. Eur J Med Chem. 209:1129172021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Park NY, Jo DS and Cho DH:
Post-translational modifications of ATG4B in the regulation of
autophagy. Cells. 11:13302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang L, Guo M, Li J, Zheng Y, Zhang S,
Xie T and Liu B: Systems biology-based discovery of a potential
Atg4B agonist (Flubendazole) that induces autophagy in breast
cancer. Mol Biosyst. 11:2860–2866. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Jing J, Wu Z, Wang J, Luo G, Lin H, Fan Y
and Zhou C: Hedgehog signaling in tissue homeostasis, cancers, and
targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3152023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jiang J: Hedgehog signaling mechanism and
role in cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 85:107–122. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Aslani S and Saad MI: Patient-derived
xenograft models in cancer research: Methodology, applications, and
future prospects. Methods Mol Biol. 2806:9–18. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yan HHN, Chan AS, Lai FPL and Leung SY:
Organoid cultures for cancer modeling. Cell Stem Cell. 30:917–937.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Huang W, Xu Z, Li S, Zhou J and Zhao B:
Living biobanks of organoids: Valuable resource for translational
research. Biopreserv Biobank. Jul 3–2024.(Epub ahead of print).
doi: 10.1089/bio.2023.0142. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Cao J, Chan WC and Chow MSS: Use of
conditional reprogramming cell, patient derived xenograft and
organoid for drug screening for individualized prostate cancer
therapy: Current and future perspectives (review). Int J Oncol.
60:522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Liu W, Ju L, Cheng S, Wang G, Qian K, Liu
X, Xiao Y and Wang X: Conditional reprogramming: Modeling
urological cancer and translation to clinics. Clin Transl Med.
10:e952020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
McKellar QA, Galbraith EA and Baxter P:
Oral absorption and bioavailability of fenbendazole in the dog and
the effect of concurrent ingestion of food. J Vet Pharmacol Ther.
16:189–198. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Yukuyama MN, Guimaraes LMF, Segovia RS,
Lameu C, de Araujo GLB, Löbenberg R, de Souza A, Henostroza MAB,
Folchini BR, Peroni CM, et al: Malignant wound-the influence of oil
components in flubendazole-loaded nanoemulsions in A549 lung cancer
xenograft-bearing mice. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol. 78:1039632022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
de Souza Gonçalves D, Yukuyama MN, Saito
Miyagi MY, Vieira Silva TJ, Lameu C, Bou-Chacra NA and de Araujo
GLB: Revisiting flubendazole through nanocrystal technology:
Statistical design, characterization and its potential inhibitory
effect on xenografted lung tumor progression in mice. J Clust Sci.
34:261–272. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Yukuyama MN, Zuo J, Park C, Yousef M,
Henostroza MAB, de Araujo GLB, Bou-Chacra NA and Löbenberg R:
Biphasic dissolution combined with modified cylinder method-a new
promising method for dissolution test in drug-loaded nanoemulsions.
Int J Pharm. 632:1225542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kosmidis C, Sapalidis K, Zarogoulidis P,
Sardeli C, Koulouris C, Giannakidis D, Pavlidis E, Katsaounis A,
Michalopoulos N, Mantalobas S, et al: Inhaled cisplatin for NSCLC:
Facts and results. Int J Mol Sci. 20:20052019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Miyagi MYS, de Oliveira Faria R, de Souza
GB, Lameu C, Tagami T, Ozeki T, Bezzon VDN, Yukuyama MN, Bou-Chacra
NA and de Araujo GLB: Optimizing adjuvant inhaled chemotherapy:
Synergistic enhancement in paclitaxel cytotoxicity by flubendazole
nanocrystals in a cycle model approach. Int J Pharm.
644:1233242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Holzbeierlein JM, Bixler BR, Buckley DI,
Chang SS, Holmes R, James AC, Kirkby E, McKiernan JM and Schuckman
AK: Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer:
AUA/SUO guideline: 2024 Amendment. J Urol. 211:533–538. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|