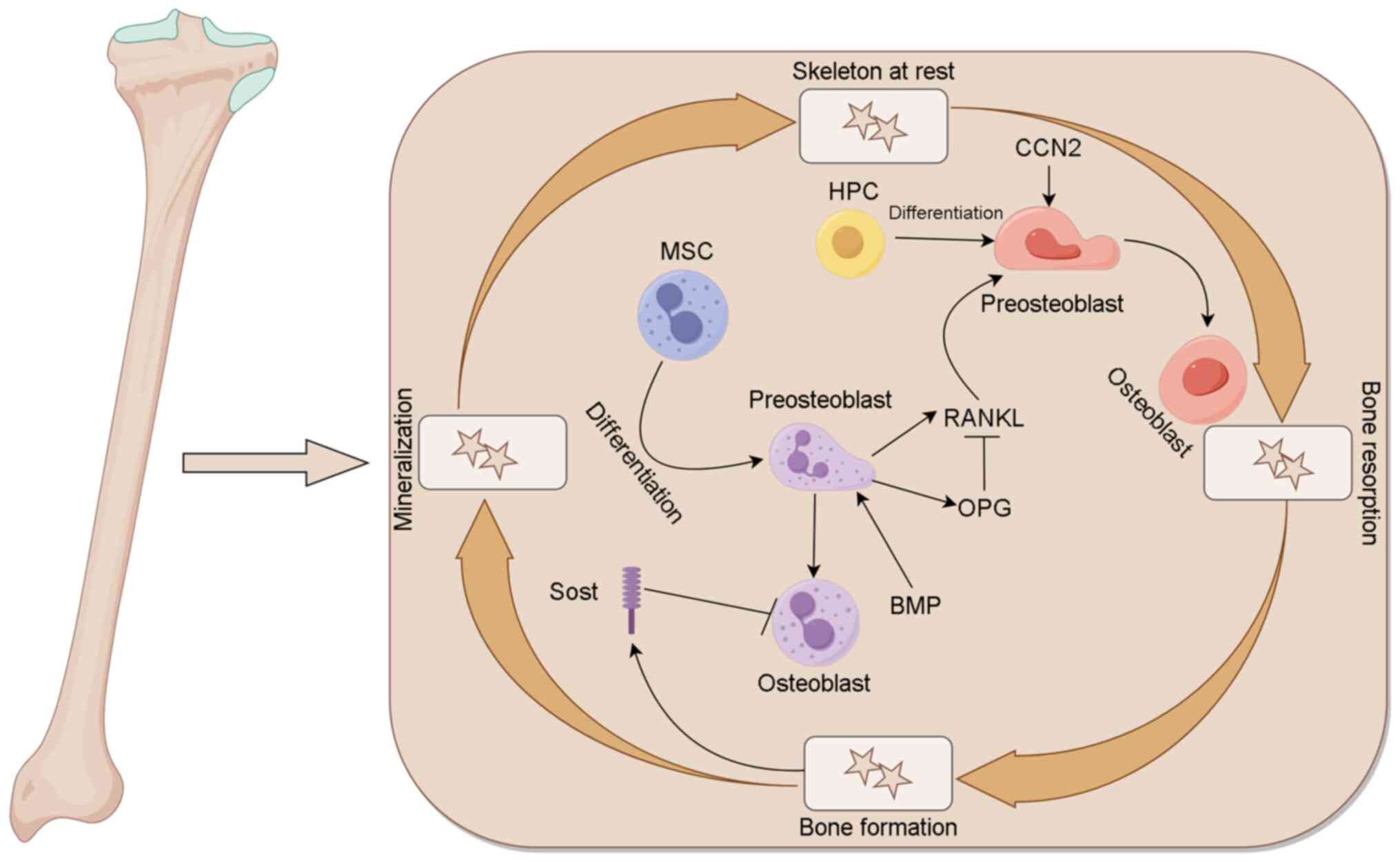
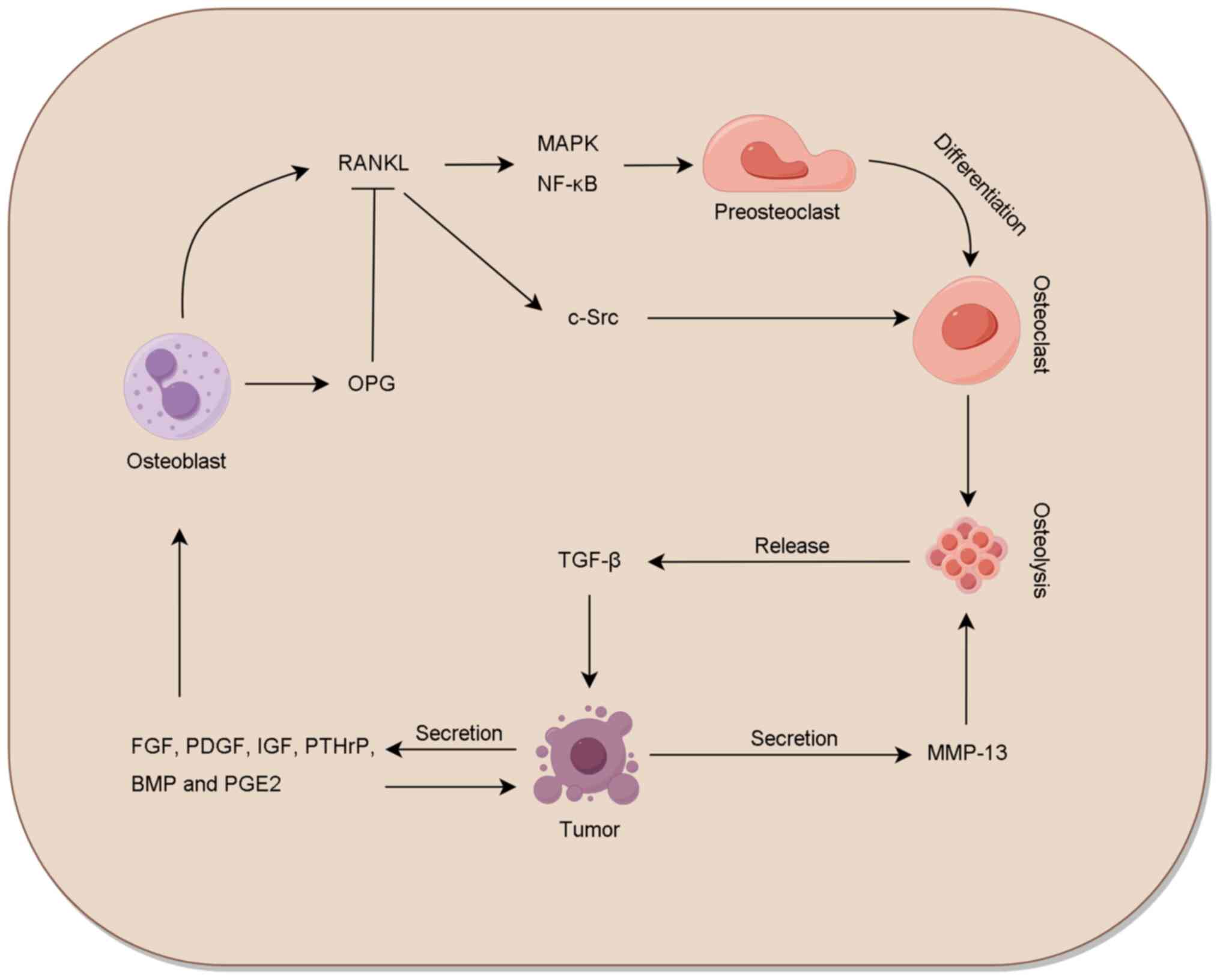
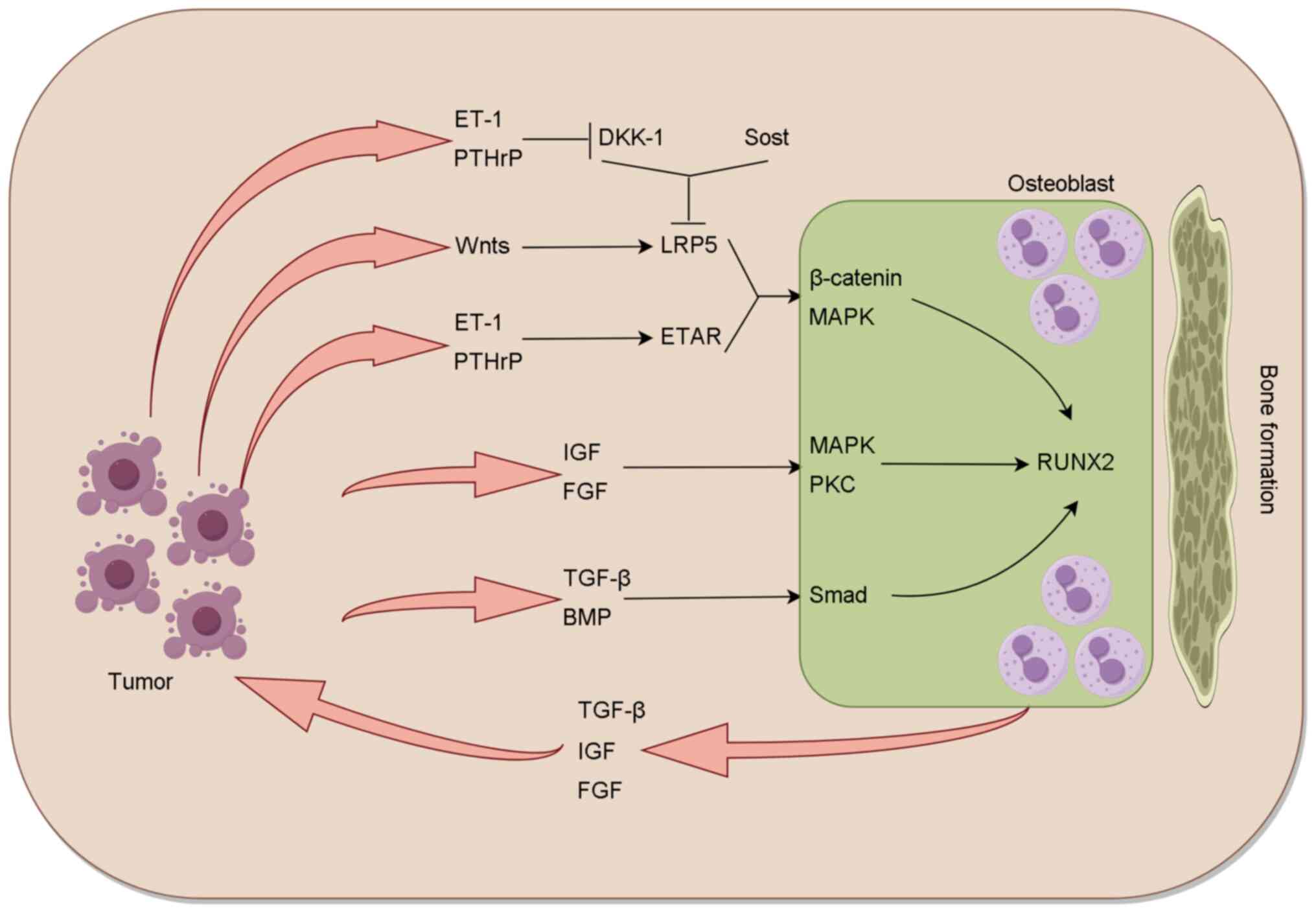
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Coleman RE, Croucher PI, Padhani AR,
Clézardin P, Chow E, Fallon M, Guise T, Colangeli S, Capanna R and
Costa L: Bone metastases. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Clézardin P, Coleman R, Puppo M, Ottewell
P, Bonnelye E, Paycha F, Confavreux CB and Holen I: Bone
metastasis: Mechanisms, therapies, and biomarkers. Physiol Rev.
101:797–855. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Papalia GF, Brigato P, Sisca L, Maltese G,
Faiella E, Santucci D, Pantano F, Vincenzi B, Tonini G, Papalia R
and Denaro V: Artificial intelligence in detection, management, and
prognosis of bone metastasis: A systematic review. Cancers (Basel).
16:27002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sousa S and Clézardin P: Bone-targeted
therapies in Cancer-induced bone disease. Calcif Tissue Int.
102:227–250. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang W, Bado IL, Hu J, Wan YW, Wu L, Wang
H, Gao Y, Jeong HH, Xu Z, Hao X, et al: The bone microenvironment
invigorates metastatic seeds for further dissemination. Cell.
184:2471–86.e20. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coleman R, Hadji P, Body JJ, Santini D,
Chow E, Terpos E, Oudard S, Bruland Ø, Flamen P, Kurth A, et al:
Bone health in cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann
Oncol. 31:1650–1663. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trompet D, Melis S, Chagin AS and Maes C:
Skeletal stem and progenitor cells in bone development and repair.
J Bone Miner Res. 39:633–654. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Boyce BF: Advances in the regulation of
osteoclasts and osteoclast functions. J Dent Res. 92:860–867. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ikebuchi Y, Aoki S, Honma M, Hayashi M,
Sugamori Y, Khan M, Kariya Y, Kato G, Tabata Y, Penninger JM, et
al: Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse
signalling. Nature. 561:195–200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamagishi T, Kawashima H, Ogose A,
Ariizumi T, Oike N, Sasaki T, Hatano H, Ohashi R, Umezu H, Ajioka Y
and Endo N: Expression profiling of Receptor-activator of nuclear
Factor-Kappa B ligand in soft tissue tumors. Tohoku J Exp Med.
248:87–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gostage J, Kostenuik P, Goljanek-Whysall
K, Bellantuono I, McCloskey E and Bonnet N: Extra-osseous roles of
the RANK-RANKL-OPG axis with a focus on skeletal muscle. Curr
Osteoporos Rep. 22:632–650. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nozawa K, Fujishiro M, Kawasaki M, Kaneko
H, Iwabuchi K, Yanagida M, Suzuki F, Miyazawa K, Takasaki Y, Ogawa
H, et al: Connective tissue growth factor promotes articular damage
by increased osteoclastogenesis in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 11:R1742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aoyama E, Kubota S, Khattab HM, Nishida T
and Takigawa M: CCN2 enhances RANKL-induced osteoclast
differentiation via direct binding to RANK and OPG. Bone.
73:242–248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren W, Sun X, Wang K, Feng H, Liu Y, Fei
C, Wan S, Wang W, Luo J, Shi Q, et al: BMP9 inhibits the bone
metastasis of breast cancer cells by downregulating CCN2
(connective tissue growth factor, CTGF) expression. Mol Biol Rep.
41:1373–1383. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sims NA and Martin TJ: Coupling the
activities of bone formation and resorption: A multitude of signals
within the basic multicellular unit. Bonekey Rep. 3:4812014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nakashima K, Zhou X, Kunkel G, Zhang Z,
Deng JM, Behringer RR and de Crombrugghe B: The novel zinc
finger-containing transcription factor osterix is required for
osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Cell. 108:17–29.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garcia J and Delany AM: MicroRNAs
regulating TGFβ and BMP signaling in the osteoblast lineage. Bone.
143:1157912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caetano-Lopes J, Canhão H and Fonseca JE:
Osteoblasts and bone formation. Acta Reumatol Port. 32:103–110.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Abhishek Shah A, Chand D, Ahamad S, Porwal
K, Chourasia MK, Mohanan K, Srivastava KR and Chattopadhyay N:
Therapeutic targeting of Wnt antagonists by small molecules for
treatment of osteoporosis. Biochem Pharmacol. 230:1165872024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
van't Hof RJ and Ralston SH: Nitric oxide
and bone. Immunology. 103:255–261. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Danilchenko S, Kalinkevich A, Zhovner M,
Kuznetsov V, Li H and Wang J: Anisotropic aspects of solubility
behavior in the demineralization of cortical bone revealed by XRD
analysis. J Biol Phys. 45:77–88. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kitcharanant N, Chattipakorn N and
Chattipakorn SC: The effect of intermittent parathyroid hormone on
bone lengthening: Current evidence to inform future effective
interventions. Osteoporos Int. 34:1657–1675. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Niwczyk O, Grymowicz M, Szczęsnowicz A,
Hajbos M, Kostrzak A, Budzik M, Maciejewska-Jeske M, Bala G,
Smolarczyk R and Męczekalski B: Bones and hormones: Interaction
between hormones of the hypothalamus, pituitary, adipose tissue and
bone. Int J Mol Sci. 24:68402023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Grigoryan S and Clines GA: Hormonal
control of bone architecture throughout the lifespan: Implications
for fracture prediction and prevention. Endocr Pract. 30:687–694.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nagy V and Penninger JM: The RANKL-RANK
Story. Gerontology. 61:534–542. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mastro AM, Gay CV and Welch DR: The
skeleton as a unique environment for breast cancer cells. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 20:275–284. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bussard KM, Gay CV and Mastro AM: The bone
microenvironment in metastasis; what is special about bone? Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 27:41–55. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sharma R, Sharma R, Khaket TP, Dutta C,
Chakraborty B and Mukherjee TK: Breast cancer metastasis: Putative
therapeutic role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Cell Oncol
(Dordr). 40:199–208. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen Q and Massagué J: Molecular pathways:
VCAM-1 as a potential therapeutic target in metastasis. Clin Cancer
Res. 18:5520–555. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lipton A: Implications of bone metastases
and the benefits of bone-targeted therapy. Semin Oncol. 37 (Suppl
2):S15–S29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
De Leon-Oliva D, Barrena-Blázquez S,
Jiménez-Álvarez L, Fraile-Martinez O, García-Montero C,
López-González L, Torres-Carranza D, García-Puente LM, Carranza ST,
Álvarez-Mon MÁ, et al: The RANK-RANKL-OPG System: A multifaceted
regulator of homeostasis, immunity, and cancer. Medicina (Kaunas).
59:17522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Huang Z, Chen X and Zhang
B: The roles of osteoprotegerin in cancer, far beyond a bone
player. Cell Death Discov. 8:2522022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Clézardin P: The role of
RANK/RANKL/osteoprotegerin (OPG) triad in cancer-induced bone
diseases: Physiopathology and clinical implications. Bull Cancer.
98:837–846. 2011.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Roodman GD: Mechanisms of bone metastasis.
N Engl J Med. 350:1655–1664. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Susperregui AR, Viñals F, Ho PW, Gillespie
MT, Martin TJ and Ventura F: BMP-2 regulation of PTHrP and
osteoclastogenic factors during osteoblast differentiation of C2C12
cells. J Cell Physiol. 216:144–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Izawa T, Zou W, Chappel JC, Ashley JW,
Feng X and Teitelbaum SL: c-Src links a RANK/αvβ3 integrin complex
to the osteoclast cytoskeleton. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2943–2953. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou S, Li J, Ying T, Wang Y, Wang Q, Li X
and Zhao F: StemRegenin 1 attenuates the RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis via inhibiting AhR-c-src-NF-κB/p-ERK MAPK-NFATc1
signaling pathway. iScience. 27:1096822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ibaragi S, Shimo T, Iwamoto M, Hassan NM,
Kodama S, Isowa S and Sasaki A: Parathyroid hormone-related peptide
regulates matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression in bone
metastatic breast cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 30:5029–5036.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Giarratana AO, Prendergast CM, Salvatore
MM and Capaccione KM: TGF-β signaling: Critical nexus of
fibrogenesis and cancer. J Transl Med. 22:5942024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Juárez P and Guise TA: TGF-β in cancer and
bone: Implications for treatment of bone metastases. Bone.
48:23–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fan C, Wang Q, Kuipers TB, Cats D, Iyengar
PV, Hagenaars SC, Mesker WE, Devilee P, Tollenaar RAEM, Mei H and
Ten Dijke P: LncRNA LITATS1 suppresses TGF-β-induced EMT and cancer
cell plasticity by potentiating TβRI degradation. EMBO J.
42:e1128062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Li Y, Drabsch Y, Pujuguet P, Ren J, van
Laar T, Zhang L, van Dam H, Clément-Lacroix P and Ten Dijke P:
Genetic depletion and pharmacological targeting of αv integrin in
breast cancer cells impairs metastasis in zebrafish and mouse
xenograft models. Breast Cancer Res. 17:282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Luis-Ravelo D, Antón I, Vicent S, Zandueta
C, Martínez S, Valencia K, Ormazábal C and Lecanda F: Divergent
effects of TGF-β inhibition in bone metastases in breast and lung
cancer. Rev Osteoporos Metab Miner. 5:79–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhu S, Chen W, Masson A and Li YP: Cell
signaling and transcriptional regulation of osteoblast lineage
commitment, differentiation, bone formation, and homeostasis. Cell
Discov. 10:712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gkotzamanidou M, Dimopoulos MA, Kastritis
E, Christoulas D, Moulopoulos LA and Terpos E: Sclerostin: A
possible target for the management of cancer-induced bone disease.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16:761–769. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pinzone JJ, Hall BM, Thudi NK, Vonau M,
Qiang YW, Rosol TJ and Shaughnessy JD: The role of Dickkopf-1 in
bone development, homeostasis, and disease. Blood. 113:517–525.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Irani S, Salajegheh A, Smith RA and Lam
AK: A review of the profile of endothelin axis in cancer and its
management. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 89:314–321. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bagnato A, Loizidou M, Pflug BR, Curwen J
and Growcott J: Role of the endothelin axis and its antagonists in
the treatment of cancer. Br J Pharmacol. 163:220–233. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xin Z, Qin L, Tang Y, Guo S, Li F, Fang Y,
Li G, Yao Y, Zheng B, Zhang B, et al: Immune mediated support of
metastasis: Implication for bone invasion. Cancer Commun (Lond).
44:967–991. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ma X and Yu J: Role of the bone
microenvironment in bone metastasis of malignant tumors-therapeutic
implications. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 43:751–761. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Baldessari C, Pipitone S, Molinaro E,
Cerma K, Fanelli M, Nasso C, Oltrecolli M, Pirola M, D'Agostino E,
Pugliese G, et al: Bone metastases and health in prostate cancer:
From pathophysiology to clinical implications. Cancers (Basel).
15:15182023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang X, Jiang P and Wang C: The role of
prostate-specific antigen in the osteoblastic bone metastasis of
prostate cancer: A literature review. Front Oncol. 13:11276372023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yonou H, Horiguchi Y, Ohno Y, Namiki K,
Yoshioka K, Ohori M, Hatano T and Tachibana M: Prostate-specific
antigen stimulates osteoprotegerin production and inhibits receptor
activator of nuclear factor-kappaB ligand expression by human
osteoblasts. Prostate. 67:840–848. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Christoph F, König F, Lebentrau S, Jandrig
B, Krause H, Strenziok R and Schostak M: RANKL/RANK/OPG cytokine
receptor system: mRNA expression pattern in BPH, primary and
metastatic prostate cancer disease. World J Urol. 36:187–192. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kuchimaru T, Hoshino T, Aikawa T, Yasuda
H, Kobayashi T, Kadonosono T and Kizaka-Kondoh S: Bone resorption
facilitates osteoblastic bone metastatic colonization by
cooperation of insulin-like growth factor and hypoxia. Cancer Sci.
105:553–559. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jin R, Sterling JA, Edwards JR, DeGraff
DJ, Lee C, Park SI and Matusik RJ: Activation of NF-kappa B
signaling promotes growth of prostate cancer cells in bone. PLoS
One. 8:e609832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Choi SW, Sun AK, Cheung JP and Ho JC:
Circulating tumour cells in the prediction of bone metastasis.
Cancers (Basel). 16:2522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Roth ES, Fetzer DT, Barron BJ, Joseph UA,
Gayed IW and Wan DQ: Does colon cancer ever metastasize to bone
first? a temporal analysis of colorectal cancer progression. BMC
Cancer. 9:2742009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Uccella S, Morris JM, Bakkum-Gamez JN,
Keeney GL, Podratz KC and Mariani A: Bone metastases in endometrial
cancer: Report on 19 patients and review of the medical literature.
Gynecol Oncol. 130:474–482. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
8:98–101. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Elkin M and Vlodavsky I: Tail vein assay
of cancer metastasis. Curr Protoc Cell Biol. Chapter
19:19.2.1-19.2.7.2001.doi: 10.1002/0471143030.cb1902s12. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kuchimaru T, Kataoka N, Nakagawa K,
Isozaki T, Miyabara H, Minegishi M, Kadonosono T and Kizaka-Kondoh
S: A reliable murine model of bone metastasis by injecting cancer
cells through caudal arteries. Nat Commun. 9:29812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Neudert M, Fischer C, Krempien B, Bauss F
and Seibel MJ: Site-specific human breast cancer (MDA-MB-231)
metastases in nude rats: Model characterisation and in vivo effects
of ibandronate on tumour growth. Int J Cancer. 107:468–477. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hoffman RM: Patient-derived orthotopic
xenografts: Better mimic of metastasis than subcutaneous
xenografts. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:451–452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Stribbling SM and Ryan AJ: The
cell-line-derived subcutaneous tumor model in preclinical cancer
research. Nat Protoc. 17:2108–2128. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Farhoodi HP, Segaliny AI, Wagoner ZW,
Cheng JL, Liu L and Zhao W: Optimization of a syngeneic murine
model of bone metastasis. J Bone Oncol. 23:1002982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Winnard PT Jr, Vesuna F, Bol GM,
Gabrielson KL, Chenevix-Trench G, Ter Hoeve ND, van Diest PJ and
Raman V: Targeting RNA helicase DDX3X with a small molecule
inhibitor for breast cancer bone metastasis treatment. Cancer Lett.
604:2172602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Han Y, Azuma K, Watanabe S, Semba K and
Nakayama J: Metastatic profiling of HER2-positive breast cancer
cell lines in xenograft models. Clin Exp Metastasis. 39:467–477.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ye X, Huang X, Fu X, Zhang X, Lin R, Zhang
W, Zhang J and Lu Y: Myeloid-like tumor hybrid cells in bone marrow
promote progression of prostate cancer bone metastasis. J Hematol
Oncol. 16:462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Zhong L, Miller HD, Zhang Y, Jin B, Ge D
and You Z: Intra-arterial injection to create bone metastasis of
prostate cancer in mice. Am J Clin Exp Urol. 8:93–100.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Simmons JK, Dirksen WP, Hildreth BE III,
Dorr C, Williams C, Thomas R, Breen M, Toribio RE and Rosol TJ:
Canine prostate cancer cell line (Probasco) produces osteoblastic
metastases in vivo. Prostate. 74:1251–1265. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Abou DS, Ulmert D, Doucet M, Hobbs RF,
Riddle RC and Thorek DL: Whole-Body and microenvironmental
localization of Radium-223 in naïve and mouse models of prostate
cancer metastasis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 108:djv3802025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Pollard HB, Levine MA, Eidelman O and
Pollard M: Pharmacological ascorbic acid suppresses syngeneic tumor
growth and metastases in hormone-refractory prostate cancer. In
Vivo. 24:249–255. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Wang N, Reeves KJ, Brown HK, Fowles AC,
Docherty FE, Ottewell PD, Croucher PI, Holen I and Eaton CL: The
frequency of osteolytic bone metastasis is determined by conditions
of the soil, not the number of seeds; evidence from in vivo models
of breast and prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kaighn ME, Narayan KS, Ohnuki Y, Lechner
JF and Jones LW: Establishment and characterization of a human
prostatic carcinoma cell line (PC-3). Invest Urol. 17:16–23.
1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Dai J, Hensel J, Wang N, Kruithof-de Julio
M and Shiozawa Y: Mouse models for studying prostate cancer bone
metastasis. Bonekey Rep. 5:7772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kozlowski JM, Fidler IJ, Campbell D, Xu
ZL, Kaighn ME and Hart IR: Metastatic behavior of human tumor cell
lines grown in the nude mouse. Cancer Res. 44:3522–3529.
1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Pettaway CA, Pathak S, Greene G, Ramirez
E, Wilson MR, Killion JJ and Fidler IJ: Selection of highly
metastatic variants of different human prostatic carcinomas using
orthotopic implantation in nude mice. Clin Cancer Res. 2:1627–1636.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Stone KR, Mickey DD, Wunderli H, Mickey GH
and Paulson DF: Isolation of a human prostate carcinoma cell line
(DU 145). Int J Cancer. 21:274–281. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Horoszewicz JS, Leong SS, Chu TM, Wajsman
ZL, Friedman M, Papsidero L, Kim U, Chai LS, Kakati S, Arya SK and
Sandberg AA: The LNCaP cell line-a new model for studies on human
prostatic carcinoma. Prog Clin Biol Res. 37:115–132.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Thalmann GN, Anezinis PE, Chang SM, Zhau
HE, Kim EE, Hopwood VL, Pathak S, von Eschenbach AC and Chung LW:
Androgen-independent cancer progression and bone metastasis in the
LNCaP model of human prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 54:2577–2581.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sobel RE and Sadar MD: Cell lines used in
prostate cancer research: A compendium of old and new lines-part 1.
J Urol. 173:342–359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Guo Q, Jin Y, Lin M, Zeng C and Zhang J:
NF-κB signaling in therapy resistance of breast cancer: Mechanisms,
approaches, and challenges. Life Sci. 348:1226842024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhou J and Ottewell PD: The role of IL-1B
in breast cancer bone metastasis. J Bone Oncol. 46:1006082024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Weilbaecher KN, Guise TA and McCauley LK:
Cancer to bone: A fatal attraction. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:411–425.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Shu ST, Nadella MV, Dirksen WP, Fernandez
SA, Thudi NK, Werbeck JL, Lairmore MD and Rosol TJ: A novel
bioluminescent mouse model and effective therapy for adult T-cell
leukemia/lymphoma. Cancer Res. 67:11859–11866. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Isaacs JT, Heston WD, Weissman RM and
Coffey DS: Animal models of the hormone-sensitive and -insensitive
prostatic adenocarcinomas, Dunning R-3327-H, R-3327-HI, and
R-3327-AT. Cancer Res. 38:4353–4359. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Padalecki SS and Guise TA: Actions of
bisphosphonates in animal models of breast cancer. Breast Cancer
Res. 4:35–41. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ooi LL, Zheng Y, Zhou H, Trivedi T,
Conigrave AD, Seibel MJ and Dunstan CR: Vitamin D deficiency
promotes growth of MCF-7 human breast cancer in a rodent model of
osteosclerotic bone metastasis. Bone. 47:795–803. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yin JJ, Mohammad KS, Käkönen SM, Harris S,
Wu-Wong JR, Wessale JL, Padley RJ, Garrett IR, Chirgwin JM and
Guise TA: A causal role for endothelin-1 in the pathogenesis of
osteoblastic bone metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:10954–10959. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Pulaski BA and Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Mouse
4T1 breast tumor model. Curr Protoc Immunol. Chapter 20: Unit 20.2.
2001.doi: 10.1002/0471142735.im2002s39. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Pulaski BA and Ostrand-Rosenberg S:
Reduction of established spontaneous mammary carcinoma metastases
following immunotherapy with major histocompatibility complex class
II and B7.1 cell-based tumor vaccines. Cancer Res. 58:1486–1493.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Lelekakis M, Moseley JM, Martin TJ, Hards
D, Williams E, Ho P, Lowen D, Javni J, Miller FR, Slavin J and
Anderson RL: A novel orthotopic model of breast cancer metastasis
to bone. Clin Exp Metastasis. 17:163–170. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Coleman RE: Metastatic bone disease:
Clinical features, pathophysiology and treatment strategies. Cancer
Treat Rev. 27:165–176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Feeley BT, Liu NQ, Conduah AH, Krenek L,
Roth K, Dougall WC, Huard J, Dubinett S and Lieberman JR: Mixed
metastatic lung cancer lesions in bone are inhibited by noggin
overexpression and Rank:Fc administration. Bone Miner Res.
21:1571–1580. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Miki T, Yano S, Hanibuchi M and Sone S:
Bone metastasis model with multiorgan dissemination of human
small-cell lung cancer (SBC-5) cells in natural killer
cell-depleted SCID mice. Oncol Res. 12:209–127. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Tannehill-Gregg SH, Levine AL, Nadella MV,
Iguchi H and Rosol TJ: The effect of zoledronic acid and
osteoprotegerin on growth of human lung cancer in the tibias of
nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis. 23:19–31. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Taube T, Beneton MN, McCloskey EV, Rogers
S, Greaves M and Kanis JA: Abnormal bone remodelling in patients
with myelomatosis and normal biochemical indices of bone
resorption. Eur J Haematol. 49:192–198. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Nakano T, Shimizu K, Kawashima O,
Kamiyoshihara M, Kakegawa S, Sugano M, Ibe T, Nagashima T, Kaira K,
Sunaga N, et al: Establishment of a human lung cancer cell line
with high metastatic potential to multiple organs: Gene expression
associated with metastatic potential in human lung cancer. Oncol
Rep. 28:1727–1735. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Yang S, Dong Q, Yao M, Shi M, Ye J, Zhao
L, Su J, Gu W, Xie W, Wang K, et al: Establishment of an
experimental human lung adenocarcinoma cell line SPC-A-1BM with
high bone metastases potency by (99m)Tc-MDP bone scintigraphy. Nucl
Med Biol. 36:313–321. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Gravina GL, Mancini A, Muzi P, Ventura L,
Biordi L, Ricevuto E, Pompili S, Mattei C, Di Cesare E, Jannini EA
and Festuccia C: CXCR4 pharmacogical inhibition reduces bone and
soft tissue metastatic burden by affecting tumor growth and
tumorigenic potential in prostate cancer preclinical models.
Prostate. 75:1227–1246. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Wu TT, Sikes RA, Cui Q, Thalmann GN, Kao
C, Murphy CF, Yang H, Zhau HE, Balian G and Chung LW: Establishing
human prostate cancer cell xenografts in bone: Induction of
osteoblastic reaction by prostate-specific antigen-producing tumors
in athymic and SCID/bg mice using LNCaP and lineage-derived
metastatic sublines. Int J Cancer. 77:887–894. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Shevrin DH, Kukreja SC, Ghosh L and Lad
TE: Development of skeletal metastasis by human prostate cancer in
athymic nude mice. Clin Exp Metastasis. 6:401–409. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Havens AM, Pedersen EA, Shiozawa Y, Ying
C, Jung Y, Sun Y, Neeley C, Wang J, Mehra R, Keller ET, et al: An
in vivo mouse model for human prostate cancer metastasis.
Neoplasia. 10:371–380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Yang M, Jiang P, Sun FX, Hasegawa S,
Baranov E, Chishima T, Shimada H, Moossa AR and Hoffman RM: A
fluorescent orthotopic bone metastasis model of human prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 59:781–786. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Fisher JL, Schmitt JF, Howard ML, Mackie
PS, Choong PF and Risbridger GP: An in vivo model of prostate
carcinoma growth and invasion in bone. Cell Tissue Res.
307:337–345. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Bonfil RD, Dong Z, Trindade Filho JC,
Sabbota A, Osenkowski P, Nabha S, Yamamoto H, Chinni SR, Zhao H,
Mobashery S, et al: Prostate cancer-associated membrane type
1-matrix metalloproteinase: A pivotal role in bone response and
intraosseous tumor growth. Am J Pathol. 170:2100–2111. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Zou M, Jiao J, Zou Q, Xu Y, Cheng M, Xu J
and Zhang Y: Multiple metastases in a novel LNCaP model of human
prostate cancer. Oncol Rep. 30:615–622. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Corey E, Quinn JE, Bladou F, Brown LG,
Roudier MP, Brown JM, Buhler KR and Vessella RL: Establishment and
characterization of osseous prostate cancer models: Intra-tibial
injection of human prostate cancer cells. Prostate. 52:20–33. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Jantscheff P, Ziroli V, Esser N, Graeser
R, Kluth J, Sukolinskaya A, Taylor LA, Unger C and Massing U:
Anti-metastatic effects of liposomal gemcitabine in a human
orthotopic LNCaP prostate cancer xenograft model. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 26:981–992. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Wetterwald A, van der Pluijm G, Que I,
Sijmons B, Buijs J, Karperien M, Löwik CW, Gautschi E, Thalmann GN
and Cecchini MG: Optical imaging of cancer metastasis to bone
marrow: A mouse model of minimal residual disease. Am J Pathol.
160:1143–1153. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Sasaki SI, Zhang D, Iwabuchi S, Tanabe Y,
Hashimoto S, Yamauchi A, Hayashi K, Tsuchiya H, Hayakawa Y, Baba T
and Mukaida N: Crucial contribution of GPR56/ADGRG1, expressed by
breast cancer cells, to bone metastasis formation. Cancer Sci.
112:4883–4893. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Kim B, Kim H, Jung S, Moon A, Noh DY, Lee
ZH, Kim HJ and Kim HH: A CTGF-RUNX2-RANKL axis in breast and
prostate cancer cells promotes tumor progression in bone. J Bone
Miner Res. 35:155–166. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Yoneda T, Michigami T, Yi B, Williams PJ,
Niewolna M and Hiraga T: Actions of bisphosphonate on bone
metastasis in animal models of breast carcinoma. Cancer.
88:2979–2988. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yi B, Williams PJ, Niewolna M, Wang Y and
Yoneda T: Tumor-derived platelet-derived growth factor-BB plays a
critical role in osteosclerotic bone metastasis in an animal model
of human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 62:917–923. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Sun J, Huang J, Lan J, Zhou K, Gao Y, Song
Z, Deng Y, Liu L, Dong Y and Liu X: Overexpression of CENPF
correlates with poor prognosis and tumor bone metastasis in breast
cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 19:2642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Hung JY, Horn D, Woodruff K, Prihoda T,
LeSaux C, Peters J, Tio F and Abboud-Werner SL: Colony-stimulating
factor 1 potentiates lung cancer bone metastasis. Lab Invest.
94:371–381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Liu H, Cheng Q, Xu DS, Wang W, Fang Z, Xue
DD, Zheng Y, Chang AH and Lei YJ: Overexpression of CXCR7
accelerates tumor growth and metastasis of lung cancer cells.
Respir Res. 21:2872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Wang Q, Zhao B, Li J, Zhao J, Wang C, Li
Q, Yang W, Xu L and Gong Y: Qilian formula inhibits tumor cell
growth in a bone metastasis model of lung cancer. Integr Cancer
Ther. 22:153473542312172742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|