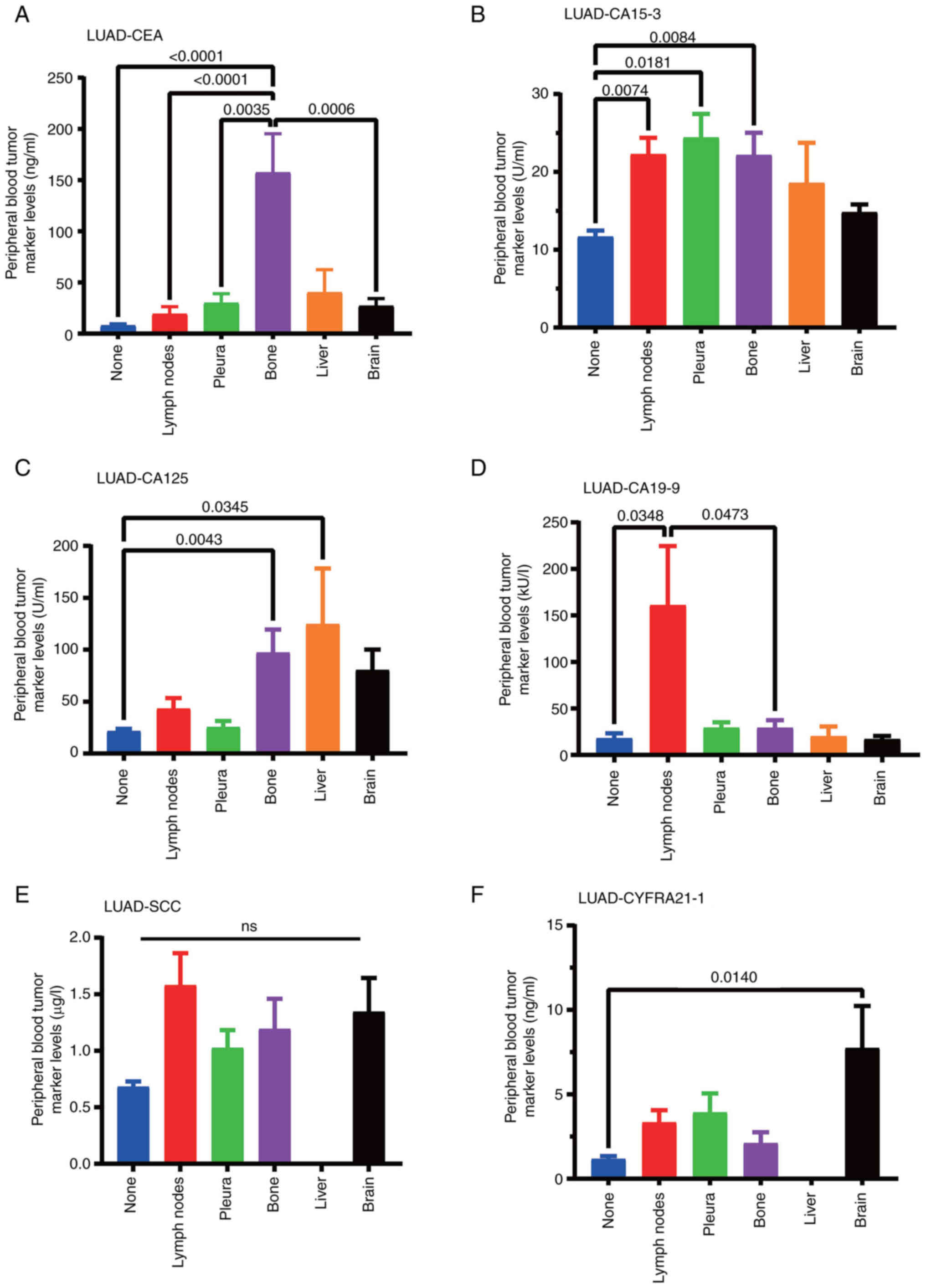
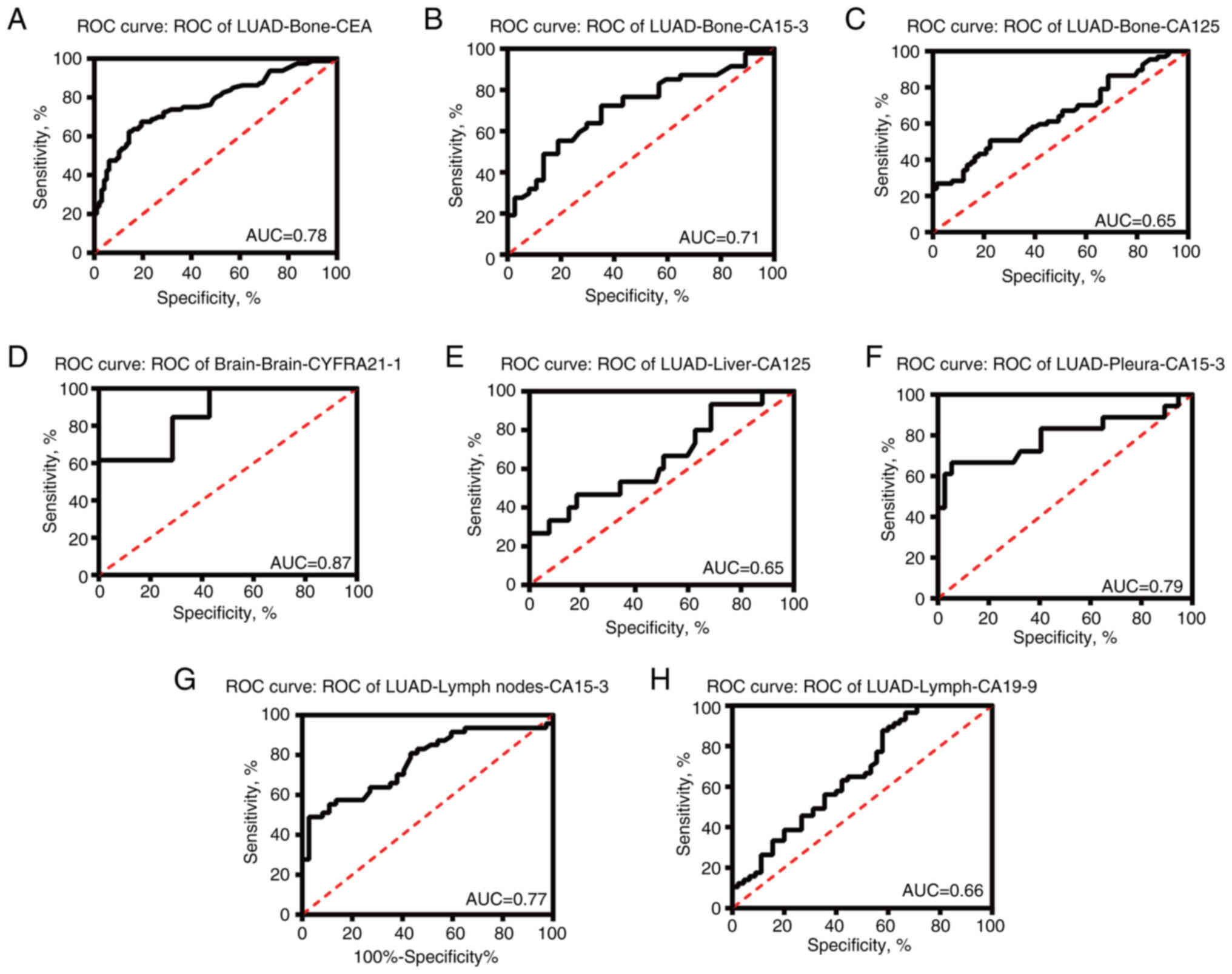
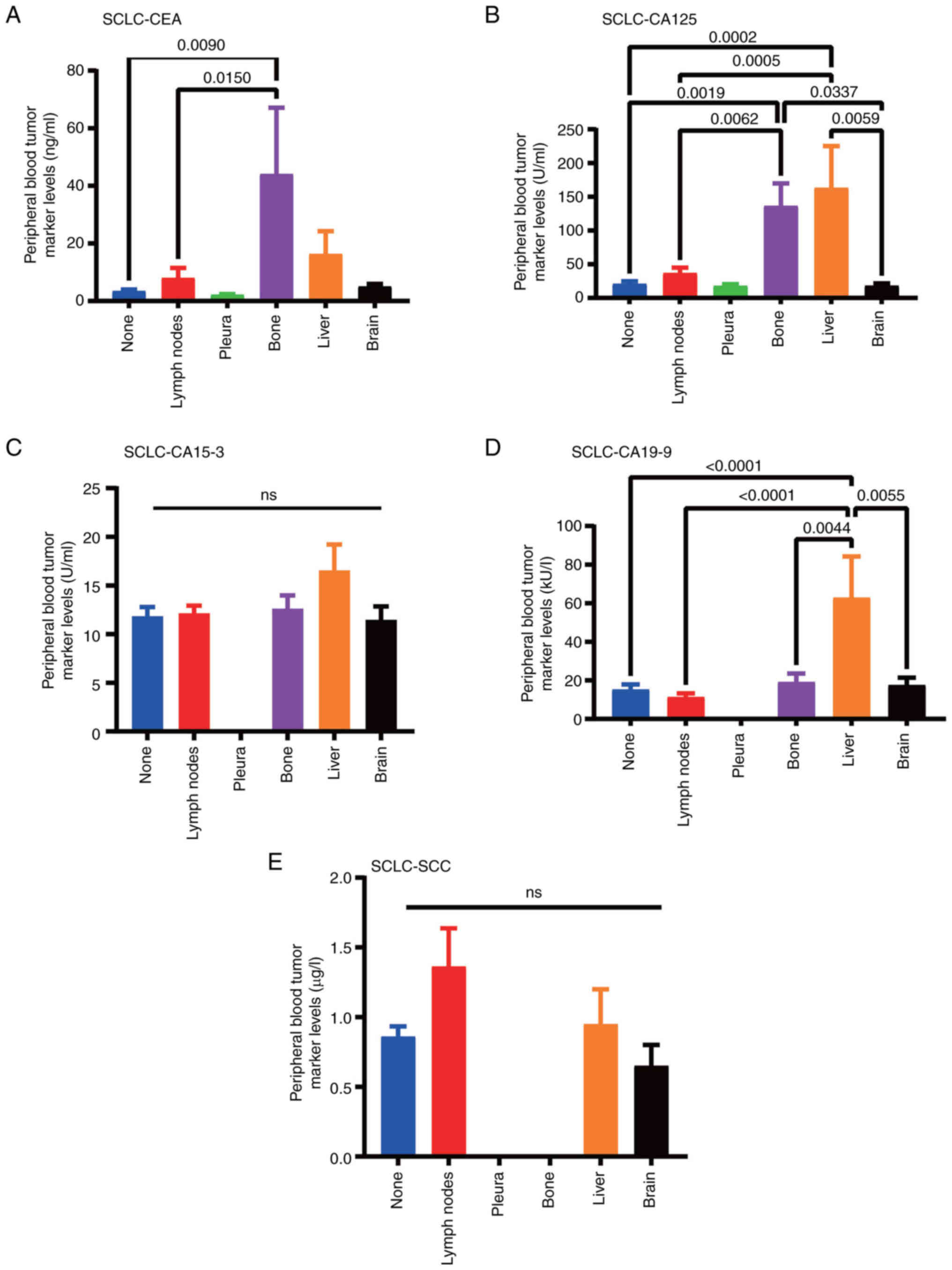
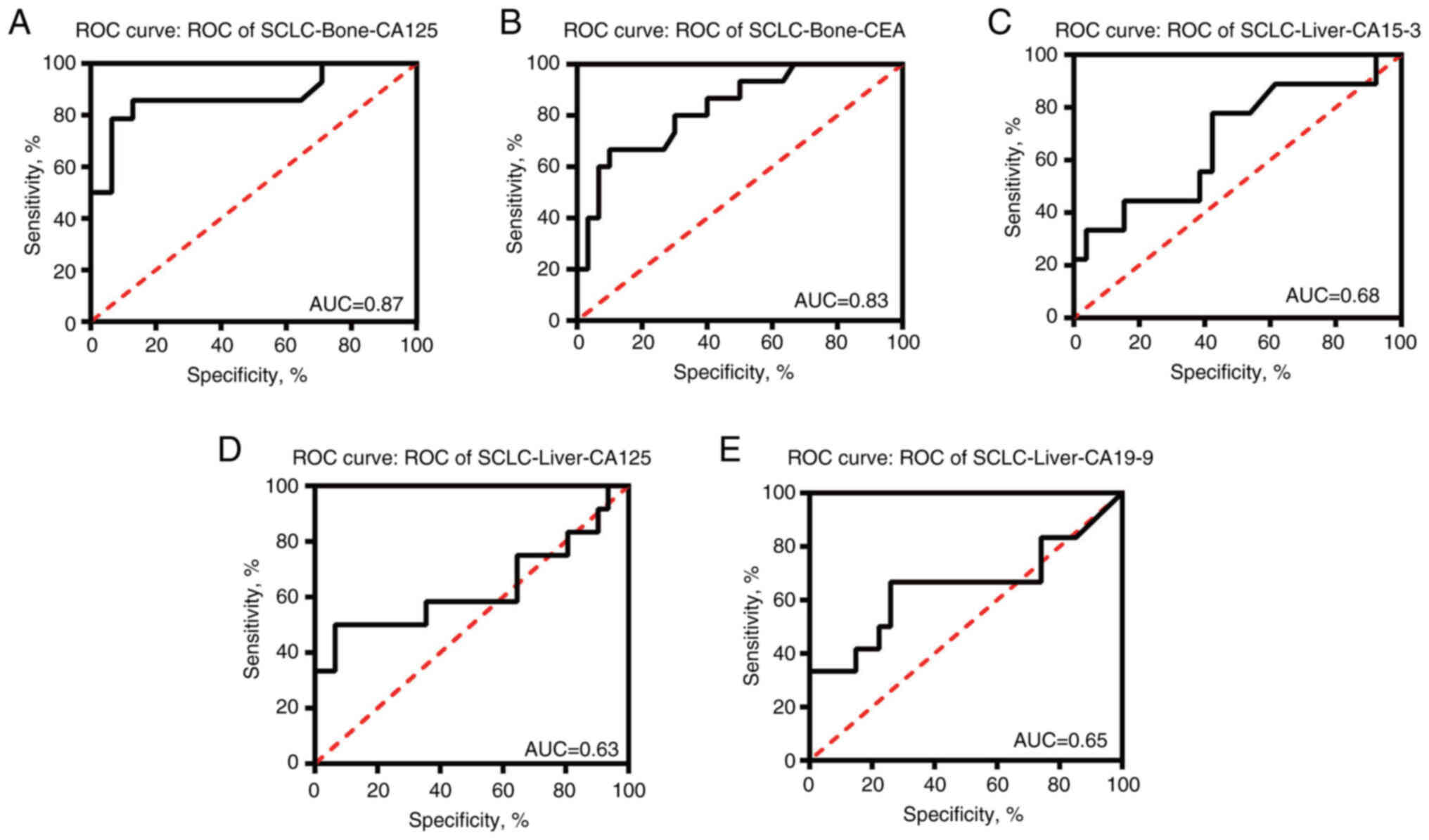
|
1
|
Regzedmaa O, Zhang H, Liu H and Chen J:
Immune checkpoint inhibitors for small cell lung cancer:
Opportunities and challenges. Onco Targets Ther. 12:4605–4620.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Howlader N, Forjaz G, Mooradian MJ, Meza
R, Kong CY, Cronin KA, Mariotto AB, Lowy DR and Feuer EJ: The
effect of advances in lung-cancer treatment on population
mortality. N Engl J Med. 383:640–649. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Frieden TR, Cobb LK, Leidig RC, Mehta S
and Kass D: Reducing premature mortality from cardiovascular and
other non-communicable diseases by one third: Achieving sustainable
development goal indicator 3.4.1. Glob Heart. 15:502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ren Y, Cao L, Wang L, Zheng S, Zhang Q,
Guo X, Li X, Chen M, Wu X, Furlong F, et al: Autophagic secretion
of HMGB1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes metastatic
potential of non-small cell lung cancer cells via NFκB signaling.
Cell Death Dis. 12:8582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Waqar SN, Samson PP, Robinson CG, Bradley
J, Devarakonda S, Du L, Govindan R, Gao F, Puri V and Morgensztern
D: Non-small-cell lung cancer with brain metastasis at
presentation. Clin Lung Cancer. 19:e373–e379. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Riihimäki M, Hemminki A, Fallah M, Thomsen
H, Sundquist K, Sundquist J and Hemminki K: Metastatic sites and
survival in lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 86:78–84. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mielgo A and Schmid MC: Liver tropism in
cancer: The hepatic metastatic niche. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Med. 10:a0372592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fanipakdel A, Seilanian Toussi M,
Rezazadeh F, Mohamadian Roshan N and Javadinia SA: Overexpression
of cancer-testis antigen melanoma-associated antigen A1 in lung
cancer: A novel biomarker for prognosis, and a possible target for
immunotherapy. J Cell Physiol. 234:12080–12086. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo H, Zhou X, Lu Y, Xie L, Chen Q, Keller
ET, Liu Q, Zhou Q and Zhang J: Translational progress on tumor
biomarkers. Thorac Cancer. 6:665–671. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abu-Asab MS, Chaouchi M, Alesci S, Galli
S, Laassri M, Cheema AK, Atouf F, VanMeter J and Amri H: Biomarkers
in the age of omics: Time for a systems biology approach. OMICS.
15:105–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Billatos E, Vick JL, Lenburg ME and Spira
AE: The airway transcriptome as a biomarker for early lung cancer
detection. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2984–2992. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Fu F, Zhang Q, Li L, Liu H, Deng
C, Xue Q, Zhao Y, Sun W, Han H, et al: Evolutionary proteogenomic
landscape from pre-invasive to invasive lung adenocarcinoma. Cell
Rep Med. 5:1013582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang H, Wang R, Cheng R, Ye Z, Zhao N,
Zhao X, Huang Y, Jiang Z, Li W, Zheng J, et al: LcProt:
Proteomics-based identification of plasma biomarkers for lung
cancer multievent, a multicentre study. Clin Transl Med.
15:e701602025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang S, Cao X, Wang Y, Leng P, Wen X, Xie
G, Luo H and Yu R: Metabolomics analysis and diagnosis of lung
cancer: Insights from diverse sample types. Int J Med Sci.
21:234–252. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi W, Cheng Y, Zhu H and Zhao L:
Metabolomics and lipidomics in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Chim Acta. 555:1178232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng L, Hu F, Huang L, Lu J, Yang X, Xu
J, Wang S, Shen Y, Zhong R, Chu T, et al: Association of
metabolomics with PD-1 inhibitor plus chemotherapy outcomes in
patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Immunother
Cancer. 12:e0081902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li X, Li S, Zhang Z and Huang D:
Association of multiple tumor markers with newly diagnosed gastric
cancer patients: A retrospective study. PeerJ. 10:e134882022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wei Z, Zhang Y, Lu H, Ying J, Zhao H and
Cai J: Serum alpha-fetoprotein as a predictive biomarker for tissue
alpha-fetoprotein status and prognosis in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl Cancer Res. 11:669–677. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi JX, Qin JJ, Ye H, Wang P, Wang KJ and
Zhang JY: Tumor associated antigens or anti-TAA autoantibodies as
biomarkers in the diagnosis of ovarian cancer: A systematic review
with meta-analysis. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 15:829–852. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fazilat-Panah D, Vakili Ahrari Roudi S,
Keramati A, Fanipakdel A, Sadeghian MH, Homaei Shandiz F,
Shahidsales S and Javadinia SA: Changes in cytokeratin 18 during
neoadjuvant chemotherapy of breast cancer: A prospective study.
Iran J Pathol. 15:117–126. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pavlopoulou A and Scorilas A: A
comprehensive phylogenetic and structural analysis of the
carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family. Genome Biol Evol.
6:1314–1326. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Suzuki T, Yajima S, Okamura A, Yoshida N,
Taniyama Y, Murakami K, Ohkura Y, Nakajima Y, Yagi K, Fukuda T, et
al: Prognostic impact of serum SCC antigen in the 566 upfront
surgery group of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A
multi-institutional study of the Japan esophageal society. Ann
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 30:24–00028. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li X, Dai D, Chen B, Tang H, Xie X and Wei
W: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of cancer
antigen 15-3 and carcinoembryonic antigen in breast cancer: A
meta-analysis including 12,993 patients. Dis Markers.
2018:98630922018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang R, Zuo CL, Zhang R and Zhu LM:
Carcinoembryonic antigen, carbohydrate antigen 199 and carbohydrate
antigen 724 in gastric cancer and their relationship with clinical
prognosis. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 15:1475–1485. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Piatek S, Panek G, Lewandowski Z,
Bidzinski M, Piatek D, Kosinski P and Wielgos M: Rising serum
CA-125 levels within the normal range is strongly associated
recurrence risk and survival of ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res.
13:1022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fischer S and Gillis J: Defining the
extent of gene function using ROC curvature. Bioinformatics.
38:5390–5397. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
National Lung Screening Trial Research
Team, . Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD,
Fagerstrom RM, Gareen IF, Gatsonis C, Marcus PM and Sicks JD:
Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic
screening. N Engl J Med. 365:395–409. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kazerooni EA, Armstrong MR, Amorosa JK,
Hernandez D, Liebscher LA, Nath H, McNitt-Gray MF, Stern EJ and
Wilcox PA: ACR CT accreditation program and the lung cancer
screening program designation. J Am Coll Radiol. 13 (Suppl
2):R30–R34. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wood DE, Kazerooni EA, Baum SL, Eapen GA,
Ettinger DS, Hou L, Jackman DM, Klippenstein D, Kumar R, Lackner
RP, et al: Lung cancer screening, version 3.2018, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
16:412–441. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fu Y, Liu J, Chen Y, Liu Z, Xia H and Xu
H: Gender disparities in lung cancer incidence in the United States
during 2001–2019. Sci Rep. 13:125812023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lewis DR, Check DP, Caporaso NE, Travis WD
and Devesa SS: US lung cancer trends by histologic type. Cancer.
120:2883–2892. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li Y, Xiao X, Li J, Han Y, Cheng C,
Fernandes GF, Slewitzke SE, Rosenberg SM, Zhu M, Byun J, et al:
Lung cancer in ever- and never-smokers: Findings from
multi-population GWAS studies. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
33:389–399. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Zhang T, Wu J, Yin S, Nan X, Du M,
Liu A and Wang P: The association between socioeconomic status,
smoking, and chronic disease in inner mongolia in northern China.
Int J Environ Res Public Health. 16:1692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Arakil N, Akhund SA, Elaasser B and
Mohammad KS: Intersecting paths: Unraveling the complex journey of
cancer to bone metastasis. Biomedicines. 12:10752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nozawa H, Yokota Y, Emoto S, Yokoyama Y,
Sasaki K, Murono K, Abe S, Sonoda H, Shinagawa T and Ishihara S:
Unexplained increases in serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels in
colorectal cancer patients during the postoperative follow-up
period: An analysis of its incidence and longitudinal pattern. Ann
Med. 55:22469972023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhao W, Li X, Wang W, Chen B, Wang L,
Zhang N, Wang Z and Yang Q: Association of preoperative serum
levels of CEA and CA15-3 with molecular subtypes of breast cancer.
Dis Markers. 2021:55291062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang L, Huang Y, Feng Z, Wang X, Li H,
Song F, Liu L, Li J, Zheng H, Wang P, et al: Comparison of breast
cancer risk factors among molecular subtypes: A case-only study.
Cancer Med. 8:1882–1892. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee JS, Park S, Park JM, Cho JH, Kim SI
and Park BW: Elevated levels of preoperative CA 15-3 and CEA serum
levels have independently poor prognostic significance in breast
cancer. Ann Oncol. 24:1225–1231. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Duan S, Cao H, Liu H, Miao L, Wang J, Zhou
X, Wang W, Hu P, Qu L and Wu Y: Development of a machine
learning-based multimode diagnosis system for lung cancer. Aging
(Albany NY). 12:9840–9854. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ayan AK, Erdemci B, Orsal E, Bayraktutan
Z, Akpinar E, Topcu A, Turkeli M and Seven B: Is there any
correlation between levels of serum ostepontin, CEA, and FDG uptake
in lung cancer patients with bone metastasis? Rev Esp Med Nucl
Imagen Mol. 35:102–106. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Terävä J, Tiainen L, Lamminmäki U,
Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL, Pettersson K and Gidwani K: Lectin
nanoparticle assays for detecting breast cancer-associated
glycovariants of cancer antigen 15-3 (CA15-3) in human plasma. PLoS
One. 14:e02194802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fakhari A, Gharepapagh E, Dabiri S and
Gilani N: Correlation of cancer antigen 15-3 (CA15-3) serum level
and bony metastases in breast cancer patients. Med J Islam Repub
Iran. 33:1422019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pan Y, Lin Y and Mi C: Clinicopathological
characteristics and prognostic risk factors of breast cancer
patients with bone metastasis. Ann Transl Med. 9:13402021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhou Y, Yu QF, Peng AF, Tong WL, Liu JM
and Liu ZL: The risk factors of bone metastases in patients with
lung cancer. Sci Rep. 7:89702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gao S, Li N, Wang S, Zhang F, Wei W, Li N,
Bi N, Wang Z and He J: Lung cancer in people's Republic of China. J
Thorac Oncol. 15:1567–1576. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang L, Liu D, Li L, Pu D, Zhou P, Jing
Y, Yu H, Wang Y, Zhu Y, He Y, et al: The important role of
circulating CYFRA21-1 in metastasis diagnosis and prognostic value
compared with carcinoembryonic antigen and neuron-specific enolase
in lung cancer patients. BMC Cancer. 17:962017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang P, Piao Y, Zhang X, Li W and Hao X:
The concentration of CYFRA 21-1, NSE and CEA in cerebro-spinal
fluid can be useful indicators for diagnosis of meningeal
carcinomatosis of lung cancer. Cancer Biomark. 13:123–130. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Song B, Shi P, Xiao J, Song Y, Zeng M, Cao
Y and Zhu X: Utility of red cell distribution width as a diagnostic
and prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep.
10:157172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ren H, Hu Y, Xie T, Jin C, Hu Y and Yang
B: Effect of gefitinib on serum EGFR and CYFRA21-1 in patients with
advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Lett. 18:4167–4175.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jiang X, Guo D, Li W, Yu T, Zhou J and
Gong J: Combination Twist1 and CA15-3 in axillary lymph nodes for
breast cancer prognosis. Mol Med Rep. 15:1123–1134. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gao Y, Park HJ, Traulsen A and Pichugin Y:
Evolution of irreversible somatic differentiation. Elife.
10:e667112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Cheng Y, Liao S, Xu G, Hu J, Guo D, Du F,
Contreras A, Cai KQ, Peri S, Wang Y, et al: NeuroD1 dictates tumor
cell differentiation in medulloblastoma. Cell Rep. 31:1077822020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pan M, Huang P, Li L, Lei P, Fang L, Zhao
L, Li Y, Huang S and Luo W: Comprehensive bioinformatics analysis
on exportins in lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell
carcinoma. J Thorac Dis. 15:1872–1891. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Qin Z, Yue M, Tang S, Wu F, Sun H, Li Y,
Zhang Y, Izumi H, Huang H, Wang W, et al: EML4-ALK fusions drive
lung adeno-to-squamous transition through JAK-STAT activation. J
Exp Med. 221:e202320282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen J, Zhang C, Xie J, Zheng X, Gu P, Liu
S, Zhou Y, Wu J, Chen Y, Wang Y, et al: Automatic lung cancer
subtyping using rapid on-site evaluation slides and serum
biological markers. Respir Res. 25:3912024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang SL, Zhang CY, Chen YQ, Li YF, Xie Z,
Zhang XC, Zhou Q, Zhong WZ, Huang J, Sun H, et al: Expression of
EGFR-mutant proteins and genomic evolution in EGFR-mutant
transformed small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Dis. 15:4620–4635.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zengin T and Önal-Süzek T: Analysis of
genomic and transcriptomic variations as prognostic signature for
lung adenocarcinoma. BMC Bioinformatics. 21 (Suppl 14):3682020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Imakita T, Fujita K, Kanai O, Terashima T
and Mio T: Small cell lung cancer transformation during
immunotherapy with nivolumab: A case report. Respir Med Case Rep.
21:52–55. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Adelstein DJ, Tomashefski JF Jr, Snow NJ,
Horrigan TP and Hines JD: Mixed small cell and non-small cell lung
cancer. Chest. 89:699–704. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Ramakrishna R and Rostomily R: Seed, soil,
and beyond: The basic biology of brain metastasis. Surg Neurol Int.
4 (Suppl 4):S256–S264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Singh M, Manoranjan B, Mahendram S,
McFarlane N, Venugopal C and Singh SK: Brain metastasis-initiating
cells: Survival of the fittest. Int J Mol Sci. 15:9117–9133. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Peixoto A, Relvas-Santos M, Azevedo R,
Santos LL and Ferreira JA: Protein glycosylation and tumor
microenvironment alterations driving cancer hallmarks. Front Oncol.
9:3802019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Hu M, Zhang R, Yang J, Zhao C, Liu W,
Huang Y, Lyu H, Xiao S, Guo D, Zhou C and Tang J: The role of
N-glycosylation modification in the pathogenesis of liver cancer.
Cell Death Dis. 14:2222023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cao Y, Yi W and Zhu Q: Glycosylation in
the tumor immune response: The bitter side of sweetness. Acta
Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 56:1184–1198. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ren X, Lin S, Guan F and Kang H:
Glycosylation targeting: A paradigm shift in cancer immunotherapy.
Int J Biol Sci. 20:2607–2621. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang S, Zhong L, Li Y, Xiao D, Zhang R,
Liao D, Lv D, Wang X, Wang J, Xie X, et al: Up-regulation of PCOLCE
by TWIST1 promotes metastasis in Osteosarcoma. Theranostics.
9:4342–4353. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|