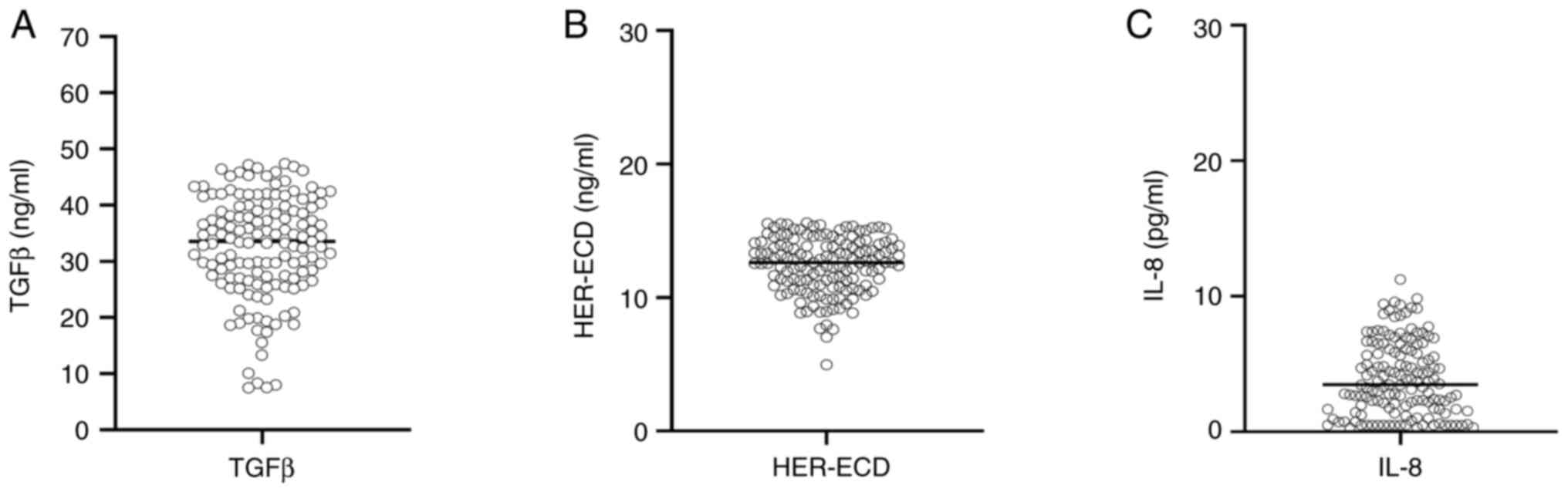
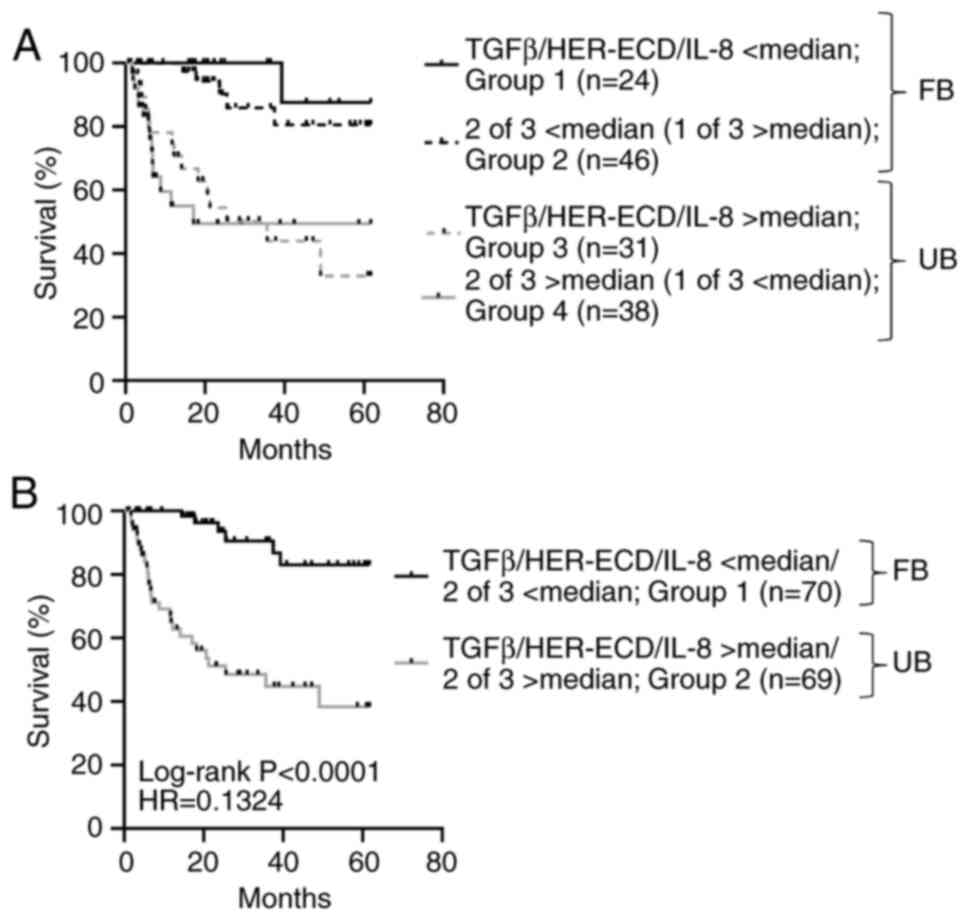
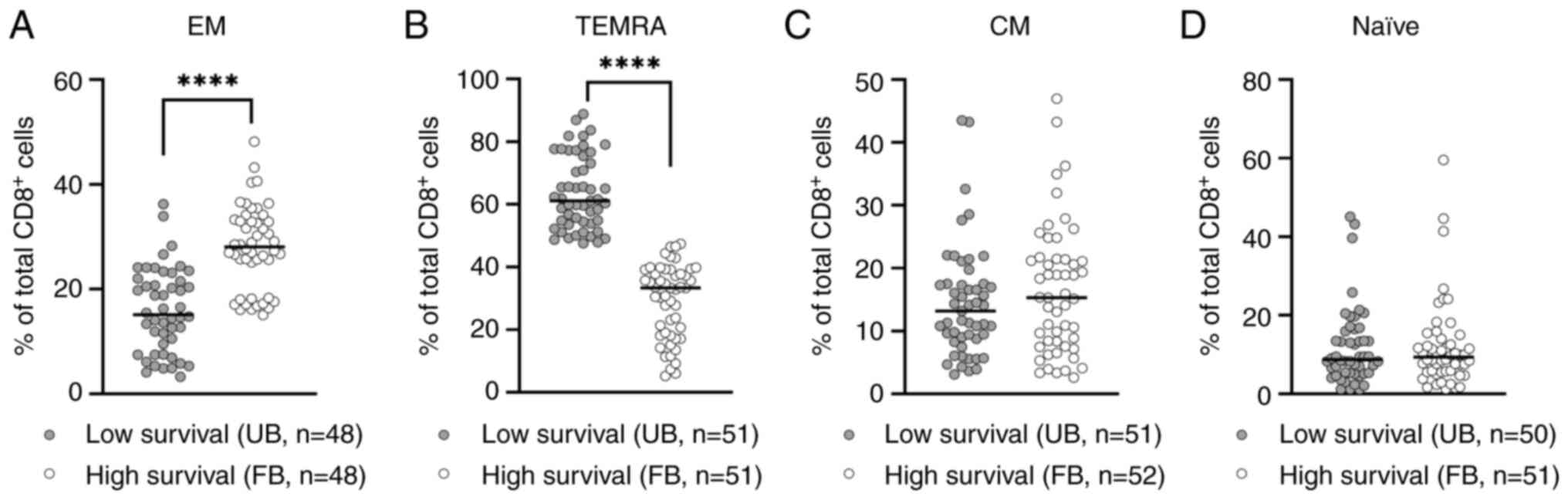
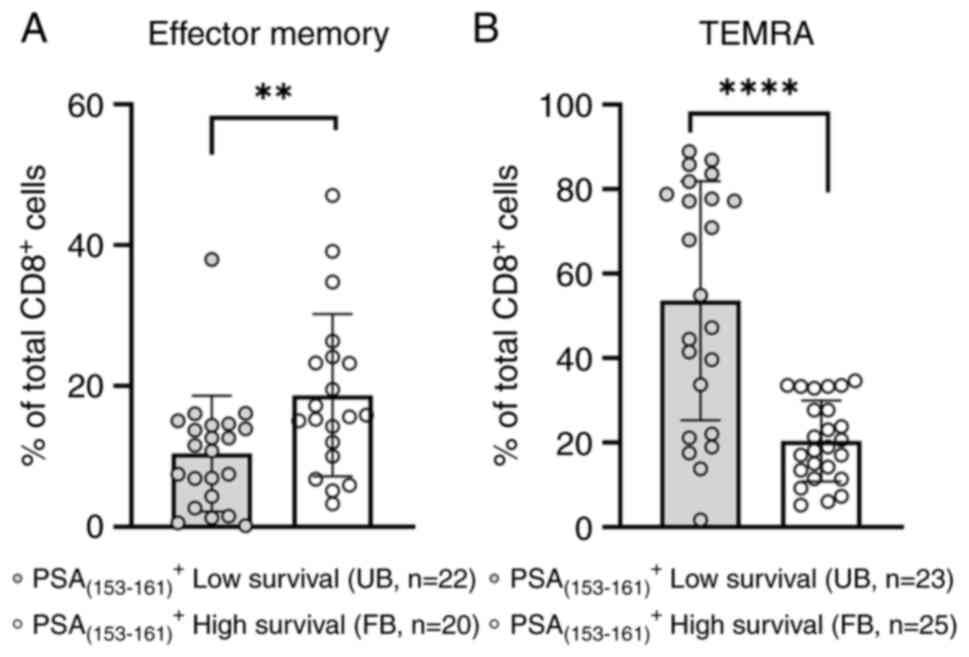
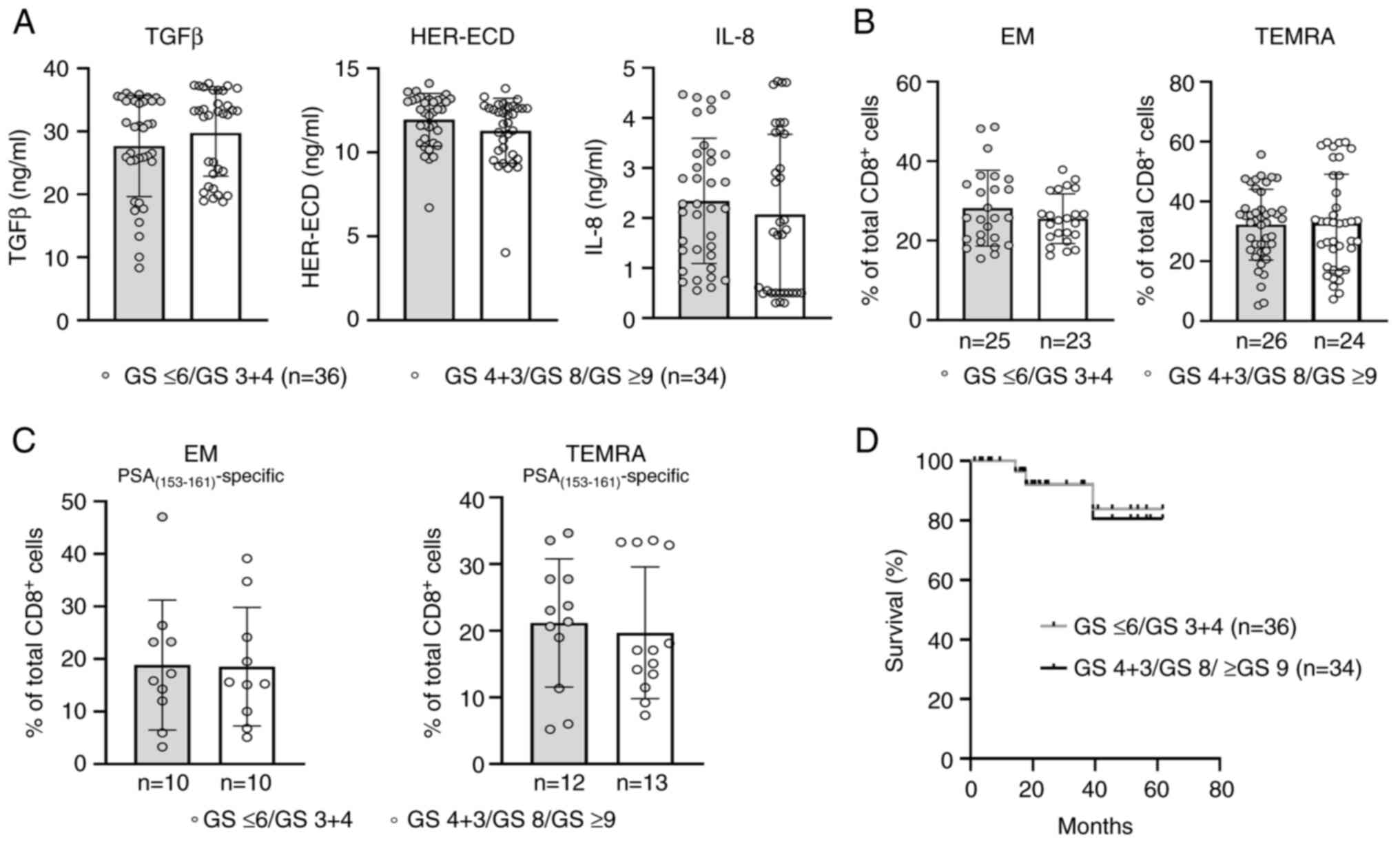
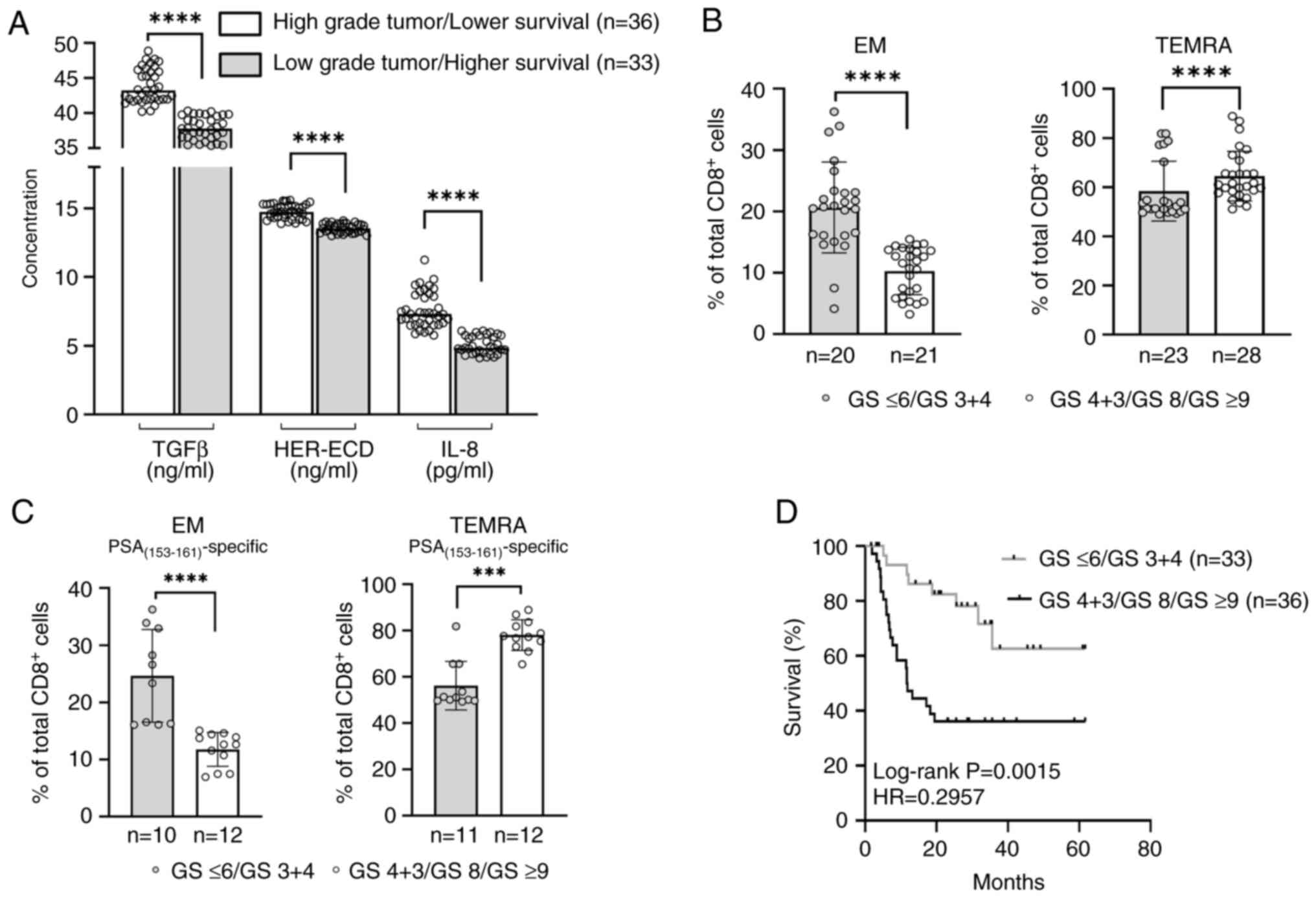
|
1
|
Welch HG and Albertsen PC: Reconsidering
prostate cancer mortality-The future of PSA screening. N Engl J
Med. 382:1557–1563. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shelley M, Harrison C, Coles B, Staffurth
J, Wilt TJ and Mason MD: Chemotherapy for hormone-refractory
prostate cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
18:CD0052472006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rebello RJ, Oing C, Knudsen KE, Loeb S,
Johnson DC, Reiter RE, Gillessen S, Van der Kwast T and Bristow RG:
Prostate cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 7:92021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cooperberg MR, Carroll PR, Dall'Era MA,
Davies BJ, Davis JW, Eggener SE, Feng FY, Lin DW, Morgan TM,
Morgans AK, et al: The state of the science on prostate cancer
biomarkers: The San Francisco Consensus statement. Eur Urol.
76:268–272. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zelic R, Garmo H, Zugna D, Stattin P,
Richiardi L, Akre O and Pettersson A: Predicting prostate cancer
death with different pretreatment risk stratification tools: A
head-to-head comparison in a nationwide cohort study. Eur Urol.
77:180–188. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Baxevanis CN, Fortis SP and Perez SA: The
balance between breast cancer and the immune system: Challenges for
prognosis and clinical benefit from immunotherapies. Semin Cancer
Biol. 72:76–89. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vesely MD and Schreiber RD: Cancer
immunoediting: Antigens, mechanisms, and implications to cancer
immunotherapy. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1284:1–5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Haen SP, Löffler MW, Rammensee HG and
Brossart P: Towards new horizons: Characterization, classification
and implications of the tumour antigenic repertoire. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 17:595–610. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mittal D, Gubin MM, Schreiber RD and Smyth
MJ: New insights into cancer immunoediting and its three component
phases-elimination, equilibrium and escape. Curr Opin Immunol.
27:16–25. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baxevanis CN and Perez SA: Cancer
dormancy: A regulatory role for endogenous immunity in establishing
and maintaining the tumor dormant state. Vaccines (Basel).
3:597–619. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baxevanis CN, Anastasopoulou EA, Voutsas
IF, Papamichail M and Perez SA: Immune biomarkers: How well do they
serve prognosis in human cancers? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 15:49–59.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perez SA, Karamouzis MV, Skarlos DV,
Ardavanis A, Sotiriadou NN, Iliopoulou EG, Salagianni ML, Orphanos
G, Baxevanis CN, Rigatos G and Papamichail M:
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cell frequency in
HER-2/neu (HER)-positive and HER-negative advanced-stage breast
cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2714–2721. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Perez SA, Kallinteris NL, Bisias S, Tzonis
PK, Georgakopoulou K, Varla-Leftherioti M, Papamichail M, Thanos A,
von Hofe E, Baxevanis CN, et al: Results from a phase I clinical
study of the novel Ii-Key/HER-2/neu(776–790) hybrid peptide vaccine
in patients with prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3495–3506.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Okegawa T, Kinjo M, Nutahara K and
Higashihara E: Pretreatment serum level of HER2/nue as a prognostic
factor in metastatic prostate cancer patients about to undergo
endocrine therapy. Int J Urol. 13:1197–1201. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Köstler WJ, Schwab B, Singer CF, Neumann
R, Rücklinger E, Brodowicz T, Tomek S, Niedermayr M, Hejna M,
Steger GG, et al: Monitoring of serum Her-2/neu predicts response
and progression-free survival to trastuzumab-based treatment in
patients with metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
10:1618–1624. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anastasopoulou EA, Voutsas IF,
Keramitsoglou T, Gouttefangeas C, Kalbacher H, Thanos A,
Papamichail M, Perez SA and Baxevanis CN: A pilot study in prostate
cancer patients treated with the AE37 Ii-key-HER-2/neu polypeptide
vaccine suggests that HLA-A*24 and HLA-DRB1*11 alleles may be
prognostic and predictive biomarkers for clinical benefit. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 64:1123–1136. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Travis MA and Sheppard D: TGF-β activation
and function in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol. 32:51–82. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: TGFβ: The molecular
Jekyll and hyde of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:506–520. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Steiner MS, Zhou ZZ, Tonb DC and Barrack
ER: Expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in prostate
cancer. Endocrinology. 135:2240–2247. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barrack ER: TGF beta in prostate cancer: A
growth inhibitor that can enhance tumorigenicity. Prostate.
31:61–70. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Perez SA, Anastasopoulou EA, Papamichail M
and Baxevanis CN: AE37 peptide vaccination in prostate cancer:
Identification of biomarkers in the context of prognosis and
prediction. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 63:1141–1150. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Voutsas IF, Anastasopoulou EA, Tzonis P,
Papamichail M, Perez SA and Baxevanis CN: Unraveling the role of
preexisting immunity in prostate cancer patients vaccinated with a
HER-2/neu hybrid peptide. J Immunother Cancer. 4:752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goulielmaki M, Stokidis S, Anagnostou T,
Voutsas IF, Gritzapis AD, Baxevanis CN and Fortis SP: Frequencies
of an immunogenic HER-2/neu epitope of CD8+ T
lymphocytes predict favorable clinical outcomes in prostate cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 24:59542023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dahal S, Chaudhary P, Jung YS and Kim JA:
Megakaryocyte-Derived IL-8 acts as a paracrine factor for prostate
cancer aggressiveness through CXCR2 activation and antagonistic AR
downregulation. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 31:210–218. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sunaga N, Kaira K, Tomizawa Y, Shimizu K,
Imai H, Takahashi G, Kakegawa S, Ohtaki Y, Nagashima T, Kasahara N,
et al: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
interleukin-8 expression and its relationship to KRAS mutation in
lung adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 110:2047–2053. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singh JK, Simões BM, Howell SJ, Farnie G
and Clarke RB: Recent advances reveal IL-8 signaling as a potential
key to targeting breast cancer stem cells. Breast Cancer Res.
15:2102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen L, Fan J, Chen H, Meng Z, Chen Z,
Wang P and Liu L: The IL-8/CXCR1 axis is associated with cancer
stem cell-like properties and correlates with clinical prognosis in
human pancreatic cancer cases. Sci Rep. 4:59112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baxevanis CN, Stokidis S, Goulielmaki M,
Gritzapis AD and Fortis SP: Peripheral blood CD8+
T-lymphocyte subsets are associated with prognosis in prostate
cancer patients. Onco. 3:165–174. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kim R, Kim S, Oh BB, Yu WS, Kim CW, Hur H,
Son SY, Yang MJ, Cho DS, Ha T, et al: Clinical application of
whole-genome sequencing of solid tumors for precision oncology. Exp
Mol Med. 56:1856–1868. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang RJ, Huang YS, An N, Hu JJ, Wu CY,
Chen YX, Chen JY, Zhao Q, Xu RH, Yuan SQ and Wang F: Pan-cancer
analysis of heterogeneity of tumor mutational burden and genomic
mutation under treatment pressure. ESMO Open. 9:1034942024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tan WY, Nagabhyrava S, Ang-Olson O, Das P,
Ladel L, Sailo B, He L, Sharma A and Ahuja N: Translation of
epigenetics in cell-free DNA liquid biopsy technology and precision
oncology. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 46:6533–6565. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Koukourakis MI, Xanthopoulou E,
Koukourakis IM, Fortis SP, Kesesidis N, Kakouratos C,
Karakasiliotis I and Baxevanis CN: Next-generation sequencing
analysis of mutations in circulating tumor DNA from the plasma of
patients with head-Neck cancer undergoing chemo-radiotherapy using
a pan-cancer cell-free assay. Curr Oncol. 30:8902–8915. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lam N, Lee Y and Farber DL: A guide to
adaptive immune memory. Nat Rev Immunol. 24:810–829. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Takahashi H, Sakakura K, Ida S,
Kawabata-Iwakawa R, Matsuyama T, Tada H, Mito I and Chikamatsu K:
Circulating naïve and effector memory T cells correlate with
prognosis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
113:53–64. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sun X, Zhai J, Sun B, Parra ER, Jiang M,
Ma W, Wang J, Kang AM, Kannan K, Pandurengan R, et al: Effector
memory cytotoxic CD3+/CD8+/CD45RO+
T cells are predictive of good survival and a lower risk of
recurrence in triple-negative breast cancer. Mod Pathol.
35:601–608. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cappuyns S, Philips G, Vandecaveye V,
Boeckx B, Schepers R, Van Brussel T, Arijs I, Mechels A, Bassez A,
Lodi F, et al: PD-1− CD45RA+ effector-memory
CD8 T cells and CXCL10+ macrophages are associated with
response to atezolizumab plus bevacizumab in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 14:78252023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wei H, Li Y, Guo Z, Ma X, Li Y, Wei X, Han
D, Zhang T, Chen X, Yan C, et al: Comparison of dynamic changes in
the peripheral CD8+ T cells function and differentiation
in ESCC patients treated with radiotherapy combined with anti-PD-1
antibody or concurrent chemoradiotherapy. Front Immunol.
13:10606952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bruni E, Cazzetta V, Donadon M, Cimino M,
Torzilli G, Spata G, Leonardi G, Dieli F, Mikulak J and Mavilio D:
Chemotherapy accelerates immune-senescence and functional
impairments of Vδ2pos T cells in elderly patients
affected by liver metastatic colorectal cancer. J Immunother
Cancer. 7:3472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zou D, Song A and Yong W: Prognostic role
of IL-8 in cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint
inhibitors: A system review and meta-analysis. Front Oncol.
13:11765742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rizzo M, Varnier L, Pezzicoli G, Pirovano
M, Cosmai L and Porta C: IL-8 and its role as a potential biomarker
of resistance to anti-angiogenic agents and immune checkpoint
inhibitors in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Front Oncol.
12:9905682022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ni Y, Soliman A, Joehlin-Price A, Rose PG,
Vlad A, Edwards RP and Mahdi H: High TGF-β signature predicts
immunotherapy resistance in gynecologic cancer patients treated
with immune checkpoint inhibition. NPJ Precis Oncol. 5:1012021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim BG, Malek E, Choi SH, Ignatz-Hoover JJ
and Driscoll JJ: Novel therapies emerging in oncology to target the
TGF-β pathway. J Hematol Oncol. 14:552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Colomer R, Montero S, Lluch A, Ojeda B,
Barnadas A, Casado A, Massutí B, Cortés-Funes H and Lloveras B:
Circulating HER2 extracellular domain and resistance to
chemotherapy in advanced breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
6:2356–2362. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Reix N, Malina C, Chenard MP, Bellocq JP,
Delpous S, Molière S, Sevrin A, Neuberger K, Tomasetto C and
Mathelin C: A prospective study to assess the clinical utility of
serum HER2 extracellular domain in breast cancer with HER2
overexpression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 160:249–259. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|