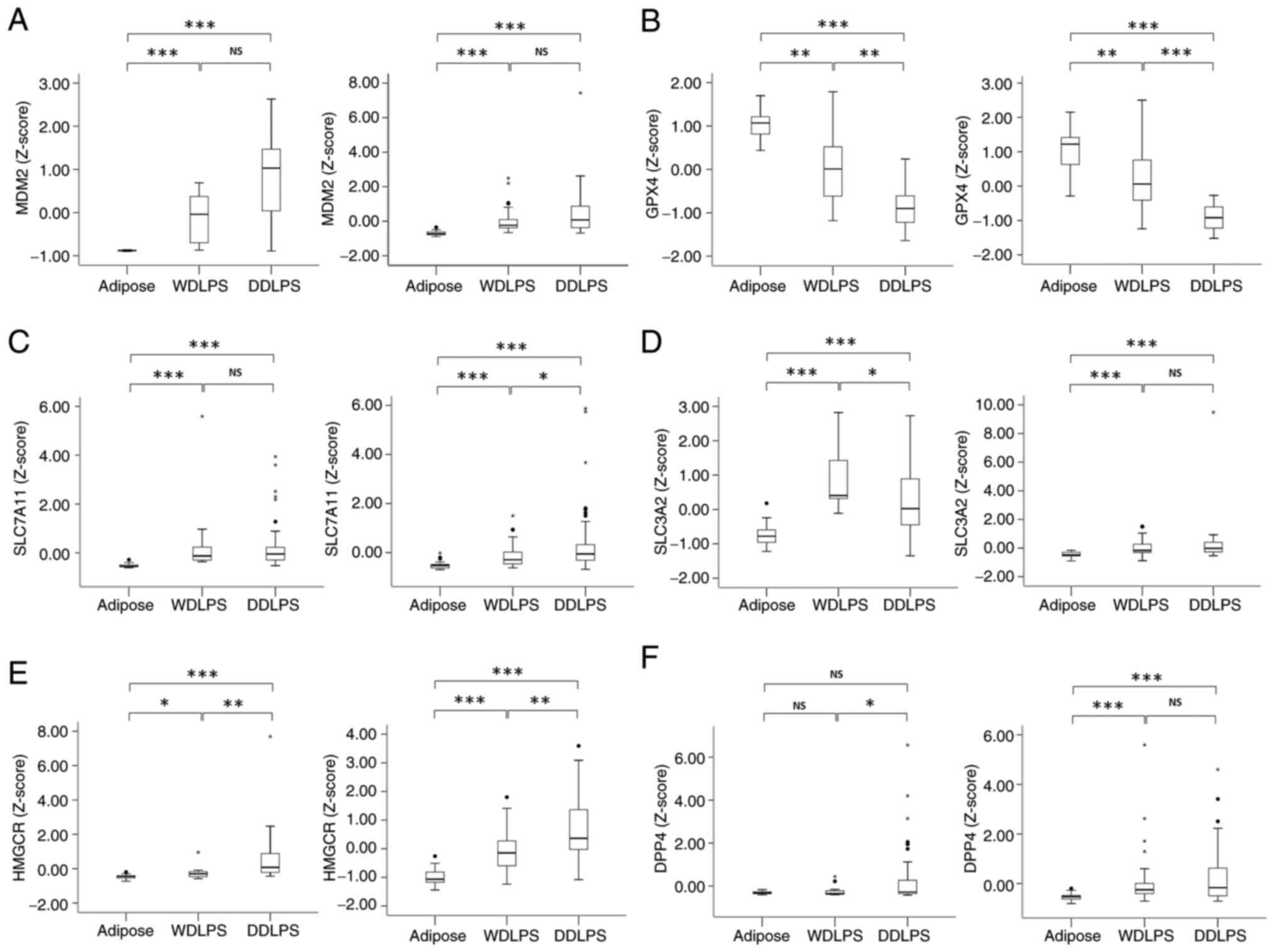
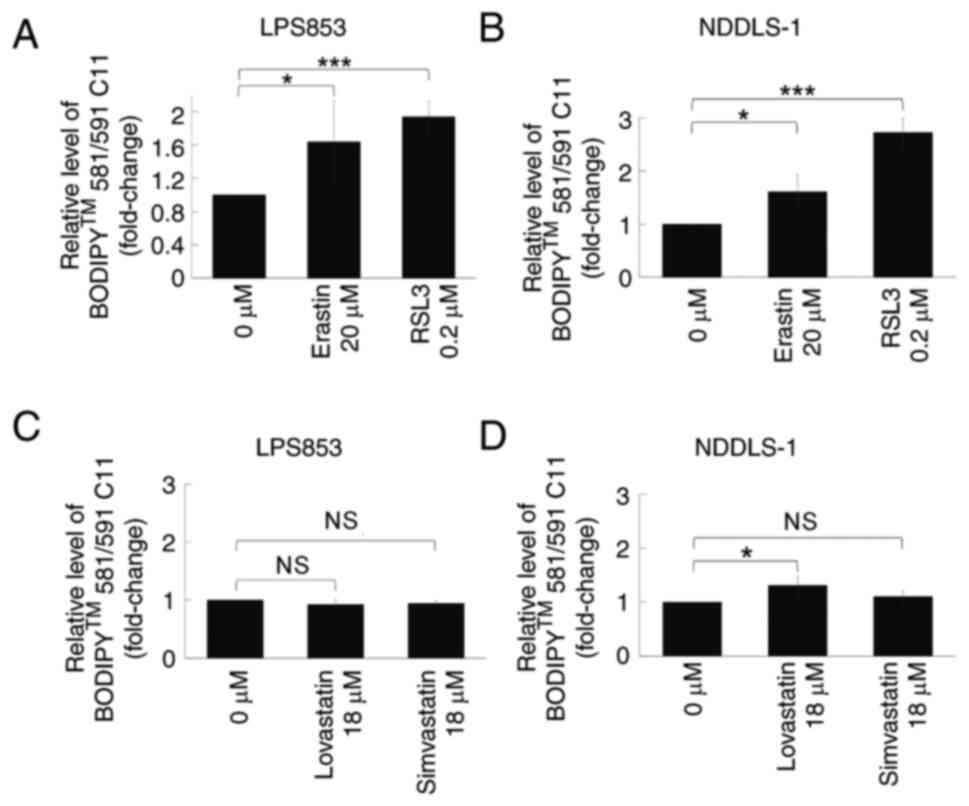
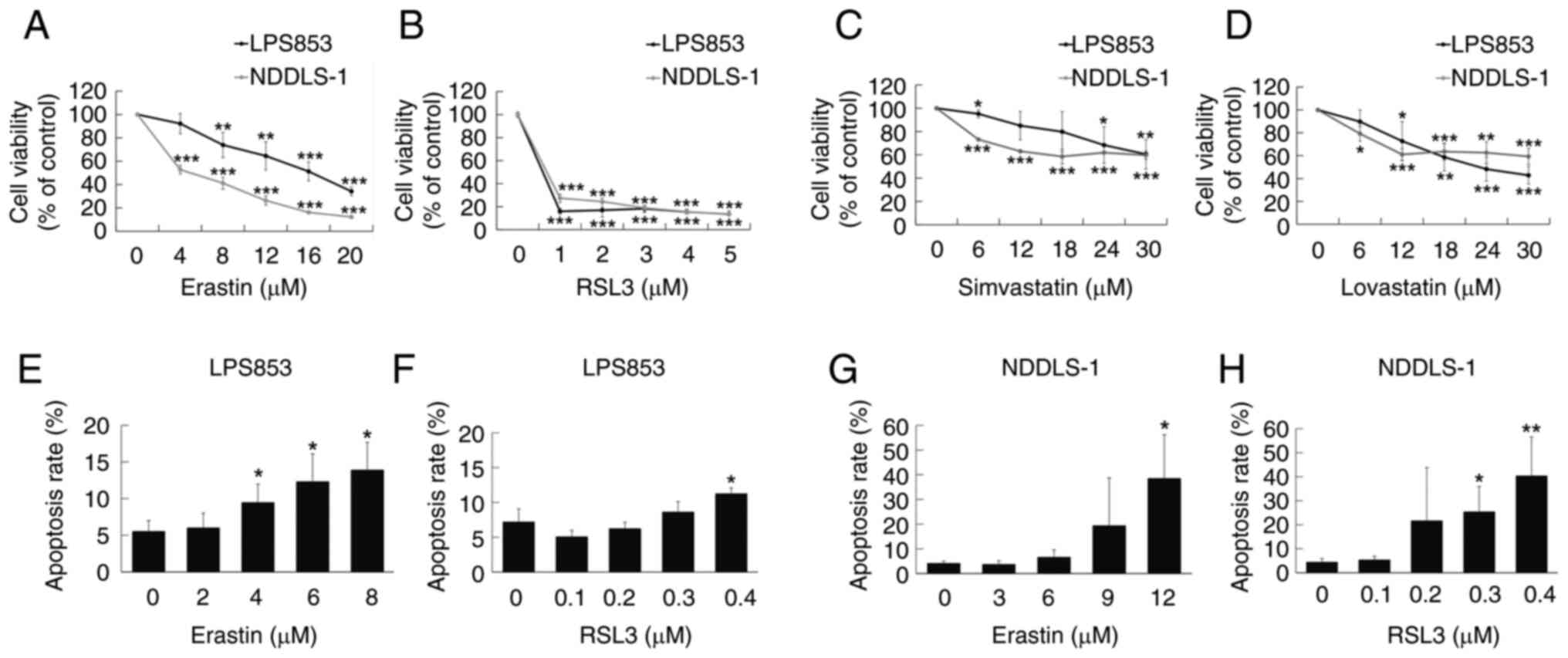
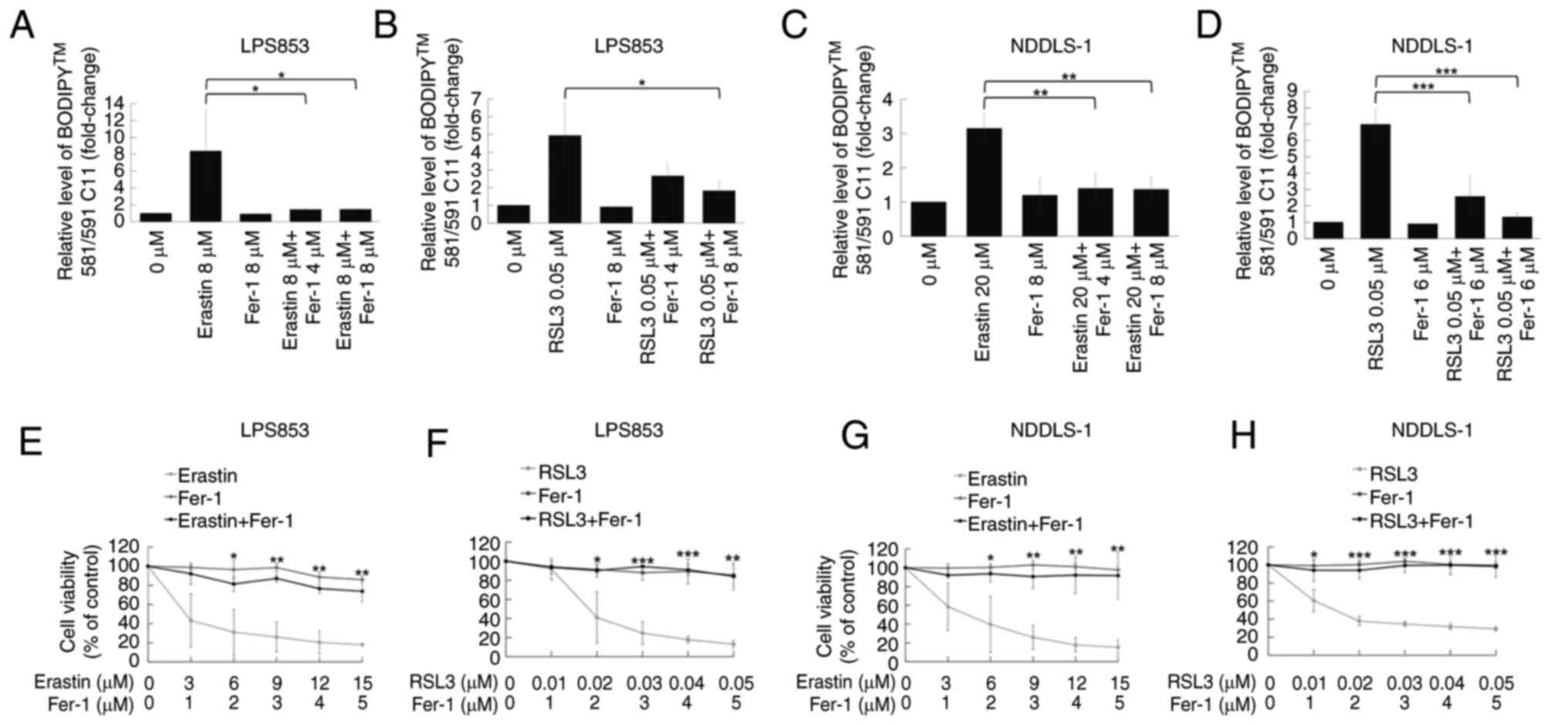
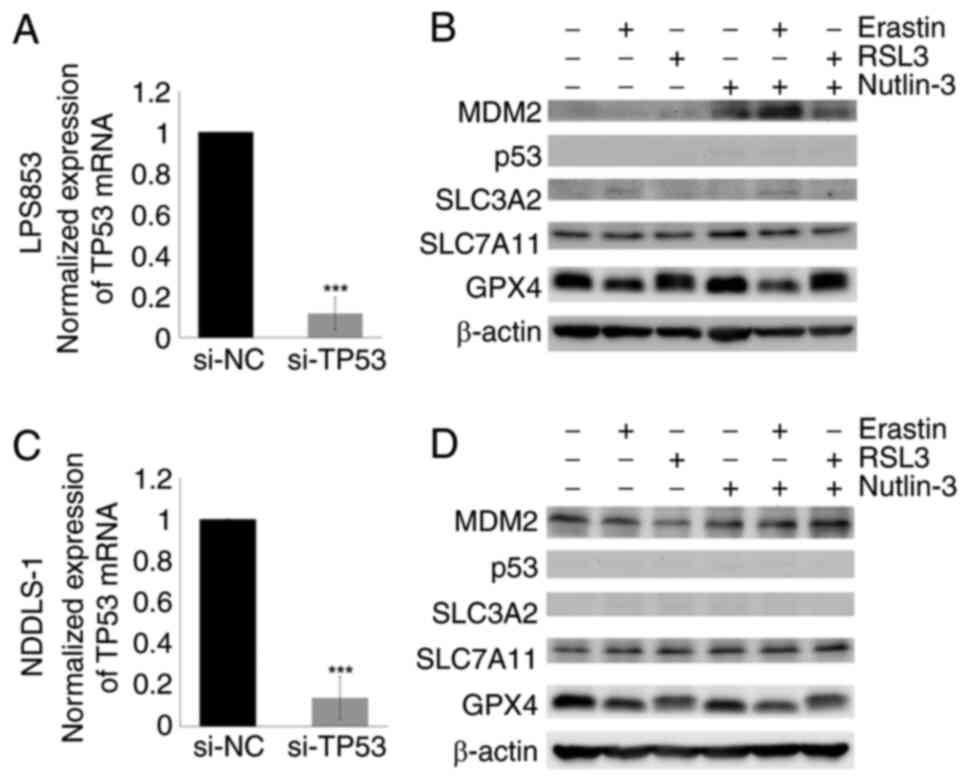
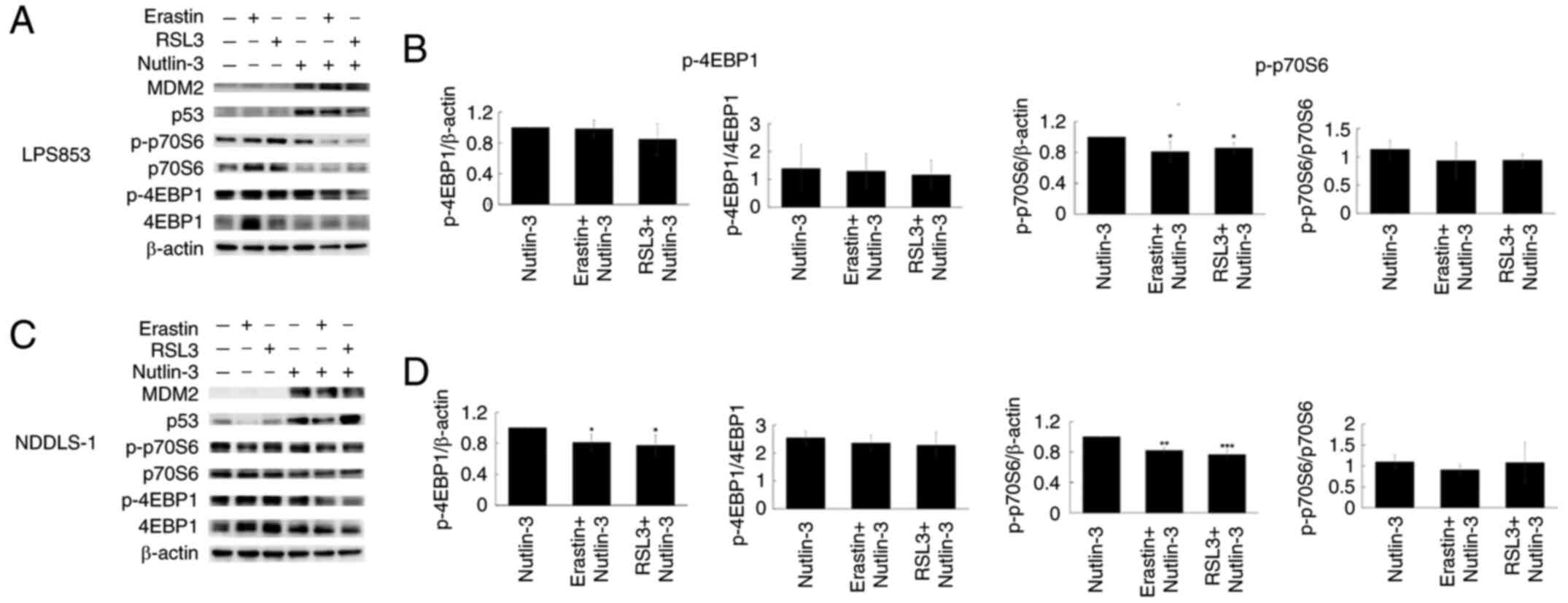
|
1
|
Hung GY, Yen CC, Horng JL, Liu CY, Chen
WM, Chen TH and Liu CL: Incidences of primary soft tissue sarcoma
diagnosed on extremities and trunk wall: A population-based study
in taiwan. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e16962015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hung GY, Horng JL, Chen PC, Lin LY, Chen
JY, Chuang PH, Chao TC and Yen CC: Incidence of soft tissue sarcoma
in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based study (2007–2013). Cancer
Epidemiol. 60:185–192. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ducimetiere F, Lurkin A, Ranchere-Vince D,
Decouvelaere AV, Peoc'h M, Istier L, Chalabreysse P, Muller C,
Alberti L, Bringuier PP, et al: Incidence of sarcoma histotypes and
molecular subtypes in a prospective epidemiological study with
central pathology review and molecular testing. PLoS One.
6:e202942011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee ATJ, Thway K, Huang PH and Jones RL:
Clinical and molecular spectrum of liposarcoma. J Clin Oncol.
36:151–159. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seddon B, Strauss SJ, Whelan J, Leahy M,
Woll PJ, Cowie F, Rothermundt C, Wood Z, Benson C, Ali N, et al:
Gemcitabine and docetaxel versus doxorubicin as first-line
treatment in previously untreated advanced unresectable or
metastatic soft-tissue sarcomas (GeDDiS): A randomised controlled
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:1397–1410. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schoffski P, Chawla S, Maki RG, Italiano
A, Gelderblom H, Choy E, Grignani G, Camargo V, Bauer S, Rha SY, et
al: Eribulin versus dacarbazine in previously treated patients with
advanced liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma: A randomised, open-label,
multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 387:1629–1637. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Demetri GD, Schoffski P, Grignani G, Blay
JY, Maki RG, Van Tine BA, Alcindor T, Jones RL, D'Adamo DR, Guo M
and Chawla S: Activity of eribulin in patients with advanced
liposarcoma demonstrated in a subgroup analysis from a randomized
phase III study of eribulin versus dacarbazine. J Clin Oncol.
35:3433–3439. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Demetri GD, von Mehren M, Jones RL,
Hensley ML, Schuetze SM, Staddon A, Milhem M, Elias A, Ganjoo K,
Tawbi H, et al: Efficacy and safety of trabectedin or dacarbazine
for metastatic liposarcoma or leiomyosarcoma after failure of
conventional chemotherapy: Results of a phase III randomized
multicenter clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 34:786–793. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Conrad M, Angeli JP, Vandenabeele P and
Stockwell BR: Regulated necrosis: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:348–366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun
X, Kang R and Tang D: Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death
Differ. 23:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir
H, Bush AI, Conrad M, Dixon SJ, Fulda S, Gascon S, Hatzios SK,
Kagan VE, et al: Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking
metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell. 171:273–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ingold I, Berndt C, Schmitt S, Doll S,
Poschmann G, Buday K, Roveri A, Peng X, Porto Freitas F, Seibt T,
et al: Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent
hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis. Cell. 172:409–422. e4212018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME,
Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji
AF, Clish CB, et al: Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by
GPX4. Cell. 156:317–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheok CF, Verma CS, Baselga J and Lane DP:
Translating p53 into the clinic. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 8:25–37. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T,
Hibshoosh H, Baer R and Gu W: Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated
activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 520:57–62. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moon SH, Huang CH, Houlihan SL, Regunath
K, Freed-Pastor WA, Morris JP, Tschaharganeh DF, Kastenhuber ER,
Barsotti AM, Culp-Hill R, et al: p53 represses the mevalonate
pathway to mediate tumor suppression. Cell. 176:564–580. e5192019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie Y, Zhu S, Song X, Sun X, Fan Y, Liu J,
Zhong M, Yuan H, Zhang L, Billiar TR, et al: The tumor suppressor
p53 limits ferroptosis by blocking DPP4 activity. Cell Rep.
20:1692–1704. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dei Tos AP, Doglioni C, Piccinin S, Sciot
R, Furlanetto A, Boiocchi M, Dal CP, Maestro R, Fletcher CD and
Tallini G: Coordinated expression and amplification of the MDM2,
CDK4, and HMGI-C genes in atypical lipomatous tumours. J Pathol.
190:531–536. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karni-Schmidt O, Lokshin M and Prives C:
The roles of MDM2 and MDMX in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 11:617–644.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Leslie PL and Zhang Y: MDM2 oligomers:
Antagonizers of the guardian of the genome. Oncogene. 35:6157–6165.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hock AK and Vousden KH: The role of
ubiquitin modification in the regulation of p53. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1843:137–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
do Patrocinio AB, Rodrigues V and Guidi
Magalhaes L: P53: Stability from the ubiquitin-proteasome system
and specific 26S proteasome inhibitors. ACS Omega. 7:3836–3843.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bang S, Kaur S and Kurokawa M: Regulation
of the p53 family proteins by the ubiquitin proteasomal pathway.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:2612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Venkatesh D, O'Brien NA, Zandkarimi F,
Tong DR, Stokes ME, Dunn DE, Kengmana ES, Aron AT, Klein AM, Csuka
JM, et al: MDM2 and MDMX promote ferroptosis by PPARalpha-mediated
lipid remodeling. Genes Dev. 34:526–543. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yen CC, Chen LT, Li CF, Chen SC, Chua WY,
Lin YC, Yen CH, Chen YC, Yang MH, Chao Y and Fletcher JA:
Identification of phenothiazine as an ETV1targeting agent in
gastrointestinal stromal tumors using the connectivity map. Int J
Oncol. 55:536–546. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chibon F, Lagarde P, Salas S, Perot G,
Brouste V, Tirode F, Lucchesi C, de Reynies A, Kauffmann A, Bui B,
et al: Validated prediction of clinical outcome in sarcomas and
multiple types of cancer on the basis of a gene expression
signature related to genome complexity. Nat Med. 16:781–787. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gobble RM, Qin LX, Brill ER, Angeles CV,
Ugras S, O'Connor RB, Moraco NH, Decarolis PL, Antonescu C and
Singer S: Expression profiling of liposarcoma yields a multigene
predictor of patient outcome and identifies genes that contribute
to liposarcomagenesis. Cancer Res. 71:2697–2705. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Doyle KR, Mitchell MA, Roberts CL, James
S, Johnson JE, Zhou Y, von Mehren M, Lev D, Kipling D and Broccoli
D: Validating a gene expression signature proposed to differentiate
liposarcomas that use different telomere maintenance mechanisms.
Oncogene. 31:265–266; author reply 267–268. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoshino J, Conte C, Fontana L,
Mittendorfer B, Imai S, Schechtman KB, Gu C, Kunz I, Rossi Fanelli
F, Patterson BW and Klein S: Resveratrol supplementation does not
improve metabolic function in nonobese women with normal glucose
tolerance. Cell Metab. 16:658–664. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nookaew I, Svensson PA, Jacobson P, Jernas
M, Taube M, Larsson I, Andersson-Assarsson JC, Sjostrom L, Froguel
P, Walley A, et al: Adipose tissue resting energy expenditure and
expression of genes involved in mitochondrial function are higher
in women than in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 98:E370–E378. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li C and Wong WH: Model-based analysis of
oligonucleotide arrays: Model validation, design issues and
standard error application. Genome Biol. 2:RESEARCH00322001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li C and Wong WH: Model-based analysis of
oligonucleotide arrays: Expression index computation and outlier
detection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:31–36. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoshida Y, Shimakawa S, Itoh N and Niki E:
Action of DCFH and BODIPY as a probe for radical oxidation in
hydrophilic and lipophilic domain. Free Radic Res. 37:861–872.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chou TC and Talalay P: Quantitative
analysis of dose-effect relationships: The combined effects of
multiple drugs or enzyme inhibitors. Adv Enzyme Regul. 22:27–55.
1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chou YS, Yen CC, Chen WM, Lin YC, Wen YS,
Ke WT, Wang JY, Liu CY, Yang MH, Chen TH and Liu CL: Cytotoxic
mechanism of PLK1 inhibitor GSK461364 against osteosarcoma: Mitotic
arrest, apoptosis, cellular senescence, and synergistic effect with
paclitaxel. Int J Oncol. 48:1187–1194. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D,
Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, Kong N, Kammlott U, Lukacs C, Klein C, et
al: In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule
antagonists of MDM2. Science. 303:844–848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tovar C, Rosinski J, Filipovic Z, Higgins
B, Kolinsky K, Hilton H, Zhao X, Vu BT, Qing W, Packman K, et al:
Small-molecule MDM2 antagonists reveal aberrant p53 signaling in
cancer: Implications for therapy. Proc NatI Acad Sci USA.
103:1888–1893. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Henze J, Muhlenberg T, Simon S, Grabellus
F, Rubin B, Taeger G, Schuler M, Treckmann J, Debiec-Rychter M,
Taguchi T, et al: p53 modulation as a therapeutic strategy in
gastrointestinal stromal tumors. PLoS One. 7:e377762012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shi Z, Naowarojna N, Pan Z and Zou Y:
Multifaceted mechanisms mediating cystine starvation-induced
ferroptosis. Nat Commun. 12:47922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang Z, Zong H, Liu W, Lin W, Sun A, Ding
Z, Chen X, Wan X, Liu Y, Hu Z, et al: Augmented ERO1alpha upon
mTORC1 activation induces ferroptosis resistance and tumor
progression via upregulation of SLC7A11. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
43:1122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yin J, Chen J, Hong JH, Huang Y, Xiao R,
Liu S, Deng P, Sun Y, Chai KXY, Zeng X, et al: 4EBP1-mediated
SLC7A11 protein synthesis restrains ferroptosis triggered by MEK
inhibitors in advanced ovarian cancer. JCI Insight. 9:e1778572024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han J, Wang L, Lv H, Liu J, Dong Y, Shi L
and Ji Q: EphA2 inhibits SRA01/04 cells apoptosis by suppressing
autophagy via activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 711:1090242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang J, Pi C and Wang G: Inhibition of
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway by apigenin induces apoptosis and autophagy
in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Biomed Pharmacother.
103:699–707. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li W, Li D, Ma Q, Chen Y, Hu Z, Bai Y and
Xie L: Targeted inhibition of mTOR by BML-275 induces
mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis and autophagy in prostate cancer.
Eur J Pharmacol. 957:1760352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Fletcher CD: The evolving classification
of soft tissue tumours-An update based on the new 2013 WHO
classification. Histopathology. 64:2–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sherr CJ, Beach D and Shapiro GI:
Targeting CDK4 and CDK6: From discovery to therapy. Cancer Discov.
6:353–367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Finn RS, Martin M, Rugo HS, Jones S, Im
SA, Gelmon K, Harbeck N, Lipatov ON, Walshe JM, Moulder S, et al:
Palbociclib and letrozole in advanced breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
375:1925–1936. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hortobagyi GN, Stemmer SM, Burris HA, Yap
YS, Sonke GS, Paluch-Shimon S, Campone M, Petrakova K, Blackwell
KL, Winer EP, et al: Updated results from MONALEESA-2, a phase III
trial of first-line ribociclib plus letrozole versus placebo plus
letrozole in hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative advanced
breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 29:1541–1547. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Goetz MP, Toi M, Campone M, Sohn J,
Paluch-Shimon S, Huober J, Park IH, Tredan O, Chen SC, Manso L, et
al: MONARCH 3: Abemaciclib as initial therapy for advanced breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35:3638–3646. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang S, Zhao Y, Aguilar A, Bernard D and
Yang CY: Targeting the MDM2-p53 protein-protein interaction for new
cancer therapy: Progress and challenges. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Med. 7:a0262452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kocik J, Machula M, Wisniewska A, Surmiak
E, Holak TA and Skalniak L: Helping the released guardian: Drug
combinations for supporting the anticancer activity of HDM2 (MDM2)
antagonists. Cancers (Basel). 11:10142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fang Y, Liao G and Yu B: Small-molecule
MDM2/X inhibitors and PROTAC degraders for cancer therapy: Advances
and perspectives. Acta Pharm Sin B. 10:1253–1278. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao Y, Aguilar A, Bernard D and Wang S:
Small-molecule inhibitors of the MDM2-p53 protein-protein
interaction (MDM2 Inhibitors) in clinical trials for cancer
treatment. J Med Chem. 58:1038–1052. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
LoRusso P, Yamamoto N, Patel MR, Laurie
SA, Bauer TM, Geng J, Davenport T, Teufel M, Li J, Lahmar M and
Gounder MM: The MDM2-p53 Antagonist brigimadlin (BI 907828) in
patients with advanced or metastatic solid tumors: Results of a
phase Ia, first-in-human, dose-escalation study. Cancer Discov.
13:1802–1813. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ray-Coquard I, Blay JY, Italiano A, Le
Cesne A, Penel N, Zhi J, Heil F, Rueger R, Graves B, Ding M, et al:
Effect of the MDM2 antagonist RG7112 on the P53 pathway in patients
with MDM2-amplified, well-differentiated or dedifferentiated
liposarcoma: An exploratory proof-of-mechanism study. Lancet Oncol.
13:1133–1140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gounder MM, Bauer TM, Schwartz GK, Weise
AM, LoRusso P, Kumar P, Tao B, Hong Y, Patel P, Lu Y, et al: A
first-in-human Phase I study of milademetan, an MDM2 inhibitor, in
patients with advanced liposarcoma, solid tumors, or lymphomas. J
Clin Oncol. 41:1714–1724. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Assi T, Kattan J, Rassy E, Nassereddine H,
Farhat F, Honore C, Le Cesne A, Adam J and Mir O: Targeting CDK4
(cyclin-dependent kinase) amplification in liposarcoma: A
comprehensive review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 153:1030292020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dickson MA, Schwartz GK, Keohan ML,
D'Angelo SP, Gounder MM, Chi P, Antonescu CR, Landa J, Qin LX,
Crago AM, et al: Progression-free survival among patients with
well-differentiated or dedifferentiated liposarcoma treated with
CDK4 inhibitor palbociclib: A phase 2 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol.
2:937–940. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Guo J, Xu B, Han Q, Zhou H, Xia Y, Gong C,
Dai X, Li Z and Wu G: Ferroptosis: A novel anti-tumor action for
cisplatin. Cancer Res Treat. 50:445–460. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ma S, Henson ES, Chen Y and Gibson SB:
Ferroptosis is induced following siramesine and lapatinib treatment
of breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 7:e23072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Trujillo-Alonso V, Pratt EC, Zong H,
Lara-Martinez A, Kaittanis C, Rabie MO, Longo V, Becker MW, Roboz
GJ, Grimm J and Guzman ML: FDA-approved ferumoxytol displays
anti-leukaemia efficacy against cells with low ferroportin levels.
Nat Nanotechnol. 14:616–622. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yamaguchi Y, Kasukabe T and Kumakura S:
Piperlongumine rapidly induces the death of human pancreatic cancer
cells mainly through the induction of ferroptosis. Int J Oncol.
52:1011–1022. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sun X, Ou Z, Chen R, Niu X, Chen D, Kang R
and Tang D: Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects
against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology.
63:173–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Brashears CB, Prudner BC, Rathore R,
Caldwell KE, Dehner CA, Buchanan JL, Lange SES, Poulin N, Sehn JK,
Roszik J, et al: Malic enzyme 1 absence in synovial sarcoma shifts
antioxidant system dependence and increases sensitivity to
ferroptosis induction with ACXT-3102. Clin Cancer Res.
28:3573–3589. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S,
Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, Kaffenberger SD, Eaton JK, Shimada
K, Aguirre AJ, et al: Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of
cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 547:453–457.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mello SS, Valente LJ, Raj N, Seoane JA,
Flowers BM, McClendon J, Bieging-Rolett KT, Lee J, Ivanochko D,
Kozak MM, et al: A p53 super-tumor suppressor reveals a tumor
suppressive p53-ptpn14-yap axis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell.
32:460–473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tombari C, Zannini A, Bertolio R, Pedretti
S, Audano M, Triboli L, Cancila V, Vacca D, Caputo M, Donzelli S,
et al: Mutant p53 sustains serine-glycine synthesis and essential
amino acids intake promoting breast cancer growth. Nat Commun.
14:67772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Fujihara KM, Corrales Benitez M, Cabalag
CS, Zhang BZ, Ko HS, Liu DS, Simpson KJ, Haupt Y, Lipton L, Haupt
S, et al: SLC7A11 Is a superior determinant of APR-246
(Eprenetapopt) response than TP53 mutation status. Mol Cancer Ther.
20:1858–1867. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Riscal R, Schrepfer E, Arena G, Cisse MY,
Bellvert F, Heuillet M, Rambow F, Bonneil E, Sabourdy F, Vincent C,
et al: Chromatin-bound MDM2 regulates serine metabolism and redox
homeostasis independently of p53. Mol Cell. 62:890–902. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Villalonga-Planells R, Coll-Mulet L,
Martinez-Soler F, Castano E, Acebes JJ, Gimenez-Bonafe P, Gil J and
Tortosa A: Activation of p53 by nutlin-3a induces apoptosis and
cellular senescence in human glioblastoma multiforme. PLoS One.
6:e185882011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Miyachi M, Kakazu N, Yagyu S, Katsumi Y,
Tsubai-Shimizu S, Kikuchi K, Tsuchiya K, Iehara T and Hosoi H:
Restoration of p53 pathway by nutlin-3 induces cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Clin Cancer Res.
15:4077–4084. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Manfe V, Biskup E, Johansen P, Kamstrup
MR, Krejsgaard TF, Morling N, Wulf HC and Gniadecki R: MDM2
inhibitor nutlin-3a induces apoptosis and senescence in cutaneous
T-cell lymphoma: role of p53. J Invest Dermatol. 132:1487–1496.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Xie Y, Lei X, Zhao G, Guo R and Cui N:
mTOR in programmed cell death and its therapeutic implications.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 71–72. 66–81. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cordero OJ: CD26 and cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 14:51942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|