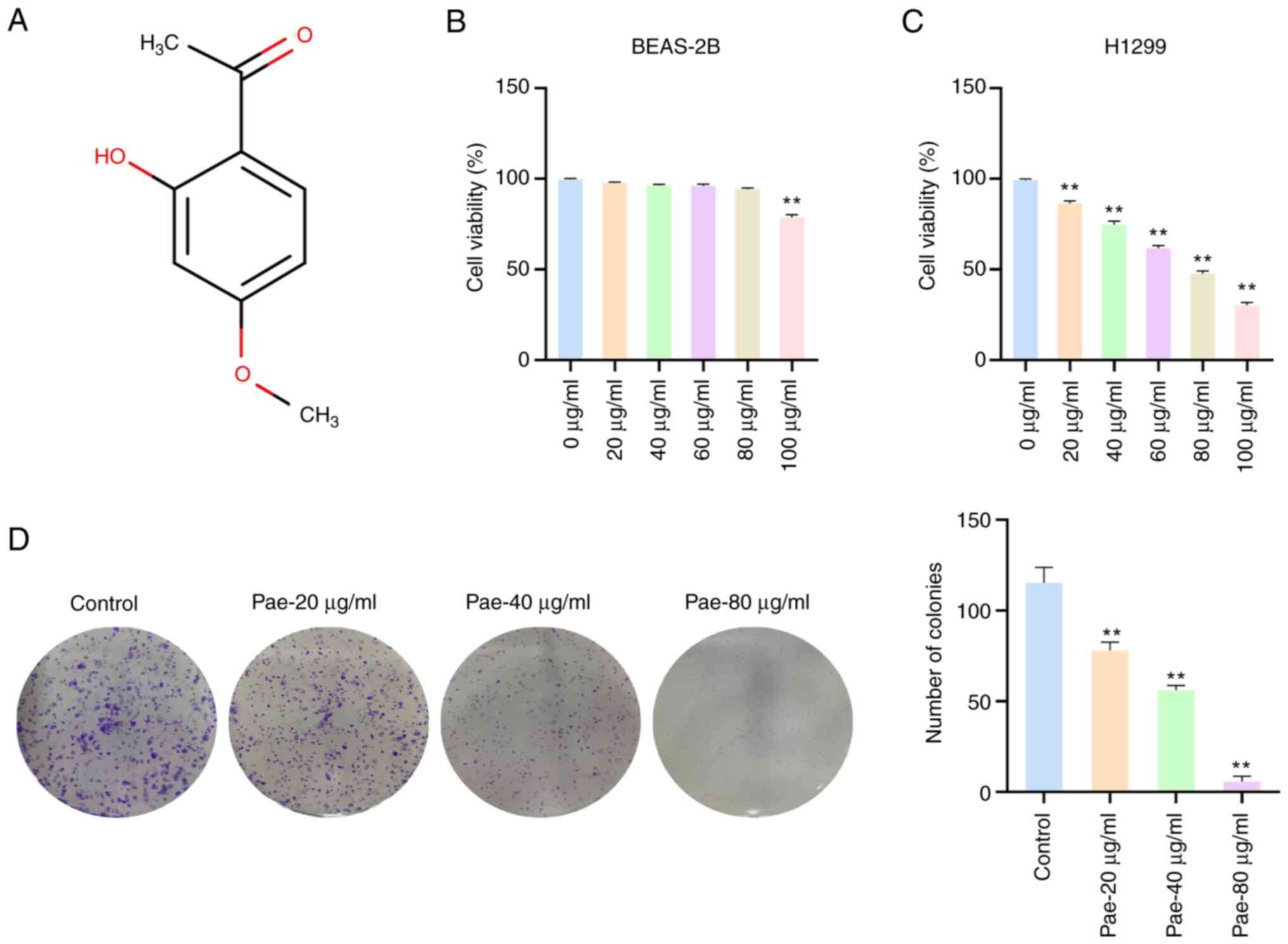
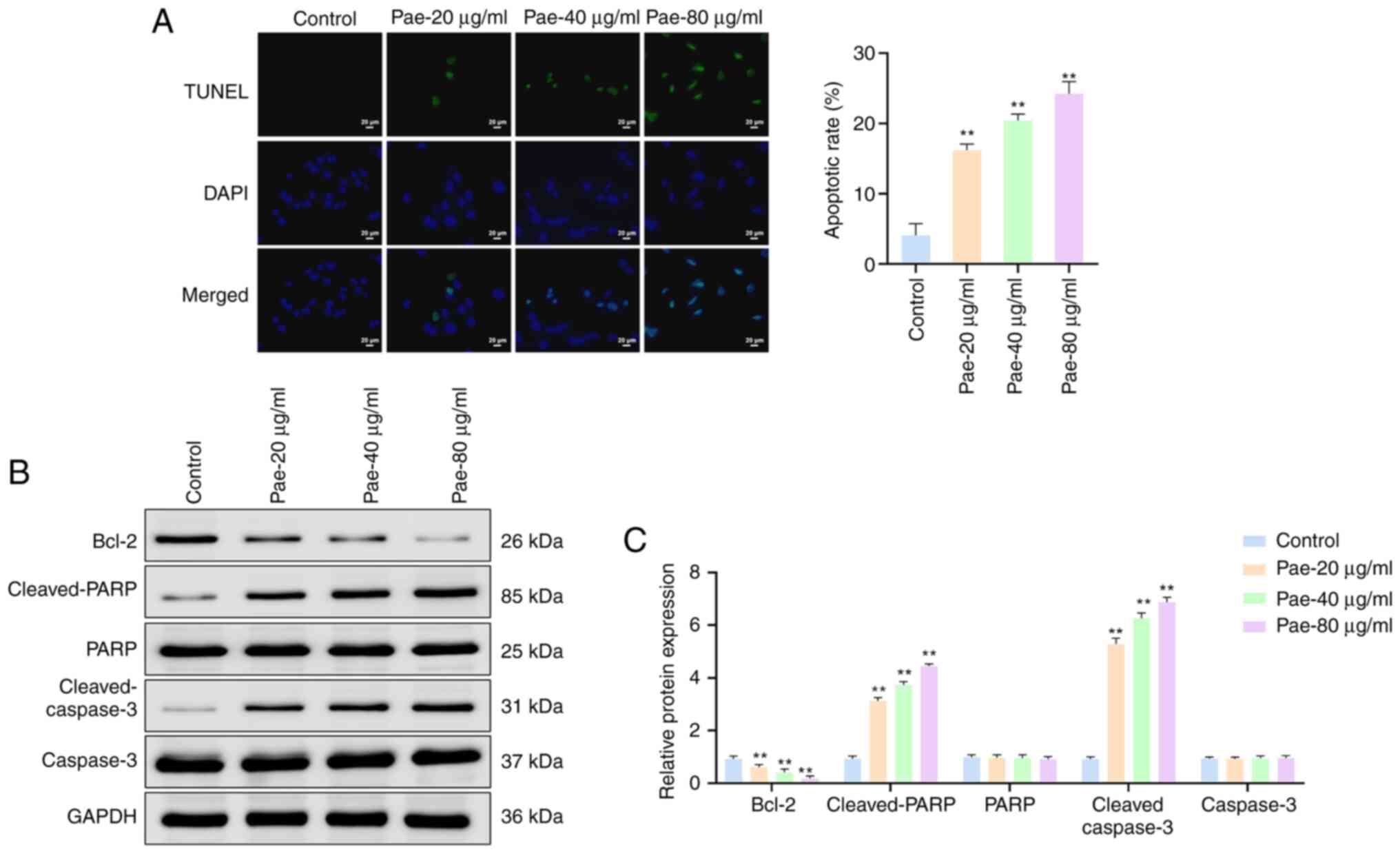
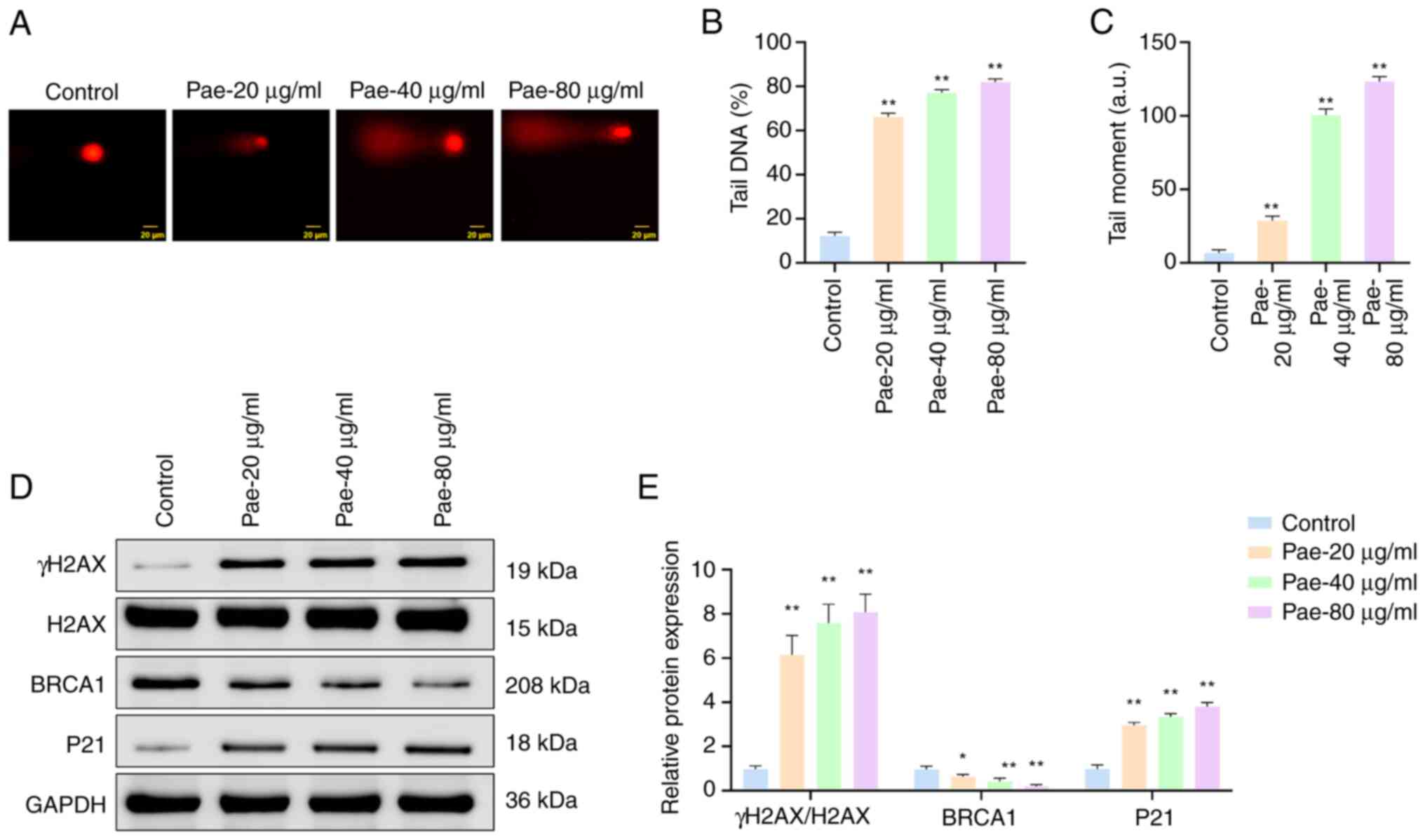
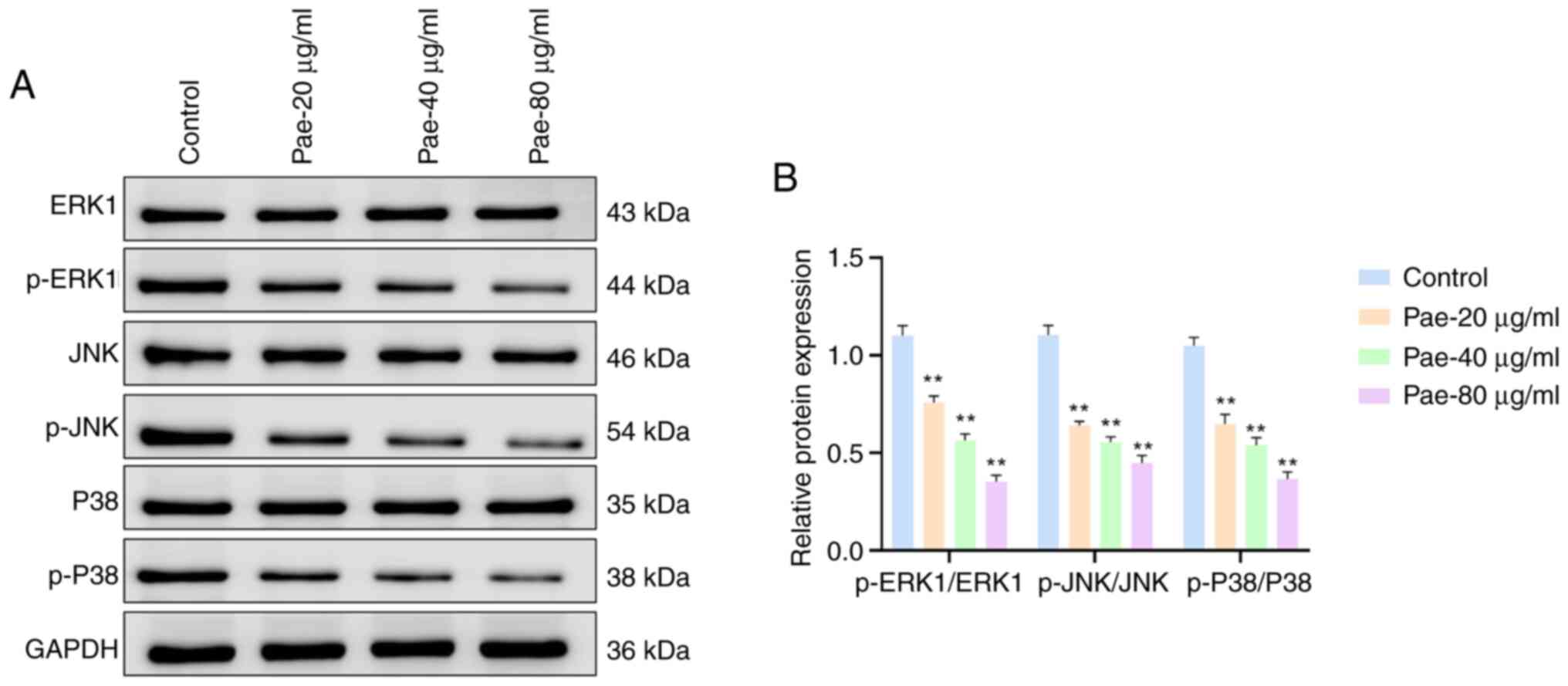
|
1
|
Wei Y, Wang L, Jin Z, Jia Q, Brcic L,
Akaba T and Chu Q: Biological characteristics and clinical
treatment of pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: A narrative review.
Transl Lung Cancer Res. 13:635–653. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Smith S, Kao S, Boyer M, Franco M and
Moore M: Treatment selection and real-world analysis of
immunotherapy with or without chemotherapy in PD-L1-high metastatic
non-small cell lung cancer. Intern Med J. 54:1337–1343. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sun M, She S, Chen H, Cheng J, Ji W, Wang
D and Feng C: Prediction model for synergistic anti-tumor
multi-compound combinations from traditional Chinese medicine based
on extreme gradient boosting, targets and gene expression data. J
Bioinform Comput Biol. 20:22500162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang X, Feng X, Du M, Li S, Wang J, Wang
Y and Liu P: Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of paeonol on
antitumor and prevention of side effects of cancer therapy. Front
Pharmacol. 14:11948612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Niu Y, Jin Y, Hao Y, Liang W, Tang F, Qin
Z, Liang T and Shi L: Paeonol interferes with lupus nephritis by
regulating M1/M2 polarization of macrophages. Mol Immunol.
169:66–77. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Wang Z, Wu X, Zhu S, Guo Q, Jin Z,
Chen Z, Zhang D, Hu W, Xu H, et al: Paeonol promotes
reendothelialization after vascular injury through activation of
c-Myc/VEGFR2 signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 17:1567–1582.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang JJ, Cai LJ, Pang K, Dong Y, Zhang
ZG, Li BB, Li R and Han CH: Paeonol inhibits proliferation and
induces cell apoptosis of human T24 and 5637 bladder cancer cells
in vitro and in vivo. Clin Transl Oncol. 23:601–611. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zuo BW, Yao WX, Fang MD, Ren J, Tu LL, Fan
RJ and Zhang YM: Boris knockout eliminates AOM/DSS-induced in situ
colorectal cancer by suppressing DNA damage repair and
inflammation. Cancer Sci. 114:1972–1985. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Du J, Song D, Li J, Li Y, Li B and Li L:
Paeonol triggers apoptosis in HeLa cervical cancer cells: The role
of mitochondria-related caspase pathway. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
239:2083–2209. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang L, Chen WX, Li LL, Cao YZ, Geng YD,
Feng XJ, Wang AY, Chen ZL, Lu Y and Shen AZ: Paeonol suppresses
proliferation and motility of nonsmall-cell lung cancer cells by
disrupting STAT3/NF-κB signaling. Front Pharmacol. 11:5726162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu LH, Shi RJ and Chen ZC: Paeonol exerts
anti-tumor activity against colorectal cancer cells by inducing
G0/G1 phase arrest and cell apoptosis via inhibiting the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 46:675–684. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng CS, Chen JX, Tang J, Geng YW, Zheng
L, Lv LL, Chen LY and Chen Z: Paeonol inhibits pancreatic cancer
cell migration and invasion through the inhibition of tgf-β1/smad
signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal-transition. Cancer Manag Res.
12:641–651. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cai M, Shao W, Yu H, Hong Y and Shi L:
Paeonol inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion and
induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating
miR-21-5p/KLF6 axis. Cancer Manag Res. 12:5931–5943. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen X, Xu Z, Lu M, Ding W, Zhong J, Deng
S, Li S, Miao J, Liu X, Wen Q, et al: Paeonol inhibits melanoma
growth by targeting PD1 through upregulation of miR-139-5p. Biochem
Biophys Res Commu. 656:86–96. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li M, Cai O, Yu Y and Tan S: Paeonol
inhibits the malignancy of Apatinib-resistant gastric cancer cells
via LINC00665/miR-665/MAPK1 axis. Phytomedicine. 96:1539032022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Yang S, Yang X, Deng D, Li J and
Dong M: Research progress of traditional Chinese Medicine monomers
in reversing multidrug resistance of breast cancer. Am J Chin Med.
51:575–594. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cai F, Li J, Zhang Y, Huang S, Liu W, Zhuo
W and Qiu C: Interaction between Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
and EMT pathway mediates the mechanism of sunitinib resistance in
renal cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 24:1752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cordelli E, Bignami M and Pacchierotti F:
Comet assay: A versatile but complex tool in genotoxicity testing.
Toxicol Res (Camb). 10:68–78. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li R, Chen Y, Yang B, Li Z, Li P, Chen Y,
Li J, He J, Wu Y, Sun Y, et al: DTX2 promotes glioma development
via regulation of HLTF. Biol Direct. 19:22024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang L, Wu L, Zhu X, Mei J and Chen Y:
Paeonol represses A549 cell glycolytic reprogramming and
proliferation by decreasing m6A modification of Acyl-CoA
dehydrogenase. Chin J Physiol. 66:248–256. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang L, Chen WX, Li LL, Cao YZ, Geng YD,
Feng XJ, Wang AY, Chen ZL, Lu Y and Shen AZ: Paeonol suppresses
proliferation and motility of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by
disrupting STAT3/NF-κB signaling. Front Pharmacol. 11:5726162020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang C, Zhang J and Guo K: Paeonol
upregulates expression of tumor suppressors TNNC1 and SCARA5,
exerting anti-tumor activity in non-small cell lung cancer cells.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 397:5241–5251. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jensen K, Bikas A, Patel A, Kushchayeva Y,
Costello J, McDaniel D, Burman K and Vasko V: Nelfinavir inhibits
proliferation and induces DNA damage in thyroid cancer cells.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 24:147–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nunna S, Huang YP, Rasa M, Krepelova A,
Annunziata F, Adam L, Käppel S, Hsu MH and Neri F: Characterization
of novel α-Mangostin and paeonol derivatives with cancer-selective
cytotoxicity. Mol Cancer Ther. 21:257–270. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sheng SQ, Yu LY, Zhou XW, Pan HY, Hu FY
and Liu JL: Paeonol prevents migration and invasion, and promotes
apoptosis of cervical cancer cells by inhibiting 5-lipoxygenase.
Mol Med Rep. 23:4012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lei Y, Li HX, Jin WS, Peng WR, Zhang CJ,
Bu LJ, Du YY, Ma T and Sun GP: The radiosensitizing effect of
Paeonol on lung adenocarcinoma by augmentation of radiation-induced
apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Radiat
Biol. 89:1079–1086. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang Z, Wang X, Rong Z, Dai L, Qin C, Wang
S and Geng W: LncRNA LINC01134 contributes to radioresistance in
hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating DNA damage response via MAPK
signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol. 12:7918892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen XM, Jia CL and Zhu ZY: Paeonol
impacts ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion and
apoptosis via modulating the transforming growth factor beta/smad3
signaling pathway. J Physiol Pharmacol. 74:2023.
|
|
29
|
Ekiert H, Klimek-Szczykutowicz M and Szopa
A: Paeonia × suffruticosa (Moutan Peony)-A review of the chemical
composition, traditional and professional use in medicine, position
in cosmetics industries, and biotechnological studies. Plants
(Basel). 11:33792022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh JM, Kang Y, Hwang JH, Park JH, Shin WH,
Mun SK, Lee JU, Yee ST and Kim H: Synthesis of 4-substituted
benzyl-2-triazole-linked-tryptamine-paeonol derivatives and
evaluation of their selective inhibitions against
butyrylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase-B. Int J Biol Macromol.
217:910–921. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang Y, Li BS, Zhang ZH, Wang Z, Wan YT,
Wu FW, Liu JC, Peng JX, Wang HY and Hong L: Paeonol repurposing for
cancer therapy: From mechanism to clinical translation. Biomed
Pharmacother. 165:1152772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hao XS, Feng PP, Zhang YY, Wang FZ, Wang
GL and Fei HR: Scutebarbatine A induces ROS-mediated DNA damage and
apoptosis in breast cancer cells by modulating MAPK and EGFR/Akt
signaling pathway. Chem Biol Interact. 378:1104872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cai J, Chen Y, Wang K, Li Y, Wu J, Yu H,
Li Q, Wu Q, Meng W, Wang H, et al: Decoding the key compounds and
mechanism of Shashen Maidong decoction in the treatment of lung
cancer. BMC Complement Med Ther. 23:1582023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kazi M, Alanazi Y, Kumar A, Shahba AA,
Rizwan Ahamad S and Alghamdi KM: Oral bioactive
self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery systems of remdesivir and
baricitinib: A paradigmatic case of drug repositioning for cancer
management. Molecules. 28:22372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ding M, Shi R, Fu F, Li M, De D, Du Y and
Li Z: Paeonol protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
by promoting Mfn2-mediated mitochondrial fusion through activating
the PKCepsilon-Stat3 pathway. J Adv Res. 47:151–162. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lv J, Zhu S, Chen H, Xu Y, Su Q, Yu G and
Ma W: Paeonol inhibits human lung cancer cell viability and
metastasis in vitro via miR-126-5p/ZEB2 axis. Drug Dev Res.
83:432–446. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|