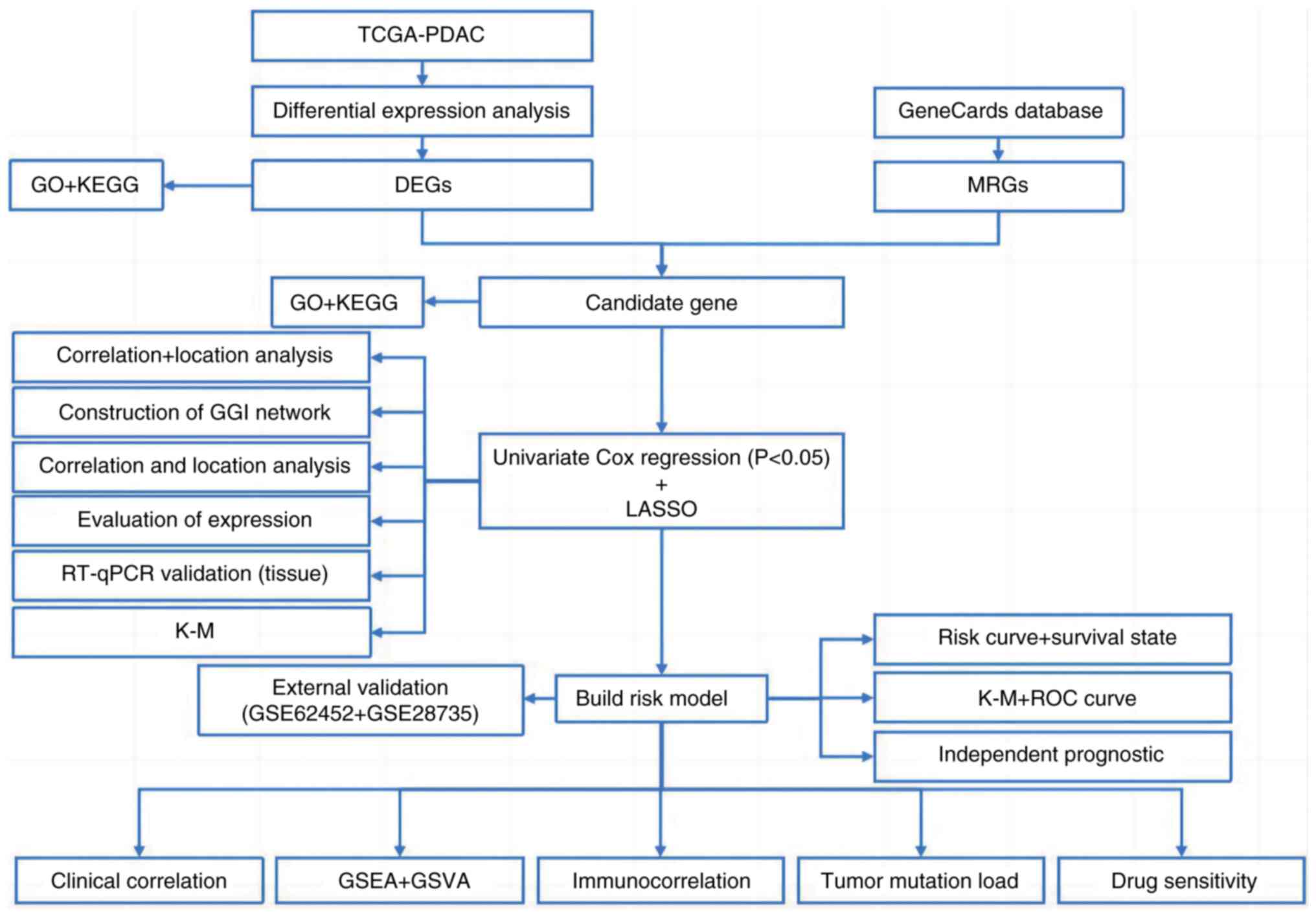
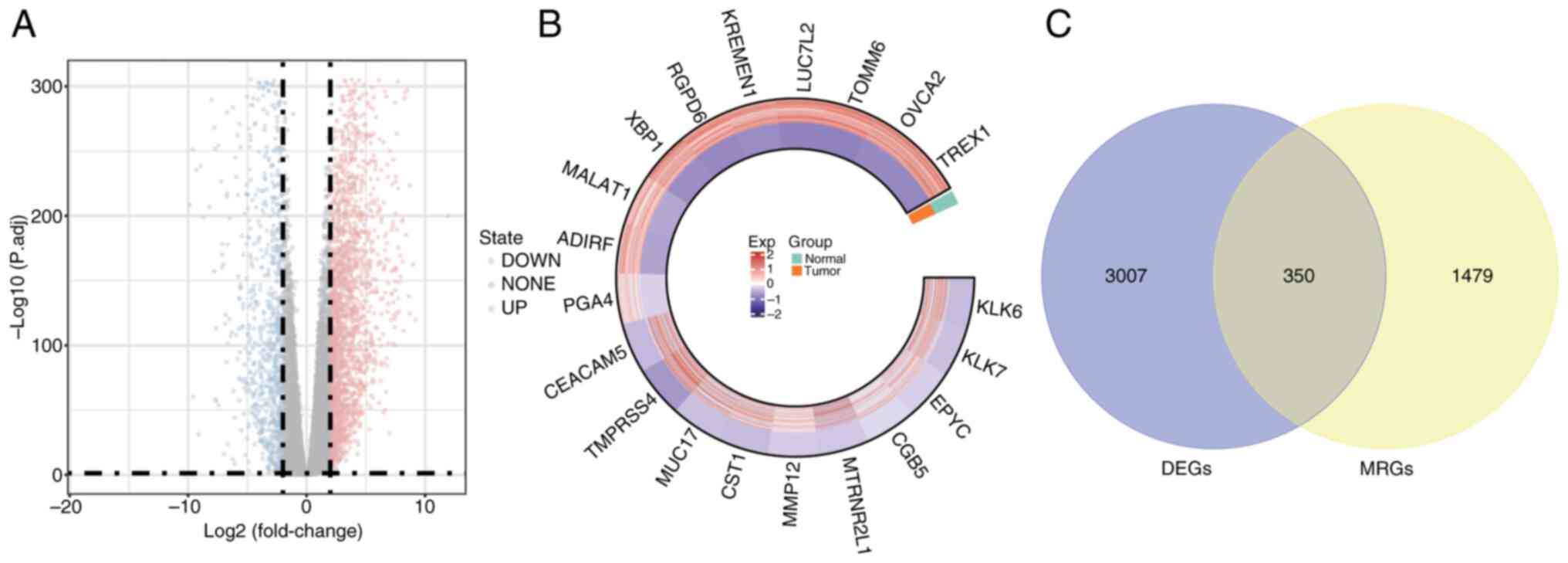
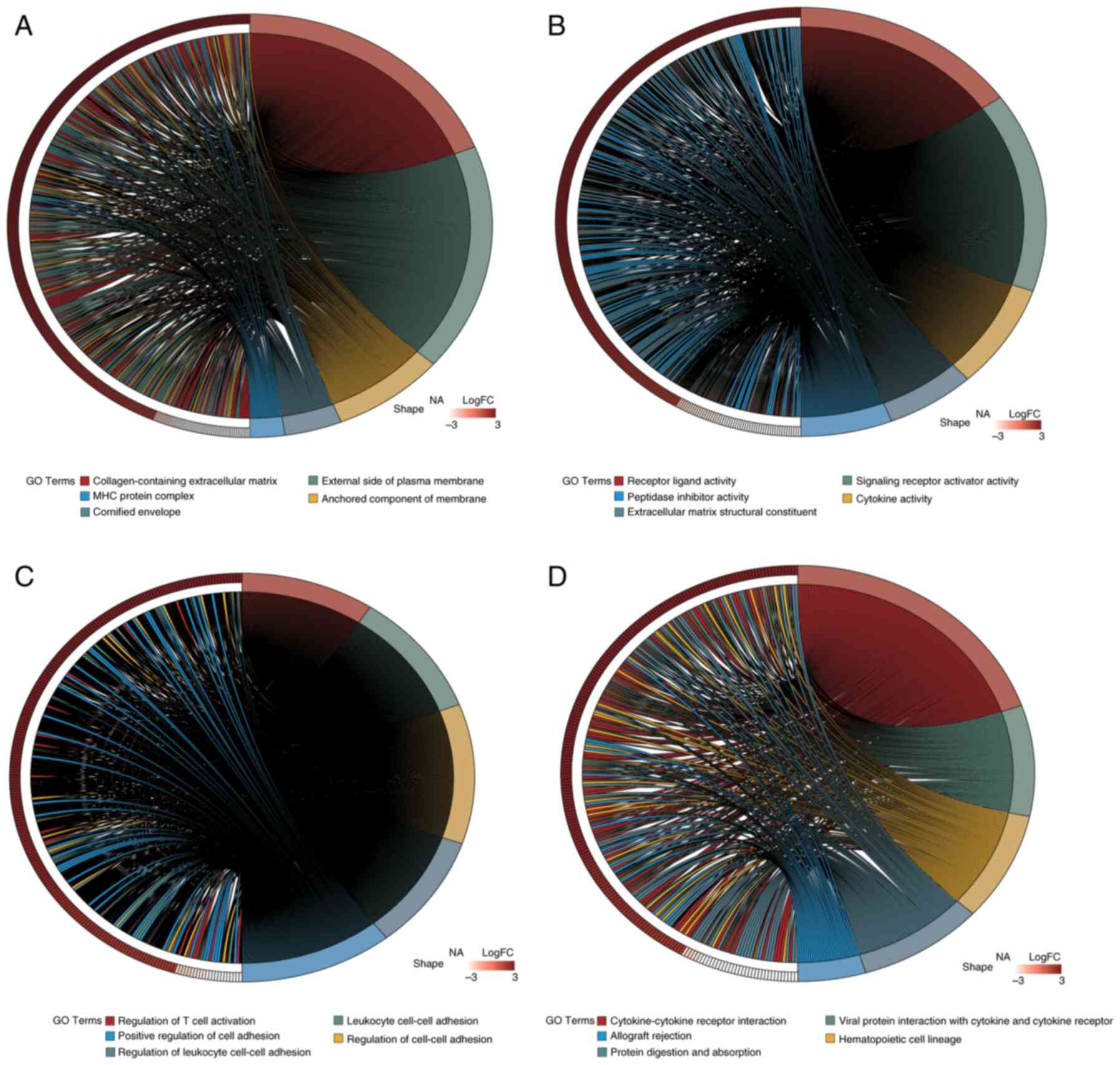
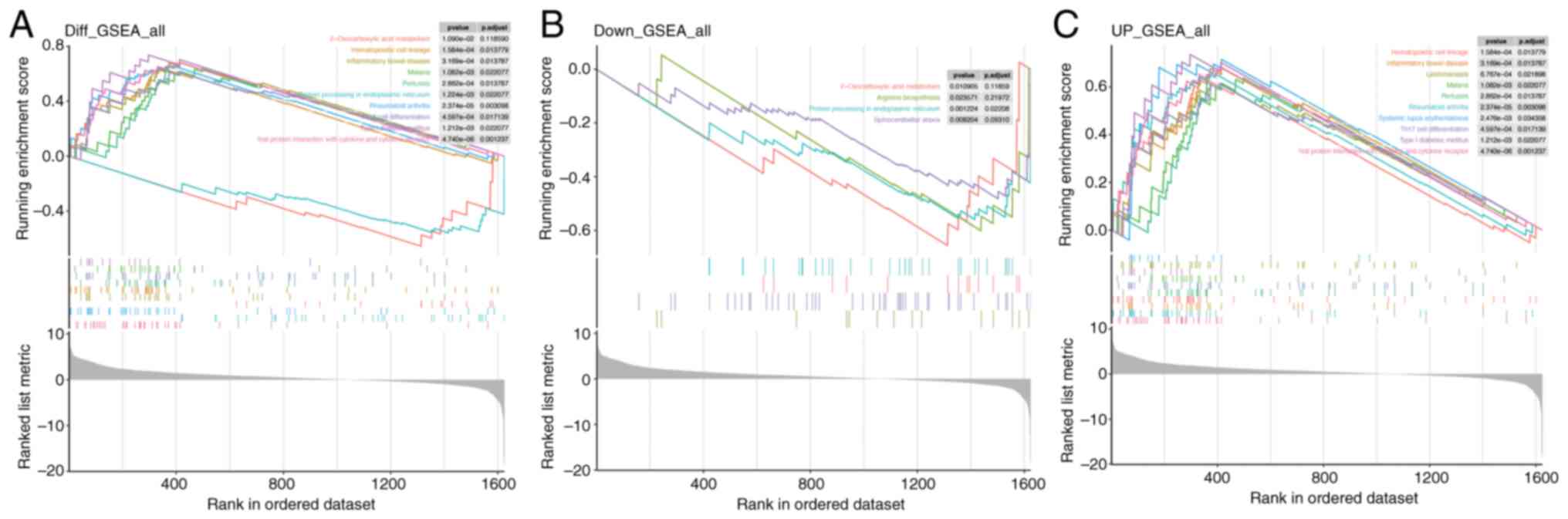
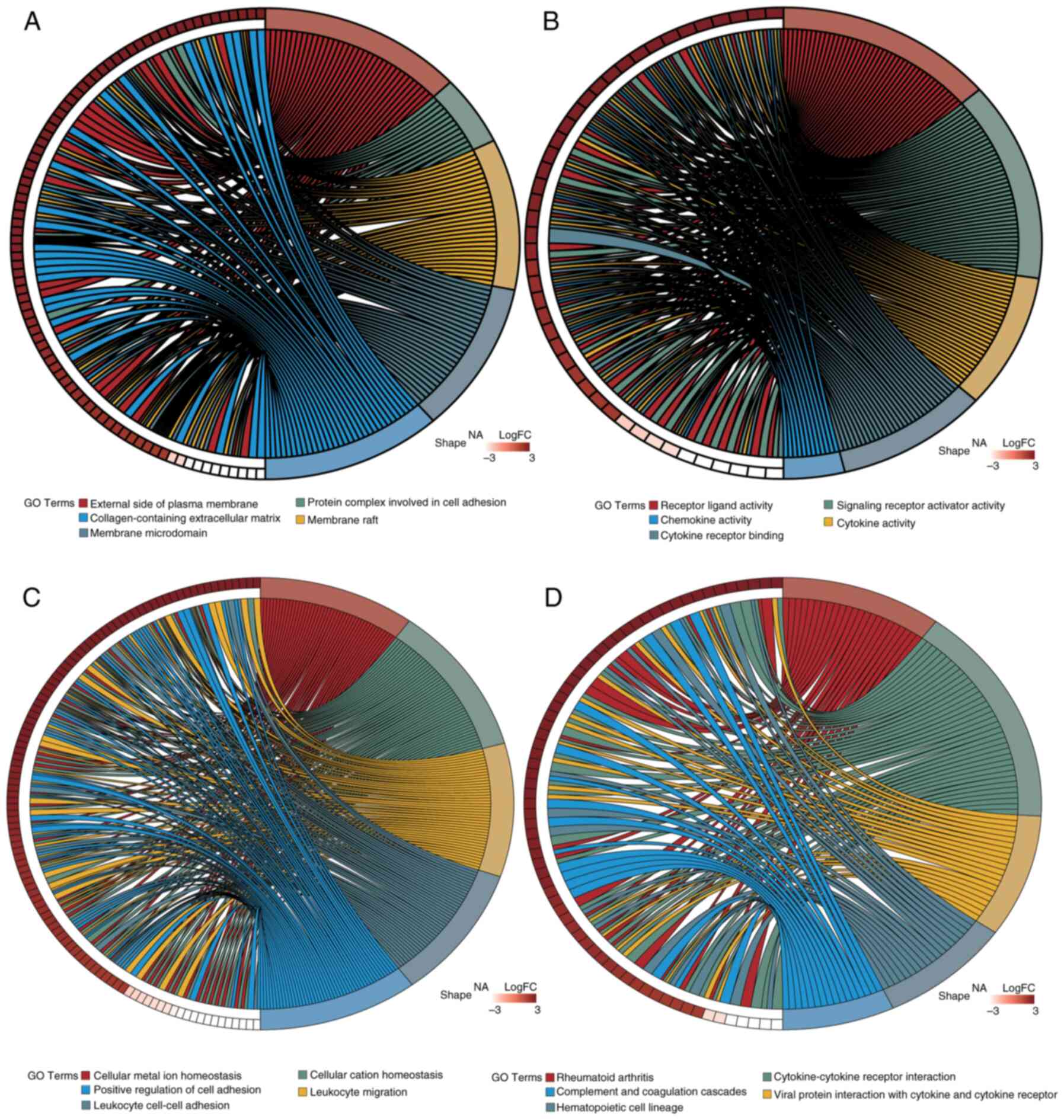
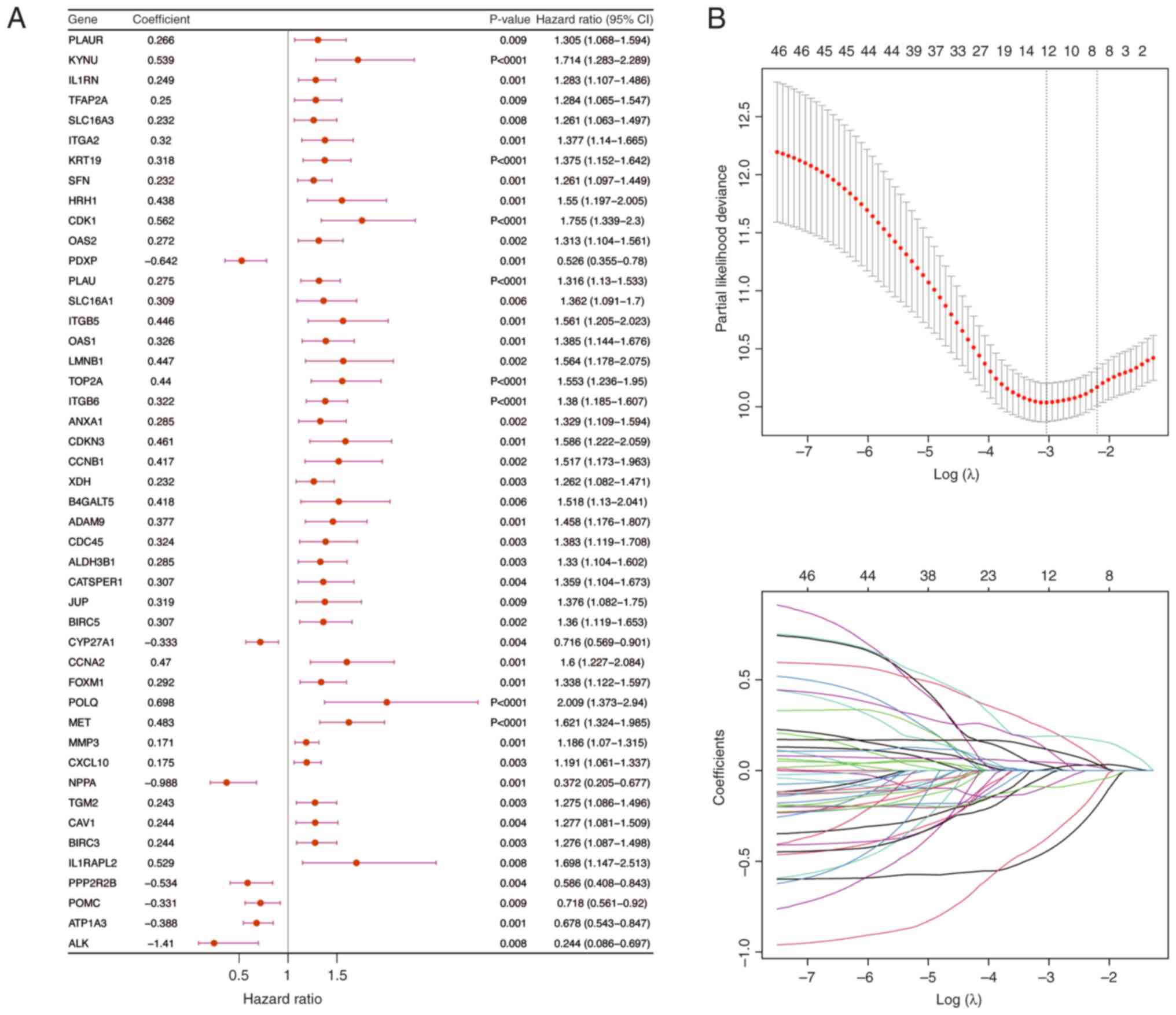
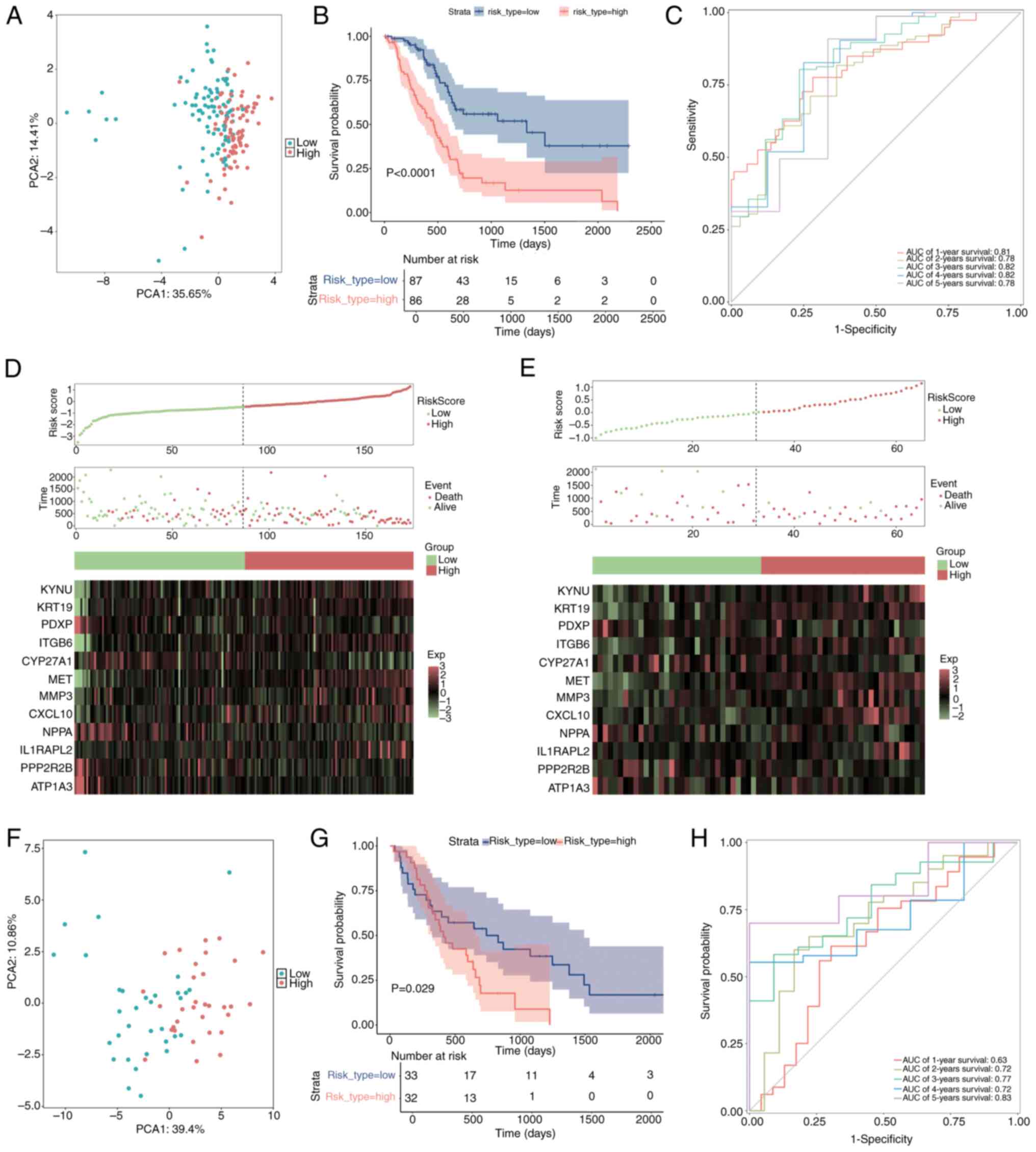
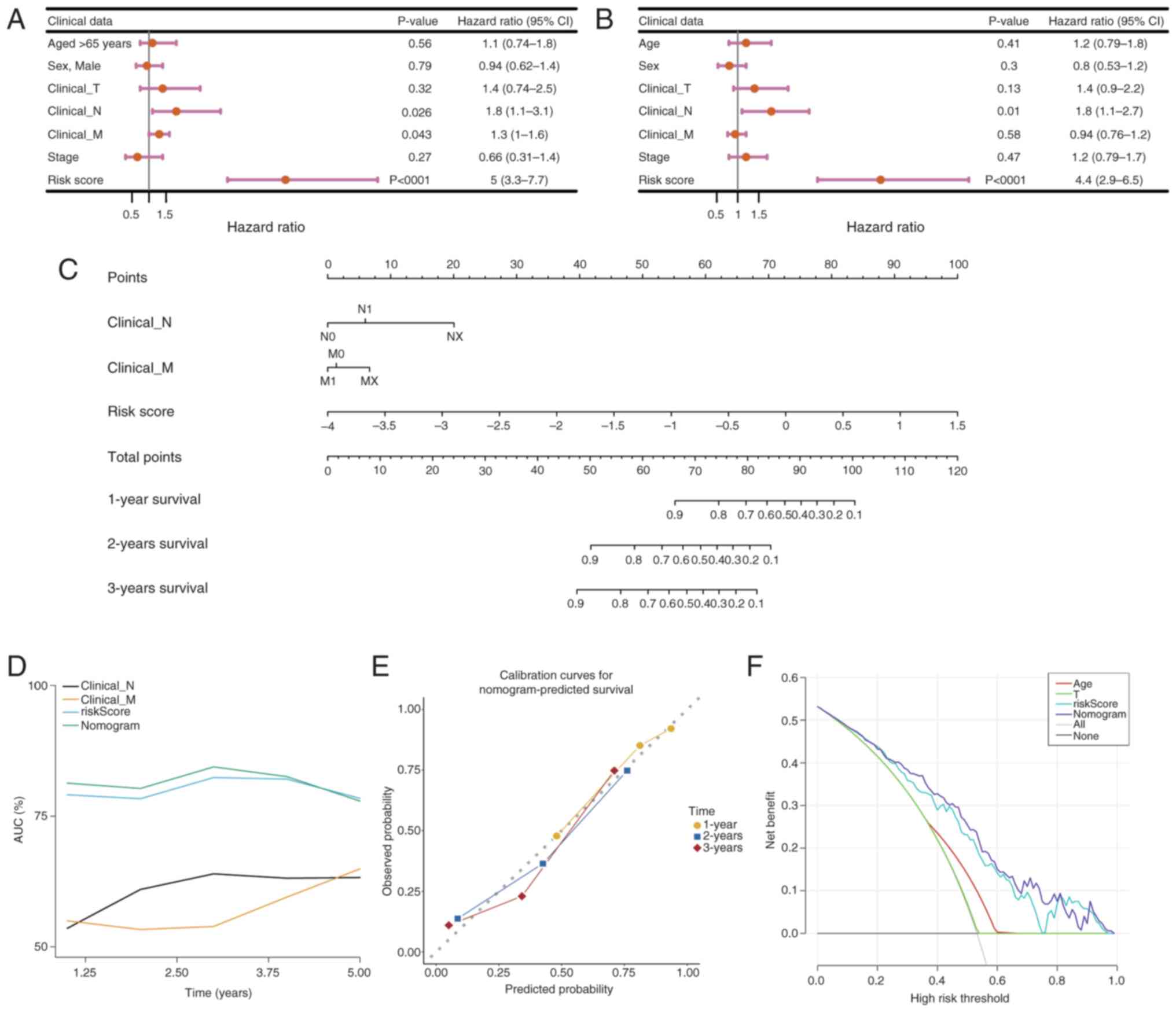
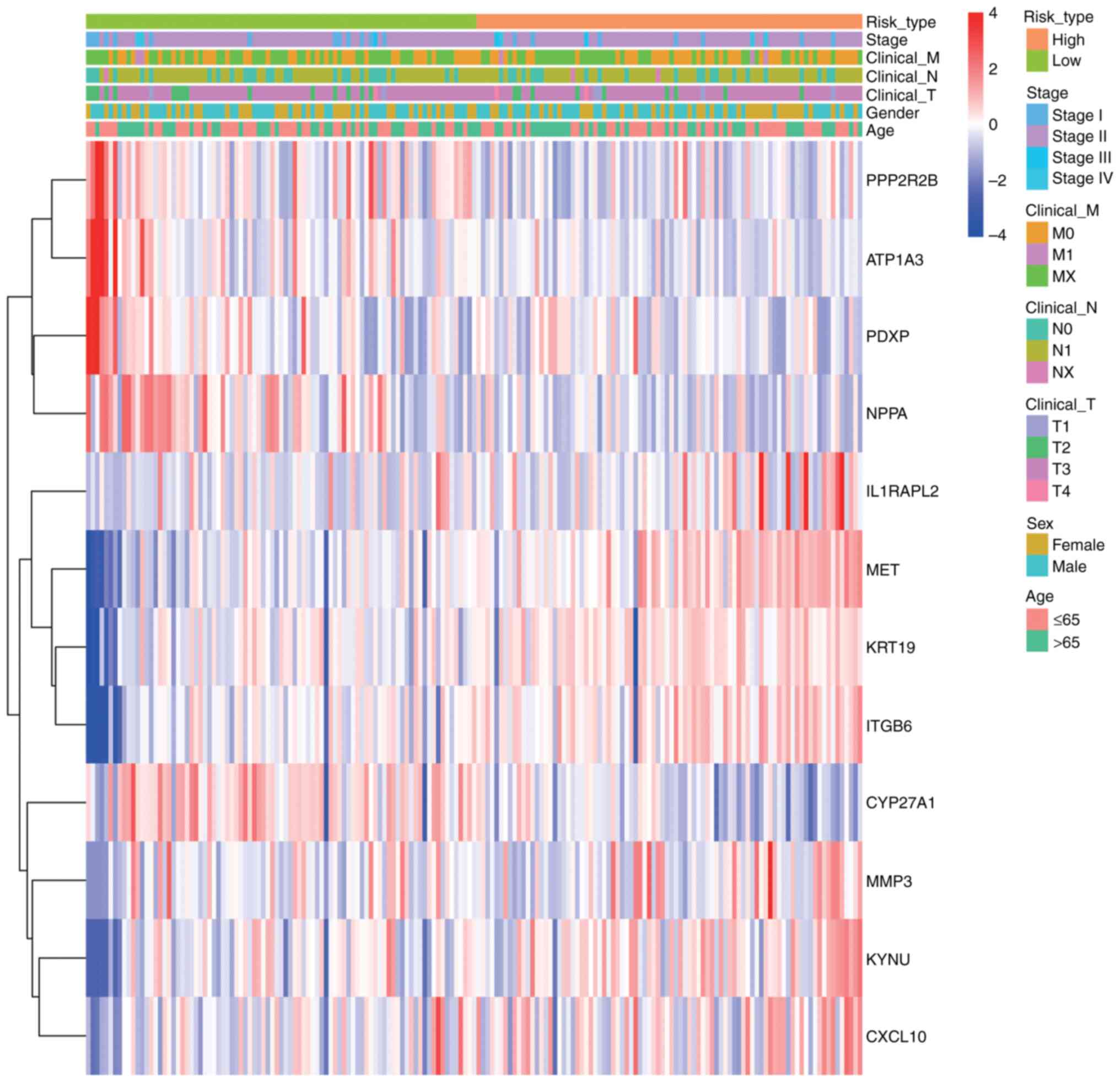
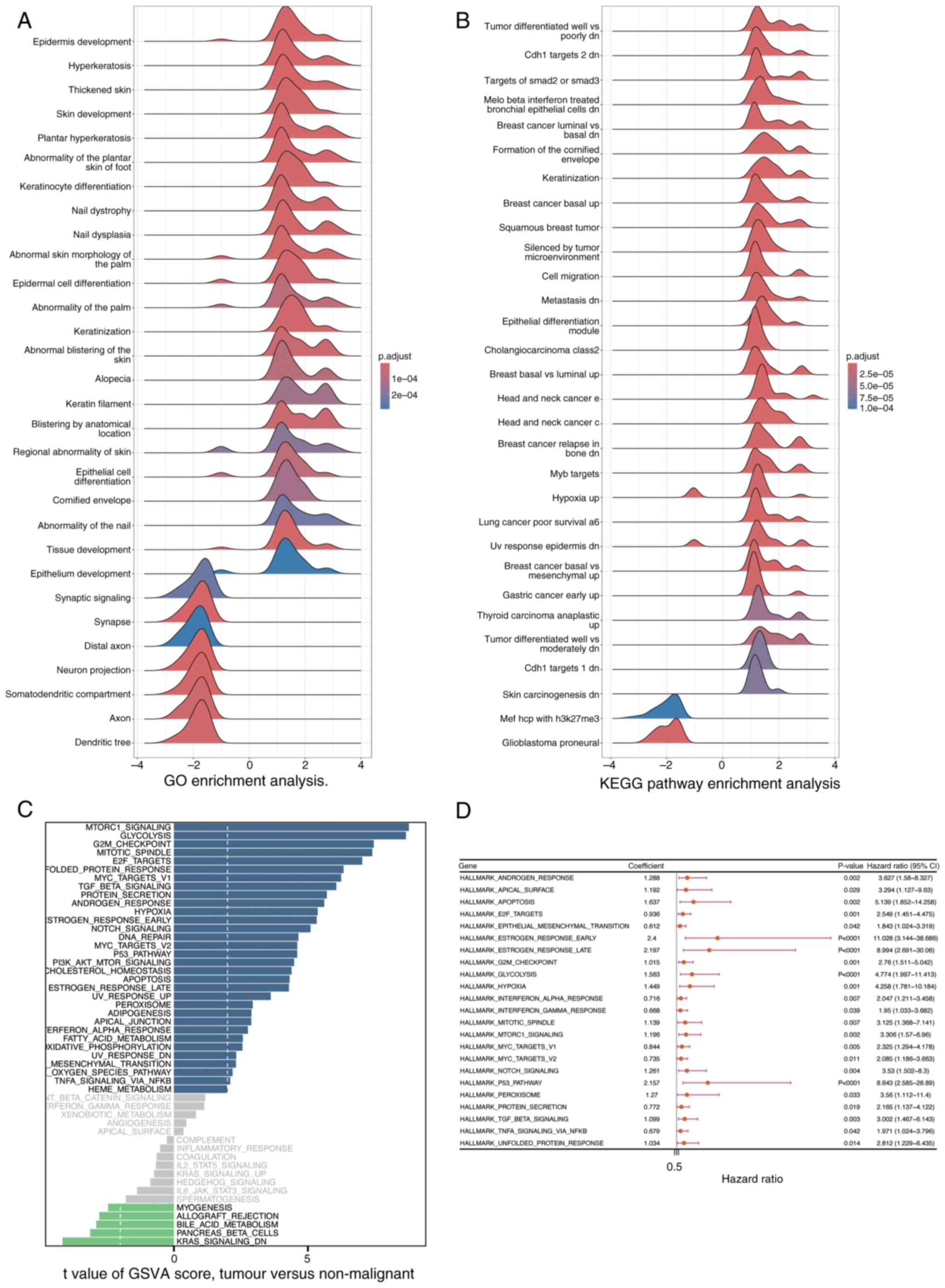
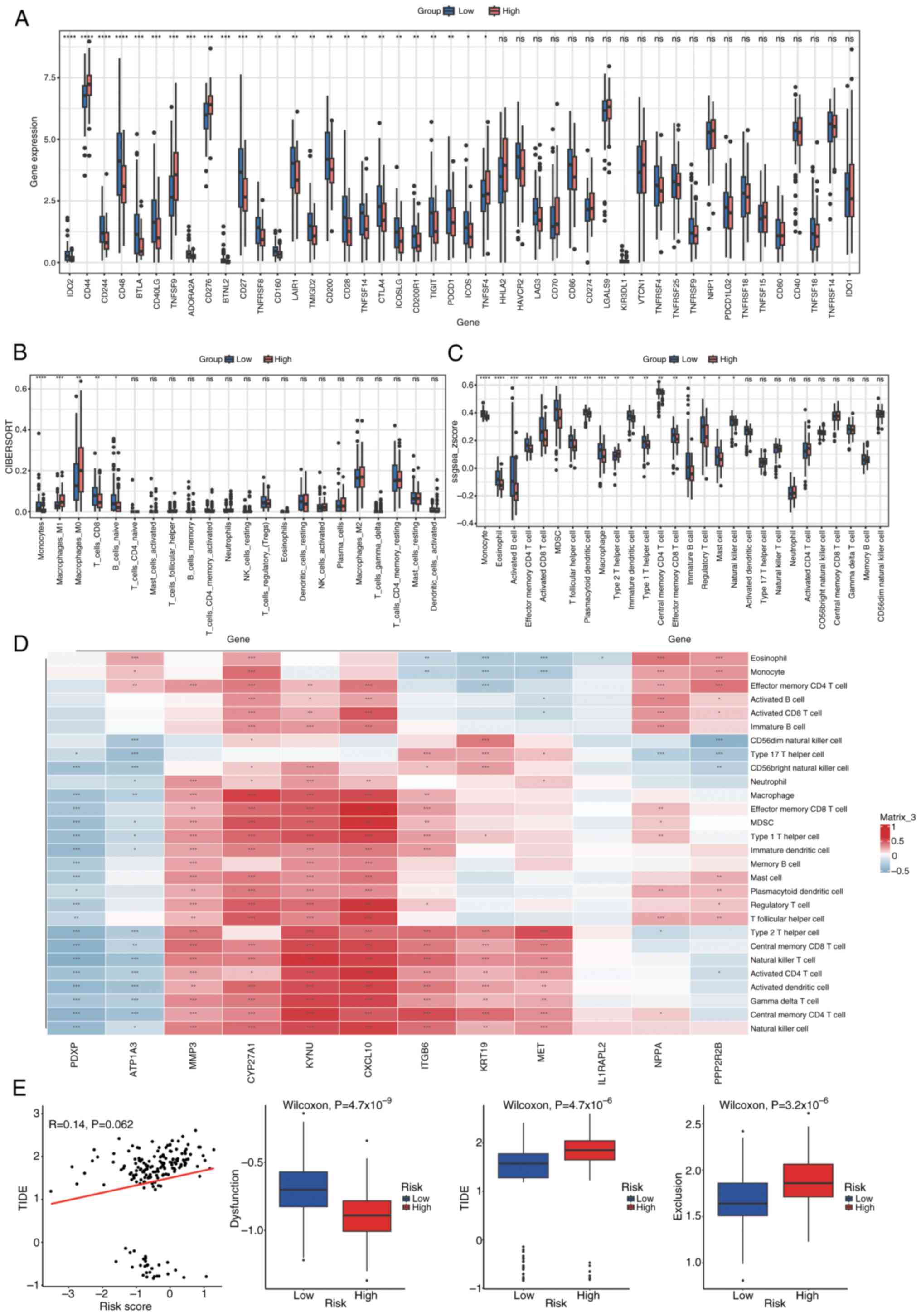
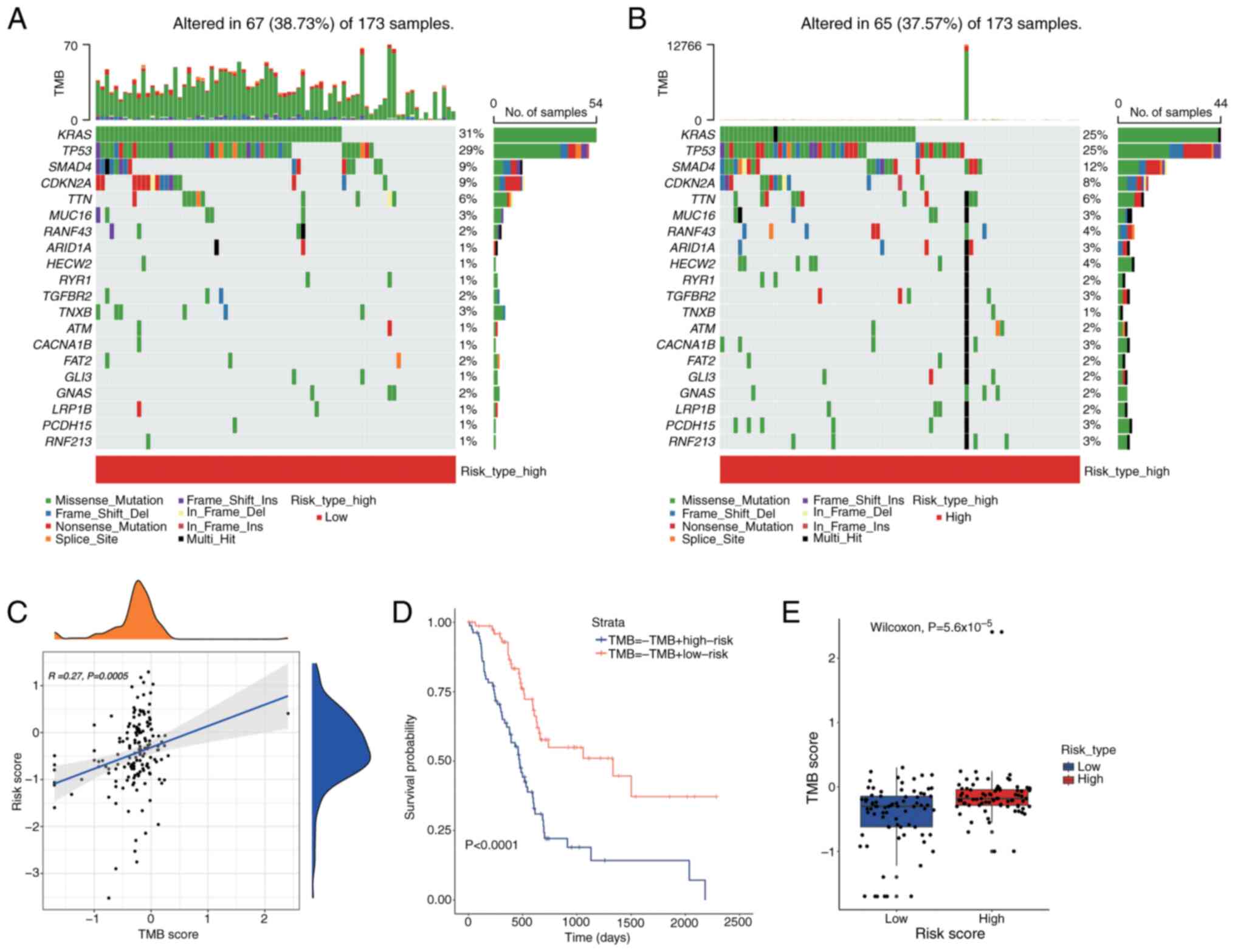
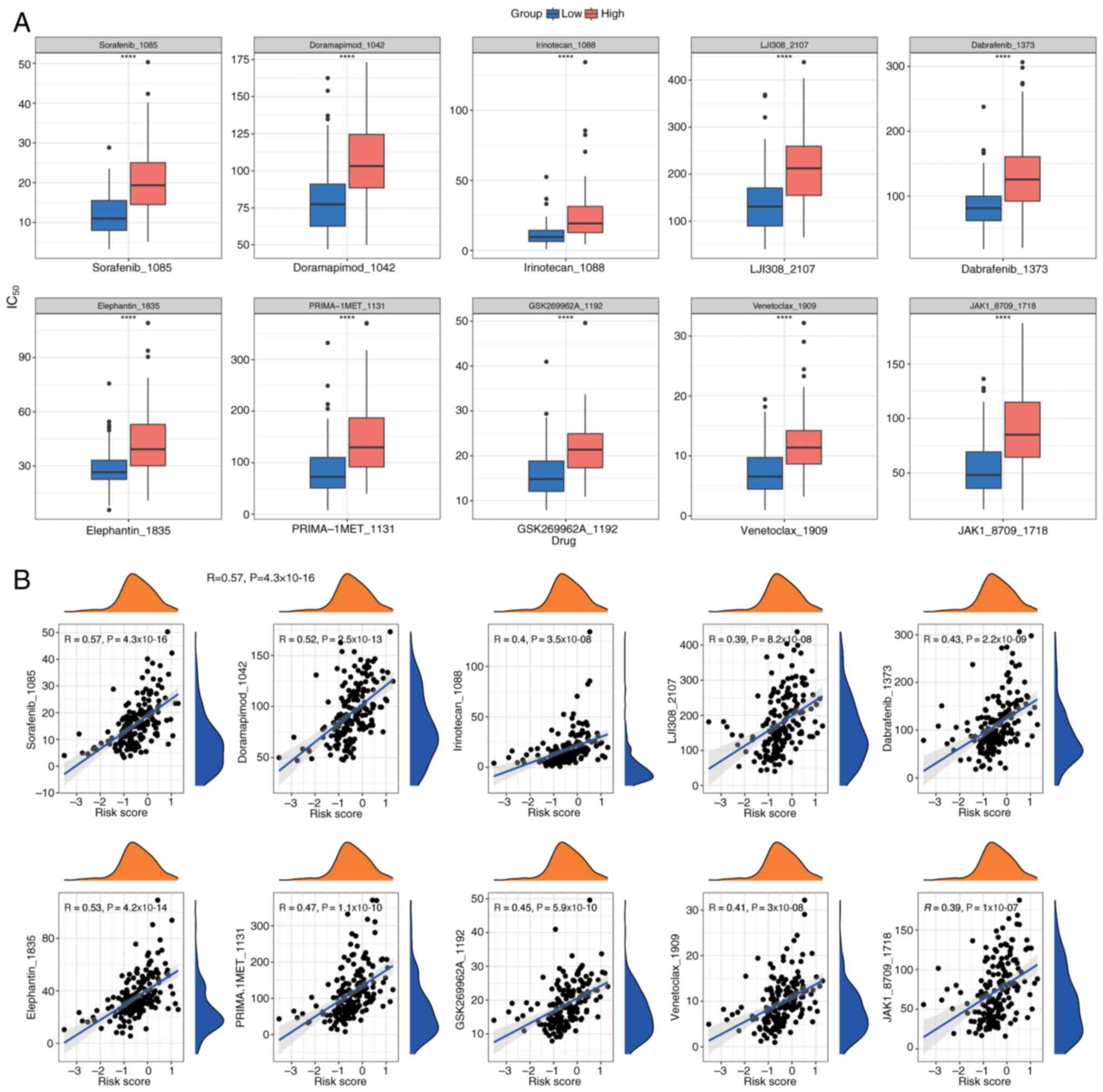
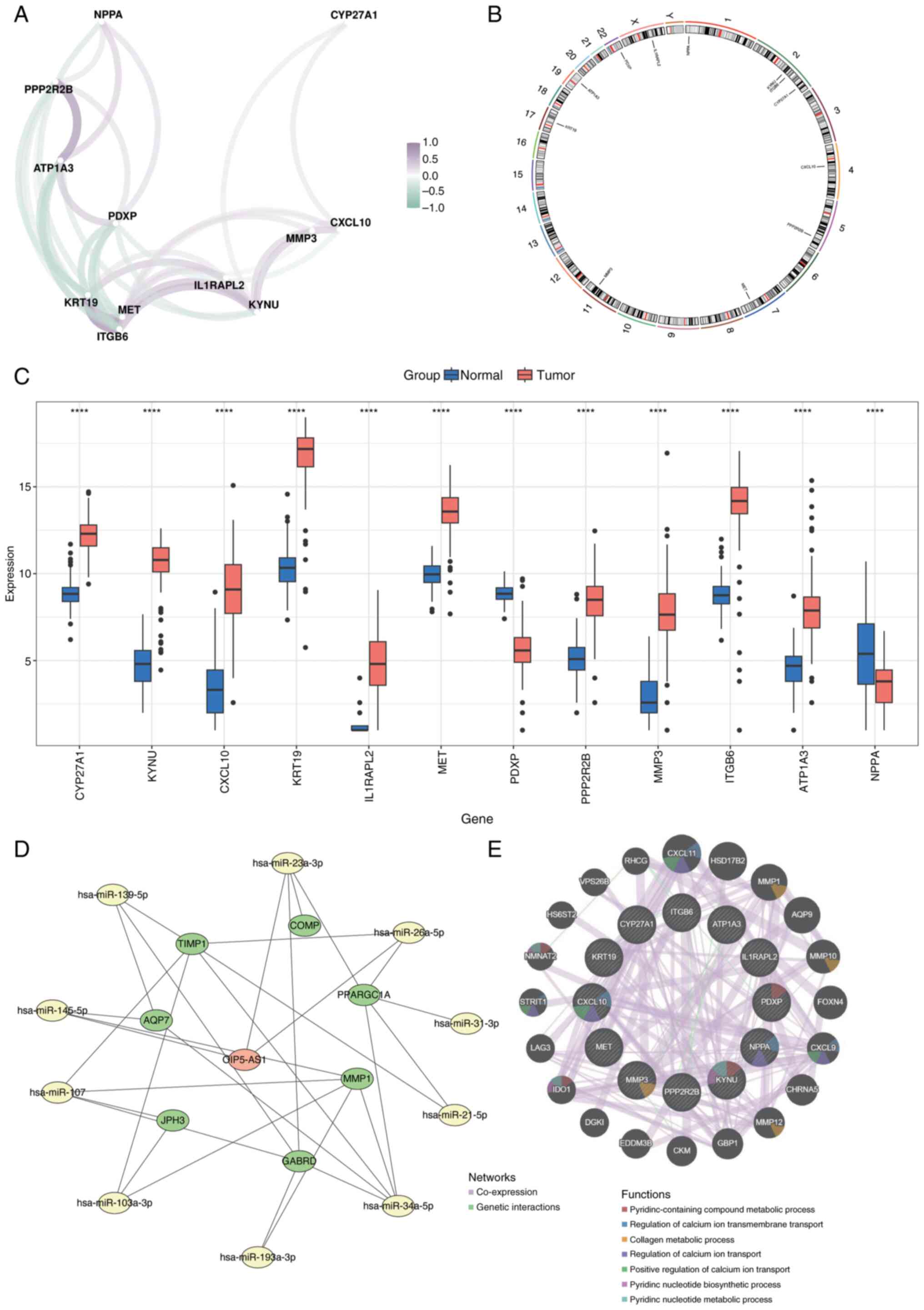
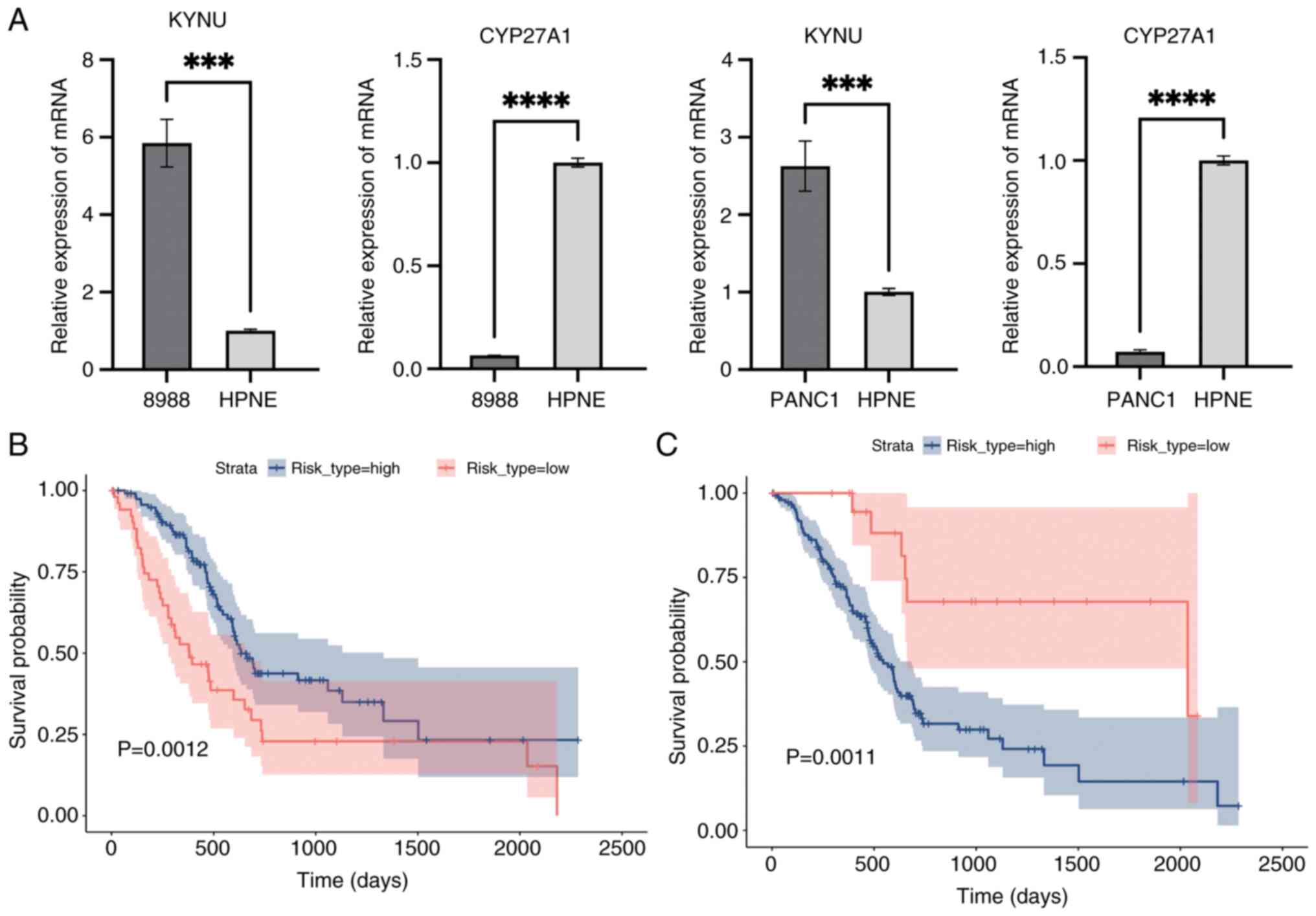
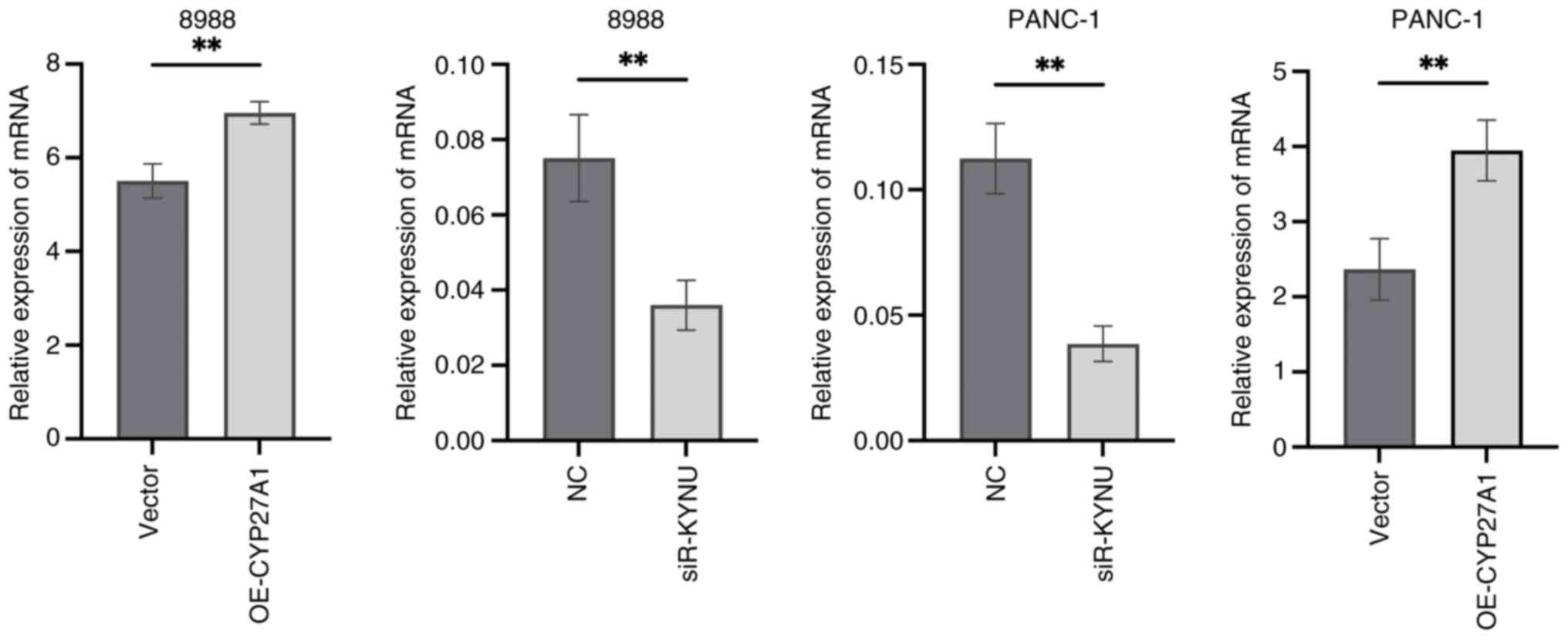
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig
AB, Fleshman JM and Matrisian LM: Projecting cancer incidence and
deaths to 2030: The unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and
pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res. 74:2913–2921.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chintamani Singhal V: Temporary closure of
open abdominal wounds by the modified sandwich-vacuum pack
technique (Br J Surg 2003; 90: 718–722). Br J Surg. 90:1452–1453.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Conroy T, Desseigne F, Ychou M, Bouché O,
Guimbaud R, Bécouarn Y, Adenis A, Raoul JL, Gourgou-Bourgade S, de
la Fouchardière C, et al: FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for
metastatic pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 364:1817–1825. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Golan T, Hammel P, Reni M, Van Cutsem E,
Macarulla T, Hall MJ, Park JO, Hochhauser D, Arnold D, Oh DY, et
al: Maintenance olaparib for germline BRCA-mutated metastatic
pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 381:317–327. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Raghavan D: Introduction: Bladder cancer.
Semin Oncol. 39:5232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li D, Xie K, Wolff R and Abbruzzese JL:
Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 363:1049–1057. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Von Hoff DD, Ervin T, Arena FP, Chiorean
EG, Infante J, Moore M, Seay T, Tjulandin SA, Ma WW, Saleh MN, et
al: Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel
plus gemcitabine. N Engl J Med. 369:1691–1703. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kanji ZS, Edwards AM, Mandelson MT, Sahar
N, Lin BS, Badiozamani K, Song G, Alseidi A, Biehl TR, Kozarek RA,
et al: Gemcitabine and taxane adjuvant therapy with chemoradiation
in resected pancreatic cancer: A novel strategy for improved
survival? Ann Surg Oncol. 25:1052–1060. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Olive KP, Jacobetz MA, Davidson CJ,
Gopinathan A, McIntyre D, Honess D, Madhu B, Goldgraben MA,
Caldwell ME, Allard D, et al: Inhibition of hedgehog signaling
enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic
cancer. Science. 324:1457–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Grant TJ, Hua K and Singh A: Molecular
pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.
144:241–275. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Duan H, Li L and He S: Advances and
prospects in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Int J
Nanomedicine. 18:3973–3988. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu J, Ji S, Liang C, Qin Y, Jin K, Liang
D, Xu W, Shi S, Zhang B, Liu L, et al: Critical role of oncogenic
KRAS in pancreatic cancer (review). Mol Med Rep. 13:4943–4949.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun H, Zhang B and Li H: The roles of
frequently mutated genes of pancreatic cancer in regulation of
tumor microenvironment. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
19:15330338209209692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hafezi S, Saber-Ayad M and Abdel-Rahman
WM: Highlights on the role of KRAS mutations in reshaping the
microenvironment of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
22:102192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
George B, Kudryashova O, Kravets A, Thalji
S, Malarkannan S, Kurzrock R, Chernyavskaya E, Gusakova M,
Kravchenko D, Tychinin D, et al: Transcriptomic-based
microenvironment classification reveals precision medicine
strategies for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology.
166:859–871.e3. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bear AS, Vonderheide RH and O'Hara MH:
Challenges and opportunities for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy.
Cancer Cell. 38:788–802. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Le DT, Uram JN, Wang H, Bartlett BR,
Kemberling H, Eyring AD, Skora AD, Luber BS, Azad NS, Laheru D, et
al: PD-1 blockade in tumors with mismatch-repair deficiency. N Engl
J Med. 372:2509–2520. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Baj J, Flieger W, Barbachowska A, Kowalska
B, Flieger M, Forma A, Teresiński G, Portincasa P, Buszewicz G,
Radzikowska-Büchner E and Flieger J: Consequences of disturbing
manganese homeostasis. Int J Mol Sci. 24:149592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin M, Colon-Perez LM, Sambo DO, Miller
DR, Lebowitz JJ, Jimenez-Rondan F, Cousins RJ, Horenstein N,
Aydemir TB, Febo M and Khoshbouei H: Mechanism of manganese
dysregulation of dopamine neuronal activity. J Neurosci.
40:5871–5891. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yanjun Y, Jing Z, Yifei S, Gangzhao G,
Chenxin Y, Qiang W, Qiang Y and Shuwen H: Trace elements in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Med. 13:e74542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao N, Zhang AS, Wortham AM, Jue S,
Knutson MD and Enns CA: The tumor suppressor, P53, decreases the
metal transporter, ZIP14. Nutrients. 9:13352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Konzack A, Jakupovic M, Kubaichuk K,
Görlach A, Dombrowski F, Miinalainen I, Sormunen R and Kietzmann T:
Mitochondrial dysfunction due to lack of manganese superoxide
dismutase promotes hepatocarcinogenesis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
23:1059–1075. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wu J, Minikes AM, Gao M, Bian H, Li Y,
Stockwell BR, Chen ZN and Jiang X: Intercellular interaction
dictates cancer cell ferroptosis via NF2-YAP signalling. Nature.
572:402–406. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Saleh SAK, Adly HM, Abdelkhaliq AA and
Nassir AM: Serum levels of selenium, zinc, copper, manganese, and
iron in prostate cancer patients. Curr Urol. 14:44–49. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang W, Chen G, Zhang W, Zhang X, Huang M,
Li C, Wang L, Lu Z and Xia J: The crucial prognostic signaling
pathways of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma were identified by
single-cell and bulk RNA sequencing data. Hum Genet. 143:1109–1129.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu X, Peng Q, Jiang X, Tan S, Yang Y, Yang
W, Han Y, Chen Y, Oyang L, Lin J, et al: Metabolic reprogramming
and epigenetic modifications in cancer: From the impacts and
mechanisms to the treatment potential. Exp Mol Med. 55:1357–1370.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhou Z, Cheng Y, Jiang Y, Liu S, Zhang M,
Liu J and Zhao Q: Ten hub genes associated with progression and
prognosis of pancreatic carcinoma identified by co-expression
analysis. Int J Biol Sci. 14:124–36. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xiang XH, Mao J and Li H: Expression and
clinical significance of centromere protein A in pancreatic cancer
based on GEO and TCGA database analysis. Chin J Pancreatol.
20:184–189. 2020.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−delta delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sahoo K and Sharma A: Understanding the
mechanistic roles of environmental heavy metal stressors in
regulating ferroptosis: Adding new paradigms to the links with
diseases. Apoptosis. 28:277–292. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rozenberg JM, Kamynina M, Sorokin M,
Zolotovskaia M, Koroleva E, Kremenchutckaya K, Gudkov A, Buzdin A
and Borisov N: The role of the metabolism of zinc and manganese
ions in human cancerogenesis. Biomedicines. 10:10722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Diessl J, Berndtsson J, Broeskamp F,
Habernig L, Kohler V, Vazquez-Calvo C, Nandy A, Peselj C,
Drobysheva S, Pelosi L, et al: Manganese-driven CoQ deficiency. Nat
Commun. 13:60612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang J and Chen X: p53 tumor suppressor
and iron homeostasis. FEBS J. 286:620–629. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ichim G, Lopez J, Ahmed SU, Muthalagu N,
Giampazolias E, Delgado ME, Haller M, Riley JS, Mason SM, Athineos
D, et al: Limited mitochondrial permeabilization causes DNA damage
and genomic instability in the absence of cell death. Mol Cell.
57:860–872. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Alaimo A, Gorojod RM, Miglietta EA,
Villarreal A, Ramos AJ and Kotler ML: Manganese induces
mitochondrial dynamics impairment and apoptotic cell death: A study
in human Gli36 cells. Neurosci Lett. 554:76–81. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Stelling MP, Soares MA, Cardoso SC, Motta
JM, de Abreu JC, Antunes MJM, de Freitas VG, Moraes JA,
Castelo-Branco MTL, Pérez CA and Pavão MSG: Manganese systemic
distribution is modulated in vivo during tumor progression and
affects tumor cell migration and invasion in vitro. Sci Rep.
11:158332021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pandey V, Fleming-Martinez A, Bastea L,
Doeppler HR, Eisenhauer J, Le T, Edenfield B and Storz P:
CXCL10/CXCR3 signaling contributes to an inflammatory
microenvironment and its blockade enhances progression of murine
pancreatic precancerous lesions. Elife. 10:e606462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gobin E, Bagwell K, Wagner J, Mysona D,
Sandirasegarane S, Smith N, Bai S, Sharma A, Schleifer R and She
JX: A pan-cancer perspective of matrix metalloproteases (MMP) gene
expression profile and their diagnostic/prognostic potential. BMC
Cancer. 19:5812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Luan H, Jian L, Huang Y, Guo Y and Zhou L:
Identification of novel therapeutic target and prognostic biomarker
in matrix metalloproteinase gene family in pancreatic cancer. Sci
Rep. 13:172112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fu J, Su X, Li Z, Deng L, Liu X, Feng X
and Peng J: HGF/c-MET pathway in cancer: From molecular
characterization to clinical evidence. Oncogene. 40:4625–4651.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Guo R, Luo J, Chang J, Rekhtman N, Arcila
M and Drilon A: MET-dependent solid tumours-molecular diagnosis and
targeted therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 17:569–587. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nie Y, Liu C, Liu Q and Zhu X: CXCL10 is a
prognostic marker for pancreatic adenocarcinoma and tumor
microenvironment remodeling. BMC Cancer. 23:1502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He S, Ma L, Baek AE, Vardanyan A, Vembar
V, Chen JJ, Nelson AT, Burdette JE and Nelson ER: Host CYP27A1
expression is essential for ovarian cancer progression. Endocr
Relat Cancer. 26:659–675. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Niu N, Shen X, Wang Z, Chen Y, Weng Y, Yu
F, Tang Y, Lu P, Liu M, Wang L, et al: Tumor cell-intrinsic
epigenetic dysregulation shapes cancer-associated fibroblasts
heterogeneity to metabolically support pancreatic cancer. Cancer
Cell. 42:869–884.e9. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Newton-Cheh C, Larson MG, Vasan RS, Levy
D, Bloch KD, Surti A, Guiducci C, Kathiresan S, Benjamin EJ, Struck
J, et al: Association of common variants in NPPA and NPPB with
circulating natriuretic peptides and blood pressure. Nat Genet.
41:348–353. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Forte M, Marchitti S, Di Nonno F,
Stanzione R, Schirone L, Cotugno M, Bianchi F, Schiavon S, Raffa S,
Ranieri D, et al: NPPA/atrial natriuretic peptide is an
extracellular modulator of autophagy in the heart. Autophagy.
19:1087–1099. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Song P, Yao X, Zhong T, Zhang S, Guo Y,
Ren W, Huang D, Duan XC, Yin YF, Zhang SS and Zhang X: The
anti-tumor efficacy of 3-(2-nitrophenyl) propionic acid-paclitaxel
(NPPA-PTX): A novel paclitaxel bioreductive prodrug. Oncotarget.
7:48467–48480. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Song W, Wang H and Wu Q: Atrial
natriuretic peptide in cardiovascular biology and disease (NPPA).
Gene. 569:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Luan Y, Xie B and Wei W: REST-repressed
lncRNA NPPA-AS1 regulates cervical cancer progression by modulating
miR-302e/DKK1/wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
122:16–28. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Malvi P, Chava S, Cai G, Hu K, Zhu LJ,
Edwards YJK, Green MR, Gupta R and Wajapeyee N: HOXC6 drives a
therapeutically targetable pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis
pathway by regulating MSK1 and PPP2R2B. Cell Rep Med. 4:1012852023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Li J, Zhang Y, Yang C and Rong R:
Discrepant mRNA and protein expression in immune cells. Curr
Genomics. 21:560–563. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ramazi S and Zahiri J: Posttranslational
modifications in proteins: Resources, tools and prediction methods.
Database (Oxford). 2021:baab0122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nalbantoglu S and Karadag A: Metabolomics
bridging proteomics along metabolites/oncometabolites and protein
modifications: Paving the way toward integrative multiomics. J
Pharm Biomed Anal. 199:1140312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gautam SK, Batra SK and Jain M: Molecular
and metabolic regulation of immunosuppression in metastatic
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 22:1182023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|