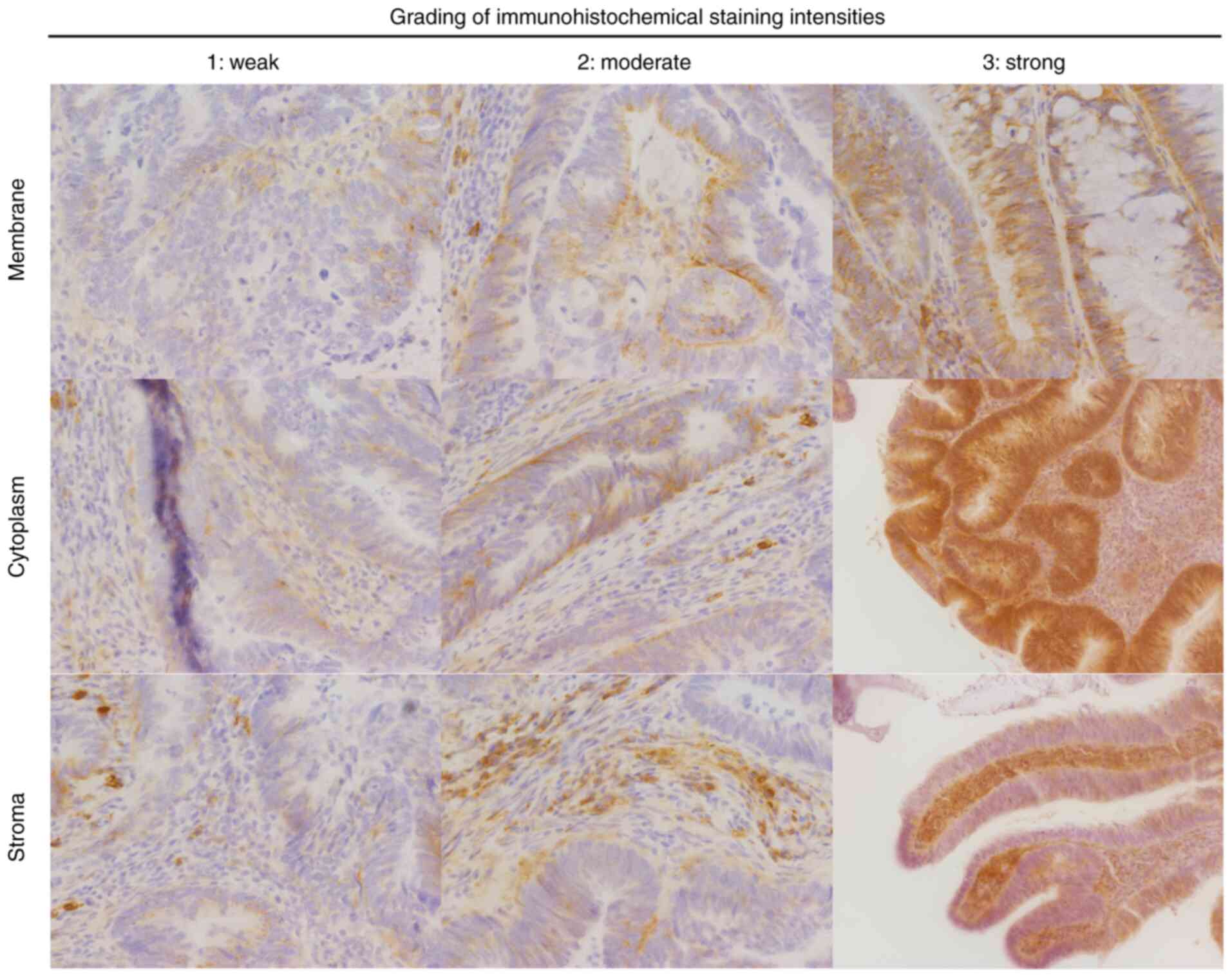
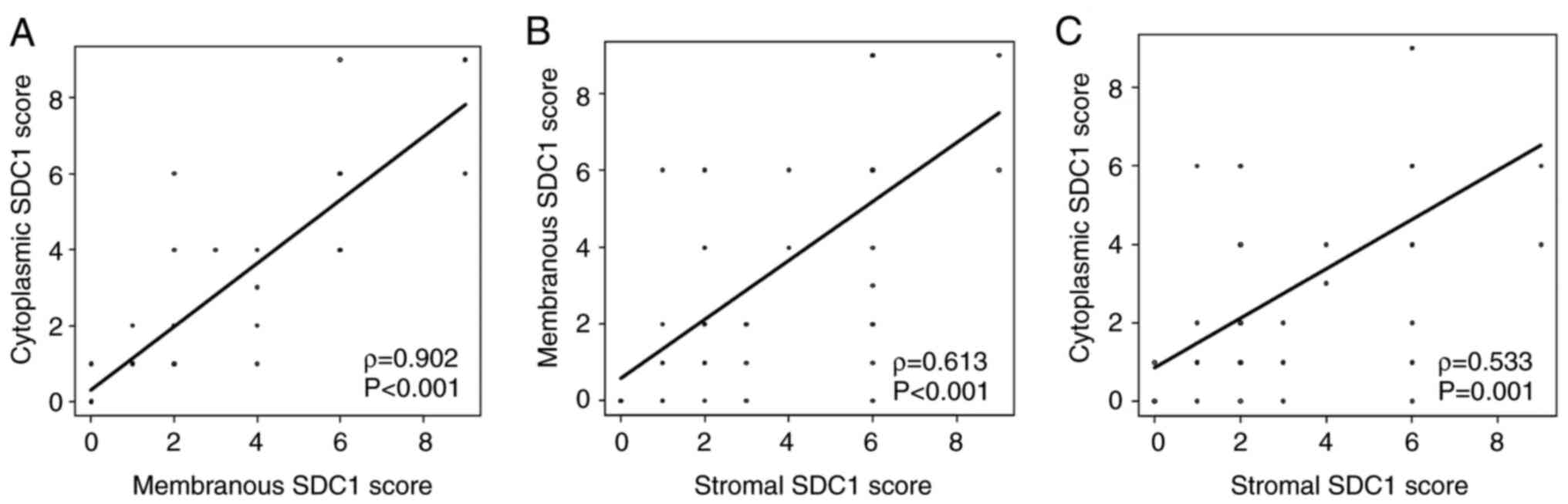
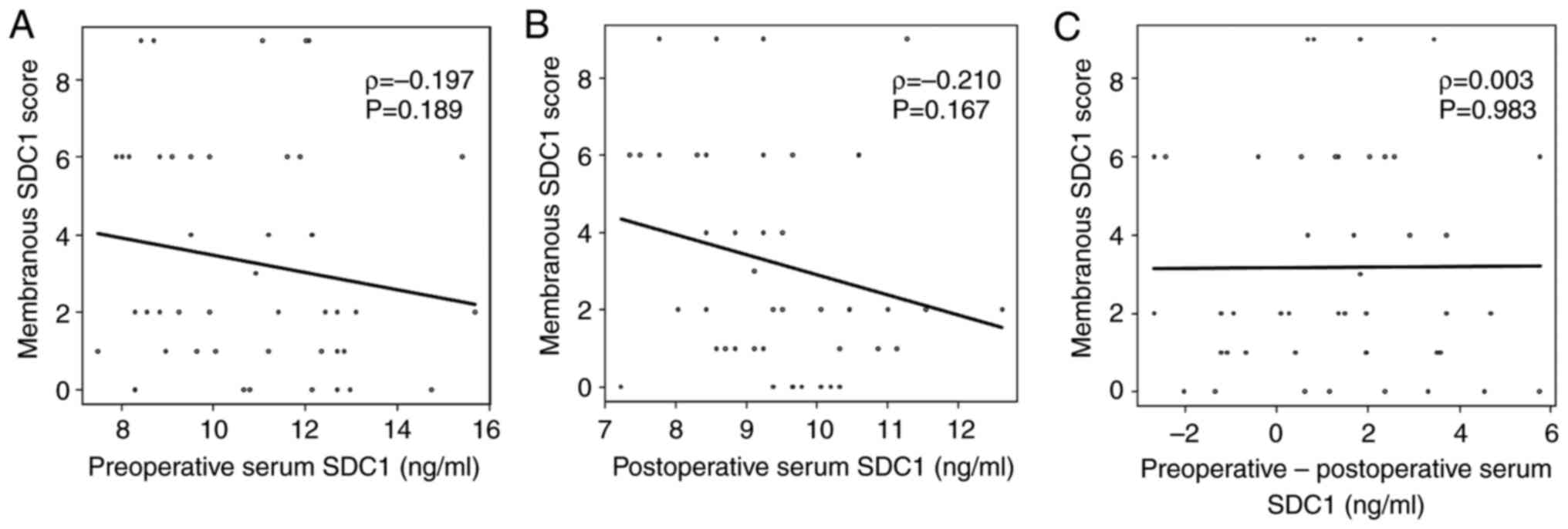
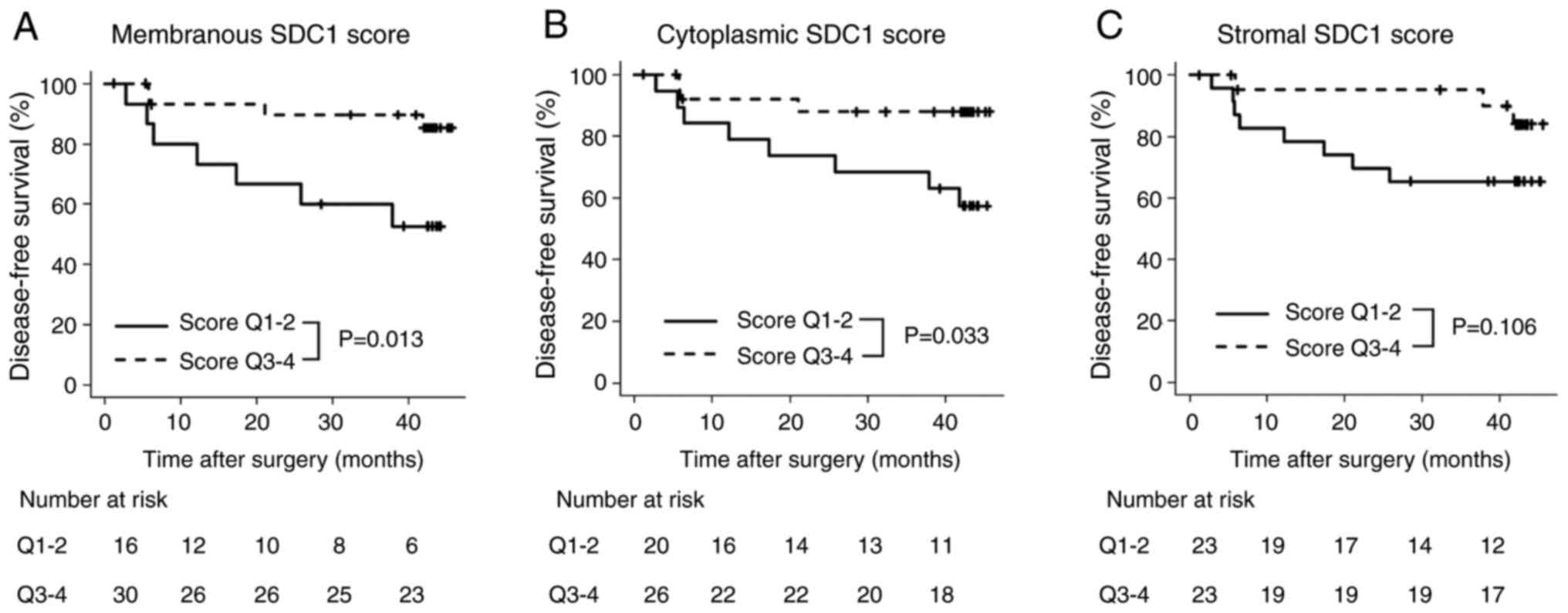
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tzang CC, Lee YW, Lin WC, Lin LH, Kang YF,
Lin TY, Wu WT and Chang KV: Evaluation of immune checkpoint
inhibitors for colorectal cancer: A network meta-analysis. Oncol
Lett. 28:5692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Batsalova T, Uzunova D, Chavdarova G,
Apostolova T and Dzhambazov B: Some glycoproteins expressed on the
surface of immune cells and cytokine plasma levels can be used as
potential biomarkers in patients with colorectal cancer.
Biomolecules. 14:13142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Szatmári T, Ötvös R, Hjerpe A and Dobra K:
Syndecan-1 in cancer: Implications for cell signaling,
differentiation, and prognostication. Dis Markers. 2015:7960522015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Teng YHF, Aquino RS and Park PW: Molecular
functions of syndecan-1 in disease. Matrix Biol. 31:3–16. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Beauvais DM, Ell BJ, McWhorter AR and
Rapraeger AC: Syndecan-1 regulates alphavbeta3 and alphavbeta5
integrin activation during angiogenesis and is blocked by
synstatin, a novel peptide inhibitor. J Exp Med. 206:691–705. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Khotskaya YB, Dai Y, Ritchie JP, MacLeod
V, Yang Y, Zinn K and Sanderson RD: Syndecan-1 is required for
robust growth, vascularization, and metastasis of myeloma tumors in
vivo. J Biol Chem. 284:26085–26095. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Maeda T, Desouky J and Friedl A:
Syndecan-1 expression by stromal fibroblasts promotes breast
carcinoma growth in vivo and stimulates tumor angiogenesis.
Oncogene. 25:1408–1412. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Couchman JR: Syndecan-1 (CD138),
carcinomas and EMT. Int J Mol Sci. 22:42272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hashimoto Y, Skacel M and Adams JC:
Association of loss of epithelial syndecan-1 with stage and local
metastasis of colorectal adenocarcinomas: An immunohistochemical
study of clinically annotated tumors. BMC Cancer. 8:1852008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Zuo D, Chen Y, Li W, Liu R, He Y,
Ren L, Zhou L, Deng T, Wang X, et al: Shed Syndecan-1 is involved
in chemotherapy resistance via the EGFR pathway in colorectal
cancer. Br J Cancer. 111:1965–1976. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Muendlein A, Severgnini L, Decker T,
Heinzle C, Leiherer A, Geiger K, Drexel H, Winder T, Reimann P,
Mayer F, et al: Circulating syndecan-1 and glypican-4 predict
12-month survival in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Front
Oncol. 12:10459952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Z, He S, Liu J, Zhi X, Yang L, Zhang J,
Zhao R, Zhang R, Li L and Wang W: High expression of SDC1 in
stromal cells is associated with good prognosis in colorectal
cancer. Anticancer Drugs. 34:479–482. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tanaka H, Hayashi H, Tomita H, Tokumaru Y,
Fukada M, Tajima JY, Yokoi R, Tsuchiya H, Kuno M, Sato Y, et al:
Association of preoperative and postoperative plasma syndecan-1 and
colorectal cancer outcome. Anticancer Res. 44:1611–1618. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ismail Y, Zakaria AS, Allam R, Götte M,
Ibrahim SA and Hassan H: Compartmental Syndecan-1 (CD138)
expression as a novel prognostic marker in triple-negative
metaplastic breast cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 253:1549942024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Union for International Cancer Control, .
TNM classification of malignant tumours. 8th Edition. Wiley
Publications; 2017
|
|
17
|
Bishop JR, Schuksz M and Esko JD: Heparan
sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature.
446:1030–1037. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei HT, Guo EN, Dong BG and Chen LS:
Prognostic and clinical significance of syndecan-1 in colorectal
cancer: A meta-analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 15:1522015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li K, Li L, Wu X, Yu J, Ma H, Zhang R, Li
Y and Wang W: Loss of SDC1 expression is associated with poor
prognosis of colorectal cancer patients in Northern China. Dis
Markers. 2019:37687082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Al-Maghrabi J: Loss of expression of
syndecan-1 is associated with tumor recurrence, metastatic
potential, and poor survival in patients with colorectal carcinoma.
Pak J Med Sci. 37:114–120. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hassan H, Greve B, Pavao MSG, Kiesel L,
Ibrahim SA and Götte M: Syndecan-1 modulates β-integrin-dependent
and interleukin-6-dependent functions in breast cancer cell
adhesion, migration, and resistance to irradiation. FEBS J.
280:2216–2227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Choi S, Lee H, Choi JR and Oh ES:
Shedding; towards a new paradigm of syndecan function in cancer.
BMB Rep. 43:305–310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yang Z, Chen S, Ying H and Yao W:
Targeting syndecan-1: New opportunities in cancer therapy. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 323:C29–C45. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kind S, Jaretzke A, Büscheck F, Möller K,
Dum D, Höflmayer D, Hinsch A, Weidemann S, Fraune C, Möller-Koop C,
et al: A shift from membranous and stromal syndecan-1 (CD138)
expression to cytoplasmic CD138 expression is associated with poor
prognosis in breast cancer. Mol Carcinog. 58:2306–2315. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kind S, Kluth M, Hube-Magg C, Möller K,
Makrypidi-Fraune G, Lutz F, Lennartz M, Rico SD, Schlomm T, Heinzer
H, et al: Increased cytoplasmic CD138 expression is associated with
aggressive characteristics in prostate cancer and is an independent
predictor for biochemical recurrence. Biomed Res Int.
2020:58453742020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim SY, Choi EJ, Yun JA, Jung ES, Oh ST,
Kim JG, Kang WK and Lee SH: Syndecan-1 expression is associated
with tumor size and EGFR expression in colorectal carcinoma: A
clinicopathological study of 230 cases. Int J Med Sci. 12:92–99.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mennerich D, Vogel A, Klaman I, Dahl E,
Lichtner RB, Rosenthal A, Pohlenz HD, Thierauch KH and Sommer A:
Shift of syndecan-1 expression from epithelial to stromal cells
during progression of solid tumours. Eur J Cancer. 40:1373–1382.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Davies EJ, Blackhall FH, Shanks JH, David
G, McGown AT, Swindell R, Slade RJ, Martin-Hirsch P, Gallagher JT
and Jayson GC: Distribution and clinical significance of heparan
sulfate proteoglycans in ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
10:5178–5186. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Juuti A, Nordling S, Lundin J, Louhimo J
and Haglund C: Syndecan-1 expression-a novel prognostic marker in
pancreatic cancer. Oncology. 68:97–106. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang N, Mosher R, Seo S, Beebe D and
Friedl A: Syndecan-1 in breast cancer stroma fibroblasts regulates
extracellular matrix fiber organization and carcinoma cell
motility. Am J Pathol. 178:325–335. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Okada H, Yoshida S, Hara A, Ogura S and
Tomita H: Vascular endothelial injury exacerbates coronavirus
disease 2019: The role of endothelial glycocalyx protection.
Microcirculation. 28:e126542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liu D, Shriver Z, Venkataraman G, El
Shabrawi Y and Sasisekharan R: Tumor cell surface heparan sulfate
as cryptic promoters or inhibitors of tumor growth and metastasis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:568–573. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|