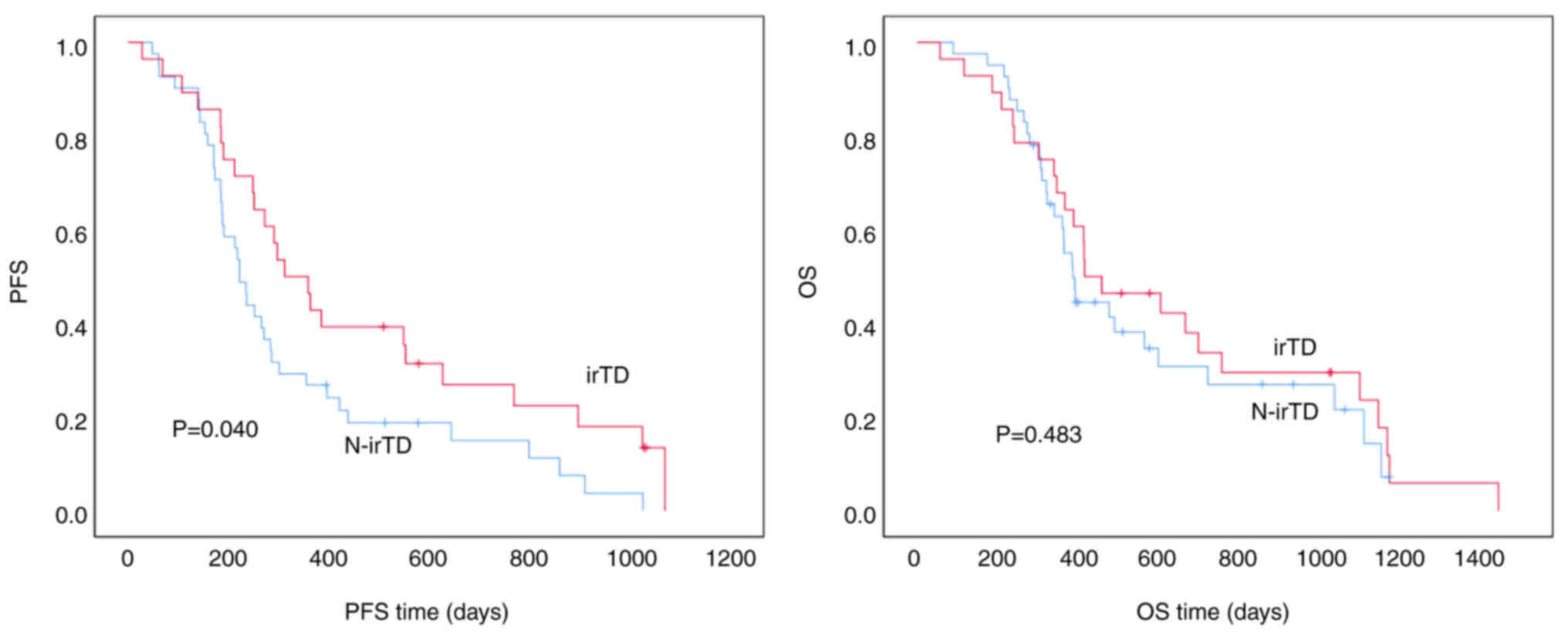
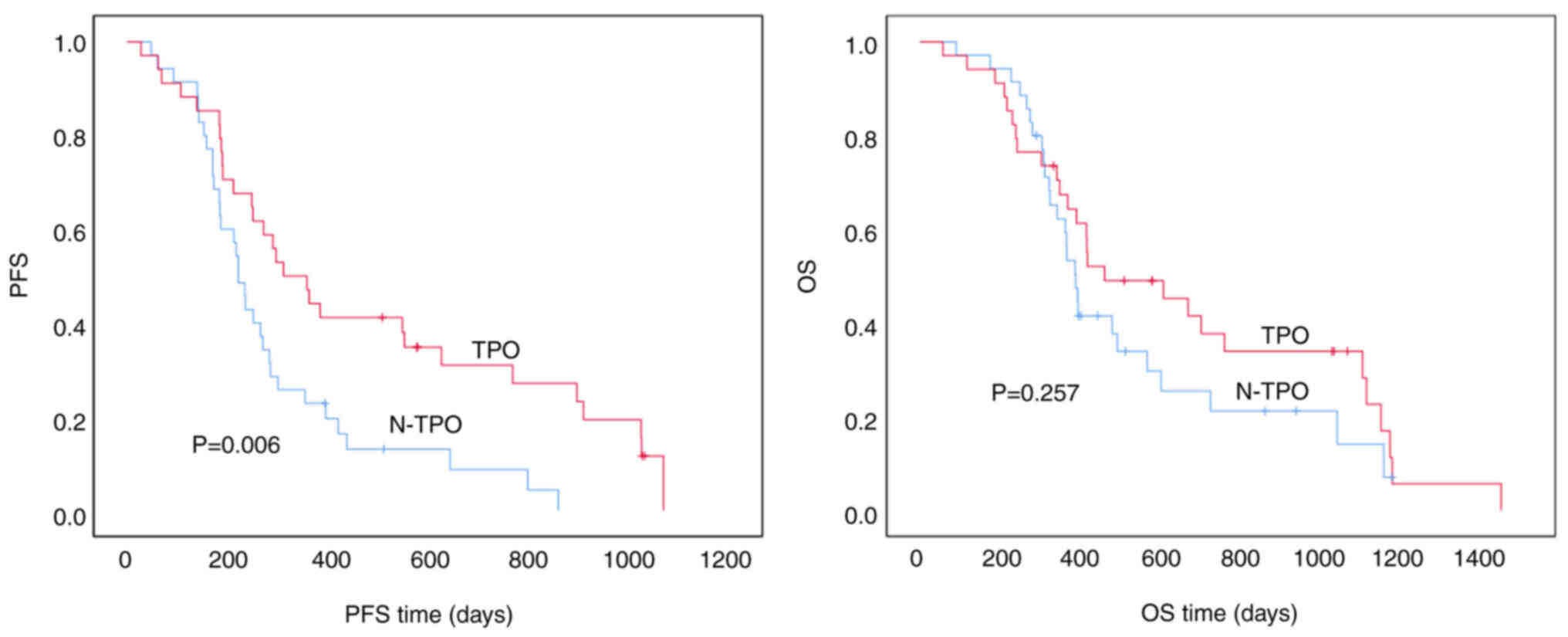
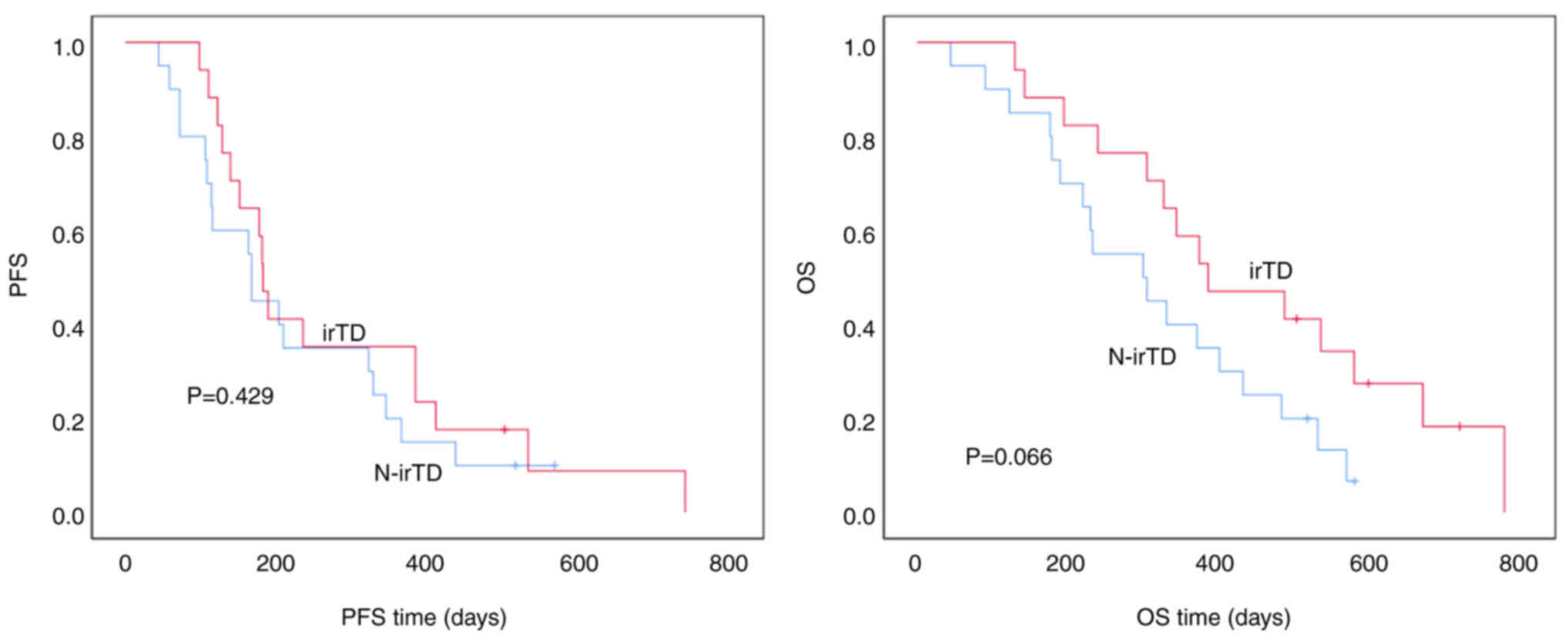
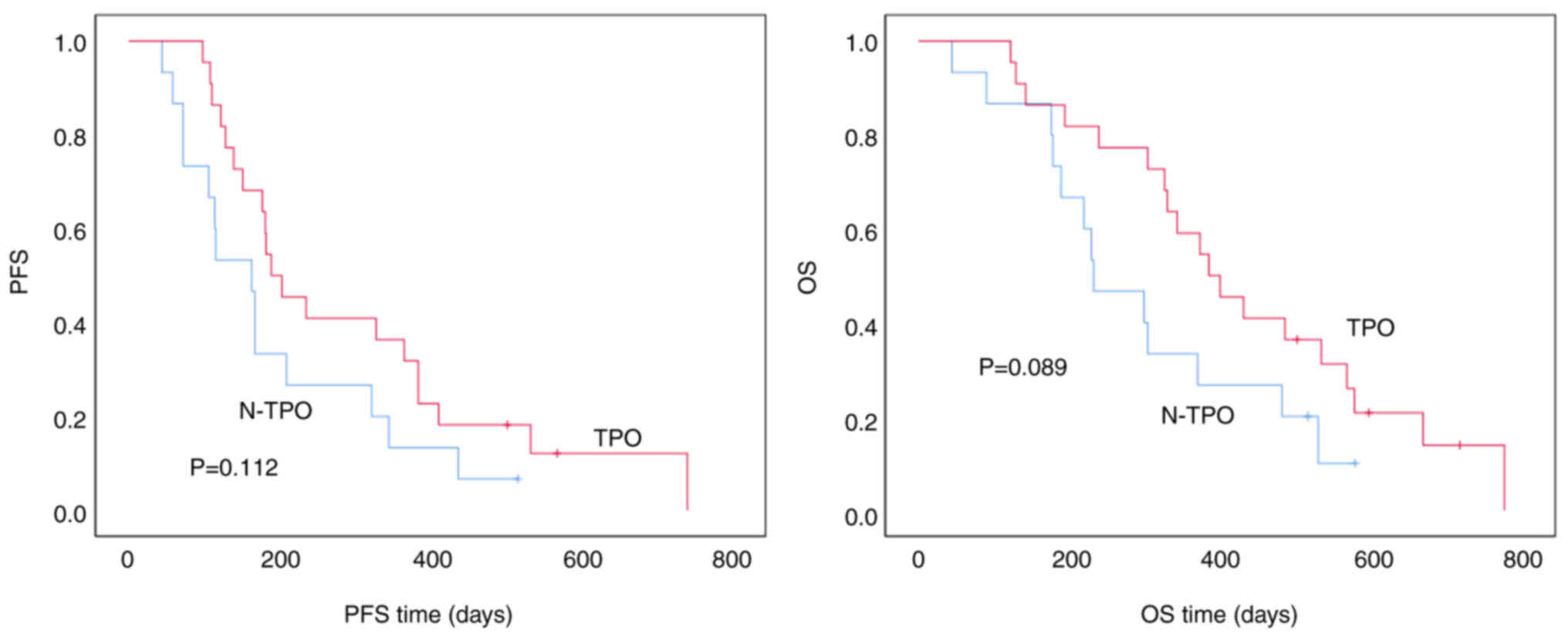
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N and Chen WQ:
Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A
secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J
(Engl). 134:783–791. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zheng RS, Chen R, Han BF, Wang SM, Li L,
Sun KX, Zeng HM, Wei WW and He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in
China, 2022. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 46:221–231. 2024.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Riely GJ, Wood DE, Ettinger DS, Aisner DL,
Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, et
al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
22:249–274. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lordick F, Carneiro F, Cascinu S, Fleitas
T, Haustermans K, Piessen G, Vogel A and Smyth EC; ESMO Guidelines
Committee. Electronic address, : simpleclinicalguidelines@esmo.org:
Gastric cancer: ESMO clinical practice guideline for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 33:1005–1020. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang FH, Zhang XT, Tang L, Wu Q, Cai MY,
Li YF, Qu XJ, Qiu H, Zhang YJ, Ying JE, et al: The Chinese society
of clinical oncology (CSCO): Clinical guidelines for the diagnosis
and treatment of gastric cancer, 2023. Cancer Commun (Lond).
44:127–172. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakayama I, Qi C, Chen Y, Nakamura Y, Shen
L and Shitara K: Claudin 18.2 as a novel therapeutic target. Nat
Rev Clin Oncol. 21:354–369. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hu HH, Wang SQ, Zhao H, Chen ZS, Shi X and
Chen XB: HER2+ advanced gastric cancer: Current state and
opportunities (Review). Int J Oncol. 64:362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yao Y, Zhou J, Song J and Chen C:
Ruxolitinib enhances gastric cancer to chemotherapy by suppressing
JAK/STAT3 and inducing mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative
stress. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 26:1–9. 2025.
|
|
10
|
Babaei S, Nikbakht M, Majd A and Mousavi
SA: Comparative effects of arsenic trioxide and chemotherapy on
Chk1 and CDC25 gene expression in gastric cancer cells AGS and
MKN45: A potential therapeutic strategy. Mol Biol Rep. 52:1982025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Janjigian YY, Shitara K, Moehler M,
Garrido M, Salman P, Shen L, Wyrwicz L, Yamaguchi K, Skoczylas T,
Bragagnoli AC, et al: First-line nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus
chemotherapy alone for advanced gastric, gastro-oesophageal
junction, and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (CheckMate 649): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 398:27–40. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kang YK, Chen LT, Ryu MH, Oh DY, Oh SC,
Chung HC, Lee KW, Omori T, Shitara K, Sakuramoto S, et al:
Nivolumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in
patients with HER2-negative, untreated, unresectable advanced or
recurrent gastric or gastrooesophageal junction cancer
(ATTRACTION-4): A randomised, multicentre, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 23:234–247. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu J, Jiang H, Pan Y, Gu K, Cang S, Han L,
Shu Y, Li J, Zhao J and Pan H: LBA53 Sintilimab plus chemotherapy
(chemo) versus chemo as. first-line treatment for advanced gastric
or gastroesophageal junction (G/GEJ) adenocarcinoma (ORIENT16):
First results of a randomized, double-blind, phase III study. Anna
Oncol. 32:S13312021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Moehler MH, Kato K, Arkenau HT, Oh DY,
Tabernero J, Cruz-Correa M, Wang H, Xu H, Li J, Yang S and Xu RH:
RATIONALE-305: Phase 3 study of tislelizumab plus chemotherapy vs.
placebo plus chemotherapy as first-line treatment (1L) of advanced
gastric or gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GC/GEJC). 2023
ASCO GI. Abstract#286.
|
|
15
|
Cruz-Correa M, Xu RH, Moehler MH, Oh DY,
Kato K, Spigel DR, Arkenau HT, Tabernero J, Zimina AV, Bai Y, et
al: Tislelizumab (TIS) plus chemotherapy (Chemo) vs. placebo (PBO)
plus chemo as first-line (1L) treatment of advanced gastric or
gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma (GC/GEJC): Final analysis
results of the RATIONALE-305 study. 2023, ESMO. Abstract LBA80.
|
|
16
|
Janjigian YY, Kawazoe A, Bai Y, Xu J,
Lonardi S, Metges JP, Yanez P, Wyrwicz LS, Shen L, Ostapenko Y, et
al: Pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy for
HER2-positive gastric or gastro-oesophageal junction
adenocarcinoma: Interim analyses from the phase 3 KEYNOTE-811
randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 402:2197–2208. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Michot JM, Bigenwald C, Champiat S,
Collins M, Carbonnel F, Postel-Vinay S, Berdelou A, Varga A,
Bahleda R, Hollebecque A, et al: Immune-related adverse events with
immune checkpoint blockade: A comprehensive review. Eur J Cancer.
54:139–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang J, Lyu M, Feng X, Liu F, Zeng R, Sun
X, Bao Z, Zhou L, Gao B, Ni L and Xiang Y: The predict factors and
clinical prognosis value of immune-related pneumonia of receiving
PD-1 inhibitor in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A
retrospective study. Int Immunopharmacol. 2142:1131402024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jhaveri KD and Wanchoo R: Adverse events
associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. JAMA. 321:1218–1219.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chang LS, Barroso-Sousa R, Tolaney SM,
Hodi FS, Kaiser UB and Min L: Endocrine toxicity of cancer
immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr Rev. 40:17–65.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang T, Lv H, Li J, Zhang S, Zhang J,
Wang S, Wang Y and Guo Z: The impact of immune-related adverse
events on the outcome of advanced gastric cancer patients with
immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment. Front Immunol.
15:15033162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grangeon M, Tomasini P, Chaleat S, Jeanson
A, Souquet-Bressand M, Khobta N, Bermudez J, Trigui Y, Greillier L,
Blanchon M, et al: Association between immune-related adverse
events and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer. 20:201–207. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koyama J, Horiike A, Yoshizawa T, Dotsu Y,
Ariyasu R, Saiki M, Sonoda T, Uchibori K, Nishikawa S, Kitazono S,
et al: Correlation between thyroid transcription factor-1
expression, immune-related thyroid dysfunction, and efficacy of
anti-programmed cell death protein-1 treatment in non-small cell
lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 11:1919–1928. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Y, Xia R, Xiao H, Pu D, Long Y, Ding
Z, Liu J and Ma X: Thyroid function abnormality induced by PD-1
inhibitors have a positive impact on survival in patients with
non-small cell lung cancer. Int Immunopharmacol. 91:1072962021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ferreira JL, Costa C, Marques B, Castro S,
Victor M, Oliveira J, Santos AP, Sampaio IL, Duarte H, Marques AP
and Torres I: Improved survival in patients with thyroid function
test abnormalities secondary to immune-checkpoint inhibitors.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 70:299–309. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kotwal A and Ryder M: Survival benefit of
endocrine dysfunction following immune checkpoint inhibitors for
nonthyroidal cancers. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes.
28:517–524. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Byrd DR,
Brookland RK, Washington MK, Gershenwald JE, Compton CC, Hess KR,
Sullivan DC, et al: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th Edition.
Springer; New York: 2017
|
|
28
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoon JH, Hong AR, Kim HK and Kang HC:
Characteristics of immune-related thyroid adverse events in
patients treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors. Endocrinol Metab
(Seoul). 36:413–423. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chilelli MG, Signorelli C, Berrios JR,
Onorato A, Nelli F, Fabbri MA, Primi F, Marrucci E, Virtuoso A,
Schirripa M, et al: Immune-related thyroid dysfunction (irTD) in
non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) correlates with response and
survival. Cancer Diagn Progn. 2:55–63. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li Z, Xia Y, Xia M, Liu C, Wang T, Liu Y
and Ren Y: Immune-related thyroid dysfunction is associated with
improved long-term prognosis in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer treated with immunotherapy: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Thorac Dis. 15:690–700. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou N, Velez MA, Bachrach B, Gukasyan J,
Fares CM, Cummings AL, Lind-Lebuffe JP, Akingbemi WO, Li DY,
Brodrick PM, et al: Immune checkpoint inhibitor induced thyroid
dysfunction is a frequent event post-treatment in NSCLC. Lung
Cancer. 161:34–41. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Horesh A, Pollack R, Nechushtan H,
Dresner-Pollak R and Neuman T: Tumor PD-L1 expression and molecular
profiling are not associated with immune checkpoint
inhibitor-induced thyroid dysfunction in advanced NSCLC patients.
Pathol Oncol Res. 29:16109512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamauchi I, Sakane Y, Fukuda Y, Fujii T,
Taura D, Hirata M, Hirota K, Ueda Y, Kanai Y, Yamashita Y, et al:
Clinical features of nivolumab-induced thyroiditis: A case series
study. Thyroid. 27:894–901. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Osorio JC, Ni A, Chaft JE, Pollina R,
Kasler MK, Stephens D, Rodriguez C, Cambridge L, Rizvi H, Wolchok
JD, et al: Antibody-mediated thyroid dysfunction during T-cell
checkpoint blockade in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer.
Ann Oncol. 28:583–589. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mazarico I, Capel I, Giménez-Palop O,
Albert L, Berges I, Luchtenberg F, García Y, Fernández-Morales LA,
De Pedro VJ, Caixàs A and Rigla M: Low frequency of positive
antithyroid antibodies is observed in patients with thyroid
dysfunction related to immune check point inhibitors. J Endocrinol
Invest. 42:1443–1450. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Okada N, Iwama S, Okuji T, Kobayashi T,
Yasuda Y, Wada E, Onoue T, Goto M, Sugiyama M, Tsunekawa T, et al:
Anti-thyroid antibodies and thyroid echo pattern at baseline as
risk factors for thyroid dysfunction induced by anti-programmed
cell death-1 antibodies: A prospective study. Br J Cancer.
122:771–777. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kobayashi T, Iwama S, Yasuda Y, Okada N,
Tsunekawa T, Onoue T, Takagi H, Hagiwara D, Ito Y, Morishita Y, et
al: Patients with antithyroid antibodies are prone to develop
destructive thyroiditis by nivolumab: A prospective study. J Endocr
Soc. 2:241–251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kimbara S, Fujiwara Y, Iwama S, Ohashi K,
Kuchiba A, Arima H, Yamazaki N, Kitano S, Yamamoto N and Ohe Y:
Association of antithyroglobulin antibodies with the development of
thyroid dysfunction induced by nivolumab. Cancer Sci.
109:3583–3590. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Izawa N, Shiokawa H, Onuki R, Hamaji K,
Morikawa K, Saji H, Ohashi H, Kasugai S, Hayakawa N, Ohara T and
Sunakawa Y: The clinical utility of comprehensive measurement of
autoimmune disease-related antibodies in patients with advanced
solid tumors receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: A
retrospective study. ESMO Open. 7:1004152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
de Moel EC, Rozeman EA, Kapiteijn EH,
Verdegaal EME, Grummels A, Bakker JA, Huizinga TWJ, Haanen JB, Toes
REM and van der Woude D: Autoantibody development under treatment
with immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Immunol Res. 7:6–11.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Brancatella A, Viola N, Brogioni S,
Montanelli L, Sardella C, Vitti P, Marcocci C, Lupi I and Latrofa
F: Graves' disease induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: A case
report and review of the literature. Eur Thyroid J. 8:192–195.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yajima K and Akise Y: A case report of
graves' disease induced by the anti-human programmed cell death-1
monoclonal antibody pembrolizumab in a bladder cancer patient. Case
Rep Endocrinol. 17:23140322019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Al Mushref M, Guido PA, Collichio FA,
Moore DT and Clemmons DR: Thyroid dysfunction, recovery, and
prognosis in melanoma patients treated with immune checkpoint
inhibitors: A RETROSPECTIVE REVIEW. Endocr Pract. 26:36–42. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Iyer PC, Cabanillas ME, Waguespack SG, Hu
MI, Thosani S, Lavis VR, Busaidy NL, Subudhi SK, Diab A and Dadu R:
Immune-Related thyroiditis with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
Thyroid. 28:1243–1251. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Basak EA, van der Meer JWM, Hurkmans DP,
Schreurs MWJ, Oomen-de Hoop E, van der Veldt AAM, Bins S, Joosse A,
Koolen SLW, Debets R, et al: Overt thyroid dysfunction and
anti-thyroid antibodies predict response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy
in cancer patients. Thyroid. 30:966–973. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kotwal A, Kottschade L and Ryder M: PD-L1
inhibitor-induced thyroiditis is associated with better overall
survival in cancer patients. Thyroid. 30:177–184. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Peiró I, Palmero R, Iglesias P, Díez JJ,
Simó-Servat A, Marín JA, Jiménez L, Domingo-Domenech E, Mancho-Fora
N, Nadal E and Villabona C: Thyroid dysfunction induced by
nivolumab: searching for disease patterns and outcomes. Endocrine.
64:605–613. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yamauchi I, Yasoda A, Matsumoto S,
Sakamori Y, Kim YH, Nomura M, Otsuka A, Yamasaki T, Saito R,
Kitamura M, et al: Incidence, features, and prognosis of
immune-related adverse events involving the thyroid gland induced
by nivolumab. PLoS One. 14:e02169542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hussaini S, Chehade R, Boldt RG, Raphael
J, Blanchette P, Vareki SM and Fernandes R: Association between
immune-related side effects and efficacy and benefit of immune
checkpoint inhibitors-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer
Treat Rev. 92:1021342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sakakida T, Ishikawa T, Uchino J, Chihara
Y, Komori S, Asai J, Narukawa T, Arai A, Kobayashi T, Tsunezuka H,
et al: Clinical features of immune-related thyroid dysfunction and
its association with outcomes in patients with advanced
malignancies treated by PD-1 blockade. Oncol Lett. 18:2140–2147.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Paderi A, Giorgione R, Giommoni E, Mela
MM, Rossi V, Doni L, Minervini A, Carini M, Pillozzi S and
Antonuzzo L: Association between immune related adverse events and
outcome in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated
with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancers (Basel). 13:8602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu Y, Chen N, Yu S, Shen W, Zhai W, Li H
and Fan Y: Association of immune-related adverse events and the
efficacy of anti-PD-(L)1 monotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer:
Adjusting for immortal-time bias. Cancer Res Treat. 56:751–764.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang J, Gao A, Wang S and Sun Y, Wu J,
Wang D, Ge Y, Li J, Sun H, Cheng Q and Sun Y: Correlation between
immune-related adverse events and efficacy of PD-(L)1 inhibitors in
small cell lung cancer: A multi-center retrospective study. Respir
Res. 25:2562024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yasuda Y, Iwama S, Sugiyama D, Okuji T,
Kobayashi T, Ito M, Okada N, Enomoto A, Ito S, Yan Y, et al: CD4+ T
cells are essential for the development of destructive thyroiditis
induced by anti-PD-1 antibody in thyroglobulin-immunized mice. Sci
Transl Med. 13:eabb74952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shimozaki K, Sukawa Y, Beppu N, Kurihara
I, Suzuki S, Mizuno R, Funakoshi T, Ikemura S, Tsugaru K, Togasaki
K, et al: Multiple immune-related adverse events and anti-tumor
efficacy: Real-world data on various solid tumors. Cancer Manag
Res. 12:4585–4593. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Nishimura T, Fujimoto H, Fujiwara T, Ito
K, Fujiwara A, Yuda H, Itani H, Naito M, Kodama S, Furuhashi K, et
al: Impact of immune-related adverse events on survival outcomes in
extensive-stage small cell lung cancer patients treated with immune
checkpoint inhibitors. Cancer Med. 13:e71882024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Reschke R, Deitert B, Enk AH and Hassel
JC: The role of tissue-resident memory T cells as mediators for
response and toxicity in immunotherapy-treated melanoma-two sides
of the same coin? Front Immunol. 15:13857812024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Postow MA, Sidlow R and Hellmann MD:
Immune-Related adverse events associated with immune checkpoint
blockade. N Engl J Med. 378:158–168. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Taylor CA, Watson RA, Tong O, Ye W,
Nassiri I, Gilchrist JJ, de Los Aires AV, Sharma PK, Koturan S,
Cooper RA, et al: IL7 genetic variation and toxicity to immune
checkpoint blockade in patients with melanoma. Nat Med.
28:2592–2600. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Song Y, Pan S, Tian J, Yu Y, Wang S, Qiu
Q, Shen Y, Yang L, Liu X, Luan J, et al: Activation of CD14+
monocytes via the IFN-γ signaling pathway is associated with
immune-related adverse events in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
receiving PD-1 inhibition combination therapy. Biomedicines.
12:11402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kashiwada T, Takano R, Ando F, Kuroda S,
Miyabe Y, Owada R, Miyanaga A, Asatsuma-Okumura T, Hashiguchi M,
Kanazawa Y, et al: Lysosomal degradation of PD-L1 is associated
with immune-related adverse events during anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy
in NSCLC patients. Front Pharmacol. 15:13847332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Foldi J, Blenman KRM, Marczyk M,
Gunasekharan V, Polanska A, Gee R, Davis M, Kahn AM, Silber A and
Pusztai L: Peripheral blood immune parameters, response, and
adverse events after neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus durvalumab in
early-stage triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
208:369–377. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|