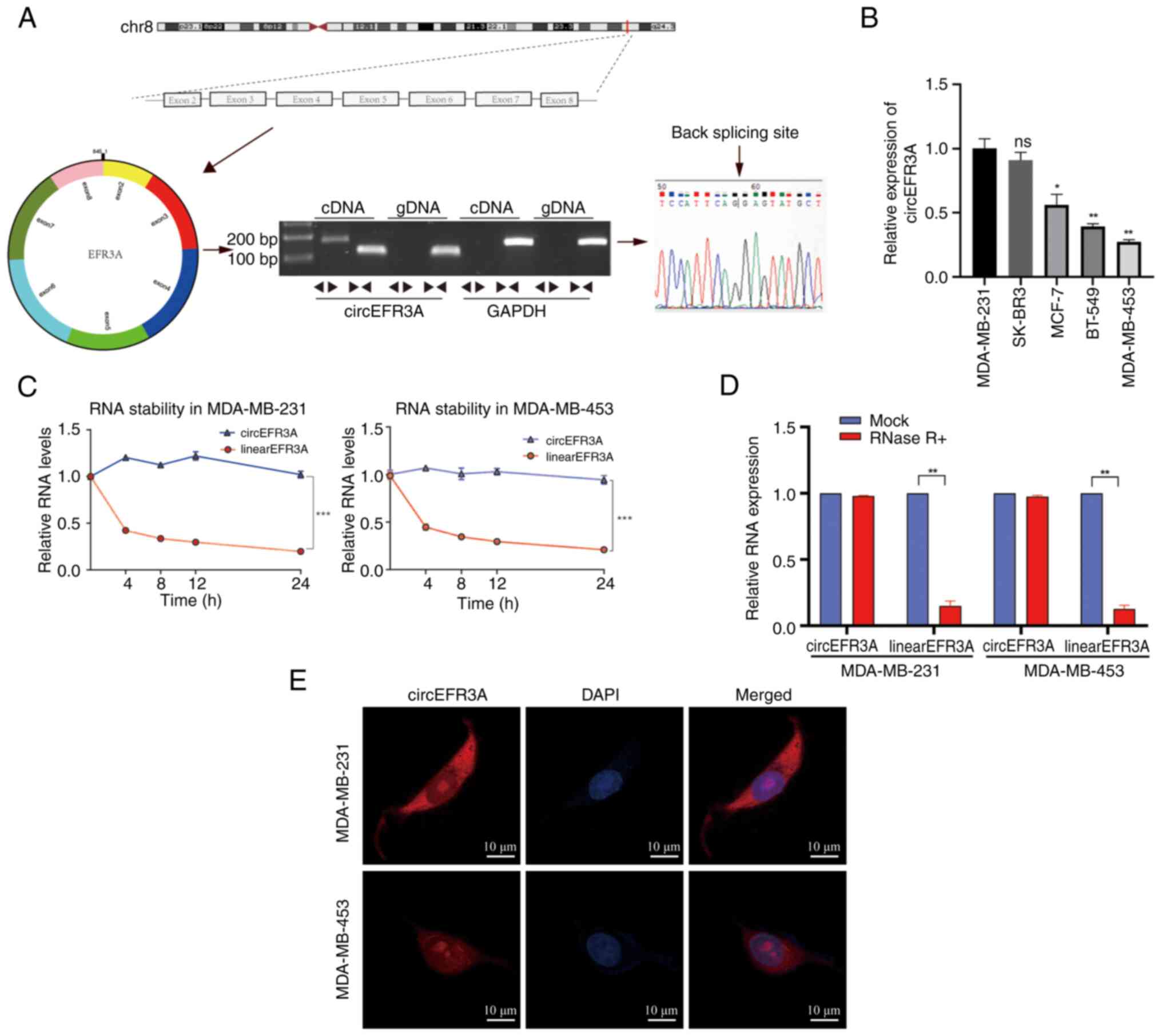
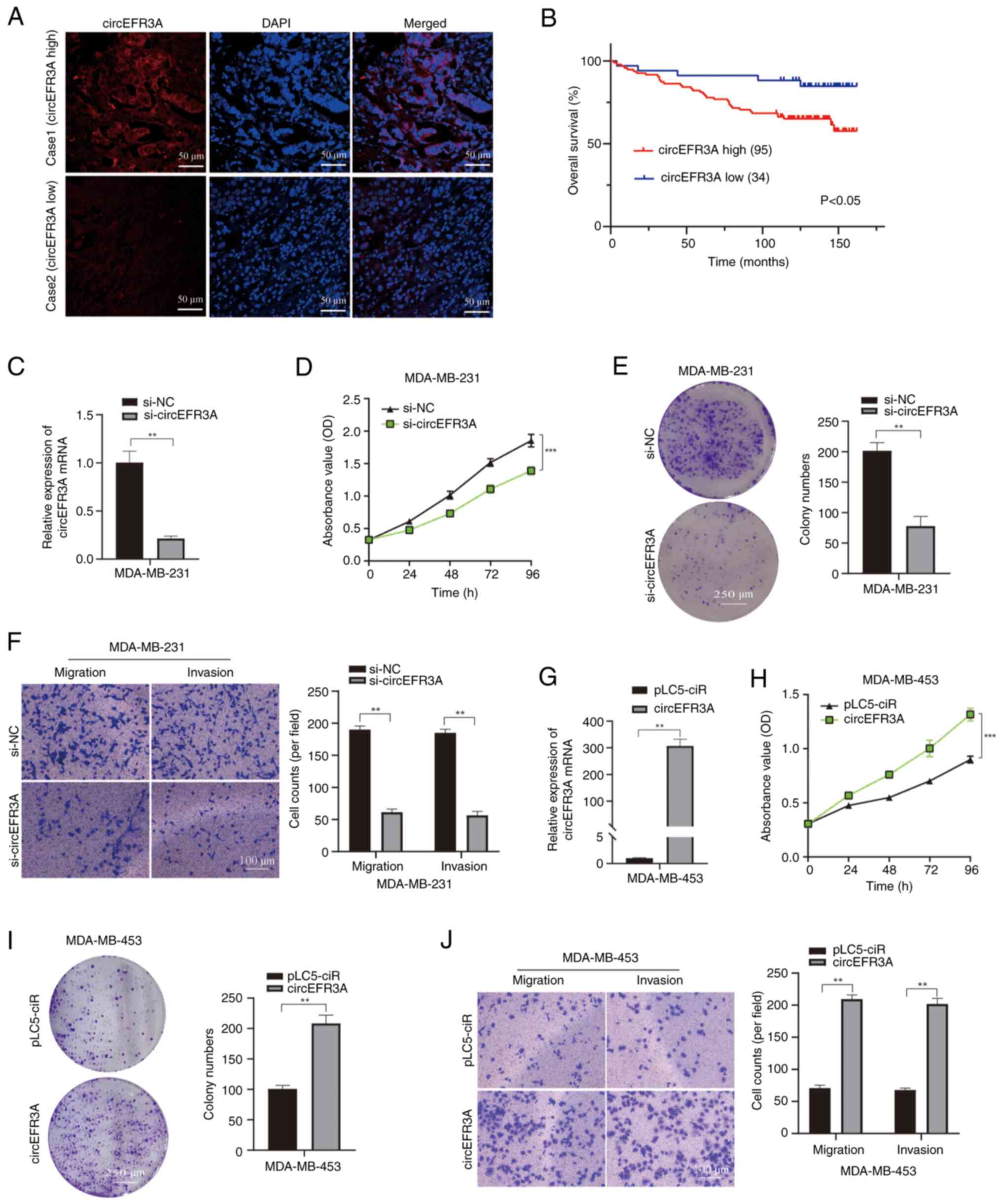
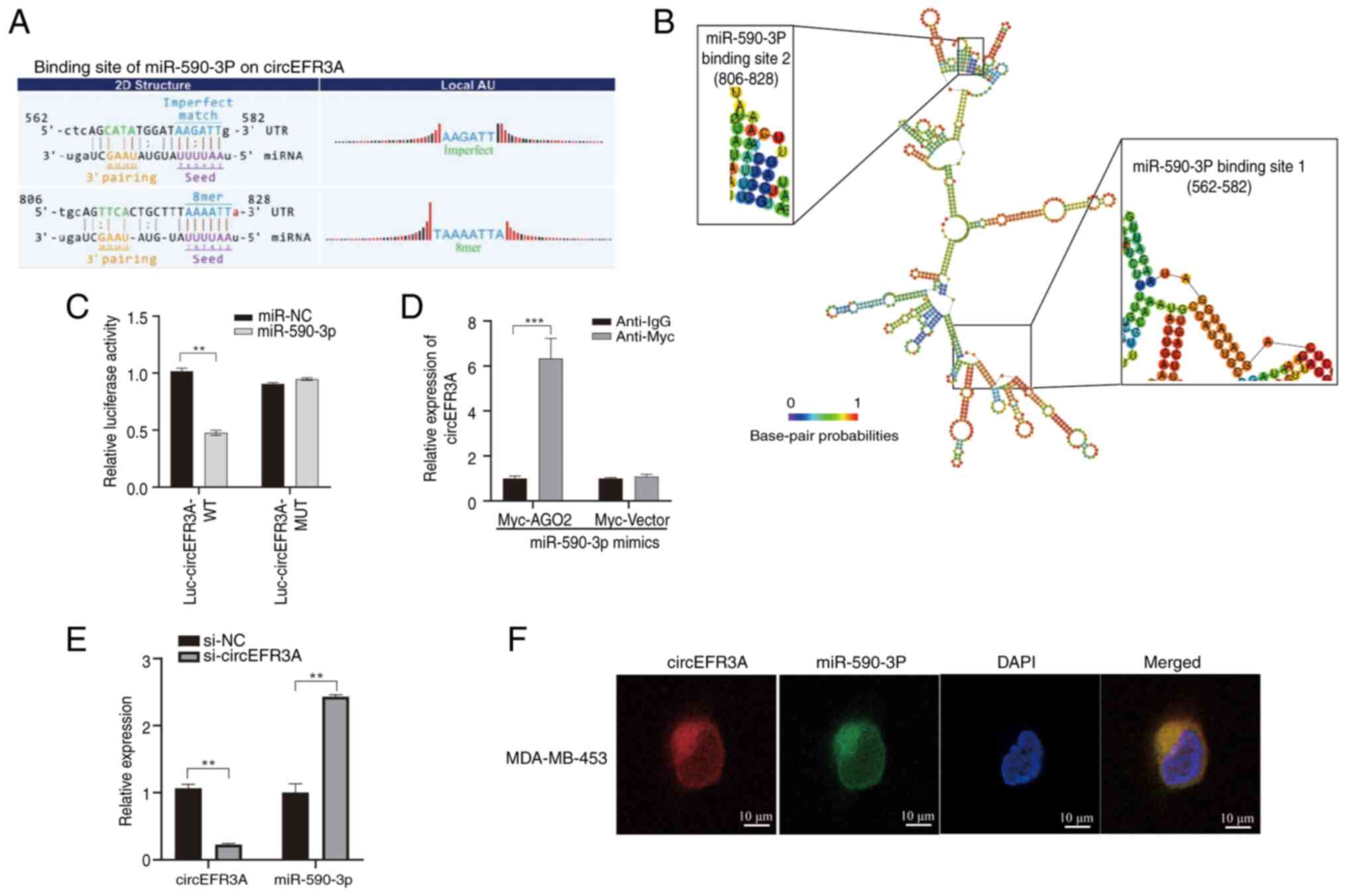
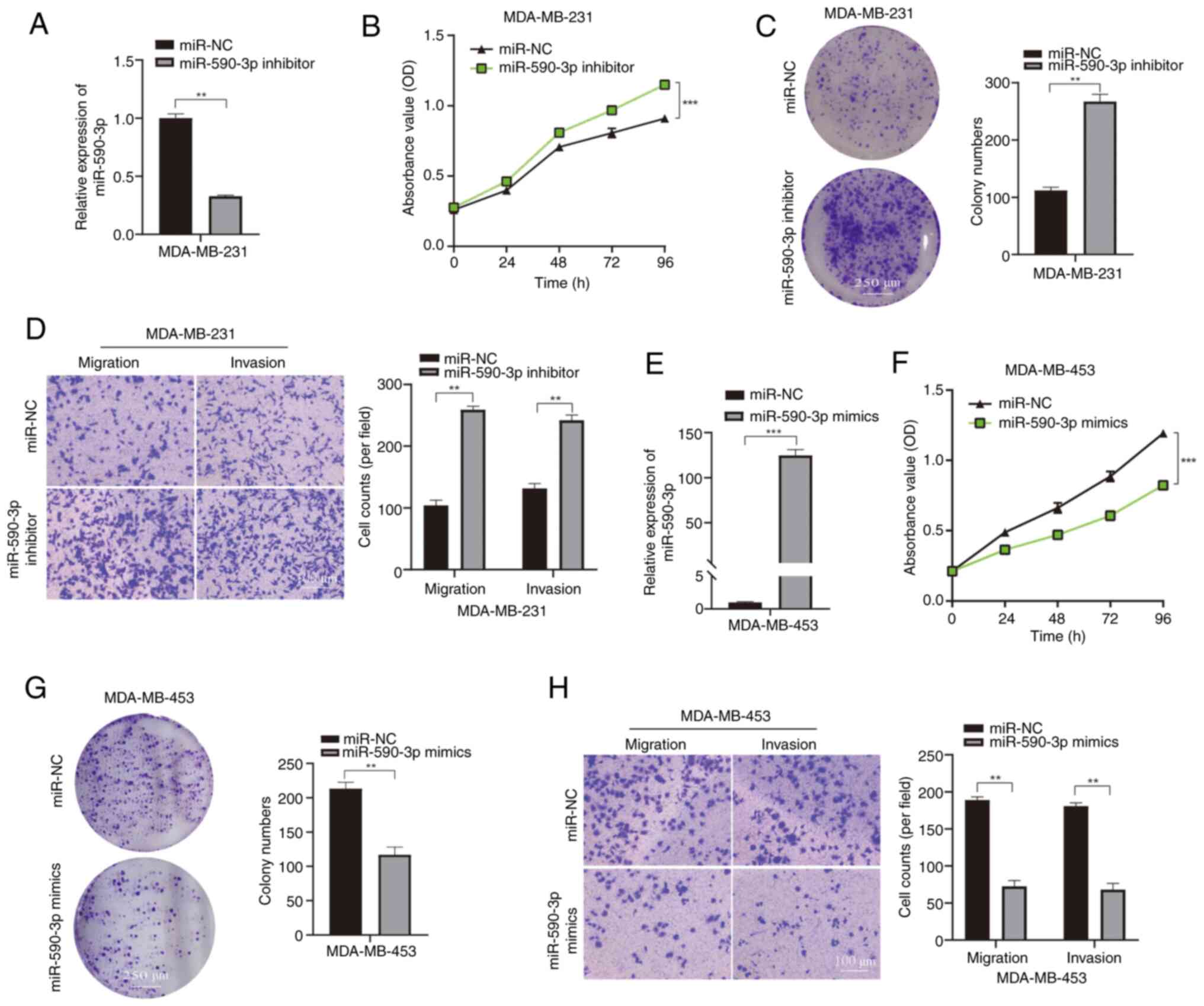
|
1
|
Fillon M: Breast cancer recurrence risk
can remain for 10 to 32 years. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:197–199.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cardoso F, Paluch-Shimon S, Senkus E,
Curigliano G, Aapro MS, André F, Barrios CH, Bergh J, Bhattacharyya
GS, Biganzoli L, et al: 5th ESO-ESMO international consensus
guidelines for advanced breast cancer (ABC 5). Ann Oncol.
31:1623–1649. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Klinge CM: Non-Coding RNAs in breast
cancer: Intracellular and intercellular communication. Noncoding
RNA. 4:402018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang
R, Sun W, Dou K and Li H: Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding
RNAs. Cancer Lett. 365:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lei M, Zheng G, Ning Q, Zheng J and Dong
D: Translation and functional roles of circular RNAs in human
cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou WY, Cai ZR, Liu J, Wang DS, Ju HQ and
Xu RH: Circular RNA: metabolism, functions and interactions with
proteins. Mol Cancer. 19:1722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu Y, Zheng W, Ji C, Wang X, Chen M, Hua
K, Deng X and Fang L: Tumor-Derived circRNAs as circulating
biomarkers for breast cancer. Front Pharmacol. 13:8118562022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang B, Wang YW and Zhang K: Interactions
between circRNA and protein in breast cancer. Gene. 895:1480192024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhu J, Li Q, Wu Z, Xu W and Jiang R:
Circular RNA-mediated miRNA sponge & RNA binding protein in
biological modulation of breast cancer. Noncoding RNA Res.
9:262–276. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gopikrishnan M, R HC, R G, Ashour HM,
Pintus G, Hammad M, Kashyap MK, C GPD and Zayed H: Therapeutic and
diagnostic applications of exosomal circRNAs in breast cancer.
Funct Integr Genomics. 23:1842023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gao D, Cui C, Jiao Y, Zhang H, Li M, Wang
J and Sheng X: Circular RNA and its potential diagnostic and
therapeutic values in breast cancer. Mol Biol Rep. 51:2582024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Weidle UH, Hsia HE and Brinkmann U: Breast
cancer: Circular RNAs mediating efficacy in preclinical in vivo
models. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 20:222–238. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liang G, Ling Y, Mehrpour M, Saw PE, Liu
Z, Tan W, Tian Z, Zhong W, Lin W, Luo Q, et al:
Autophagy-associated circRNA circCDYL augments autophagy and
promotes breast cancer progression. Mol Cancer. 19:652020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu S, Lu J, Zhu H, Wu F, Mo Y, Xie L, Song
C, Liu L, Xie X, Li Y, et al: A novel axis of
circKIF4A-miR-637-STAT3 promotes brain metastasis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 581:2165082024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fu B, Liu W, Zhu C, Li P, Wang L, Pan L,
Li K, Cai P, Meng M, Wang Y, et al: Circular RNA circBCBM1 promotes
breast cancer brain metastasis by modulating miR-125a/BRD4 axis.
Int J Biol Sci. 17:3104–3117. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ju C, Zhou M, Du D, Wang C, Yao J, Li H,
Luo Y, He F and He J: EIF4A3-mediated circ_0042881 activates the
RAS pathway via miR-217/SOS1 axis to facilitate breast cancer
progression. Cell Death Dis. 14:5592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song H, Zhao Z, Ma L, Zhao W, Hu Y and
Song Y: Novel exosomal circEGFR facilitates triple negative breast
cancer autophagy via promoting TFEB nuclear trafficking and
modulating miR-224-5p/ATG13/ULK1 feedback loop. Oncogene.
43:821–836. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stelzer G, Rosen N, Plaschkes I, Zimmerman
S, Twik M, Fishilevich S, Stein TI, Nudel R, Lieder I, Mazor Y, et
al: The genecards suite: From gene data mining to disease genome
sequence analyses. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 54:1 30 1–1 30 33.
2016. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Witkos TM, Koscianska E and Krzyzosiak WJ:
Practical aspects of microRNA target prediction. Curr Mol Med.
11:93–109. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW,
Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB and Kjems J: The biogenesis, biology and
characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 20:675–691. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dolgin E: Why rings of RNA could be the
next blockbuster drug. Nature. 622:22–24. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu CX and Chen LL: Circular RNAs:
Characterization, cellular roles, and applications. Cell.
185:23902022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Zhang X, Xu Y, Fang S, Ji Y, Lu
L, Xu W, Qian H and Liang ZF: Circular RNA and its roles in the
occurrence, development, diagnosis of cancer. Front Oncol.
12:8457032022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Trybus M, Hryniewicz-Jankowska A,
Wojtowicz K, Trombik T, Czogalla A and Sikorski AF: EFR3A: A new
raft domain organizing protein? Cell Mol Biol Lett. 28:862023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gupta AR, Pirruccello M, Cheng F, Kang HJ,
Fernandez TV, Baskin JM, Choi M, Liu L, Ercan-Sencicek AG, Murdoch
JD, et al: Rare deleterious mutations of the gene EFR3A in autism
spectrum disorders. Mol Autism. 5:312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu H, Ye B, Zhang L, Wang Q, Liu Z, Ji S,
Liu Q, Lv J, Ma Y, Xu Y, et al: Efr3a insufficiency attenuates the
degeneration of spiral ganglion neurons after hair cell loss. Front
Mol Neurosci. 10:862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Adhikari H, Kattan WE, Kumar S, Zhou P,
Hancock JF and Counter CM: Oncogenic KRAS is dependent upon an
EFR3A-PI4KA signaling axis for potent tumorigenic activity. Nat
Commun. 12:52482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pang H, Zheng Y, Zhao Y, Xiu X and Wang J:
miR-590-3p suppresses cancer cell migration, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in glioblastoma multiforme by
targeting ZEB1 and ZEB2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 468:739–745.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Youssef AI, Khaled GM and Amleh A:
Functional role and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of the
miR-590-3p/MDM2 axis in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer.
23:3962023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ge X and Gong L: MiR-590-3p suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma growth by targeting TEAD1. Tumour Biol.
39:10104283176959472017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bruno T, Catena V, Corleone G, Cortile C,
Cappelletto MC, Bellei B, De Nicola F, Amadio B, Gumenyuk S,
Marchesi F, et al: Che-1/miR-590-3p/TAZ axis sustains multiple
myeloma disease. Leukemia. 38:877–882. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang Y, Chang J, Jiang W, Ye X and Zhang
S: Long non-coding RNA CASC9/microRNA-590-3p axis participates in
lutein-mediated suppression of breast cancer cell proliferation.
Oncol Lett. 22:5442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yan M, Ye L, Feng X, Shi R, Sun Z, Li Z
and Liu T: MicroRNA-590-3p inhibits invasion and metastasis in
triple-negative breast cancer by targeting Slug. Am J Cancer Res.
10:965–974. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shan Q, Qu F, Yang W and Chen N: Effect of
LINC00657 on apoptosis of breast cancer cells by regulating
miR-590-3p. Cancer Manag Res. 12:4561–4571. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ricciardelli C, Bianco-Miotto T, Jindal S,
Butler LM, Leung S, McNeil CM, O'Toole SA, Ebrahimie E, Millar EKA,
Sakko AJ, et al: The magnitude of androgen receptor positivity in
breast cancer is critical for reliable prediction of disease
outcome. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2328–2341. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bhattarai S, Klimov S, Mittal K,
Krishnamurti U, Li XB, Oprea-Ilies G, Wetherilt CS, Riaz A,
Aleskandarany MA, Green AR, et al: Prognostic role of androgen
receptor in triple negative breast cancer: A multi-institutional
study. Cancers (Basel). 11:9952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Sang M, Meng L, Ma C, Liu S, Sang M, Chang
S, Liu F, Lian Y and Geng C: Effect of AR antagonist combined with
PARP1 inhibitor on sporadic triple-negative breast cancer bearing
AR expression and methylation-mediated BRCA1 dysfunction. Biomed
Pharmacother. 111:169–177. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Traina TA, Miller K, Yardley DA, Eakle J,
Schwartzberg LS, O'Shaughnessy J, Gradishar W, Schmid P, Winer E,
Kelly C, et al: Enzalutamide for the treatment of androgen
receptor-expressing triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
36:884–890. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bonnefoi H, Grellety T, Tredan O,
Saghatchian M, Dalenc F, Mailliez A, L'Haridon T, Cottu P,
Abadie-Lacourtoisie S, You B, et al: A phase II trial of
abiraterone acetate plus prednisone in patients with
triple-negative androgen receptor positive locally advanced or
metastatic breast cancer (UCBG 12-1). Ann Oncol. 27:812–818. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu Y, Zhu XZ, Xiao Y, Wu SY, Zuo WJ, Yu
Q, Cao AY, Li JJ, Yu KD, Liu GY, et al: Subtyping-based platform
guides precision medicine for heavily pretreated metastatic
triple-negative breast cancer: The FUTURE phase II umbrella
clinical trial. Cell Res. 33:389–402. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jiang P and Xia B: Circular RNA EFR3A
promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma progression through modulating
the miR-654-3p/EFR3A axis. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand).
69:111–117. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|