Introduction
AML is a malignant clonal proliferative disease of
hematopoietic stem cells. The diagnosis and therapy of AML have
advanced in recent years due to continuous research and an improved
understanding of the etiology of the disease (1). Numerous targeted small-molecule
inhibitors have been approved for the treatment of AML, which have
demonstrated favorable curative results, including chemotherapy and
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (2). AML has a poor prognosis and a high
rate of recurrence (1,2). Thus, further research to explore novel
therapeutic drugs to improve the prognosis of AML is required. The
diagnosis of AML is primarily dependent on clinical presentation
and pathological features, particularly the presence of specific
gene mutations, such as RUNX1 and TP53, which are often associated
with poor prognosis. In addition, according to World Health
Organization (WHO) standards, the diagnosis of AML requires that
the proportion of primitive cells (blastocytes) in the bone marrow
or peripheral blood be at or above 20%. Comprehensive analysis of
these factors is essential for accurate diagnosis and effective
treatment planning (3).
With an increasing understanding of iron metabolism
and the identification of ferroptosis as a novel type of regulated
cell death dependent on iron, novel therapeutic options have
emerged in recent years (4,5). The ability to induce effective tumor
cell death, while protecting healthy cells is critical for cancer
therapy. For tumor survival and growth, cancerous cells require
larger quantities of iron than healthy cells (6). Given their dependency on iron, tumor
cells are more vulnerable to iron-induced apoptosis (7,8).
Regulation of the ferroptotic pathway to prevent the development
and growth of malignancies has garnered increasing interest in
recent years (9–11). The present review aims to provide an
overview of ferroptosis in the incidence, development, prognosis
and as a potential therapeutic target of AML.
Mechanisms of ferroptosis
Ferroptosis, a unique type of cell death
characterized by the buildup of lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS)
and iron dependency, was initially described by Dixon et al
(12) in 2012. Ferroptosis
describes a mode of cell death distinct from apoptosis, necrosis
and autophagy. Ferroptosis is characterized by reduced
mitochondrial volume, increased lipid bilayer density, and
diminished or absent mitochondrial cristae, while the cell membrane
and the nuclear morphology remain unaffected (13,14).
In biological terms, lipid peroxide metabolism is catalyzed by
reduced glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) activity and intracellular
glutathione (GSH) levels (15).
Ferroptosis is induced by the Fenton reaction, in which
Fe2+ oxidizes lipids and generates significant
quantities of ROS (16,17).
Ferroptosis mechanisms can be broadly classified
into four categories: i) The GSH/GPX4 pathway, ii) the inhibitory
system Xc, iii) the mevalonate (MVA) pathway; and iv) p53
regulation (Fig. 1) (13). The solute carrier family 7 member 11
(SLC7A11) and SLC3A2 subunits constitute the amino acid
anti-transporter system Xc, which is present in the cell membranes
of various cell types (18,19). Glutamate and cystine are imported
and exported by system Xc in a 1:1 ratio. The cystine that is
imported into the cell is reduced to form GSH. In the presence of
GPX, GSH can reduce ROS. GPX4 is a crucial regulator of
iron-induced mortality in the GPX family (20). GPX4 converts lipid hydrogen peroxide
(R-OOH) to lipid alcohols (R-OH), which limits iron-dependent lipid
ROS generation and protects membrane integrity from damage induced
by ROS buildup (21). The MVA
pathway synthesizes isoprene units such as isopentenyl
pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) from
acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) (22). This pathway also contributes to
stabilization of the transport RNA (tRNA) needed for selenocysteine
incorporation into selenoproteins, through protein isoprenylation.
A key selenoprotein affected is GPX4, which clears toxic lipid
peroxides to suppress oxidative cell damage. Inhibition of the MVA
pathway, by statins for example, reduces IPP/DMAPP production and
selenoprotein synthesis, which reduces GPX4 activity (23,24).
This impairs the elimination of lipid peroxides and sensitizes
cells to ferroptosis. However, an impaired mevalonate pathway also
reduces the synthesis of coenzyme Q10, an antioxidant that partners
with ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1) and NADH to neutralize
the toxic lipid radicals that accumulate in cells. Thus, the
coenzyme Q10-FSP1-NADH system acts in an anti-ferroptotic manner,
downstream of mevalonate pathway inhibition to delay the induction
of iron-mediated oxidative cell death (25).
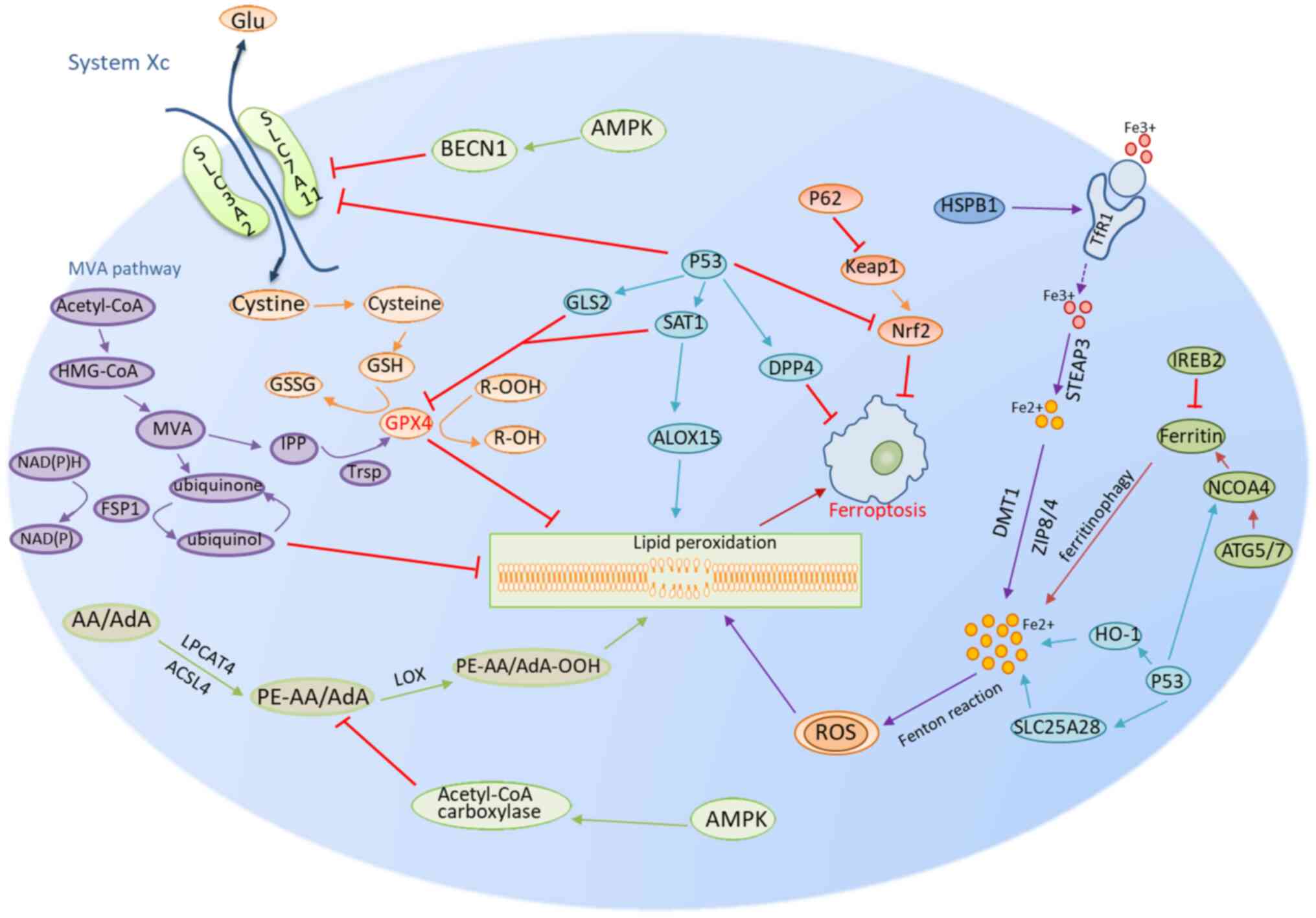 | Figure 1.Mechanisms of ferroptosis encompass a
number of pathways, including those related to GSH/GPX4, iron
metabolism and lipid metabolism. The GSH/GPX4 pathway includes
system Xc and the MVA pathways and part of the p53 pathway. Iron
metabolism is the second group, which involves other regulatory
mechanisms in part of the Nrf2, NCOA4, IREB2, HSPB1 and the p53
partial pathway. The lipid metabolism route is the third group,
involving factors such as p53-SAT1-ALOX15, ACSL4 and LPCAT3. AMPK
signaling represents the fourth class of regulatory mechanisms
involved in ferroptosis (A single arrow means promotion of the
process and a red T arrow means inhibition of the pathway.
Different colors represent different metabolic processes). GSH,
glutathione; GPX4, glutathione peroxidase 4; GSSG, oxidized
glutathione; SLC7A11, solute carrier family 7 member 11; SLC3A2,
solute carrier family 3 member 2; R-OOH, lipid hydrogen peroxide;
R-OH, lipid alcohols; MVA pathway, mevalonate pathway; HMG-CoA,
hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA; IPP, isopentenyl pyrophosphate; TRSP,
selenocysteine-specific transfer RNA; FSP1, ferroptosis suppressor
protein 1; GLS2, glutaminase 2; SAT1, spermine N1-acetyltransferase
1; LOX, lipoxygenase; ALOX15, arachidonate-15-lipoxygenase; BECN1,
beclin 1; DPP4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; Keap1, ECH associated
protein 1; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2;
HSPB1, heat shock protein family B (small) member 1; TfR1,
transferrin receptor 1; STEAP3, six-transmembrane epithelial
antigen of prostate 3; STEAP family member 3; DMT1, divalent metal
transporter 1; ZIP8/4, zinc transporter ZIP8/4; NCOA4, nuclear
receptor coactivator 4; ATG5/7, autophagy protein 5; HO-1, heme
oxygenase 1; SLC25A28, solute carrier family 25 member 28; AMPK,
AMP-activated protein kinase; AA, arachidonic acid; AdA, AdA,
adrenoyl derivatives; PE-AA/AdA, phosphatidylethanolamines;
Acetyl-CoA, acetyl coenzyme A; LPCAT3, lysophospholipid
acyltransferase. |
Ferroptosis is regulated by p53 via two mechanisms
(26,27). Ferroptosis has been reported to be
inhibited by p53 in colorectal cancer cells through the formation
of a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4)-p53 complex and the subsequent
translocation of the DPP4 enzyme from the cell membrane to the
nucleus. This process reduces the activity of DPP4 on the cell
membrane, thereby decreasing lipid peroxidation and ultimately
inhibiting ferroptosis (28).
p53-mediated inhibition of ferroptosis also increases SLC7A11
expression levels through the inhibition of Nrf2-mediated gene
expression, which leads to increased GSH synthesis and lipid
peroxide clearance (29,30). p53 can also contribute to
ferroptosis through several approaches: i) The suppression of
system Xc, which reduces cystine uptake and GSH production
(28); and ii) transcriptional
activation of glutaminase-2 to decrease GSH levels and GPX4
activity (27). The latter
mechanism is related to iron metabolism, such as via the p62-kelch
like ECH associated protein 1 (Keap1)-nuclear factor erythroid
2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) regulatory pathway, nuclear receptor
coactivator 4 (NCOA4) pathway that is related to ferritin
metabolism, iron responsive element binding protein 2 (IREB2), p53
and heat shock protein family B (small) member 1 (HSPB) regulatory
pathways (13). Intracellular iron
levels are crucial in order to maintain intracellular homeostasis
and increased iron levels can induce a Fenton reaction, which
results in the formation of intracellular ROS. Lipid peroxidation
processes can be induced by excess levels of ROS and lead to
ferroptosis (31). The transferrin
receptor 1 (TfR1) is a membrane protein that binds to the
Fe3+/transferrin complex, which allows iron to be
released into endocytic vesicles inside the cell (9). Once inside the vesicles,
Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ by the iron reductase
enzyme, STEAP. Fe2+ then enters the cytosol, creating an
unstable pool of free iron known as the labile iron pool (LIP)
(32). The LIP is regulated by
either the zinc-iron regulatory proteins ZIP8 and ZIP14, or the
divalent metal transport protein 1 (33). The iron from the LIP can be stored
inside the protein ferritin or transferred back out of the cell via
the iron export protein ferroportin (FPN) to keep the LIP levels
low and prevent iron-induced cell death. Through the utilization of
TfR1 and FPN, cells can control iron import and export to meet its
needs while avoiding excess free iron that could cause oxidative
damage (34). In 2016, Sun et
al (35) demonstrated that the
p62-Keap1-Nrf2 pathway controls the suppression of ferroptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. The antioxidant response is notably
regulated by Nrf2, which can reduce ferroptosis and improve tumor
chemotherapy response and radiation resistance (36). Keap1 targets Nrf2 for ubiquitination
and degradation, thus inhibiting Nrf2 (37,38).
p62 is a multifunctional autophagy receptor, and the accumulation
of p62 reduces the inhibition of Keap1 and promote the release of
Nrf2 (39).
Within the NCOA4 pathway, a process known as
ferritin phagocytosis, which is mediated by the cargo receptor
NCOA4, can cause a subsequent release of iron into the cytoplasm to
reduce iron toxicity (40).
Ferritin is made up of the ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH1) and the
ferritin light chain (FTL) (41).
Erastin-induced ferroptosis was inhibited by increasing the
expression levels of FTL and FTH1 while significantly decreasing
the expression levels of IREB2, a crucial transcription factor of
iron metabolism (42,43). Heat shock protein family B (small)
member 1 (HSPB1) overexpression can further raise intracellular
iron content by increasing TRF1 expression and preventing
ferroptosis (44). Previous studies
have uncovered additional mechanisms by which p53 regulates
ferroptosis by modulating iron metabolism and availability
(45). p53 promotes ferroptosis by
transcriptionally activating TfR1 and the mitochondrial iron
importer solute carrier family 25 member 28 (SLC25A28), which
results in increased uptake and accumulation of reactive iron, that
sensitizes cells to oxidative damage (46). In addition, p53 can drive the
degradation of the iron-storage protein ferritin by activating
NCOA4. This results in the release of stored iron to further
increase reactive intracellular iron levels (47). Conversely, p53 can also increase the
expression of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) which reduces overall
cellular iron levels. By decreasing iron availability, HO-1
activity inhibits lipid peroxidation and suppresses ferroptosis
sensitivity (48).
The third mechanism is related to lipid metabolism
pathways, such as the p53-SAT1-arachidonic acid lipoxygenase 15
(ALOX15), ACSL4 and lysophospholipid acyltransferase (LPCAT3)
pathways (9). The process of lipid
peroxidation is crucial to ferroptosis. Spermine
N1-acetyltransferase 1 (SAT1) is the transcriptional target of p53
in the p53-SAT1-ALOX15 pathway, and activation of SAT1 can induce
lipid peroxidation to encourage ferroptosis, which is tightly
connected through ALOX15 control (13). Lipid peroxidation is initiated by
the formation of arachidonic acid (AA)/adrenoyl derivatives (AdA).
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) such as AA and AdA are
esterified to form PUFA-PL complexes (PE-AA/AdA) under the action
of ACSL4 and LPCAT, resulting in the accumulation of PE-AA/AdA in
the cell membrane to produce lipid peroxides via LOX activity and
Fenton reactions, which induce ferroptosis (49). The enzymatic pathway utilizes LOXs,
which are non-heme iron-containing dioxygenases. PE-AA/AdA serve as
substrates for 15-LOX to form phospholipid hydroperoxides
(PE-AA/AdA-OOH) (36,40). These peroxyl radicals propagate
further peroxidation of neighboring PUFAs (32). In addition, in the non-enzymatic
pathway, free redox-active iron reacts with PE-AA/AdA via Fenton
reactions to generate membrane-destabilizing lipid peroxides
(50). In both pathways, the
iron-dependent peroxidation of membrane PUFAs catalyzed by
PE-AA/AdA intermediates results in excessive free radical damage,
depletion of antioxidants, loss of membrane integrity and
ultimately, execution of regulated ferroptotic cell death (9,51).
Finally, there are other regulatory pathways
involved in ferroptosis, such as the AMP-activated protein kinase
(AMPK) signaling pathway. AMPK acts as a sensor of the cellular
energy status and contributes to the preservation of energy
homeostasis (52). To prevent PUFA
biosynthesis and ferroptosis, AMPK can mediate the phosphorylation
of acetyl-CoA carboxylase. However, AMPK also inhibits
SLC7A11-mediated cystine transport and increases ferroptosis by
modulating the phosphorylation of beclin1 (BECN1) (15,53).
Role of ferroptosis in the development and
progression of AML
AML is a heterogeneous disease characterized by
constitutively activated oncogenic signals, high mortality rates
and a poor prognosis. It is typically treated with chemotherapy and
patient survival rates are poor (54). Therefore, novel therapeutic
approaches are required to improve the management of the disease
(55). Iron serves a role in
hematopoiesis and is a necessary component of human cells. After
interacting with the transferrin-iron complex, the membrane protein
TfR1 releases iron via endocytosis. When TfR1 expression is
suppressed, iron deprivation reduces the ability of hematopoietic
stem cells to regenerate and affects the proliferation and
differentiation of hematopoietic progenitor cells. ROS
accumulation, induced by excessive iron, can result in oxidative
stress which can damage proteins, DNA, lipids and even induce cell
death (14,53). Patients with AML frequently exhibit
severe symptoms resulting from iron overload, primarily due to the
extensive blood transfusions required to manage anemia caused by
abnormal erythropoiesis and chemotherapy. These symptoms include
heart failure, liver fibrosis, diabetes, endocrine disorders,
fatigue, and weakness, significantly impacting the patients'
quality of life and prognosis (40). Additionally, the rapid proliferation
of specific hematopoietic precursor cells in patients with AML
leads to an increased demand for iron (56). Thus, given the tendency for
iron-overload and the iron dependency of AML, the induction of
ferroptosis represents a promising therapeutic approach (40,56).
GPX4 is an antioxidant enzyme that uses GSH to
transform toxic lipid peroxides into non-toxic lipols, thereby
protecting cells from ferroptosis. Previous studies (49,57)
have demonstrated that GPX4 is upregulated in AML cells, which
enables cells to restrict ferroptosis through reduced lipid
peroxide levels, which ultimately increases AML cell survival and
drug resistance (58).
Consequently, GPX4 serves a critical role in AML progression and
represents a promising therapeutic target. The survival pathway of
cancer cells, particularly the antioxidant response regulated by
Nrf2, serves a crucial role in the defense against apoptosis, which
is a key factor in cancer cell survival (59). Nrf2 has been linked to the
development of AML and previous studies suggest that it can be
regulated by NF-κB in AML. This activation of the Nrf2-dependent
antioxidant defense response provides growth advantages and
resistance to treatment for AML cells (60).
Lipid metabolism and ferroptosis are intricately
intertwined, as the emergence of lipid peroxides is one of the
hallmarks of ferroptosis (61). In
patients with AML, lipid homeostasis is disrupted, and PUFAs and
other unsaturated fatty acids present in AML cells contribute to
the onset and progression of the disease (62). Although there is limited research on
the mechanisms underlying the development of AML, it is clear that
further investigation is necessary to elucidate the specific
molecular mechanisms involved (Table
I).
 | Table I.Factors influencing the association
between ferroptosis and AML. |
Table I.
Factors influencing the association
between ferroptosis and AML.
| Factor | Effect | Effect on the
occurrence and development of AML |
|---|
| TfR1 | A membrane protein
that when bound to a transferrin-iron complex, promotes the
internalization of iron through siderocytosis. | Elevated iron
levels in AML cells, coupled with an imbalance in iron metabolism
further increase the susceptibility of AML cells to
ferroptosis |
| GPX4 | An antioxidant
enzyme that uses GSH to reduce lipid peroxides to non-toxic
lipols. | GPX4 is upregulated
in AML cells, allowing for the effective inhibition of ferroptosis
by reducing lipid peroxide levels. |
| Nrf2 | A key regulator of
the antioxidant response, Nrf2 is implicated in AML cell
survival. | NF-κB activates
Nrf2, increasing the antioxidant capacity of AML cells, thus
promoting their proliferation and enhancing their resistance to
chemotherapy. |
| PUFA | The peroxidation of
PUFAs in the cell membrane results in the production of lipid
peroxides. | The abnormally high
levels of fatty acid metabolism in AML cells serves an important
role in the occurrence and development of AML by influencing lipid
metabolism. |
Ferroptosis in AML therapy
AML is the most common type of leukemia in adults
and is typically treated with chemotherapy. However, chemotherapy
can have severe side effects and cause drug resistance in leukemia
cells (63). Although hematopoietic
stem cell transplantation can cure AML in a number of cases, its
widespread use is limited. For instance, the relapse rate
post-transplant is relatively high, particularly among high-risk
patients. In addition, patients face significant infection risks
during and after the transplantation process. Therefore, there is
an urgent need for more effective and accessible treatment for AML.
Recent studies have shown that inducers of ferroptosis, a process
that involves the buildup of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and
lipid peroxidation, have potential to treat certain types of cancer
(64,65).
Numerous substances, including eprenetapopt
(APR-246), aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family member A2 (ALDH3A2),
poly(lactic acid)-glycolic acid-encapsulated glycyrrhetinic acids
(GCMNPs), glutathione-bioimprinted nanoparticles targeting of
N6-methyladenosine FTO demethylase (GNPIPP12MA), gold nanorods
(GnR) functionalized with chitosan and a 12-mer peptide 12
(GnRA-CSP12) and GCFN, have been found to induce ferroptosis in AML
cells by disrupting the balance between GSH and ROS and inhibiting
GPX4 synthesis (51,66–69).
In a study by Birsen et al (66), APR-246 was reported to induce
ferroptosis in AML cells by decreasing GSH concentration and
increasing ROS and lipid peroxides. This treatment may be effective
for different subtypes of patients with AML, as it works regardless
of the presence of p53 mutations. It was also reported that
ferroptosis inducers, RAS-selective lethal (RSL3) and
FINO2, a 1,2-dioxolane, increased the antileukemic
activity of APR-246 in AML in vitro (70,71).
In phase II studies of myelodysplastic syndromes/AML with APR-246,
adverse neurological events were reported in over one-third of
patients who received APR-246 (72). Additionally, previous research has
demonstrated an association between ferroptosis and neurological
disorders, particularly neurodegenerative disorders (73). ALDH3A2 is an aldehyde dehydrogenase
that is present in both healthy myeloid cells and primary AML cells
(67). It is essential for the
detoxification of aliphatic aldehydes and the synthesis of 16- and
18-carbon fatty acids. Yusuf et al (67) reported that AML cells that were
deficient in ALDH3A2 had altered biosynthetic pathways, exhibited
increased oxidative damage and had an altered cellular lipid
composition. It was reported that lipid peroxidation was associated
with the induction of ferric death and an increase in
lysophospholipids was observed experimentally, particularly in the
absence of polyunsaturated fatty acid tails as a marker of
ferroptosis. Moreover, ALDH3A2 depletion caused ferroptosis in
leukemia cells and acted synergistically with GPX4 inhibition.
Furthermore, ALDH3A2 depletion caused iron depletion in leukemia
cells and preserved normal hematopoietic function. Hence, the
inhibition of ALDH3A2 in combination with ferroptosis inducer
drugs, particularly GPX4 inhibitors, may be a potential treatment
for AML (67).
CircKDM4C is a cyclic RNA produced by the KDM4C
gene. According to Dong et al (74), circKDM4C increases p53 expression
levels by regulating the microRNA (miRNA) hsa-let-7b-5p.
Specifically, circKDM4C acts as a sponge for hsa-let-7b-5p,
reducing its inhibitory effect on p53, thereby enhancing p53
expression levels. The increase in p53 expression levels lead to an
increase in intracellular iron concentration and ROS expression
levels and caused ferroptosis in AML cells. Initially identified as
a regulator of cell proliferation in Caenorhabditis elegans,
miRNA hsa-let-7 was found to be upregulated in AML. Previous
research has demonstrated that p53 can block the cystine system by
downregulating SLC7A11, which in turn decreases GPX4 activity. This
decrease in GPX4 activity led to a decrease in the antioxidant
capacity of leukemia cells and an accumulation of ROS, causing
ferroptosis (75). As a result,
circKDM4C presents a potential target for the treatment of patients
with AML.
Yu et al (76) developed a ferroptosis-inducing
nanotherapeutic drug (GCFN) based on glutathione reactive cysteine
polymer. To evaluate the efficacy of GCFN in treating AML, a mouse
model of aggressive AML was developed. GCFN could effectively
induce lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis in AML cells by reducing
the expression levels of intracellular GSH and inhibiting the
activity of GPX4, thus providing a basis for GCFN as a potential
treatment for AML.
Immunotherapy is a valuable therapeutic method that
has been successfully applied in clinical settings. Breaking
autoantigen immune tolerance is essential for antitumor
immunotherapy (51). Targeted
therapies are a promising research strategy because they have been
shown to enhance tumor immunity by activating T cells, modulating
the tumor microenvironment, enhancing antigen presentation and
inhibiting immune checkpoints, thereby improving treatment
effectiveness and reducing the likelihood of recurrence (77,78).
For example, studies have found that the combination of GCMNPs with
PD-L1 blockers may potentially improve efficacy in the management
of leukemia (68). GNPIPP12MA
enhances anti-leukemia immunity by increasing cytotoxic T cell
infiltration (79). GnRA-CSP12
disrupts intracellular REDOX balance, regulates epigenetic
transcriptomics, and further enhances cytotoxic response of T
cells. These combination therapies have shown promising results in
preclinical models, showing great potential to improve the
treatment of leukemia (80).
GCMNPs are highly specific to cancer cells and have
low toxicity in AML (68). Through
the inhibition of GPX4, GCMNPs can induce ferroptosis in AML cells,
which increases lipid peroxide levels (51). In this study, a mouse model of AML
was successfully used to evaluate the immune response to cancer
immunotherapy, particularly against AML and colorectal cancer.
Encouragingly, the animals did not experience any weight loss or
damage to kidney, heart, liver or lung tissue during treatment.
This result not only demonstrates the efficacy of the treatment,
but also highlights its safety, providing valuable insights for
future cancer immunotherapies. This demonstrates the significant
value of the AML mouse model in assessing the efficacy and safety
of cancer immunotherapy. Ferumoxytol and GCMNPs can also work
together to increase the Fenton reaction and cause ferroptosis.
Additionally, the combination of GCMNPs, Ferumoxytol and anti-PD-L1
improved T cell immune responses against leukemia (68).
In AML, fat mass and obesity-associated protein
(FTO), an N6-methyladenosine (m6A) demethylase, contributes to
carcinogenesis by preventing the expression of immune checkpoint
genes, particularly LILRB4. Knockdown of FTO reduced the growth of
leukemia stem cells and prevented leukemia cells from escaping the
immune system (79). GNPIPP12MA is
an FTO inhibitor-loaded GSH-bioimprinted nanocomposite (69). Through the FTO/m6A pathway,
GNPIPP12MA induces GSH depletion to inactivate GPX4, inhibit the
decrease in LPO, increase intracellular iron accumulation and lead
to the selective ferroptosis of AML cells. GNPIPP12MA therefore has
a wide range of anti-AML effects at relatively low doses.
Additionally, GNPIPP12MA could improve antileukemic immunity by
increased infiltration of cytotoxic T cells (69,79).
Nanoparticles of gold hexadecyltrimethylammonium
bromide and sodium oleate are used as a binary surfactant
combination to create GnRA-CSP12 (80), which are GnRs with various aspect
ratios. GnRA-CSP12 is selectively taken up by leukemia cells
through targeted endocytosis, disrupting the intracellular redox
balance, inducing ferroptosis and regulating epitranscriptomics by
eliminating Fe2+-dependent m6A demethylase activity.
This enhances the cytotoxic response of T cells, thereby improving
immunotherapy efficacy. Specifically, GnRs reduced GSH expression
levels through the formation of Au-S bonds with GSH, disrupting the
GSH/ROS balance and ferroptosis of leukemia cells. In the AML mouse
model treated with GnRs, no changes in body weight or pathological
alterations in major organs were observed and no significant toxic
effects or side effects were detected.
The regulation of ferroptosis also involves a number
of signaling molecules and pathways. For example, the quinazolinone
derivatives, Erastin and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1)
(81), regulate ferroptosis through
the JNK/p38 pathway, while dihydroartemisinin (DHA) and
typhaneoside (TYP) regulate ferroptosis through the AMPK signaling
pathway (82,83). 4-amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl
retinate (ATPR) modulates ferroptosis via Nrf2 signaling (84). Imetelstat influences ferroptosis by
modulation of the ACSL4 and FADS2 molecular signaling pathways
(85). Finally, Honokiol regulates
ferroptosis by upregulating the expression levels of heme oxygenase
1 (HMOX1) (86).
The discovery of Erastin was initially prompted by
its ability to selectively induce cell death in cancer cells with
mutant RAS (87). In a study
conducted by Yu et al (88),
it was demonstrated that Erastin increased the susceptibility of
non-acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) AML cells to
chemotherapeutic drugs cytarabine and doxorubicin in an
RAS-independent manner. Erastin-induced ferroptosis activates the
JNK and p38 signaling pathways, but not the ERK/MAPK pathway. Low
doses of Erastin, in part due to ferroptosis, increased the
susceptibility of non-APL AML cells to cytarabine and
doxorubicin.
HMGB1 is a transcription factor that is crucial to
the etiology and chemotherapeutic resistance of leukemia (89). Wen et al (81) demonstrated that HMGB1 is directly
involved in Erastin-induced ferroptosis and is a significant
regulator of the process. It was reported that the RAS-JNK/p38
pathway is utilized by HMGB1 to regulate Erastin-mediated
ferroptosis and the in vivo examination of HMGB1 expression
levels did not have a significant impact on experimental
animals.
DHA, a natural antimalarial compound found in the
Chinese herb Artemisia annua, has been reported to
significantly inhibit the activity of AML cells (82,90).
DHA activates AMPK phosphorylation to downregulate the activity of
the mTOR/p70S6k signaling pathway, induces autophagy in AML cells,
speeds up ferritin degradation, increases the size of the unstable
iron pool, increases cell ROS accumulation and ultimately causes
ferroptosis in AML cells.
TYP is a major flavonoid compound extracted from
typha pollen. Zhu et al (83) reported that TYP serves a significant
role in inhibiting the proliferation of AML cells by promoting the
activation of the AMPK signal, inducing significant autophagy of
AML cells and ultimately causing ferritin degradation, ROS
accumulation and ferroptosis. They reportedly assessed the toxicity
of TYP by observing weight changes and pathological changes in
major organs such as the liver, spleen, kidney and lungs in mice
during treatment. The results showed that no weight loss or
pathological changes in major organs were observed in mice treated
with TYP, indicating a low level of toxicity and good safety.
An all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) derivative known
as ATPR, which was designed and synthesized by Du et al
(84), exhibits more potent
anticancer properties compared with ATRA. ATPR-mediated induction
acts through the regulation of iron homeostasis and ROS levels by
inhibiting the expression of Nrf2. Nrf2 is an important antioxidant
reaction factor and its inhibition results in an increase in the
sensitivity of cells to oxidative stress, which promotes autophagy
(91). In addition, ATPR also
regulates iron homeostasis by increasing ROS levels, a mechanism
that may involve the degradation of ferritin and iron
metabolism-related proteins, thereby releasing bound iron and
increasing LIP and ROS levels, further inducing ferroptosis
(92).
Imetelstat is a small oligonucleotide inhibitor of
telomerase, a ribonucleoprotein complex that protects and prolongs
the telomeres at the end of chromosomes, a process that is involved
in cellular senescence and cellular aging (85). Imetelstat acts as a potent inducer
of ferroptosis, by promoting excessive lipid peroxidation and
oxidative stress in AML, via regulation of PUFA metabolism, which
is itself mediated by ACSL4 and FADS2. The preclinical efficacy of
imetelstat was evaluated using an AML patient-derived xenograft
model. The combination of imetelstat and standard induction
chemotherapy, consisting of cytarabine and anthracycline, induced
oxidative stress, causing AML cells to become sensitive to
imetelstat-induced lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis, which
increased the efficacy of chemotherapy on AML. This demonstrated
that imetelstat could effectively reduce the burden of AML and
delay the recurrence following oxidative stress-induced
chemotherapy (85).
Honokiol is a bioactive bisphenol phytochemical that
can be isolated from the bark, seed balls and leaves of trees
belonging to the genus Magnolia (86). It has potent antioxidant,
anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic and anticancer properties.
Notably, honokiol triggers ferroptosis in AML cells by increasing
the expression levels of HMOX1, and furthermore, zinc
protoporphyrin, an HMOX1 inhibitor, prevented the honokiol-induced
ferroptosis of several AML cell lines (THP-1, U-937 and SKM-1
cells) (86). However, the
potential of honokiol as a broad-spectrum antileukemic therapy
remains to be determined.
In recent years, remarkable progress has been made
in the study of drugs targeting ferroptosis drugs for AML. These
drugs include small molecule inhibitors, natural compounds and
drugs prepared using nanotechnology, which have demonstrated
potential therapeutic effects in clinical trials (Table II). Nevertheless, the value of
these drugs compared with standard AML treatments still requires
further evaluation. Future studies should focus on the safety,
efficacy and long-term effects of these drugs in clinical use to
determine their practical use in the treatment of AML, with the
goal of improving the accuracy of prognostic predictions and
developing personalized treatment plans. The varying sensitivities
of different subgroups of patients with AML to various treatments,
as well as individual differences between patients should be taken
into consideration in further research. This research will be of
notable significance to improve the survival rates and quality of
life of patients.
 | Table II.Mechanisms by which drugs or target
genes induce ferroptosis. |
Table II.
Mechanisms by which drugs or target
genes induce ferroptosis.
| Drug or ferroptosis
inducer | Mechanisms |
|---|
| APR-246 | Inhibition of GSH
synthesis |
| ALDH3A2 | Inhibition of GPX4
activity |
| circKDM4C | Upregulated
p53 |
| GCFN | Inhibition of GPX4
activity |
| GCMNPs | Inhibition of GPX4
activity |
| GNPIPP12MA | Inhibition of GPX4
activity |
| GNRa-CSP12 | Inhibition of GSH
synthesis |
| Erastin | Activation of
JNK/p38 pathway |
| HMGB1 | Activation of
RAS-JNK/p38 pathway |
| DHA | Activation of AMPK
pathway |
| TYP | Activation of AMPK
pathway |
| ATPR | Inhibition of Nrf2
activity |
| Imetelstat | Activation of ACSL4
and FADS2 activity |
| Honokiol | Activation of HMOX1
activity |
Ferroptosis and the prognosis of AML
Dysregulated maturation and differentiation of
hematopoietic stem cells and malignant cloning are associated with
the formation and progression of AML, a heterogeneous hematological
disease (93). The clinical
effectiveness in patients with AML was significantly increased
following the optimization of targeted treatment and hematopoietic
stem cell transplantation, specifically reflected in the
significant increases in complete remission rates and overall
survival. However, the long-term survival of patients is still
limited and patient prognosis remains poor. The association between
ferroptosis-related genes (FRG) and the prognosis of AML has
garnered interest, due to interest in ferroptosis as a possible
therapeutic target for the management of cancer. To improve patient
risk adaptation therapy, it is necessary to investigate the
prognostic significance of FRGs by establishing a clinical
prognostic model for predicting survival risk in patients with AML
(Table III).
 | Table III.High-risk and protective genes
associated with ferroptosis. |
Table III.
High-risk and protective genes
associated with ferroptosis.
| High-risk
genes | Protective
genes |
|---|
| HSPB1, CHAC1,
CISD1, DPP4, GPX4, AIFM2, SQLE, PGD, ACSF2, ZFPM2, ZNF560, ZSCAN4,
HMX2, HRASLS, LGALS1, LHX6, CCL23, FAM155B, CD44, FH, SESN2,
LPCAT3, ACSL5, SOCS1, AKR1C2 and SOCS1 | DNAJB6, MXRA5,
PCDHB12, PRINS, TMEM56, TWIST1, ASTN1, DLL3, EFNB3, FOXL1, ACSL6
and G3BP1 |
A previous study showed the normalized levels of
each FRG and the regression coefficients were used to create the
AML risk score, which was based on the sum of numerous clinical
variables (94). The normalized
level of each FRG and its regression coefficient were used to
calculate the AML risk score. Then, based on a median risk score,
patients with AML were split into low-risk and high-risk groups.
According to the survival analysis, the mortality rate in the
low-risk group was significantly reduced and overall survival was
significantly increased. Cox regression analysis was used to
develop a combined risk score using the clinical characteristics of
patients with AML using data from TCGA, such as age and sex
(95). The prognostic risk score
model was employed as a prognostic factor independent of other
clinical parameters to successfully guide prognosis prediction,
based on the multivariate Cox regression analysis, but it has not
yet been implemented in clinical practice (96). Another study on the prognosis of two
FRGs, DNAJ heat shock protein family member B6 (DNAJB6) and HSPB1,
showed they were favorably and adversely correlated with the
prognosis of patients with AML, respectively, in a prognostic model
created using copy number variation (CNV)-driven FRGs (96). A total of eight ferroptosis
regulators PGD, ACSF2, CISD1, DPP4, GPX4ADDIN, SQLE, AIFM2 and
CHAC1] were used to create a predictive model, and were all
associated with poor prognosis in patients with AML (97,98).
In another study, ZFPM2, ZNF560, ZSCAN4, HMX2, HRASLS, LGALS1,
LHX6, CCL23 and FAM155B were high-risk genes for prognosis in
patients with AML in the prognostic model created using 18
regulators of ferroptosis (99),
whereas MXRA5, PCDHB12, PRINS, TMEM56, TWIST1, ASTN1, DLL3, EFNB3
and FOXL1 were genes associated with a favorable prognosis. Another
prognostic risk model for AML based on 12 FRGS, including 10
high-risk genes (GPX4, CD44, CISD1, SESN2, LPCAT3, AIFM2, AKR1C2,
SOCS1, ACSL5 and HSPB1) and two protective genes (ACSL6 and G3BP1)
(100), showed that these genes
served an important role in regulating ferroptosis and tumor
development (101). In
vitro research demonstrated that HIVEP3 was a factor in
ferroptosis. Using a LASSO model, the integration of HIVEP3 with
AIFM2 and LPCAT3 increased the precision of HIVEP3 for predicting a
worse prognosis in patients with AML (102). In recent years, the function of
these genes and their importance in cancer prognosis have become a
focus of increased research. These studies contribute to the
understanding of the molecular mechanisms of cancer and may guide
future treatment strategies.
DNAJB6 acts as a molecular chaperone protein that
functions with Hsp70 to ensure the correct folding of proteins
(103). The naturally increased
expression of DNAJB6 has been found to decrease GPX4 activity,
leading to an increase in ferroptosis. In certain types of cancer,
such as esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, downregulated DNAJB6
expression levels have been associated with anticancer effects.
Conversely, in AML, low DNAJB6 expression levels were associated
with an improved prognosis, which suggested that it may act as a
protective factor (104). DNAJB6
is a member of the small heat shock protein family, and as such,
HSPB1 is involved in regulating cytoskeletal organization and
preventing the aggregation of abnormally folded proteins (105). In breast cancer, non-small cell
lung cancer, gastric cancer, and prostate cancer, aberrant
expression levels of HSPB1 have been associated with aggressive
tumor behavior, chemotherapy resistance, and poor prognosis.
However, in AML, HSPB1 expression levels are downregulated and are
considered a negative prognostic factor, based on hazard ratio
analysis. The phosphorylated form of HSPB1 has been shown to
inhibit apoptosis and induce autophagy, while reducing cellular
iron uptake and lipid ROS production, which may serve protective
roles in AML (106).
As an antioxidant enzyme, AIFM2 operates in
conjunction with GPX4 and GSH to inhibit phospholipid peroxidation
and prevent ferroptosis (95,107).
In certain types of cancer, such as cervical cancer and
hepatocellular carcinoma, the expression levels of AIFM2 have been
associated with a reduction in tumor formation (108). As a crucial rate-limiting enzyme
in cholesterol metabolism, SQLE activity is positively correlated
with the proliferation and metastasis of various types of cancers
and may impact tumor prognosis (109). Its high expression is typically
associated with poor prognosis. The enzyme PGD mediates the pentose
phosphate pathway and is often upregulated in certain types of
tumors, such as glioblastoma and breast cancer. It potentially
promotes the proliferation and survival of tumor cells by modifying
their energy metabolism (110).
ACSF2 is an acyl-CoA synthetase whose role in AML is unknown, but
has been found to correlate with prognosis in other diseases. For
example, in hepatocellular carcinoma, high expression of ACSF2 is
associated with shorter overall survival and relapse-free survival,
predicting worsening prognostics. In contrast, in diabetic
nephropathy, increased expression of ACSF2 is associated with
tubular damage and predicts disease progressibility. The mechanisms
and effects of this enzyme in different diseases are still being
studied, but its importance in prognosis has attracted widespread
attention (96,111). CHAC1 is suggested to regulate
ferroptosis by influencing intracellular GSH levels (112). CISD1 participates in intracellular
iron accumulation and oxidative damage, and may potentially affect
ferroptosis (113). Specifically,
CHAC1, as part of the endoplasmic reticulum stress response
pathway, induces ferroptosis by regulating glutathione depletion,
promoting intracellular iron accumulation and lipid peroxidation.
DPP4 has been suggested to regulate ferroptosis by impacting
membrane-associated lipid peroxidation processes. GPX, which
functions as an antioxidant enzyme, directly inhibits lipid
peroxidation and prevents ferroptosis (114).
Twist-related protein 1 (TWIST), as a pivotal factor
in cell transformation, plays a crucial role in the process of
normal cells becoming cancerous. Studies have reported that its
activity can regulate the cell cycle process in AML cells,
enhancing their responsiveness to chemotherapy drugs and increasing
the sensitivity of AML patients to treatment, ultimately improving
prognosis. Research on TWIST1 in AML primarily focuses on
laboratory studies conducted in cell and animal models (115). As an unconventional ligand in the
Notch signaling pathway, the upregulation of DLL3 may exert a
regulatory effect on the growth and division process of AML cells,
which in certain cases is associated with improved survival
(116). For instance, in SCLC,
high expression of DLL3 has been linked to the responsiveness of
certain treatments. Specifically, DLL3-targeted therapies, such as
antibody-drug conjugates and T-cell engagers, have shown promising
efficacy in clinical trials against tumors with high DLL3
expression (117). LGALS1 is
commonly associated with the immunomodulatory function of cells.
Research has shown that its expression may support AML cells in
evading immune system surveillance and may be linked to increased
drug resistance, leading to a poor prognosis (118,119).
Studies have confirmed that PHKG2′s role in
regulating polyunsaturated fatty acid peroxidation could impact the
sensitivity of cells to ferroptosis inducers, such as Erastin, and
potentially affect the ferroptosis process (120). HSD17B11, an enzyme that
participates in the reduction or oxidation of sex hormones, may be
involved in the regulation of ferroptosis in RSL3-resistant cells
(121). Six-transmembrane
epithelial antigen of prostate 3 (STEAP3), a metal reductase, can
convert iron from Fe3+ to Fe2+ and is
involved in the transcription of cell death genes and regulation of
ferroptosis, particularly through its role in p53-mediated
processes (122). HRAS, an
important member of the cell signaling network, may enhance the
sensitivity of AML patients to cytarabine (123). Through high-throughput drug
screening and single-cell genomic analysis, studies have found that
HRAS mutations are associated with the sensitivity to certain
drugs, such as cytarabine (124).
These studies suggest that HRAS mutations may enhance the response
of AML cells to cytarabine by altering cell signaling pathways.
However, their impact on ferroptosis inducers may vary between
different types of cancers. For example, in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma, KRAS mutations are the most common early genetic
alterations and are closely associated with ferroptosis sensitivity
(125). On the other hand, in
NSCLC, patients with KRAS mutations show lower responsiveness to
ferroptosis inducers (126). ARNTL
inhibits ferroptosis by suppressing EGLN2 transcription and
activating the pro-survival transcription factor HIF1A, and
upregulation of ARNTL can increase susceptibility to anticancer
drugs (127). SLC38A1, a mediator
of glutamine uptake and lipid peroxidation metabolism, is important
for iron apoptosis and high expression levels of SLC38A1 have been
associated with a poor prognosis for patients with AML (128).
LPCAT3, a key player in the ferroptosis mechanism of
cells, facilitates the incorporation of PUFAs into phospholipids,
which are essential substrates for lipid peroxidation in
ferroptosis (129). Inhibition of
LPCAT3 reduced lipid peroxidation, which lead to reduced
sensitivity of cells to ferroptosis inducers, such as RSL3 and
Erastin (130). Consequently, the
regulation of LPCAT3 may significantly impact the occurrence of
ferroptosis in patients with AML and potentially serve as a novel
therapeutic target for AML treatment. These findings provide
promising research directions for the treatment of AML.
FRGs are a major focus of current research on the
prognosis of patients with AML as an independent prognostic factor.
Further research is required to determine whether the evaluation of
FRGs paired with other dysregulated molecular mechanisms may
increase the accuracy of predictive models.
Future perspective and conclusion
In contrast with apoptotic, necrotic and autophagic
cell death, ferroptosis is an iron-dependent mode of programmed
cell death, more recently identified. Since Dixon et al
(12) initially described
ferroptosis in 2012, an increasing body of data has indicated that
ferroptosis is directly linked to the incidence, progression and
inhibition of several diseases, however research remains limited
regarding its role in AML (131).
The present review discusses the primary mechanisms
of ferroptosis and its role in the prognosis and targeted therapy
of AML. In the study of AML, ferroptosis is considered to be a
complex process involving several signaling pathways, including the
GSH/GPX4 pathway, iron metabolism, lipid metabolism and AMPK
signaling. As AML cells can escape ferroptosis through several
pathways, future treatment strategies should target multiple
pathways to ensure that ferroptosis can effectively occur. Certain
existing compounds, such as APR-246 and ATPR, have shown potential
in inducing ferroptosis in AML cells, but the interaction of
ferroptosis with other cell death pathways, such as autophagy and
chemotherapy resistance, should also be considered. Advances in
nanotechnology offer novel opportunities to precisely target AML
cells, potentially inducing ferroptosis while reducing adverse
reactions. Through the establishment of a genetic prognostic risk
model, the search for FRGs that are closely related to AML may help
predict the prognosis of AML and may improve the clinical
application of ferroptosis treatment. However, the current
understanding of ferroptosis mechanisms and drug resistance in AML
remains incomplete, and the targeting of ferroptosis, through the
use of small molecule inhibitors, natural compounds and drug
nano-administration, provides novel research directions and
therapeutic possibilities for the treatment of AML.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation
of Shandong Province (grant nos. ZR2022MH310 and ZR2023MH376).
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
WZ drafted the manuscript. WW, MZ, TZ, HC and RT
contributed to the acquisition, analysis and interpretation of
data. XF and JW revised the manuscript. All authors read and
approved the final manuscript. Data authentication is not
applicable.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
Glossary
Abbreviations
Abbreviations:
|
GSH
|
glutathione
|
|
GPX4
|
glutathione peroxidase 4
|
|
Nrf2
|
nuclear factor erythroid 2-related
factor 2
|
|
AMP
|
adenosine 5′-monophosphate
|
|
AMPK
|
AMP-activated protein kinase
|
|
MVA pathway
|
mevalonate pathway
|
|
HMG-CoA
|
hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA
|
|
Acetyl-CoA
|
acetyl coenzyme A
|
|
IPP
|
isopentenyl pyrophosphate
|
|
DMAPP
|
dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
|
|
LIP
|
labile iron pool
|
|
FPN
|
ferroportin
|
|
FTH1
|
ferritin heavy chain 1
|
|
FT
|
ferritin light chain
|
|
TRSP
|
selenocysteine-specific transfer
RNA
|
|
FSP1
|
ferroptosis suppressor protein 1
|
|
HO-1
|
heme oxygenase 1
|
|
SLC25A28
|
solute carrier family 25 member
28
|
|
TfR1
|
transferrin receptor 1
|
|
NCOA4
|
nuclear receptor coactivator 4
|
|
IREB2
|
iron responsive element binding
protein 2
|
|
HSPB1
|
heat shock protein family B (small)
member 1
|
|
STEAP3
|
six-transmembrane epithelial antigen
of prostate 3
|
|
DMT1
|
divalent metal transporter 1
|
|
Keap1
|
ECH associated protein
|
|
SAT1
|
spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1
|
|
ALOX15
|
arachidonate-15-lipoxygenase
|
|
GLS2
|
glutaminase
|
|
AA
|
arachidonic acid
|
|
AdA
|
adrenoyl derivatives
|
|
PE-AA/AdA
|
phosphatidylethanolamines
|
|
PUFAs
|
polyunsaturated fatty acids
|
|
BECN1
|
beclin 1
|
|
SLC7A11
|
solute carrier family 7 member 11
|
|
ROS
|
reactive oxygen species
|
|
APR-246
|
Eprenetapopt
|
|
ALDH3A2
|
aldehyde dehydrogenase 3 family
member A2
|
|
circKDM4C
|
circular RNA derived from the KDM4C
gene
|
|
GCMNPs
|
poly(lactic acid)-glycolic
acid-encapsulated glycyrrhetinic acids
|
|
TYP
|
typhaneoside
|
|
HMOX1
|
heme oxygenase 1
|
|
HMGB1
|
high mobility group box 1
|
|
DHA
|
dihydroartemisinin
|
|
GNPIPP12MA
|
glutathione-bioimprinted
nanoparticles targeting N6-methyladenosine FTO demethylase
|
|
GnRA-CSP12
|
gold nanorods functionalized with
chitosan and a 12-mer peptide12
|
|
RSL3
|
RAS-selective lethal
|
|
ATRA
|
all-trans retinoic acid
|
|
ATPR
|
4-amino-2-trifluoromethyl-phenyl
retinate
|
|
FRG
|
ferroptosis-related genes
|
|
DNAJB6
|
DNAJ heat shock protein family member
B6
|
|
TWIST
|
twist-related protein 1
|
|
LPCAT3
|
lysophospholipid acyltransferase
|
References
|
1
|
Medinger M, Heim D, Halter JP, Lengerke C
and Passweg JR: Diagnosis and therapy of acute myeloid leukemia.
Ther Umsch. 76:481–486. 2019.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pelcovits A and Niroula R: Acute myeloid
leukemia: A review. R I Med J. 103:38–40. 2020.
|
|
3
|
Shimony S, Stahl M and Stone RM: Acute
myeloid leukemia: 2023 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification,
and management. Am J Hematol. 98:502–526. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ren Y, Mao X, Xu H, Dang Q, Weng S, Zhang
Y, Chen S, Liu S, Ba Y, Zhou Z, et al: Ferroptosis and EMT: Key
targets for combating cancer progression and therapy resistance.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 80:2632023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang C, Liu X, Jin S, Chen Y and Guo R:
Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: A novel approach to reversing drug
resistance. Mol Cancer. 21:472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J, He D, Zhang C, Duan C
and Li B: Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: Opportunities and
challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 12:342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lei G, Zhuang L and Gan B: Targeting
ferroptosis as a vulnerability in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
22:381–396. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liang C, Zhang X, Yang M and Dong X:
Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. Adv
Mater. 31:e19041972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liang D, Minikes AM and Jiang X:
Ferroptosis at the intersection of lipid metabolism and cellular
signaling. Mol Cell. 82:2215–2227. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Balihodzic A, Prinz F, Dengler MA, Calin
GA, Jost PJ and Pichler M: Non-coding RNAs and ferroptosis:
Potential implications for cancer therapy. Cell Death Differ.
29:1094–1106. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hirschhorn T and Stockwell BR: The
development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
133:130–143. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11:882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stockwell BR, Jiang X and Gu W: Emerging
mechanisms and disease relevance of ferroptosis. Trends Cell Biol.
30:478–490. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ and Tang
D: Ferroptosis: Machinery and regulation. Autophagy. 17:2054–2081.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Su Y, Zhao B, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Lv
H, AlQudsy LHH and Shang P: Ferroptosis, a novel pharmacological
mechanism of anti-cancer drugs. Cancer Lett. 483:127–136. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miotto G, Rossetto M, Di Paolo ML, Orian
L, Venerando R, Roveri A, Vučković AM, Bosello Travain V, Zaccarin
M, Zennaro L, et al: Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis
inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol. 28:1013282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu T, Ding W, Ji X, Ao X, Liu Y, Yu W and
Wang J: Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cancer
therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 23:4900–4912. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R and Kroemer G:
Ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell
Res. 31:107–125. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu Y, Wan Y, Jiang Y, Zhang L and Cheng
W: GPX4: The hub of lipid oxidation, ferroptosis, disease and
treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1878:1888902023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Forcina GC and Dixon SJ: GPX4 at the
crossroads of lipid homeostasis and ferroptosis. Proteomics.
19:e18003112019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xing K, Bian X, Shi D, Dong S, Zhou H,
Xiao S, Bai J and Wu W: miR-612 Enhances RSL3-Induced ferroptosis
of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via mevalonate pathway. J
Hepatocell Carcinoma. 10:2173–2185. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ou M, Jiang Y, Ji Y, Zhou Q, Du Z, Zhu H
and Zhou Z: Role and mechanism of ferroptosis in neurological
diseases. Mol Metab. 61:1015022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Noe R, Inglese N, Romani P, Serafini T,
Paoli C, Calciolari B, Fantuz M, Zamborlin A, Surdo NC, Spada V, et
al: Organic Selenium induces ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer
cells. Redox Biol. 68:1029622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng J and Conrad M: The metabolic
underpinnings of ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 32:920–937. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xia J, Si H, Yao W, Li C, Yang G, Tian Y
and Hao C: Research progress on the mechanism of ferroptosis and
its clinical application. Exp Cell Res. 409:1129322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Liu J, Zhang C, Wang J, Hu W and Feng Z:
The regulation of ferroptosis by tumor suppressor p53 and its
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 21:83872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lei P, Bai T and Sun Y: Mechanisms of
ferroptosis and relations with regulated cell death: A Review.
Front Physiol. 10:1392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu R, Wang W and Zhang W: Ferroptosis and
the bidirectional regulatory factor p53. Cell Death Discov.
9:1972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang H, Guo M, Wei H and Chen Y: Targeting
p53 pathways: Mechanisms, structures, and advances in therapy.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park E and Chung SW: ROS-mediated
autophagy increases intracellular iron levels and ferroptosis by
ferritin and transferrin receptor regulation. Cell Death Dis.
10:8222019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis turns 10:
Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic
applications. Cell. 185:2401–2421. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fuhrmann DC and Brune B: A graphical
journey through iron metabolism, microRNAs, and hypoxia in
ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 54:1023652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bayir H, Dixon SJ, Tyurina YY, Kellum JA
and Kagan VE: Ferroptotic mechanisms and therapeutic targeting of
iron metabolism and lipid peroxidation in the kidney. Nat Rev
Nephrol. 19:315–336. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R
and Tang D: Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects
against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology.
63:173–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li D and Li Y: The interaction between
ferroptosis and lipid metabolism in cancer. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 5:1082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zheng XJ, Chen WL, Yi J, Li W, Liu JY, Fu
WQ, Ren LW, Li S, Ge BB, Yang YH, et al: Apolipoprotein C1 promotes
glioblastoma tumorigenesis by reducing KEAP1/NRF2 and CBS-regulated
ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 43:2977–2992. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zheng XJ, Chen WL, Yi J, Li W, Liu JY, Fu
WQ, Ren LW, Li S, Ge BB, Yang YH, et al: Author Correction:
Apolipoprotein C1 promotes glioblastoma tumorigenesis by reducing
KEAP1/NRF2 and CBS-regulated ferroptosis. Acta Pharmacol Sin. May
13–2024.doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01271-2 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
39
|
Zimta AA, Cenariu D, Irimie A, Magdo L,
Nabavi SM, Atanasov AG and Berindan-Neagoe I: The role of Nrf2
activity in cancer development and progression. Cancers (Basel).
11:17552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Grignano E, Birsen R, Chapuis N and
Bouscary D: From iron chelation to overload as a therapeutic
strategy to induce ferroptosis in leukemic cells. Front Oncol.
10:5865302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zeng F, Nijiati S, Tang L, Ye J, Zhou Z
and Chen X: Ferroptosis detection: From approaches to applications.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 62:e2023003792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang D:
Broadening horizons: The role of ferroptosis in cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 18:280–296. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Koppula P, Zhuang L and Gan B: Cystine
transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: Ferroptosis, nutrient
dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell. 12:599–620. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun X, Ou Z, Xie M, Kang R, Fan Y, Niu X,
Wang H, Cao L and Tang D: HSPB1 as a novel regulator of ferroptotic
cancer cell death. Oncogene. 34:5617–5625. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Y and Gu W: p53 in ferroptosis
regulation: The new weapon for the old guardian. Cell Death Differ.
29:895–910. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gong D, Chen M, Wang Y, Shi J and Hou Y:
Role of ferroptosis on tumor progression and immunotherapy. Cell
Death Discov. 8:4272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu Y and Gu W: The complexity of
p53-mediated metabolic regulation in tumor suppression. Semin
Cancer Biol. 85:4–32. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gao Y, Zhang H, Wang J, Li F, Li X, Li T,
Wang C, Li L, Peng R, Liu L, et al: Annexin A5 ameliorates
traumatic brain injury-induced neuroinflammation and neuronal
ferroptosis by modulating the NF-kB/HMGB1 and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways.
Int Immunopharmacol. 114:1096192023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ursini F and Maiorino M: Lipid
peroxidation and ferroptosis: The role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic
Biol Med. 152:175–185. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pope LE and Dixon SJ: Regulation of
ferroptosis by lipid metabolism. Trends Cell Biol. 33:1077–1087.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao L, Zhou X, Xie F and Zhang L, Yan H,
Huang J, Zhang C, Zhou F, Chen J and Zhang L: Ferroptosis in cancer
and cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Commun (Lond). 42:88–116. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lee H, Zandkarimi F, Zhang Y, Meena JK,
Kim J, Zhuang L, Tyagi S, Ma L, Westbrook TF, Steinberg GR, et al:
Energy-stress-mediated AMPK activation inhibits ferroptosis. Nat
Cell Biol. 22:225–234. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Song X, Zhu S, Chen P, Hou W, Wen Q, Liu
J, Xie Y, Liu J, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, et al: AMPK-Mediated BECN1
phosphorylation promotes ferroptosis by directly blocking system
Xc-Activity. Curr Biol. 28:2388–2399. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Winer ES: Secondary acute myeloid
leukemia: A primary challenge of diagnosis and treatment. Hematol
Oncol Clin North Am. 34:449–463. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Su Y, Zhao B, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Shen Y, Lv
H, AlQudsy LHH and Shang P: Ferroptosis, a novel pharmacological
mechanism of anti-cancer drugs. Cancer Lett. 483:127–136. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Farge T, Saland E, de Toni F, Aroua N,
Hosseini M, Perry R, Bosc C, Sugita M, Stuani L, Fraisse M, et al:
Chemotherapy-Resistant human acute myeloid leukemia cells are not
enriched for leukemic stem cells but require oxidative metabolism.
Cancer Discov. 7:716–735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Akiyama H, Zhao R, Ostermann LB, Li Z,
Tcheng M, Yazdani SJ, Moayed A, Pryor ML II, Slngh S, Baran N, et
al: Correction: Mitochondrial regulation of GPX4
inhibition-mediated ferroptosis in acute myeloid leukemia.
Leukemia. 38:9262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Auberger P, Favreau C, Savy C, Jacquel A
and Robert G: Emerging role of glutathione peroxidase 4 in myeloid
cell lineage development and acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Mol Biol
Lett. 29:982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhong X, Zhang Z, Shen H, Xiong Y, Shah
YM, Liu Y, Fan XG and Rui L: Hepatic NF-κB-Inducing kinase and
inhibitor of NF-κB kinase subunit α promote liver oxidative stress,
ferroptosis, and liver injury. Hepatol Commun. 5:1704–1720. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Rushworth SA, Zaitseva L, Murray MY, Shah
NM, Bowles KM and MacEwan DJ: The high Nrf2 expression in human
acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-κB and underlies its
chemo-resistance. Blood. 120:5188–5198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Akiyama H, Zhao R, Ostermann LB, Li Z,
Tcheng M, Yazdani SJ, Moayed A, Pryor ML II, Slngh S, Baran N, et
al: Mitochondrial regulation of GPX4 inhibition-mediated
ferroptosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 38:729–740. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pabst T, Kortz L, Fiedler GM, Ceglarek U,
Idle JR and Beyoğlu D: The plasma lipidome in acute myeloid
leukemia at diagnosis in relation to clinical disease features. BBA
Clin. 7:105–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Strickland SA and Vey N: Diagnosis and
treatment of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 171:1036072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Roberts MD, Langston AA and Heffner LJ:
Acute myeloid leukemia in young adults: Does everyone need a
transplant? J Oncol Pract. 15:315–320. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Barriga F, Ramirez P, Wietstruck A and
Rojas N: Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Clinical use and
perspectives. Biol Res. 45:307–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Birsen R, Larrue C, Decroocq J, Johnson N,
Guiraud N, Gotanegre M, Cantero-Aguilar L, Grignano E, Huynh T,
Fontenay M, et al: APR-246 induces early cell death by ferroptosis
in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 107:403–416. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Yusuf RZ, Saez B, Sharda A, van Gastel N,
Yu VWC, Baryawno N, Scadden EW, Acharya S, Chattophadhyay S, Huang
C, et al: Aldehyde dehydrogenase 3a2 protects AML cells from
oxidative death and the synthetic lethality of ferroptosis
inducers. Blood. 136:1303–1316. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li Q, Su R, Bao X, Cao K, Du Y, Wang N,
Wang J, Xing F, Yan F, Huang K and Feng S: Glycyrrhetinic acid
nanoparticles combined with ferrotherapy for improved cancer
immunotherapy. Acta Biomater. 144:109–120. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Cao K, Du Y, Bao X, Han M, Su R, Pang J,
Liu S, Shi Z, Yan F and Feng S: Glutathione-Bioimprinted
nanoparticles targeting of N6-methyladenosine FTO Demethylase as a
strategy against leukemic stem cells. Small. 18:e21065582022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Peng X, Zhang MQ, Conserva F, Hosny G,
Selivanova G, Bykov VJ, Arnér ES and Wiman KG: APR-246/PRIMA-1MET
inhibits thioredoxin reductase 1 and converts the enzyme to a
dedicated NADPH oxidase. Cell Death Dis. 4:e8812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ali D, Jonsson-Videsater K, Deneberg S,
Bengtzén S, Nahi H, Paul C and Lehmann S: APR-246 exhibits
anti-leukemic activity and synergism with conventional
chemotherapeutic drugs in acute myeloid leukemia cells. Eur J
Haematol. 86:206–215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sallman DA, DeZern AE, Garcia-Manero G,
Steensma DP, Roboz GJ, Sekeres MA, Cluzeau T, Sweet KL, McLemore A,
McGraw KL, et al: Eprenetapopt (APR-246) and azacitidine in
TP53-Mutant myelodysplastic syndromes. J Clin Oncol. 39:1584–1594.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang Y, Tang B, Zhu J, Yu J, Hui J, Xia S
and Ji J: Emerging mechanisms and targeted therapy of ferroptosis
in neurological diseases and Neuro-oncology. Int J Biol Sci.
18:4260–4274. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dong LH, Huang JJ, Zu P, Liu J, Gao X, Du
JW and Li YF: CircKDM4C upregulates P53 by sponging hsa-let-7b-5p
to induce ferroptosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Environ Toxicol.
36:1288–1302. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kang R, Kroemer G and Tang D: The tumor
suppressor protein p53 and the ferroptosis network. Free Radic Biol
Med. 133:162–168. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yu Y, Meng Y, Xu X, Tong T, He C, Wang L,
Wang K, Zhao M, You X, Zhang W, et al: A Ferroptosis-inducing and
leukemic cell-Targeting drug nanocarrier formed by Redox-Responsive
cysteine polymer for acute myeloid leukemia therapy. ACS Nano.
17:3334–3345. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lang X, Green MD, Wang W, Yu J, Choi JE,
Jiang L, Liao P, Zhou J, Zhang Q, Dow A, et al: Radiotherapy and
immunotherapy promote tumoral lipid oxidation and ferroptosis via
synergistic repression of SLC7A11. Cancer Discov. 9:1673–1685.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xu H, Ye D, Ren M, Zhang H and Bi F:
Ferroptosis in the tumor microenvironment: Perspectives for
immunotherapy. Trends Mol Med. 27:856–867. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Su R, Dong L, Li Y, Gao M, Han L,
Wunderlich M, Deng X, Li H, Huang Y, Gao L, et al: Targeting FTO
suppresses cancer stem cell maintenance and immune evasion. Cancer
Cell. 38:79–96. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Du Y, Han M, Cao K, Li Q, Pang J, Dou L,
Liu S, Shi Z, Yan F and Feng S: Gold nanorods exhibit intrinsic
therapeutic activity via controlling N6-methyladenosine-based
Epitranscriptomics in acute myeloid leukemia. ACS Nano.
15:17689–17704. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wen Q, Liu J, Kang R, Zhou B and Tang D:
The release and activity of HMGB1 in ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 510:278–283. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chen GQ, Benthani FA, Wu J, Liang D, Bian
ZX and Jiang X: Artemisinin compounds sensitize cancer cells to
ferroptosis by regulating iron homeostasis. Cell Death Differ.
27:242–254. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhu HY, Huang ZX, Chen GQ, Sheng F and
Zheng YS: Typhaneoside prevents acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
through suppressing proliferation and inducing ferroptosis
associated with autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
516:1265–1271. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Du Y, Bao J, Zhang MJ, Li LL, Xu XL, Chen
H, Feng YB, Peng XQ and Chen FH: Targeting ferroptosis contributes
to ATPR-induced AML differentiation via ROS-autophagy-lysosomal
pathway. Gene. 755:1448892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Bruedigam C, Porter AH, Song A, Vroeg In
de Wei G, Stoll T, Straube J, Cooper L, Cheng G, Kahl VFS, Sobinoff
AP, et al: Imetelstat-mediated alterations in fatty acid metabolism
to induce ferroptosis as a therapeutic strategy for acute myeloid
leukemia. Nat Cancer. 5:47–65. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lai X, Sun Y, Zhang X, Wang D, Wang J,
Wang H, Zhao Y, Liu X, Xu X, Song H, et al: Honokiol induces
ferroptosis by upregulating HMOX1 in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Front Pharmacol. 13:8977912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Gan B: How erastin assassinates cells by
ferroptosis revealed. Protein Cell. 14:84–86. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Yu Y, Xie Y, Cao L, Yang L, Yang M, Lotze
MT, Zeh HJ, Kang R and Tang D: The ferroptosis inducer erastin
enhances sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells to
chemotherapeutic agents. Mol Cell Oncol. 2:e10545492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Ye F, Chai W, Xie M, Yang M, Yu Y, Cao L
and Yang L: HMGB1 regulates erastin-induced ferroptosis via
RAS-JNK/p38 signaling in HL-60/NRAS(Q61L) cells. Am J Cancer Res.
9:730–739. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Du J, Wang T, Li Y, Zhou Y, Wang X, Yu X,
Ren X, An Y, Wu Y, Sun W, et al: DHA inhibits proliferation and
induces ferroptosis of leukemia cells through autophagy dependent
degradation of ferritin. Free Radic Biol Med. 131:356–369. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Nishizawa H, Yamanaka M and Igarashi K:
Ferroptosis: Regulation by competition between NRF2 and BACH1 and
propagation of the death signal. FEBS J. 290:1688–1704. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Du Y, Zhang MJ, Li LL, Xu XL, Chen H, Feng
YB, Li Y, Peng XQ and Chen FH: ATPR triggers acute myeloid
leukaemia cells differentiation and cycle arrest via the
RARalpha/LDHB/ERK-glycolysis signalling axis. J Cell Mol Med.
24:6952–6965. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Pelcovits A and Niroula R: Acute myeloid
leukemia: A review. R I Med J (2013). 103:38–40. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yin Z, Li F, Zhou Q, Zhu J, Liu Z, Huang
J, Shen H, Ou R, Zhu Y, Zhang Q and Liu S: A ferroptosis-related
gene signature and immune infiltration patterns predict the overall
survival in acute myeloid leukemia patients. Front Mol Biosci.
9:9597382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Prada-Arismendy J, Arroyave JC and
Rothlisberger S: Molecular biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia.
Blood Rev. 31:63–76. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Han C, Zheng J, Li F, Guo W and Cai C:
Novel prognostic signature for acute myeloid leukemia:
Bioinformatics analysis of combined CNV-driven and
ferroptosis-related genes. Front Genet. 13:8494372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Song Y, Tian S, Zhang P, Zhang N, Shen Y
and Deng J: Construction and validation of a novel
Ferroptosis-Related prognostic model for acute myeloid leukemia.
Front Genet. 12:7086992022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Wei J, Xie Q, Liu X, Wan C, Wu W, Fang K,
Yao Y, Cheng P, Deng D and Liu Z: Identification the prognostic
value of glutathione peroxidases expression levels in acute myeloid
leukemia. Ann Transl Med. 8:6782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Chen Z, Wu T, Yan Z and Zhang M:
Identification and validation of an 11-Ferroptosis related gene
signature and its correlation with immune checkpoint molecules in
glioma. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6525992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Huang X, Zhou D, Ye X and Jin J: A novel
ferroptosis-related gene signature can predict prognosis and
influence immune microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia. Bosn J
Basic Med Sci. 22:608–628. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Zhu L, Yang F, Wang L, Dong L, Huang Z,
Wang G, Chen G and Li Q: Identification the ferroptosis-related
gene signature in patients with esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Cell Int. 21:1242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Zhang X, Zhang X, Liu K, Li W, Wang J, Liu
P and Ma W: HIVEP3 cooperates with ferroptosis gene signatures to
confer adverse prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Med.
11:5050–5065. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Jiang B, Zhao Y, Shi M, Song L, Wang Q,
Qin Q, Song X, Wu S, Fang Z and Liu X: DNAJB6 promotes ferroptosis
in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 65:1999–2008.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Meng E, Shevde LA and Samant RS:
Retraction: Emerging roles and underlying molecular mechanisms of
DNAJB6 in cancer. Oncotarget. 14:6692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Liang Y, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Ye F, Luo D, Li
Y, Jin Y, Han D, Wang Z, Chen B, et al: HSPB1 facilitates
chemoresistance through inhibiting ferroptotic cancer cell death
and regulating NF-κB signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Death
Dis. 14:4342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yan XS, Sun YJ, Du J, Niu WY, Qiao H and
Yin XC: Effects of ferroptosis-related gene HSPB1 on acute myeloid
leukemia. Int J Lab Hematol. June 2–2024.(Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Ma Z, Ye W, Huang X, Li X, Li F, Lin X, Hu
C, Wang J, Jin J, Zhu B and Huang J: The ferroptosis landscape in
acute myeloid leukemia. Aging (Albany NY). 15:13486–13503. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Guo S, Li F, Liang Y, Zheng Y, Mo Y, Zhao
D, Jiang Z, Cui M, Qi L, Chen J, et al: AIFM2 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by enhancing mitochondrial
biogenesis through activation of SIRT1/PGC-1α signaling.
Oncogenesis. 12:462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Sun Q, Liu D, Cui W, Cheng H, Huang L,
Zhang R, Gu J, Liu S, Zhuang X, Lu Y, et al: Cholesterol mediated
ferroptosis suppression reveals essential roles of Coenzyme Q and
squalene. Commun Biol. 6:11082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Shi J, Wu P, Sheng L, Sun W and Zhang H:
Ferroptosis-related gene signature predicts the prognosis of
papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 21:6692021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Song Y, Tian S, Zhang P, Zhang N, Shen Y
and Deng J: Construction and validation of a novel
Ferroptosis-Related Prognostic model for acute myeloid leukemia.
Front Genet. 12:7086992021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Dixon SJ, Patel DN, Welsch M, Skouta R,
Lee ED, Hayano M, Thomas AG, Gleason CE, Tatonetti NP, Slusher BS
and Stockwell BR: Pharmacological inhibition of Cystine-glutamate
exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis.
Elife. 3:e025232014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhang X, Peng T, Li C, Ai C, Wang X, Lei
X, Li G and Li T: Inhibition of CISD1 alleviates mitochondrial
dysfunction and ferroptosis in mice with acute lung injury. Int
Immunopharmacol. 130:1116852024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Xie Y, Zhu S, Song X, Sun X, Fan Y, Liu J,
Zhong M, Yuan H, Zhang L, Billiar TR, et al: The tumor suppressor
p53 limits ferroptosis by blocking DPP4 activity. Cell Rep.
20:1692–1704. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhang L, Song A, Yang QC, Li SJ, Wang S,
Wan SC, Sun J, Kwok RTK, Lam JWY, Deng H, et al: Integration of
AIEgens into covalent organic frameworks for pyroptosis and
ferroptosis primed cancer immunotherapy. Nat Commun. 14:53552023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wang J, Zhuo Z, Wang Y, Yang S, Chen J,
Wang Y, Geng S, Li M, Du X, Lai P, et al: Identification and
validation of a prognostic Risk-scoring model based on
Ferroptosis-associated cluster in acute myeloid leukemia. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:8002672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Rudin CM, Reck M, Johnson ML, Blackhall F,
Hann CL, Yang JC, Bailis JM, Bebb G, Goldrick A, Umejiego J and
Paz-Ares L: Emerging therapies targeting the delta-like ligand 3
(DLL3) in small cell lung cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 16:662023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Ruvolo PP, Ma H, Ruvolo VR, Zhang X, Post
SM and Andreeff M: LGALS1 acts as a pro-survival molecule in AML.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1867:1187852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Sun J, Lu P, Guan S and Liu S:
Heterogeneity analysis of pancreatic cancer and identification of
molecular subtypes of tumor cells based on CEACAM5, LGALS1 and
CENPF gene expression. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 43:1567–1576.
2023.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhu W, Liu D, Lu Y, Sun J, Zhu J, Xing Y,
Ma X, Wang Y, Ji M and Jia Y: PHKG2 regulates RSL3-induced
ferroptosis in Helicobacter pylori related gastric cancer. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 740:1095602023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Sabatier M, Birsen R, Lauture L, Mouche S,
Angelino P, Dehairs J, Goupille L, Boussaid I, Heiblig M, Boet E,
et al: C/EBPα confers dependence to fatty acid anabolic pathways
and vulnerability to lipid oxidative Stress-Induced ferroptosis in
FLT3-mutant leukemia. Cancer Discov. 13:1720–1747. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Chen X, Hu S, Han Y, Cai Y, Lu T, Hu X,
Chu Y, Zhou X and Wang X: Ferroptosis-related STEAP3 acts as
predictor and regulator in diffuse large B cell lymphoma through
immune infiltration. Clin Exp Med. 23:2601–2617. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Dai E, Han L, Liu J, Xie Y, Zeh HJ, Kang
R, Bai L and Tang D: Ferroptotic damage promotes pancreatic
tumorigenesis through a TMEM173/STING-dependent DNA sensor pathway.
Nat Commun. 11:63392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Sadeghi M, Moslehi A, Kheiry H, Kiani FK,
Zarei A, Khodakarami A, Karpisheh V, Masjedi A, Rahnama B,
Hojjat-Farsangi M, et al: The sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia
cells to cytarabine is increased by suppressing the expression of
Heme oxygenase-1 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha. Cancer Cell
Int. 24:2172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Bartolacci C, Andreani C, El-Gammal Y and
Scaglioni PP: Lipid metabolism regulates oxidative stress and
ferroptosis in RAS-Driven cancers: A perspective on cancer
progression and therapy. Front Mol Biosci. 8:7066502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Diao J, Jia Y, Dai E, Liu J, Kang R, Tang
D, Han L, Zhong Y and Meng L: Ferroptotic therapy in cancer:
Benefits, side effects, and risks. Mol Cancer. 23:892024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Chen X, Song X, Li J, Zhang R, Yu C, Zhou
Z, Liu J, Liao S, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, et al: Identification of
HPCAL1 as a specific autophagy receptor involved in ferroptosis.
Autophagy. 19:54–74. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zhang H and Sun C, Sun Q, Li Y, Zhou C and
Sun C: Susceptibility of acute myeloid leukemia cells to
ferroptosis and evasion strategies. Front Mol Biosci.
10:12757742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Liu J, Kang R and Tang D: Signaling
pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. FEBS J.
289:7038–7050. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Cui J, Wang Y, Tian X, Miao Y, Ma L, Zhang
C, Xu X, Wang J, Fang W and Zhang X: LPCAT3 is transcriptionally
regulated by YAP/ZEB/EP300 and collaborates with ACSL4 and YAP to
determine ferroptosis sensitivity. Antioxid Redox Signal.
39:491–511. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
De Voeght A, Jaspers A, Beguin Y, Baron F
and De Prijck B: Overview of the general management of acute
leukemia for adults. Rev Med Liege. 76:470–475, (In French).
PubMed/NCBI
|















