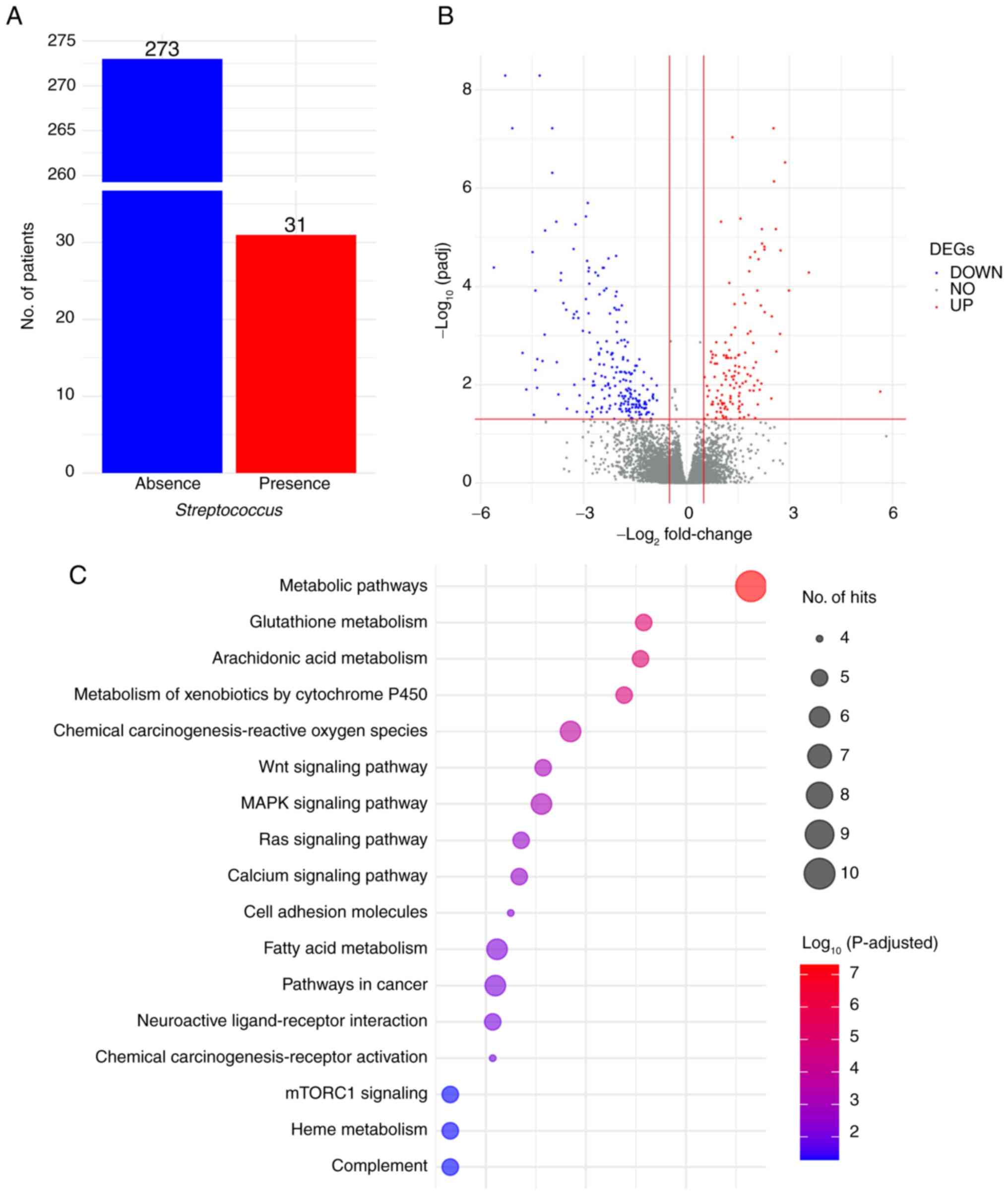
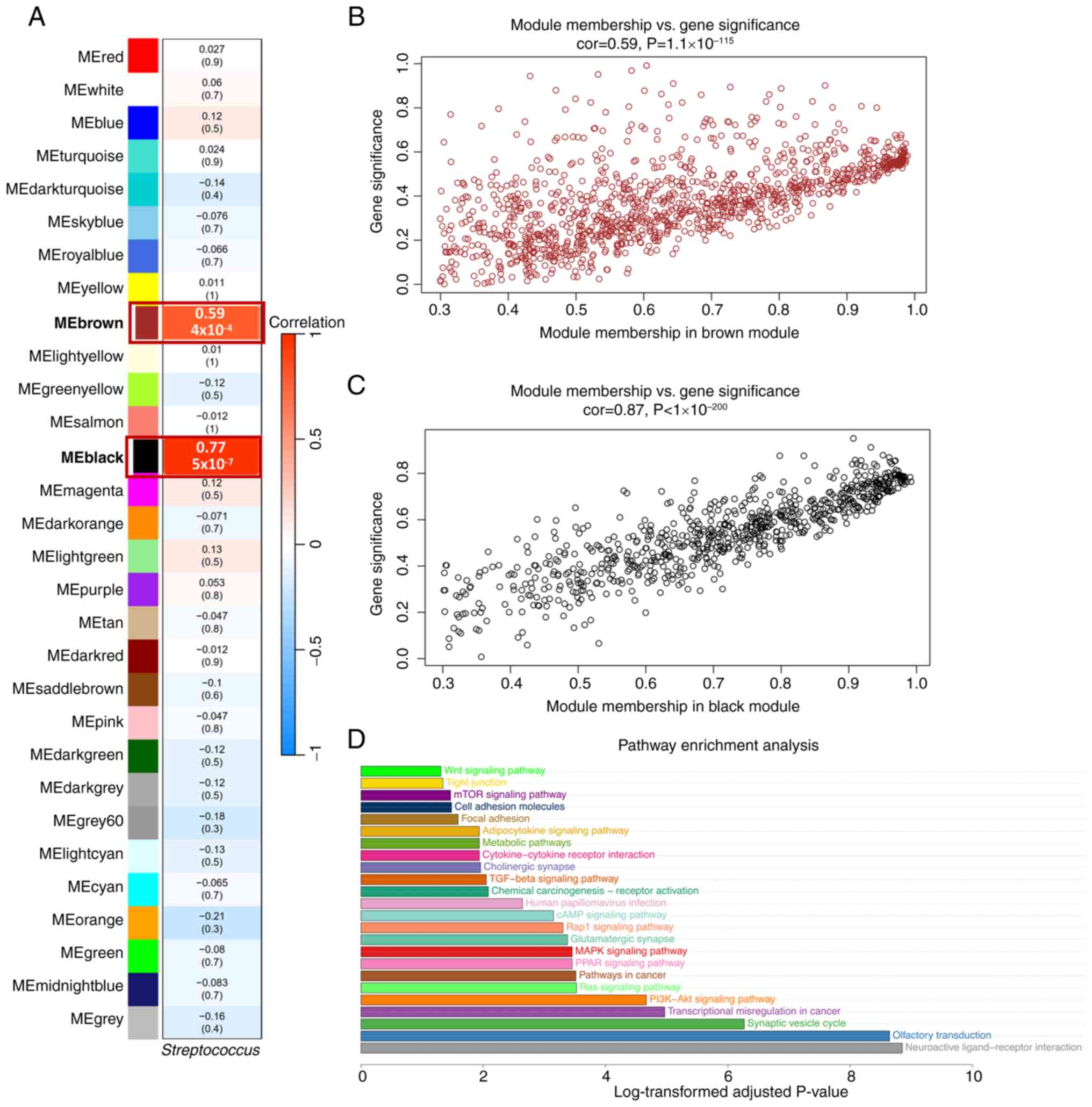
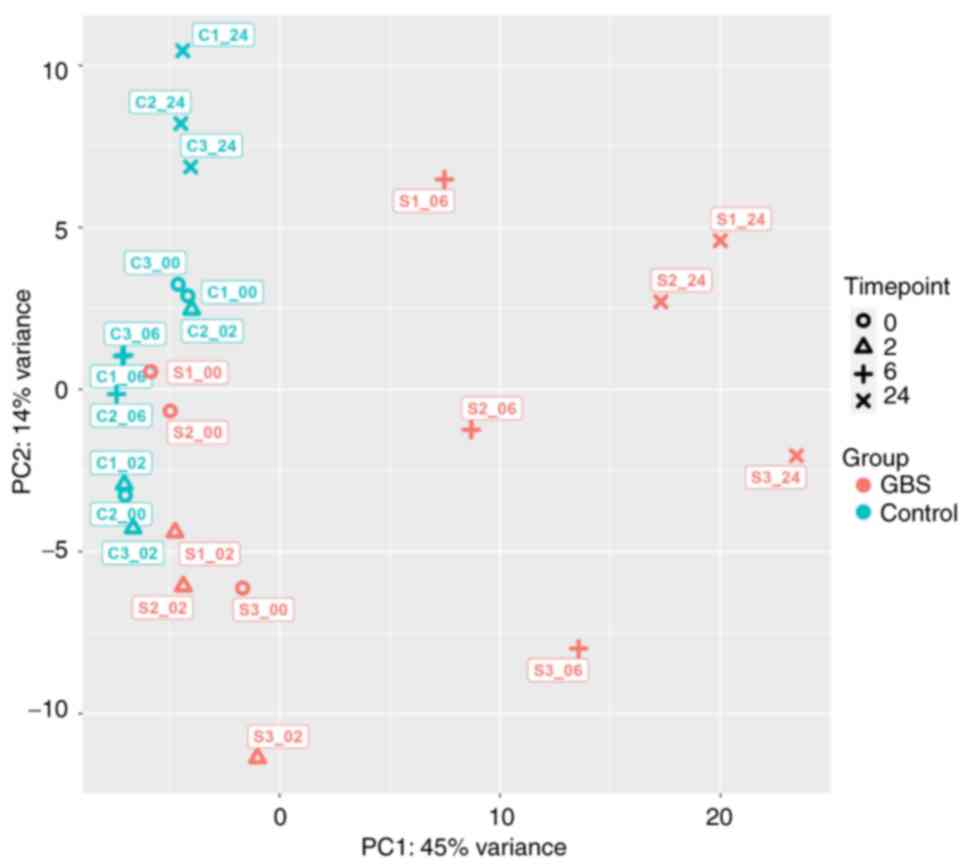
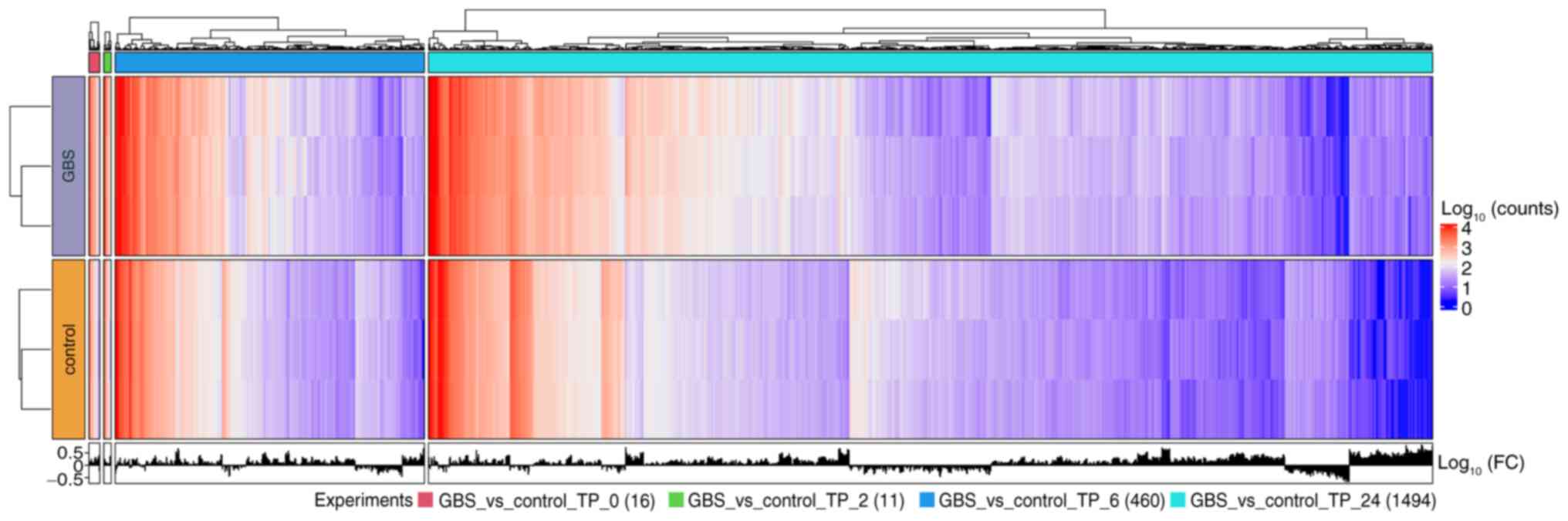
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Burmeister CA, Khan SF, Schäfer G, Mbatani
N, Adams T, Moodley J and Prince S: Cervical cancer therapies:
Current challenges and future perspectives. Tumour Virus Res.
13:2002382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Couvreur K, Naert E, De Jaeghere E,
Tummers P, Makar A, De Visschere P, Van Bockstal M, Van Dorpe J, De
Neve W, Denys H and Vandecasteele K: Neo-adjuvant treatment of
adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix results in
significantly different pathological complete response rates. BMC
Cancer. 18:11012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blake SJ, Wolf Y, Boursi B and Lynn DJ:
Role of the microbiota in response to and recovery from cancer
therapy. Nat Rev Immunol. 24:308–325. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun J, Chen F and Wu G: Potential effects
of gut microbiota on host cancers: Focus on immunity, DNA damage,
cellular pathways, and anticancer therapy. ISME J. 17:1535–1551.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu S, Ding X, Kong Y, Acharya S, Wu H,
Huang C, Liang Y, Nong X and Chen H: The feature of cervical
microbiota associated with the progression of cervical cancer among
reproductive females. Gynecol Oncol. 163:348–357. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tango CN, Seo SS, Kwon M, Lee DO, Chang HK
and Kim MK: Taxonomic and functional differences in cervical
microbiome associated with cervical cancer development. Sci Rep.
10:97202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu X, Zhang Y, Yu L, Shi X, Min M, Xiong
L, Pan J, Liu P, Wu G and Gao G: A cross-sectional analysis about
bacterial vaginosis, high-risk human papillomavirus infection, and
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia in Chinese women. Sci Rep.
12:66092022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Audirac-Chalifour A, Torres-Poveda K,
Bahena-Román M, Téllez-Sosa J, Martínez-Barnetche J,
Cortina-Ceballos B, López-Estrada G, Delgado-Romero K,
Burguete-García AI, Cantú D, et al: Cervical microbiome and
cytokine profile at various stages of cervical cancer: A pilot
study. PLoS One. 11:e01532742016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nguyen HDT, Le TM, Lee E, Lee D, Choi Y,
Cho J, Park NJ, Chong GO, Seo I and Han HS: Relationship between
human papillomavirus status and the cervicovaginal microbiome in
cervical cancer. Microorganisms. 11:14172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu J, Wu Y, Quan L, Yang W, Lang J, Tian G
and Meng B: Research of cervical microbiota alterations with human
papillomavirus infection status and women age in Sanmenxia area of
China. Front Microbiol. 13:10046642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mulato-Briones IB, Rodriguez-Ildefonso IO,
Jiménez-Tenorio JA, Cauich-Sánchez PI, Méndez-Tovar MDS,
Aparicio-Ozores G, Bautista-Hernández MY, González-Parra JF,
Cruz-Hernández J, López-Romero R, et al: Cultivable microbiome
approach applied to cervical cancer exploration. Cancers (Basel).
16:3142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kang GU, Jung DR, Lee YH, Jeon SY, Han HS,
Chong GO and Shin JH: Potential association between vaginal
microbiota and cervical carcinogenesis in korean women: A cohort
study. Microorganisms. 294:2942021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Armistead B, Oler E, Adams Waldorf K and
Rajagopal L: The double life of Group B streptococcus: Asymptomatic
colonizer and potent pathogen. J Mol Biol. 431:2914–2931. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Aksu B and Yanilmaz O: Group B
streptococci induce interleukin 8 production in human cervical
epithelial cell cultures: The role of capsule polysaccharide. Clin
Exp Health Sci. 9:49–52. 2018.
|
|
16
|
Maisey HC, Doran KS and Nizet V: Recent
advances in understanding the molecular basis of group B
Streptococcus virulence. Expert Rev Mol Med. 10:e272008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Patras KA, Rösler B, Thoman ML and Doran
KS: Characterization of host immunity during persistent vaginal
colonization by Group B Streptococcus. Mucosal Immunol.
8:1339–1348. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Patras KA, Wang NY, Fletcher EM, Cavaco
CK, Jimenez A, Garg M, Fierer J, Sheen TR, Rajagopal L and Doran
KS: Group B Streptococcus CovR regulation modulates host immune
signalling pathways to promote vaginal colonization. Cell
Microbiol. 15:1154–1167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang C, Liu Y, Gao W, Pan Y, Gao Y, Shen
J and Xiong H: The direct and indirect association of cervical
microbiota with the risk of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
Cancer Med. 7:2172–2179. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee YH, Kang GU, Jeon SY, Tagele SB, Pham
HQ, Kim MS, Ahmad S, Jung DR, Park YJ, Han HS, et al: Vaginal
microbiome-based bacterial signatures for predicting the severity
of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Diagnostics (Basel).
10:10132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mutz KO, Heilkenbrinker A, Lönne M, Walter
JG and Stahl F: Transcriptome analysis using Next-generation
sequencing. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 24:22–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahmed W: RNA-seq resolving host-pathogen
interactions: Advances and applications. Ecol Genet Genom.
15:1000572020.
|
|
23
|
Nathan S: Transcriptome profiling to
understand Host-bacteria interactions: Past, present and future.
ScienceAsia. 46:503–513. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yip HYK and Papa A: Signaling pathways in
cancer: Therapeutic targets, combinatorial treatments, and new
developments. Cells. 10:6592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kwon OS, Kim W, Cha HJ and Lee H: In
silico drug repositioning: From Large-scale transcriptome data to
therapeutics. Arch Pharm Res. 42:879–889. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Poore GD, Kopylova E, Zhu Q, Carpenter C,
Fraraccio S, Wandro S, Kosciolek T, Janssen S, Metcalf J, Song SJ,
et al: Microbiome analyses of blood and tissues suggest cancer
diagnostic approach. Nature. 579:567–574. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang B and Horvath S: A general framework
for weighted gene co-expression network analysis. Stat Appl Genet
Mol Biol. 4:172005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kolberg L, Raudvere U, Kuzmin I, Adler P,
Vilo J and Peterson H: g:Profiler-interoperable web service for
functional enrichment analysis and gene identifier mapping (2023
update). Nucleic Acids Res. 51:W207–W212. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kuleshov MV, Jones MR, Rouillard AD,
Fernandez NF, Duan Q, Wang Z, Koplev S, Jenkins SL, Jagodnik KM,
Lachmann A, et al: Enrichr: A comprehensive gene set enrichment
analysis web server 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 44:W90–W97.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liberzon A, Birger C, Thorvaldsdóttir H,
Ghandi M, Mesirov JP and Tamayo P: The molecular signatures
database hallmark gene set collection. Cell Syst. 1:417–425. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wickham H: ggplot2: Elegant graphics for
data analysis. second edition. Springer-Verlag; New York: 2016
|
|
35
|
Ewels P, Magnusson M, Lundin S and Käller
M: MultiQC: Summarize analysis results for multiple tools and
samples in a single report. Bioinformatics. 32:3047–3048. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Andrews S: FastQC: A Quality Control Tool
for High Throughput Sequence Data. 2010.
|
|
37
|
Martin M: Cutadapt Removes Adapter
Sequences From High-Throughput Sequencing Reads. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow
J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M and Gingeras TR: STAR:
Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 29:15–21.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lefol Y, Korfage T, Mjelle R, Prebensen C,
Lüders T, Müller B, Krokan H, Sarno A, Alsøe L; CONSORTIUM
LEMONAID, ; et al: TiSA: TimeSeriesAnalysis-A pipeline for the
analysis of longitudinal transcriptomics data. NAR Genom Bioinform.
5:lqad0202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nilsen G, Borgan Ø, LiestØl K and
Lingjærde OC: Identifying clusters in genomics data by recursive
partitioning. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol. 12:637–652. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lamb J, Crawford ED, Peck D, Modell JW,
Blat IC, Wrobel MJ, Lerner J, Brunet JP, Subramanian A, Ross KN, et
al: The connectivity map: Using gene-expression signatures to
connect small molecules, genes, and disease. Science.
313:1929–1935. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Samart K, Tuyishime P, Krishnan A and Ravi
J: Reconciling multiple connectivity scores for drug repurposing.
Brief Bioinform. 22:bbab1612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Subramanian A, Narayan R, Corsello SM,
Peck DD, Natoli TE, Lu X, Gould J, Davis JF, Tubelli AA, Asiedu JK,
et al: A next generation connectivity map: L1000 platform and the
first 1,000,000 profiles. Cell. 171:1437–1452.e17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ritz C, Baty F, Streibig JC and Gerhard D:
Dose-response analysis using R. PLoS One. 10:e01460212015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zheng S, Wang W, Aldahdooh J, Malyutina A,
Shadbahr T, Tanoli Z, Pessia A and Tang J: Synergy Finderplus:
Toward better interpretation and annotation of drug combination
screening datasets. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 20:587–596.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xia T, Xu LL, Guo PY, Shi WT, Cheng YQ and
Liu AJ: Synergism of amlodipine and telmisartan or candesartan on
blood pressure reduction by using SynergyFinder 3.0 and probability
sum test in vivo. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 11:e010642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Holm S: A simple sequentially rejective
multiple test procedure a simple sequentially rejective multiple
test procedure. Stat Medics. 6:65–70. 1979.
|
|
49
|
Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Li M, Meng F, Yu Z, Chen
Y and Cui G: Combination of SB431542, CHIR99021 and PD0325901 has a
synergic effect on abrogating valproic acid-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness in HeLa, 5637 and
SCC-15 cells. Oncol Rep. 41:3545–3554. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ye H, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Xia J, Mao X and Yu
X: The restraining effect of baicalein and U0126 on human cervical
cancer cell line HeLa. Mol Med Rep. 16:957–963. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang EJ and Chang JH: PD98059 induces the
apoptosis of human cervical cancer cells by regulating the
expression of Bcl2 and ERK2. J Exp Biomed Sci. 17:291–295.
2011.
|
|
52
|
Zahmatyar M, Kharaz L, Abiri Jahromi N,
Jahanian A, Shokri P and Nejadghaderi SA: The safety and efficacy
of binimetinib for lung cancer: A systematic review. BMC Pulm Med.
24:3792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tran B and Cohen MS: The discovery and
development of binimetinib for the treatment of melanoma. Expert
Opin Drug Discov. 15:745–754. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fu K, Cheung AHK, Wong CC, Liu W, Zhou Y,
Wang F, Huang P, Yuan K, Coker OO, Pan Y, et al: Streptococcus
anginosus promotes gastric inflammation, atrophy, and
tumorigenesis in mice. Cell. 187:882–896. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kumar R, Herold JL, Schady D, Davis J,
Kopetz S, Martinez-Moczygemba M, Murray BE, Han F, Li Y, Callaway
E, et al: Streptococcus gallolyticus subsp. gallolyticus
promotes colorectal tumor development. PLoS Pathog.
13:e10064402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Song X, Liu B, Zhao G, Pu X, Liu B, Ding M
and Xue Y: Streptococcus pneumoniae promotes migration and
invasion of A549 cells in vitro by activating mTORC2/AKT through
up-regulation of DDIT4 expression. Front Microbiol. 13:10462262022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Choi Y, Han HS, Chong GO, Le TM, Nguyen
HDT, Lee OE, Lee D, Seong WJ, Seo I and Cha HH: Updates on Group B
streptococcus infection in the field of obstetrics and gynecology.
Microorganisms. 10:23982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hsieh HY, Lu CH and Wang L: Long-term
treatment outcomes/toxicities of definite chemoradiotherapy
(intensity-modulated radiation therapy) for early-stage ‘bulky’
cervical cancer and survival impact of histological subtype. J
Formos Med Assoc. 122:221–229. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Pan X, Yang W, Wen Z, Li F, Tong L and
Tang W: Does adenocarcinoma have a worse prognosis than squamous
cell carcinoma in patients with cervical cancer? A real-world study
with a propensity score matching analysis. J Gynecol Oncol.
31:e802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Guo Y, Pan W, Liu S, Shen Z, Xu Y and Hu
L: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis (Review). Exp Ther
Med. 19:1997–2007. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Burotto M, Chiou VL, Lee JM and Kohn EC:
The MAPK pathway across different malignancies: A new perspective.
Cancer. 120:3446–3456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Alto NM and Orth K: Subversion of cell
signaling by pathogens. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
4:a0061142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Guo Y, Pan W, Liu S, Shen Z, Xu Y and Hu
L: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med.
19:1997–2007. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lavoie H, Gagnon J and Therrien M: ERK
signalling: A master regulator of cell behaviour, life and fate.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:607–632. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Raingeaud J, Gupta S, Rogers JS, Dickens
M, Han J, Ulevitch RJ and Davis RJ: Pro-inflammatory cytokines and
environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J
Biol Chem. 270:7420–7426. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Tian T, Li X and Zhang J: mTOR signaling
in cancer and mtor inhibitors in solid tumor targeting therapy. Int
J Mol Sci. 20:7552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zou Z, Tao T, Li H and Zhu X: MTOR
signaling pathway and mTOR inhibitors in cancer: Progress and
challenges. Cell Biosci. 10:312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ben-Sahra I and Manning BD: mTORC1
signaling and the metabolic control of cell growth. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 45:72–82. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pópulo H, Lopes JM and Soares P: The mTOR
signalling pathway in human cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 13:1886–1918.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fisher FM and Maratos-Flier E:
Understanding the physiology of FGF21. Annu Rev Physiol.
78:223–241. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Meng D, Yang Q, Wang H, Melick CH, Navlani
R, Frank AR and Jewell JL: Glutamine and asparagine activate mTORC1
independently of Rag GTPases. J Biol Chem. 295:2890–2899. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gobert AP, Latour YL, Asim M, Finley JL,
Verriere TG, Barry DP, Milne GL, Luis PB, Schneider C, Rivera ES,
et al: Bacterial pathogens hijack the innate immune response by
activation of the reverse transsulfuration pathway. mBio.
10:e02174–19. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xing J, Kornhauser JM, Xia Z, Thiele EA
and Greenberg ME: Nerve growth factor activates extracellular
Signal-regulated kinase and p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase
pathways to stimulate CREB serine 133 Phosphorylation. Mol Cell
Biol. 18:1946–1955. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yang HT, Cohen P and Rousseau S:
IL-1β-stimulated activation of ERK1/2 and p38α MAPK mediates the
transcriptional up-regulation of IL-6, IL-8 and GRO-α in HeLa
cells. Cell Signal. 20:375–380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Li S, Deng P, Wang M, Liu X, Jiang M,
Jiang B, Yang L and Hu J: IL-1α and IL-1β promote NOD2-induced
immune responses by enhancing MAPK signaling. Lab Invest.
99:1321–1334. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Liu W, Feng Z, Qu N, Li R and Niu Y: NUPR1
contribution to autophagy in primary bone tumor cells by regulating
the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Acta Medica Mediterranea.
38:1223–1228. 2022.
|
|
77
|
Yang C, Xu X, Dong X, Yang B, Dong W, Luo
Y, Liu X, Wu Y and Wang J: DDIT3/CHOP promotes autophagy in
chondrocytes via SIRT1-AKT pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell
Res. 1868:1190742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Fan T, Wang X, Zhang S, Deng P, Jiang Y,
Liang Y, Jie S, Wang Q, Li C, Tian G, et al: NUPR1 promotes the
proliferation and metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells
by activating TFE3-dependent autophagy. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 7:1302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang Y, Huang J, Chen W, Wang RH, Kao MC,
Pan YR, Chan SH, Tsai KW, Kung HJ, Lin KT and Wang LH:
Dysregulation of cystathionine γ-lyase promotes prostate cancer
progression and metastasis. EMBO Rep. 20:e459862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lin H, Liu S, Gao W and Liu H: DDIT3
modulates cancer stemness in gastric cancer by directly regulating
CEBPβ. J Pharm Pharmacol. 72:807–815. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Krall AS, Xu S, Graeber TG, Braas D and
Christofk HR: Asparagine promotes cancer cell proliferation through
use as an amino acid exchange factor. Nat Commun. 7:114572016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gelfo V, Romaniello D, Mazzeschi M, Sgarzi
M, Grilli G, Morselli A, Manzan B, Rihawi K and Lauriola M: Roles
of il-1 in cancer: From tumor progression to resistance to targeted
therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 21:60092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Molloy NH, Read DE and Gorman AM: Nerve
growth factor in cancer cell death and survival. Cancers (Basel).
3:510–530. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sui Y, Liu Q, Xu C, Ganesan K, Ye Z, Li Y,
Wu J, Du B, Gao F, Song C and Chen J: Non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease promotes breast cancer progression through upregulated
hepatic fibroblast growth factor 21. Cell Death Dis. 15:672024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tyrrell GJ, Kennedy A, Shokoples SE and
Sherburne RK: Binding and invasion of HeLa and MRC-5 cells by
Streptococcus agalactiae. Microbiology (Reading).
148:3921–3931. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker H,
Schwab U and Stein H: Cell cycle analysis of a cell
proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the
monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol. 133:1710–1715. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Schlfiter C, Duchrow M, Wohlenberg C,
Becker MHG, Key G, Flad HD and Gerdes J: The cell
Proliferation-associated antigen of antibody Ki-67: A very large,
ubiquitous nuclear protein with numerous repeated elements,
representing a new kind of cell cycle-maintaining proteins. J Cell
Biol. 123:513–522. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Uxa S, Castillo-Binder P, Kohler R,
Stangner K, Müller GA and Engeland K: Ki-67 gene expression. Cell
Death Differ. 28:3357–3370. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Burnham CAD, Shokoples SE and Tyrrell GJ:
Invasion of HeLa cells by group B streptococcus requires the
phosphoinositide-3-kinase signalling pathway and modulates
phosphorylation of host-cell Akt and glycogen synthase kinase-3.
Microbiology (Reading). 153:4240–4252. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ji J and Zheng PS: Activation of mTOR
signaling pathway contributes to survival of cervical cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 117:103–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Li XW, Tuergan M and Abulizi G: Expression
of MAPK1 in cervical cancer and effect of MAPK1 gene silencing on
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and metastasis. Asian
Pac J Trop Med. 8:937–943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Weth FR, Hoggarth GB, Weth AF, Paterson E,
White MPJ, Tan ST, Peng L and Gray C: Unlocking hidden potential:
Advancements, approaches, and obstacles in repurposing drugs for
cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 130:703–715. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
K W To K and Cho WCS: Drug repurposing for
cancer therapy in the era of precision medicine. Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 15:895–903. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Colombo N, McMeekin DS, Schwartz PE, Sessa
C, Gehrig PA, Holloway R, Braly P, Matei D, Morosky A, Dodion PF,
et al: Ridaforolimus as a single agent in advanced endometrial
cancer: Results of a single-arm, phase 2 trial. Br J Cancer.
108:1021–1026. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chon HS, Kang S, Lee JK, Apte SM, Shahzad
MM, Williams-Elson I and Wenham RM: Phase I study of oral
ridaforolimus in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in
patients with solid tumor cancers. BMC Cancer. 17:4072017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Finn RS, Ahn DH, Javle MM, Tan BR Jr,
Weekes CD, Bendell JC, Patnaik A, Khan GN, Laheru D, Chavira R, et
al: Phase 1b investigation of the MEK inhibitor binimetinib in
patients with advanced or metastatic biliary tract cancer. Invest
New Drugs. 36:1037–1043. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Woodfield SE, Zhang L, Scorsone KA, Liu Y
and Zage PE: Binimetinib inhibits MEK and is effective against
neuroblastoma tumor cells with low NF1 expression. BMC Cancer.
16L:1722016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Anttila JV, Shubin M, Cairns J, Borse F,
Guo Q, Mononen T, Vázquez-García I, Pulkkinen O and Mustonen V:
Contrasting the impact of cytotoxic and cytostatic drug therapies
on tumour progression. PLoS Comput Biol. 15:e10074932019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Hua H, Kong Q, Zhang H, Wang J, Luo T and
Jiang Y: Targeting mTOR for cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol.
12:712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Formisano L, Napolitano F, Rosa R, D'Amato
V, Servetto A, Marciano R, De Placido P, Bianco C and Bianco R:
Mechanisms of resistance to mTOR inhibitors. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 147:1028862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J,
Rojo F, Salmena L, Alimonti A, Egia A, Sasaki AT, Thomas G, Kozma
SC, et al: Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation
through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin
Invest. 118:3065–3074. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Li Q, Li Z, Luo T and Shi H: Targeting the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR and RAF/MEK/ERK pathways for cancer therapy. Mol
Biomed. 3:472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Pitts TM, Newton TP, Bradshaw-Pierce EL,
Addison R, Arcaroli JJ, Klauck PJ, Bagby SM, Hyatt SL, Purkey A,
Tentler JJ, et al: Dual pharmacological targeting of the map kinase
and pi3k/mtor pathway in preclinical models of colorectal cancer.
PLoS One. 9:e1130372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|