|
1
|
Padala SA and Barsouk A, Thandra KC,
Saginala K, Mohammed A, Vakiti A, Rawla P and Barsouk A:
Epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. World J Oncol. 11:79–87.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rose TL and Kim WY: Renal cell carcinoma:
A review. JAMA. 332:1001–1010. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
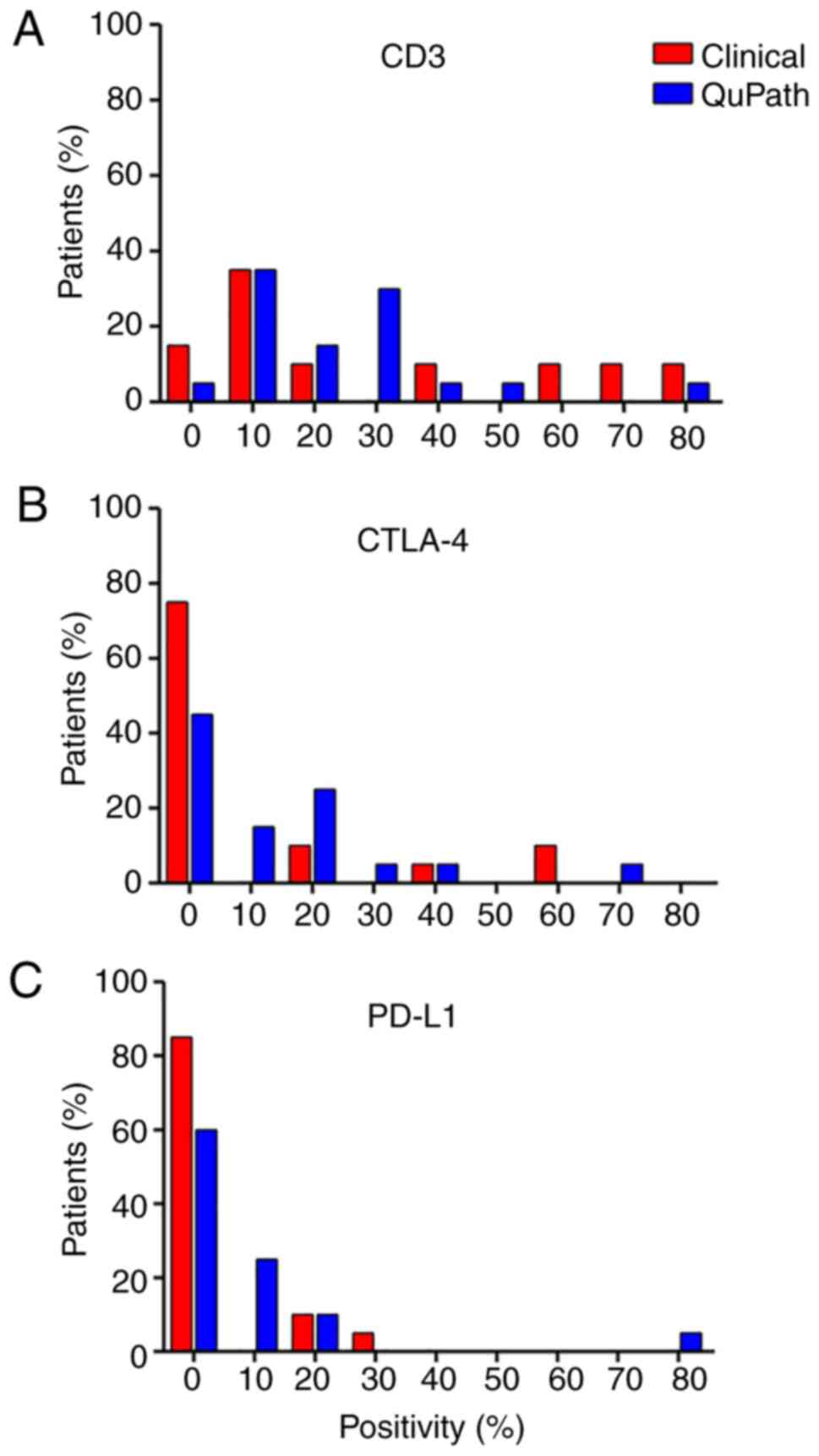
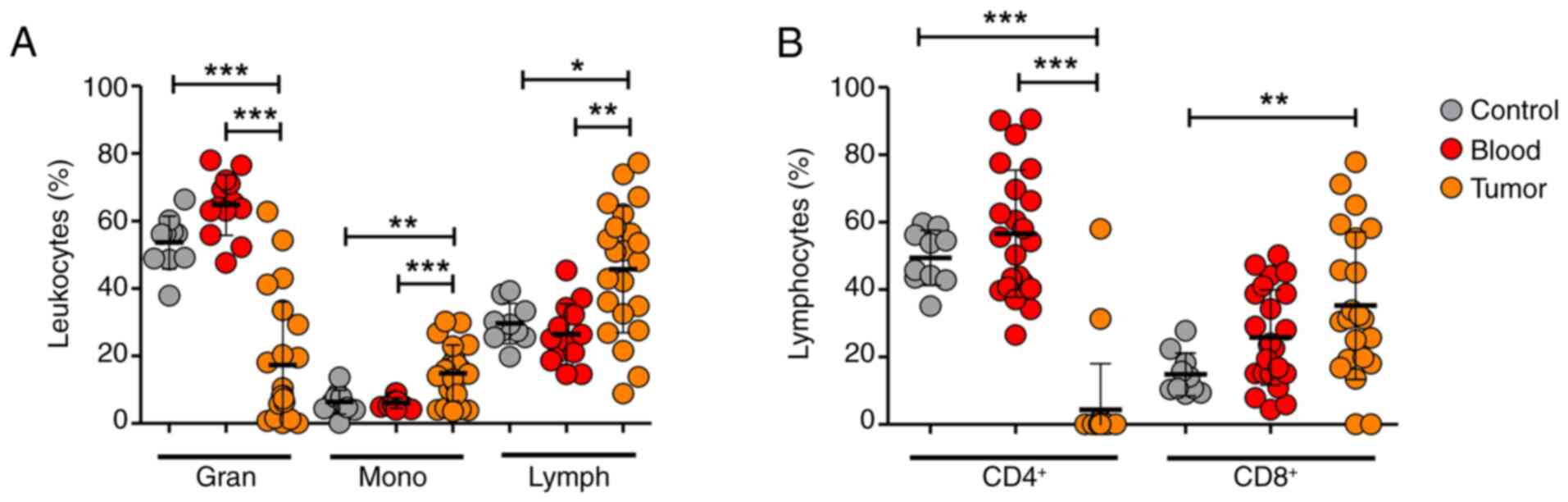
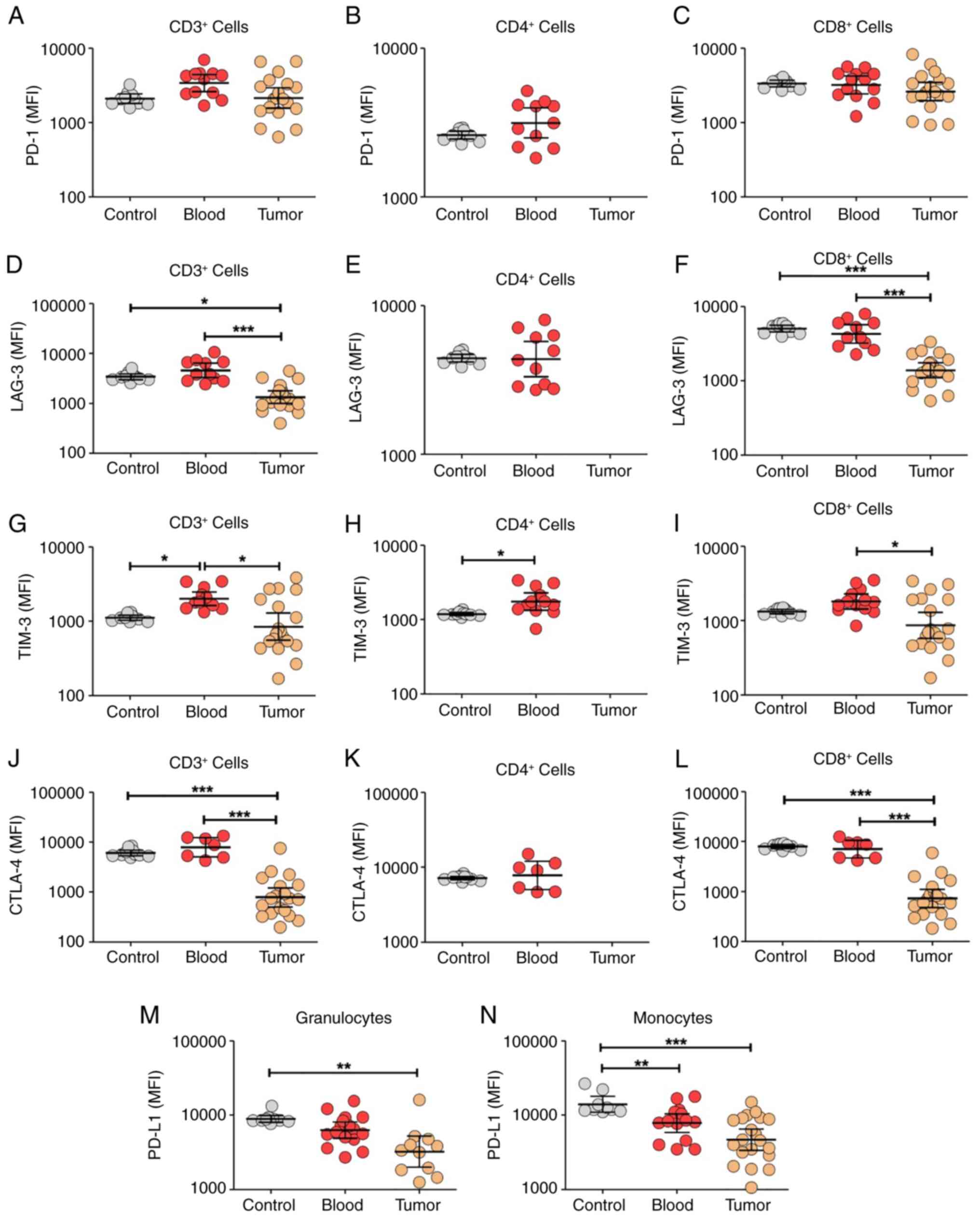
Di S, Gong M, Lv J, Yang Q, Sun Y, Tian Y,
Qian C, Chen W, Zhou W, Dong K, et al: Glycolysis-related biomarker
TCIRG1 participates in the regulation of renal cell carcinoma
progression and tumor immune microenvironment by affecting aerobic
glycolysis and AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
23:1862023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ma G, Wang Z, Liu J, Fu S, Zhang L, Zheng
D, Shang P and Yue Z: Quantitative proteomic analysis reveals
sophisticated metabolic alteration and identifies FMNL1 as a
prognostic marker in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Cancer.
12:6563–6575. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scosyrev E, Messing EM, Sylvester R and
Van Poppel H: exploratory subgroup analyses of renal function and
overall survival in European organization for research and
treatment of cancer randomized trial of nephron-sparing surgery
versus radical nephrectomy. Eur Urol Focus. 3:599–605. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bahadoram S, Davoodi M, Hassanzadeh S,
Bahadoram M, Barahman M and Mafakher L: Renal cell carcinoma: An
overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. G Ital
Nefrol. 39:2022–vol3. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
González-Garza R, Gutiérrez-González A,
Salinas-Carmona M and Mejía-Torres M: Biomarkers for evaluating the
clinical response to immune checkpoint inhibitors in renal cell
carcinoma (Review). Oncol Rep. 52:1642024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang X, Liu G, Li Y and Pan Y: Immune
checkpoint: The novel target for antitumor therapy. Genes Dis.
8:25–37. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Motzer RJ, Alyasova A, Ye D, Karpenko A,
Li H, Alekseev B, Xie L, Kurteva G, Kowalyszyn R, Karyakin O, et
al: Phase II trial of second-line everolimus in patients with
metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RECORD-4). Ann Oncol. 27:441–448.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Motzer RJ, Tannir NM, McDermott DF,
Frontera OA, Melichar B, Choueiri TK, Plimack ER, Barthélémy P,
Porta C, George S, et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab versus
sunitinib in advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
378:1277–1290. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Motzer RJ, Penkov K, Haanen J, Rini B,
Albiges L, Campbell MT, Venugopal B, Kollmannsberger C, Negrier S,
Uemura M, et al: Avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib for
advanced renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 380:1103–1115. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rini BI, Powles T, Atkins MB, Escudier B,
McDermott DF, Suarez C, Bracarda S, Stadler WM, Donskov F, Lee JL,
et al: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab versus sunitinib in patients
with previously untreated metastatic renal cell carcinoma
(IMmotion151): A multicentre, open-label, phase 3, randomised
controlled trial. Lancet. 393:2404–2415. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang DY, Salem JE, Cohen JV, Chandra S,
Menzer C, Ye F, Zhao S, Das S, Beckermann KE, Ha L, et al: Fatal
toxic effects associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. JAMA
Oncol. 4:1721–1728. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Saliby RM, Saad E, Kashima S, Schoenfeld
DA and Braun DA: Update on biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma.
American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book. 44:22024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amin MB; American Joint Committee on
Cancer, : American Cancer Society: AJCC cancer staging manual,
Eight edition/editor-in-chief, Mahul B, Amin, MD, FCAP; Stephen B.
Edge, MD, FACS [and 16 others]; Donna M. Gress, RHIT, CTR-Technical
editor; Laura R. Meyer, CAPM-Managing editor. American Joint
Committee on Cancer, Springer; Chicago IL: 2017
|
|
16
|
Organisation mondiale de la santé, Centre
international de recherche sur le cancer, . Urinary and male
genital tumours. 5th ed. International agency for research on
cancer; Lyon: 2022
|
|
17
|
Bankhead P, Loughrey MB, Fernández JA,
Dombrowski Y, McArt DG, Dunne PD, McQuaid S, Gray RT, Murray LJ,
Coleman HG, et al: QuPath: Open source software for digital
pathology image analysis. Sci Rep. 7:168782017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kazama A, Bilim V, Tasaki M, Anraku T,
Kuroki H, Shirono Y, Murata M, Hiruma K and Tomita Y:
Tumor-infiltrating immune cell status predicts successful response
to immune checkpoint inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma. Sci Rep.
12:203862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wu C, Cui Y, Liu J, Ma L, Xiong Y, Gong Y,
Zhao Y, Zhang X, Chen S, He Q, et al: Noninvasive evaluation of
tumor immune microenvironment in patients with clear cell renal
cell carcinoma using metabolic parameter from preoperative
2-[18F]FDG PET/CT. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
48:4054–4066. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ohe C, Yoshida T, Ikeda J, Tsuzuki T,
Ohashi R, Ohsugi H, Atsumi N, Yamaka R, Saito R, Yasukochi Y, et
al: Histologic-based tumor-associated immune cells status in clear
cell renal cell carcinoma correlates with gene signatures related
to cancer immunity and clinical outcomes. Biomedicines. 10:3232022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Möller K, Fraune C, Blessin NC, Lennartz
M, Kluth M, Hube-Magg C, Lindhorst L, Dahlem R, Fisch M, Eichenauer
T, et al: Tumor cell PD-L1 expression is a strong predictor of
unfavorable prognosis in immune checkpoint therapy-naive clear cell
renal cell cancer. Int Urol Nephrol. 53:2493–2503. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ozbek E, Besiroglu H, Ozer K, Horsanali MO
and Gorgel SN: Systemic immune inflammation index is a promising
non-invasive marker for the prognosis of the patients with
localized renal cell carcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol. 52:1455–1463.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kawashima A, Kanazawa T, Kidani Y, Yoshida
T, Hirata M, Nishida K, Nojima S, Yamamoto Y, Kato T, Hatano K, et
al: Tumour grade significantly correlates with total dysfunction of
tumour tissue-infiltrating lymphocytes in renal cell carcinoma. Sci
Rep. 10:62202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheaib JG, Patel HD, Johnson MH, Gorin MA,
Haut ER, Canner JK, Allaf ME and Pierorazio PM: Stage-specific
conditional survival in renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy.
Urol Oncol. 38:6.e1–6.e7. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Giraldo NA, Becht E, Vano Y, Petitprez F,
Lacroix L, Validire P, Sanchez-Salas R, Ingels A, Oudard S, Moatti
A, et al: Tumor-Infiltrating and peripheral blood T-cell
immunophenotypes predict early relapse in localized clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 23:4416–4428. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jung M, Lee JA, Yoo SY, Bae JM, Kang GH
and Kim JH: Intratumoral spatial heterogeneity of
tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes is a significant factor for
precisely stratifying prognostic immune subgroups of microsatellite
instability-high colorectal carcinomas. Mod Pathol. 35:2011–2022.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mei Z, Liu Y, Liu C, Cui A, Liang Z, Wang
G, Peng H, Cui L and Li C: Tumour-infiltrating inflammation and
prognosis in colorectal cancer: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. Br J Cancer. 110:1595–1605. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tewari N, Zaitoun AM, Arora A, Madhusudan
S, Ilyas M and Lobo DN: The presence of tumour-associated
lymphocytes confers a good prognosis in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma: An immunohistochemical study of tissue microarrays.
BMC Cancer. 13:4362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rathore AS, Kumar S, Konwar R, Makker A,
Negi MPS and Goel MM: CD3+, CD4+ & CD8+ tumour infiltrating
lymphocytes (TILs) are predictors of favourable survival outcome in
infiltrating ductal carcinoma of breast. Indian J Med Res.
140:361–369. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kahlmeyer A, Stöhr CG, Hartmann A, Goebell
PJ, Wullich B, Wach S, Taubert H and Erlmeier F: Expression of PD-1
and CTLA-4 are negative prognostic markers in renal cell carcinoma.
J Clin Med. 8:7432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kawakami F, Sircar K, Rodriguez-Canales J,
Fellman BM, Urbauer DL, Tamboli P, Tannir NM, Jonasch E, Wistuba
II, Wood CG and Karam JA: PD-L1 and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes
status in patients with renal cell carcinoma and sarcomatoid
dedifferentiation. Cancer. 123:4823–4831. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bi Q, Liu Y, Yuan T, Wang H, Li B, Jiang
Y, Mo X, Lei Y, Xiao Y, Dong S, et al: Predicted CD4+ T cell
infiltration levels could indicate better overall survival in
sarcoma patients. J Int Med Res. 49:03000605209815392021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shah W, Yan X, Jing L, Zhou Y, Chen H and
Wang Y: A reversed CD4/CD8 ratio of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes
and a high percentage of CD4+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells are
significantly associated with clinical outcome in squamous cell
carcinoma of the cervix. Cell Mol Immunol. 8:59–66. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paul S, Chhatar S, Mishra A and Lal G:
Natural killer T cell activation increases iNOS+CD206- M1
macrophage and controls the growth of solid tumor. J Immunother
Cancer. 7:2082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li J, Moresco P and Fearon DT:
Intratumoral NKT cell accumulation promotes antitumor immunity in
pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 121:e24039171212024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nishida K, Kawashima A, Kanazawa T, Kidani
Y, Yoshida T, Hirata M, Yamamoto K, Yamamoto Y, Sawada M, Kato R,
et al: Clinical importance of the expression of CD4+CD8+ T cells in
renal cell carcinoma. Int Immunol. 32:347–357. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Menard LC, Fischer P, Kakrecha B, Linsley
PS, Wambre E, Liu MC, Rust BJ, Lee D, Penhallow B, Orduno NM and
Nadler SG: Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) tumors display large
expansion of double positive (DP) CD4+CD8+ T cells with expression
of exhaustion markers. Front Immunol. 9:27282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zelba H, Bedke J, Hennenlotter J, Mostböck
S, Zettl M, Zichner T, Chandran A, Stenzl A, Rammensee HG and
Gouttefangeas C: PD-1 and LAG-3 dominate checkpoint
receptor-mediated T-cell inhibition in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer
Immunol Res. 7:1891–1899. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Young M, Tapia JC, Szabados B, Jovaisaite
A, Jackson-Spence F, Nally E and Powles T: NLR outperforms low
hemoglobin and high platelet count as predictive and prognostic
biomarker in metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with immune
checkpoint inhibitors. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 22:1020722024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ishihara H, Takagi T, Kondo T, Fukuda H,
Tachibana H, Yoshida K, Iizuka J, Okumi M, Ishida H and Tanabe K:
Predictive impact of an early change in serum C-reactive protein
levels in nivolumab therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Urol Oncol. 38:526–532. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Noguchi G, Nakaigawa N, Umemoto S,
Kobayashi K, Shibata Y, Tsutsumi S, Yasui M, Ohtake S, Suzuki T,
Osaka K, et al: C-reactive protein at 1 month after treatment of
nivolumab as a predictive marker of efficacy in advanced renal cell
carcinoma. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 86:75–85. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei F, Zhong S, Ma Z, Kong H, Medvec A,
Ahmed R, Freeman GJ, Krogsgaard M and Riley JL: Strength of PD-1
signaling differentially affects T-cell effector functions. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:E2480–E2489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tsujikawa T, Kumar S, Borkar RN, Azimi V,
Thibault G, Chang YH, Balter A, Kawashima R, Choe G, Sauer D, et
al: Quantitative multiplex immunohistochemistry reveals
myeloid-inflamed tumor-immune complexity associated with poor
prognosis. Cell Rep. 19:203–217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Pichler R, Siska PJ, Tymoszuk P, Martowicz
A, Untergasser G, Mayr R, Weber F, Seeber A, Kocher F, Barth DA, et
al: A chemokine network of T cell exhaustion and metabolic
reprogramming in renal cell carcinoma. Front Immunol.
14:10951952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Denize T, Jegede OA, Matar S, El Ahmar N,
West DJ, Walton E, Bagheri AS, Savla V, Laimon YN, Gupta S, et al:
PD-1 Expression on intratumoral regulatory T cells is associated
with lack of benefit from anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic
clear-cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res.
30:803–813. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cai C, Xu YF, Wu ZJ, Dong Q, Li MY, Olson
JC, Rabinowitz YM, Wang LH and Sun Y: Tim-3 expression represents
dysfunctional tumor infiltrating T cells in renal cell carcinoma.
World J Urol. 34:561–567. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yeong J, Zhao Z, Lim JCT, Li H, Thike AA,
Koh VCY, Teh BT, Kanesvaran R, Toh CK, Tan PH and Khor LY: PD-L1
expression is an unfavourable prognostic indicator in Asian renal
cell carcinomas. J Clin Pathol. 73:463–469. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Warren AY and Harrison D: WHO/ISUP
classification, grading and pathological staging of renal cell
carcinoma: Standards and controversies. World J Urol. 36:1913–1926.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|