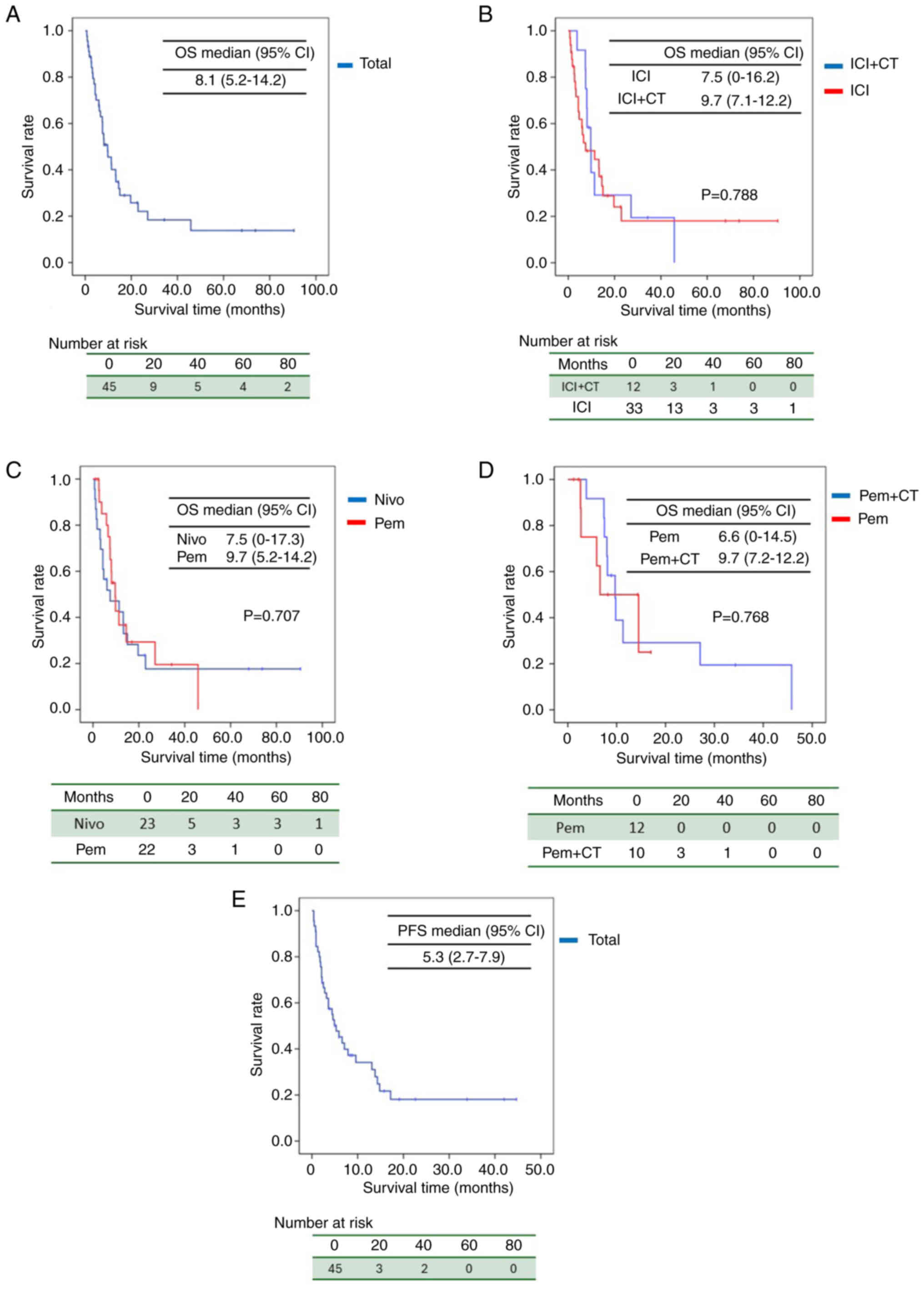
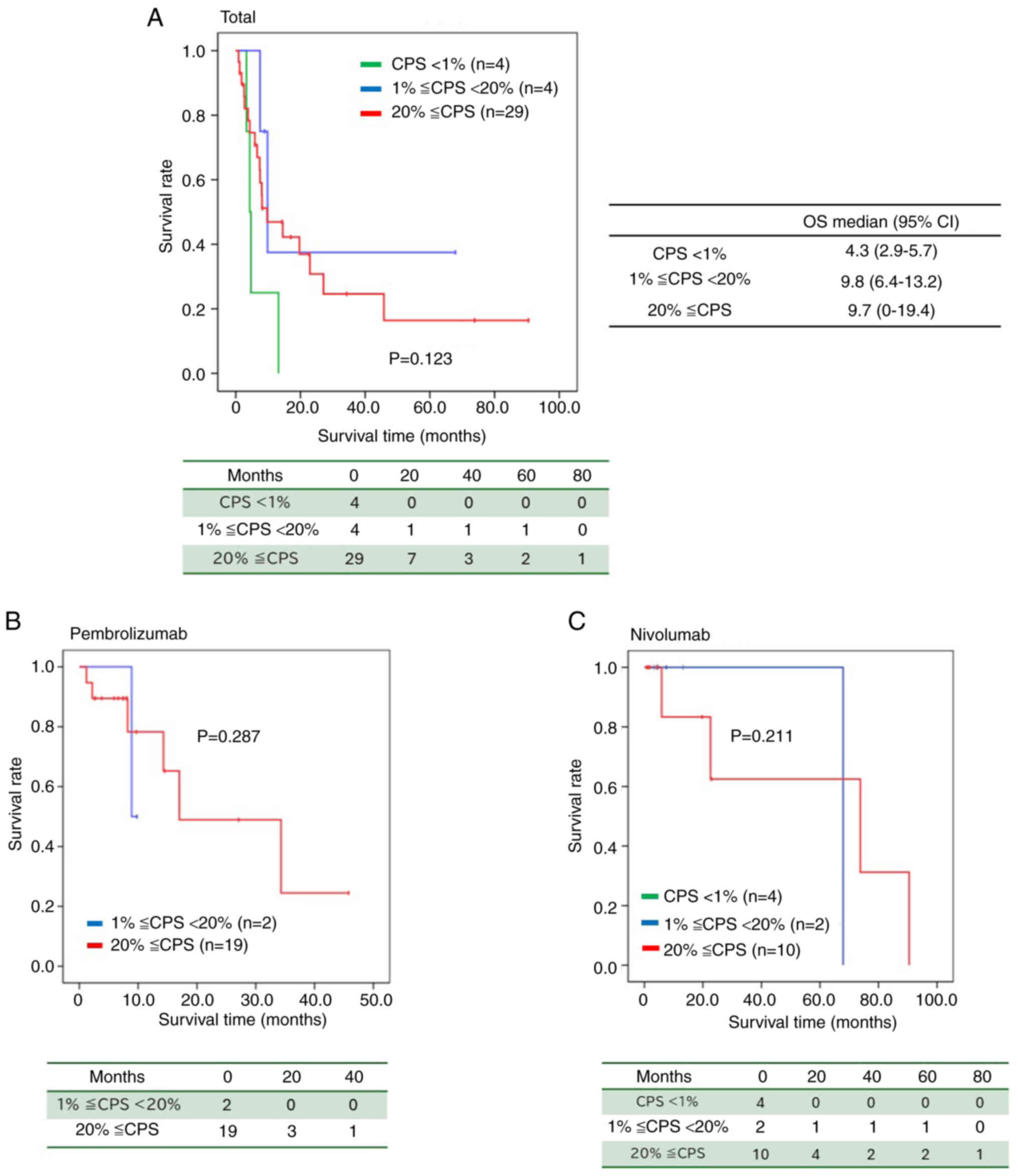
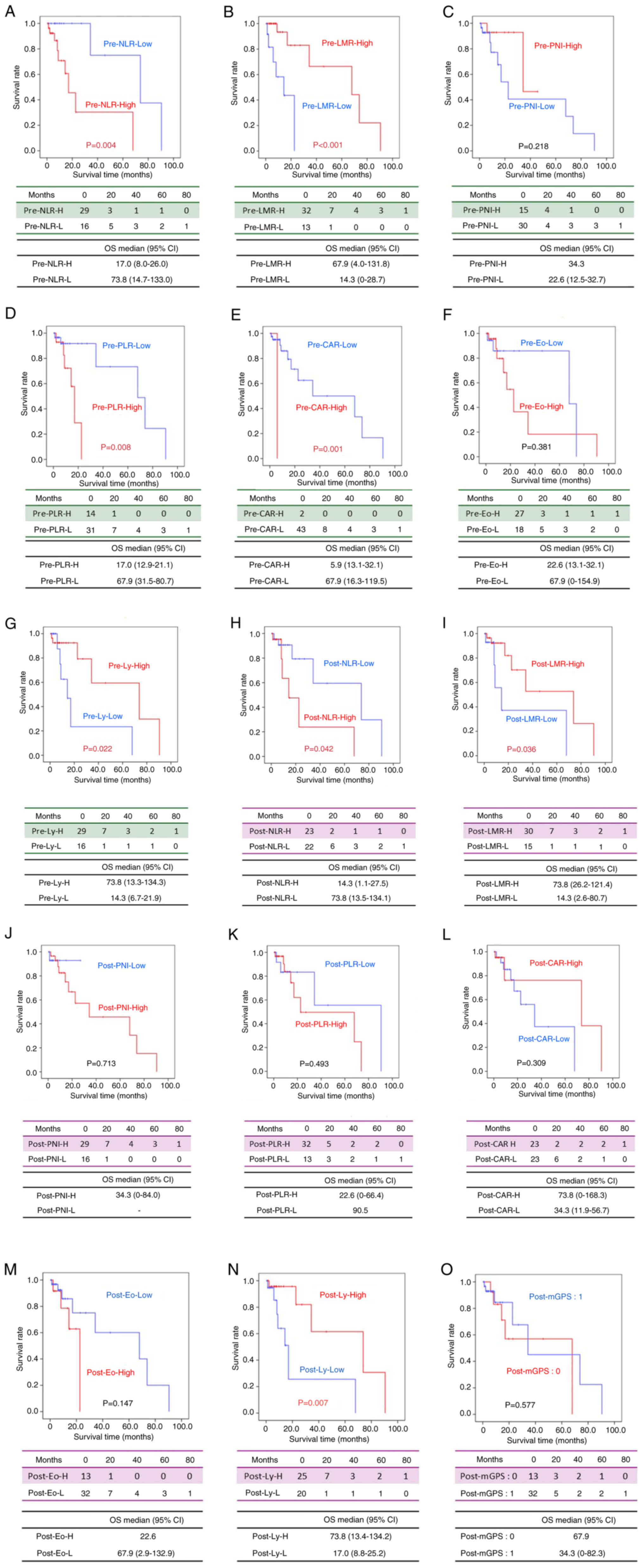
|
1
|
Werning JW: Oral cancer: Diagnosis,
management, and rehabilitation. 1st Edition. Thieme Medical
Publishing Group; New York, USA: pp. 12007
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Olson CM, Burda BU, Beil T and Whitlock
EP: Screening for oral cancer: A targeted evidence update for the
U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Rockville (MD): Agency for
Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2013
|
|
4
|
Vermorken JB, Mesia R, Rivera F, Remenar
E, Kawecki A, Rottey S, Erfan J, Zabolotnyy D, Kienzer HR, Cupissol
D, et al: Platinum-based chemotherapy plus cetuximab in head and
neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1116–1127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ferris RL, Blumenschein G Jr, Fayette J,
Guigay J, Colevas AD, Licitra L, Harrington K, Kasper S, Vokes EE,
Even C, et al: Nivolumab for recurrent Squamous-cell carcinoma of
the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 375:1856–1867. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cohen EEW, Soulières D, Le Tourneau C,
Dinis J, Licitra L, Ahn MJ, Soria A, Machiels JP, Mach N, Mehra R,
et al: Pembrolizumab versus standard therapy for recurrent or
metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-048): A
randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 393:156–167. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanna GJ, Schoenfeld JD and Ferris RL:
Immunotherapy approaches in head and neck cancer: Current and
emerging strategies. Front Immunol. 13:8409042022.
|
|
8
|
Zhang P, Su DM, Liang M and Fu J:
Chemopreventive agents induce programmed death-1-ligand 1 (PD-L1)
surface expression in breast cancer cells and promote
PD-L1-mediated T cell apoptosis. Mol Immunol. 45:1470–1476. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu
VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA and Kinzler KW: Cancer genome landscapes.
Science. 339:1546–1558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fridman WH, Pagès F, Sautès-Fridman C and
Galon J: The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical
outcome. Nat Rev Cancer. 12:298–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Forrest LM, McMillan DC, McArdle CS,
Angerson WJ and Dunlop DJ: Evaluation of cumulative prognostic
scores based on the systemic inflammatory response in patients with
inoperable Non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 89:1028–1030.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shibutani M, Maeda K, Nagahara H, Iseki Y,
Hirakawa K and Ohira M: The significance of the C-reactive protein
to albumin ratio as a marker for predicting survival and monitoring
chemotherapeutic effectiveness in patients with unresectable
metastatic colorectal cancer. Springerplus. 5:17982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
An X, Ding PR, Li YH, Wang FH, Shi YX,
Wang ZQ, He YJ, Xu RH and Jiang WQ: Elevated neutrophil to
lymphocyte ratio predicts survival in advanced pancreatic cancer.
Biomarkers. 15:516–522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu Y, Li C, Zhao J, Yang L, Liu F, Zheng
H, Wang Z and Xu Y: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios predict chemotherapy outcomes and
prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer and synchronous liver
metastasis. World J Surg Oncol. 14:2892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang L, Huang Y, Zhou L, Dai Y and Hu G:
High pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a predictor of
poor survival prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma:
Systematic review and meta-analysis. Head Neck. 41:1525–1535. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rassouli A, Saliba J, Castano R, Hier M
and Zeitouni AG: Systemic inflammatory markers as independent
prognosticators of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head
Neck. 37:103–110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takenaka Y, Oya R, Kitamiura T, Ashida N,
Shimizu K, Takemura K, Yamamoto Y and Uno A: Platelet count and
platelet-lymphocyte ratio as prognostic markers for head and neck
squamous cell carcinoma: Meta-analysis. Head Neck. 40:2714–2723.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bardash Y, Olson C, Herman W, Khaymovich
J, Costantino P and Tham T: Platelet-lymphocyte ratio as a
predictor of prognosis in head and neck cancer: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Oncol Res Treat. 42:665–677. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nishikawa D, Suzuki H, Koide Y, Beppu S,
Kadowaki S, Sone M and Hanai N: Prognostic markers in head and neck
cancer patients treated with nivolumab. Cancers (Basel).
10:4662018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mohammed FF, Poon I, Zhang L, Elliott L,
Hodson ID, Sagar SM and Wright J: Acute-phase response reactants as
objective biomarkers of radiation-induced mucositis in head and
neck cancer. Head Neck. 34:985–993. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kano S, Homma A, Hatakeyama H, Mizumachi
T, Sakashita T, Kakizaki T and Fukuda S: Pretreatment
lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio as an independent prognostic factor
for head and neck cancer. Head Neck. 39:247–253. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ikeguchi M: Glasgow prognostic score and
neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio are good prognostic indicators after
radical neck dissection for advanced squamous cell carcinoma in the
hypopharynx. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 401:861–866. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Turri-Zanoni M, Salzano G, Lambertoni A,
Giovannardi M, Karligkiotis A, Battaglia P and Castelnuovo P:
Prognostic value of pretreatment peripheral blood markers in
paranasal sinus cancer: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio. Head Neck. 39:730–736. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mikoshiba T, Ozawa H, Saito S, Ikari Y,
Nakahara N, Ito F, Watanabe Y, Sekimizu M, Imanishi Y and Ogawa K:
Usefulness of hematological inflammatory markers in predicting
severe side-effects from induction chemotherapy in head and neck
cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 39:3059–3065. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yasumatsu R, Wakasaki T, Hashimoto K,
Nakashima K, Manako T, Taura M, Matsuo M and Nakagawa T: Monitoring
the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio may be useful for predicting the
anticancer effect of nivolumab in recurrent or metastatic head and
neck cancer. Head Neck. 41:2610–2618. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ferrucci PF, Ascierto PA, Pigozzo J, Del
Vecchio M, Maio M, Antonini Cappellini GC, Guidoboni M, Queirolo P,
Savoia P, Mandalà M, et al: Baseline neutrophils and derived
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: Prognostic relevance in metastatic
melanoma patients receiving ipilimumab. Ann Oncol. 27:732–738.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kiriu T, Yamamoto M, Nagano T, Hazama D,
Sekiya R, Katsurada M, Tamura D, Tachihara M, Kobayashi K and
Nishimura Y: The time-series behavior of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio is useful as a predictive marker in non-small cell lung
cancer. PLoS One. 13:e01930182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sacdalan DB, Lucero JA and Sacdalan DL:
Prognostic utility of baseline neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in
patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors: A review and
meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther. 11:955–965. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Diem S, Schmid S, Krapf M, Flatz L, Born
D, Jochum W, Templeton AJ and Früh M: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte
ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) as prognostic
markers in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated
with nivolumab. Lung Cancer. 111:176–181. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bagley SJ, Kothari S, Aggarwal C, Bauml
JM, Alley EW, Evans TL, Kosteva JA, Ciunci CA, Gabriel PE, Thompson
JC, et al: Pretreatment neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a marker
of outcomes in nivolumab-treated patients with advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 106:1–7. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jain S, Harris J and Ware J: Platelets:
Linking hemostasis and cancer. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:2362–2367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nieswandt B, Hafner M, Echtenacher B and
Männel DN: Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is
impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 59:1295–1300. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
C: TNM classification of malignant tumours. 8th Edition.
Wiley-Blackwell; Hoboken, NJ: 2016
|
|
34
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Granot Z and Jablonska J: Distinct
functions of neutrophil in cancer and its regulation. Mediators
Inflamm. 2015:7010672015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ferris RL: Immunology and immunotherapy of
head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 33:3293–3304. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Pettersen K, Andersen S, Degen S, Tadini
V, Grosjean J, Hatakeyama S, Tesfahun AN, Moestue S, Kim J, Nonstad
U, et al: Cancer cachexia associates with a systemic
autophagy-inducing activity mimicked by cancer cell-derived IL-6
trans-signaling. Sci Rep. 7:20462017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tanoue K, Tamura S, Kusaba H, Shinohara Y,
Ito M, Tsuchihashi K, Shirakawa T, Otsuka T, Ohmura H, Isobe T, et
al: Predictive impact of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio for
recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
receiving nivolumab. Sci Rep. 11:27412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Duffy SA, Taylor JM, Terrell JE, Islam M,
Li Y, Fowler KE, Wolf GT and Teknos TN: Interleukin-6 predicts
recurrence and survival among head and neck cancer patients.
Cancer. 113:750–757. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Riedel F, Zaiss I, Herzog D, Götte K, Naim
R and Hörmann K: Serum levels of interleukin-6 in patients with
primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res.
25:2761–2765. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ravishankaran P and Karunanithi R:
Clinical significance of preoperative serum interleukin-6 and
C-reactive protein level in breast cancer patients. World J Surg
Oncol. 9:182011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
McKeown DJ, Brown DJ, Kelly A, Wallace AM
and McMillan DC: The relationship between circulating
concentrations of C-reactive protein, inflammatory cytokines and
cytokine receptors in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Br
J Cancer. 91:1993–1995. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Inoue Y, Iwata T, Okugawa Y, Kawamoto A,
Hiro J, Toiyama Y, Tanaka K, Uchida K, Mohri Y, Miki C and Kusunoki
M: Prognostic significance of a systemic inflammatory response in
patients undergoing multimodality therapy for advanced colorectal
cancer. Oncology. 84:100–107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matsuki T, Okamoto I, Fushimi C, Sawabe M,
Kawakita D, Sato H, Tsukahara K, Kondo T, Okada T, Tada Y, et al:
Hematological predictive markers for recurrent or metastatic
squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck treated with
nivolumab: A multicenter study of 88 patients. Cancer Med.
9:5015–5024. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ueki Y, Takahashi T, Ota H, Shodo R,
Yamazaki K and Horii A: Predicting the treatment outcome of
nivolumab in recurrent or metastatic head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma: Prognostic value of combined performance status and
modified Glasgow prognostic score. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.
277:2341–2347. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Niwa K, Kawakita D, Nagao T, Takahashi H,
Saotome T, Okazaki M, Yamazaki K, Okamoto I, Hirai H, Saigusa N, et
al: Multicentre, retrospective study of the efficacy and safety of
nivolumab for recurrent and metastatic salivary gland carcinoma.
Sci Rep. 10:169882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Minohara K, Matoba T, Kawakita D, Takano
G, Oguri K, Murashima A, Nakai K, Iwaki S, Hojo W, Matsumura A, et
al: Novel Prognostic Score for recurrent or metastatic head and
neck cancer patients treated with Nivolumab. Sci Rep. 11:169922021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Matsuo M, Yasumatsu R, Masuda M, Toh S,
Wakasaki T, Hashimoto K, Jiromaru R, Manako T and Nakagawa T:
Inflammation-based prognostic score as a prognostic biomarker in
patients with recurrent and/or metastatic head and neck squamous
cell carcinoma treated with nivolumab therapy. In Vivo. 36:907–917.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wagner DD: New links between inflammation
and thrombosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:1321–1324. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Stone RL, Nick AM, McNeish IA, Balkwill F,
Han HD, Bottsford-Miller J, Rupairmoole R, Armaiz-Pena GN, Pecot
CV, Coward J, et al: Paraneoplastic thrombocytosis in ovarian
cancer. N Engl J Med. 366:610–618. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhang L, Ma W, Qiu Z, Kuang T, Wang K, Hu
B and Wang W: Prognostic nutritional index as a prognostic
biomarker for gastrointestinal cancer patients treated with immune
checkpoint inhibitors. Front Immunol. 14:12199292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shoji F, Takeoka H, Kozuma Y, Toyokawa G,
Yamazaki K, Ichiki M and Takeo S: Pretreatment prognostic
nutritional index as a novel biomarker in non-small cell lung
cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors. Lung
Cancer. 136:45–51. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tachinami H, Tomihara K, Yamada SI, Ikeda
A, Imaue S, Hirai H, Nakai H, Sonoda T, Kurohara K, Yoshioka Y, et
al: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as an early marker of outcomes
in patients with recurrent oral squamous cell carcinoma treated
with nivolumab. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 61:320–326. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhou XH, Obuchowski NA and McClish DK:
Statistical methods in diagnostic medicine. 2nd Edition. John Wiley
& Sons; New Jersey: 2011, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Valero C, Lee M, Hoen D, Zehir A, Berger
MF, Seshan VE, Chan TA and Morris LGT: Response rates to anti-PD-1
immunotherapy in microsatellite-stable solid tumors with 10 or more
mutations per megabase. JAMA Oncol. 7:739–743. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Iwasa YI, Kitoh R, Yokota Y, Hori K,
Kasuga M, Kobayashi T, Kanda S and Takumi Y: Post-treatment
neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio is a prognostic factor in head and neck
cancers treated with nivolumab. Cancer Diagn Progn. 4:182–188.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shaverdian N, Lisberg AE, Bornazyan K,
Veruttipong D, Goldman JW, Formenti SC, Garon EB and Lee P:
Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of
pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: A
secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:895–903. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Öjlert ÅK, Nebdal D, Lund-Iversen M,
Åstrøm Ellefsen R, Brustugun OT, Gran JM, Halvorsen AR and Helland
Å: Immune checkpoint blockade in the treatment of advanced
non-small cell lung cancer-predictors of response and impact of
previous radiotherapy. Acta Oncol. 60:149–156. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Shankar B, Zhang J, Naqash AR, Forde PM,
Feliciano JL, Marrone KA, Ettinger DS, Hann CL, Brahmer JR,
Ricciuti B, et al: Multisystem immune-related adverse events
associated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for treatment of
non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 6:1952–1956. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hsiehchen D, Naqash AR, Espinoza M, Von
Itzstein MS, Cortellini A, Ricciuti B, Owen DH, Laharwal M, Toi Y,
Burke M, et al: Association between immune-related adverse event
timing and treatment outcomes. Oncoimmunology. 11:20171622022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang M, Zhai X, Li J, Guan J, Xu S, Li Y
and Zhu H: The role of cytokines in predicting the response and
adverse events related to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front
Immunol. 12:6703912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fehrenbacher L, Spira A, Ballinger M,
Kowanetz M, Vansteenkiste J, Mazieres J, Park K, Smith D,
Artal-Cortes A, Lewanski C, et al: Atezolizumab versus docetaxel
for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer
(POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled
trial. Lancet. 387:1837–1846. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sanmamed MF, Perez-Gracia JL, Schalper KA,
Fusco JP, Gonzalez A, Rodriguez-Ruiz ME, Oñate C, Perez G, Alfaro
C, Martín-Algarra S, et al: Changes in serum interleukin-8 (IL-8)
levels reflect and predict response to anti-PD-1 treatment in
melanoma and non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Ann Oncol.
28:1988–1995. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
McGranahan N, Furness AJ, Rosenthal R,
Ramskov S, Lyngaa R, Saini SK, Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, Birkbak
NJ, Hiley CT, et al: Clonal neoantigens elicit T cell
immunoreactivity and sensitivity to immune checkpoint blockade.
Science. 351:1463–1469. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Miao D, Margolis CA, Vokes NI, Liu D,
Taylor-Weiner A, Wankowicz SM, Adeegbe D, Keliher D, Schilling B,
Tracy A, et al: Genomic correlates of response to immune checkpoint
blockade in microsatellite-stable solid tumors. Nat Genet.
50:1271–1281. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Giroux Leprieur E, Hélias-Rodzewicz Z,
Takam Kamga P, Costantini A, Julie C, Corjon A, Dumenil C, Dumoulin
J, Giraud V, Labrune S, et al: Sequential ctDNA whole-exome
sequencing in advanced lung adenocarcinoma with initial durable
tumor response on immune checkpoint inhibitor and late progression.
J Immunother Cancer. 8:e0005272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Guibert N, Jones G, Beeler JF, Plagnol V,
Morris C, Mourlanette J, Delaunay M, Keller L, Rouquette I, Favre
G, et al: Targeted sequencing of plasma cell-free DNA to predict
response to PD1 inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer.
Lung Cancer. 137:1–6. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhang W, Li Y, Lyu J, Shi F, Kong Y, Sheng
C, Wang S and Wang Q: An aging-related signature predicts favorable
outcome and immunogenicity in lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Sci.
113:891–903. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Borghaei H, Paz-Ares L, Horn L, Spigel DR,
Steins M, Ready NE, Chow LQ, Vokes EE, Felip E, Holgado E, et al:
Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell
lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 373:1627–1639. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Arbour KC, Mezquita L, Long N, Rizvi H,
Auclin E, Ni A, Martínez-Bernal G, Ferrara R, Lai WV, Hendriks LEL,
et al: Impact of baseline steroids on efficacy of programmed cell
death-1 and programmed death-ligand 1 blockade in patients with
non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 36:2872–2878. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liu C, Guo H, Mao H, Tong J, Yang M and
Yan X: An up-to-date investigation into the correlation between
proton pump inhibitor use and the clinical efficacy of immune
checkpoint inhibitors in advanced solid cancers: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol. 12:7532342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ochi N, Ichihara E, Takigawa N, Harada D,
Inoue K, Shibayama T, Hosokawa S, Kishino D, Harita S, Oda N, et
al: The effects of antibiotics on the efficacy of immune checkpoint
inhibitors in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer differ based
on PD-L1 expression. Eur J Cancer. 149:73–81. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|