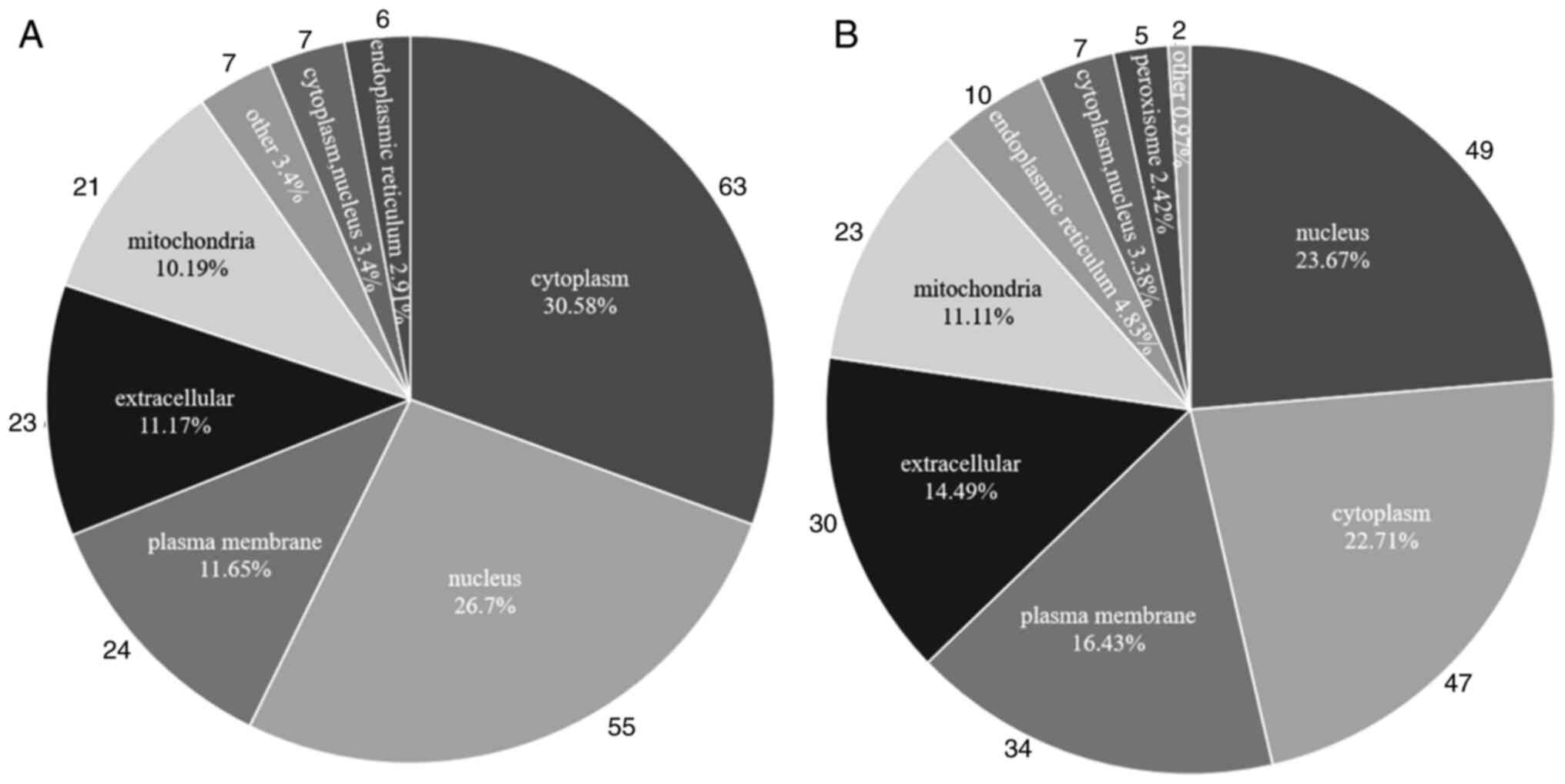
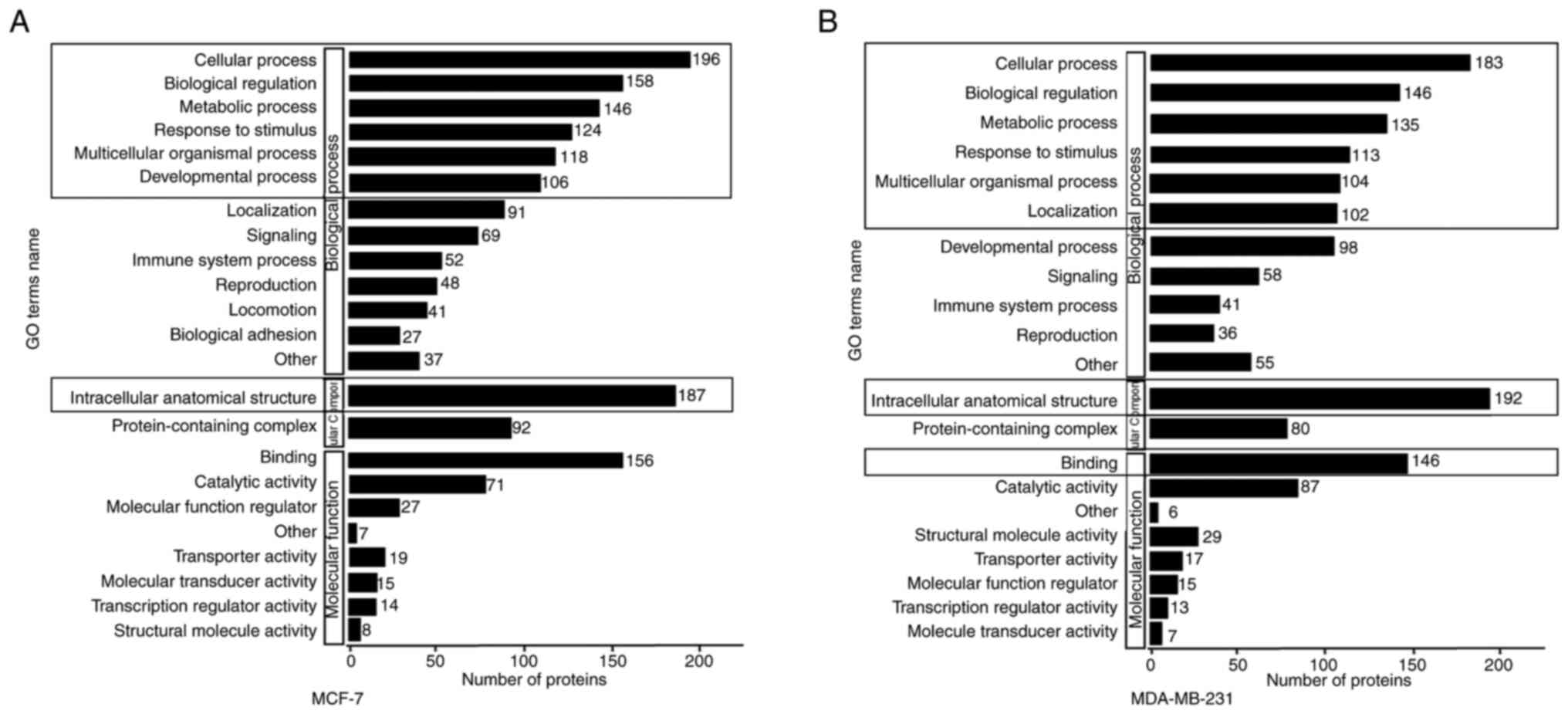
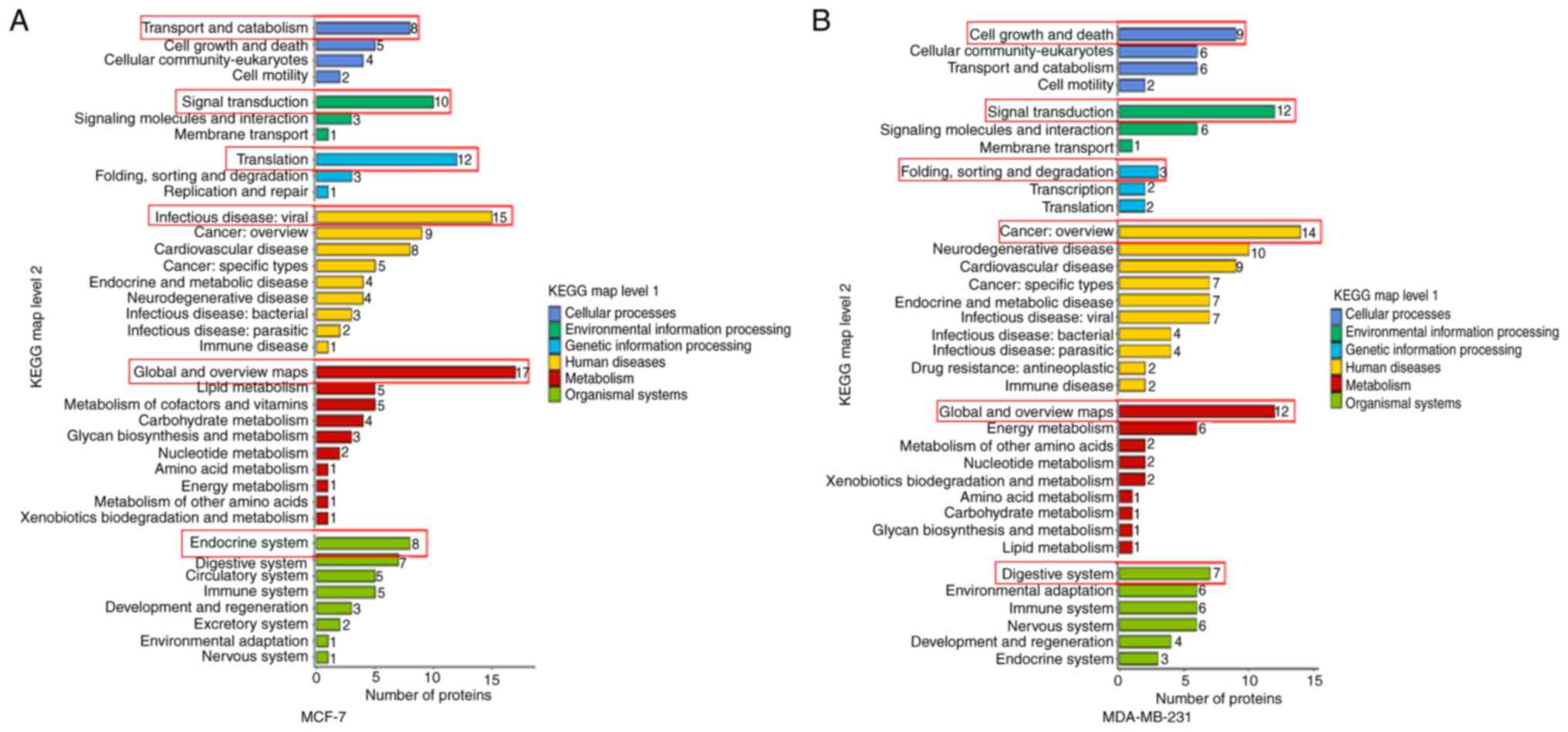
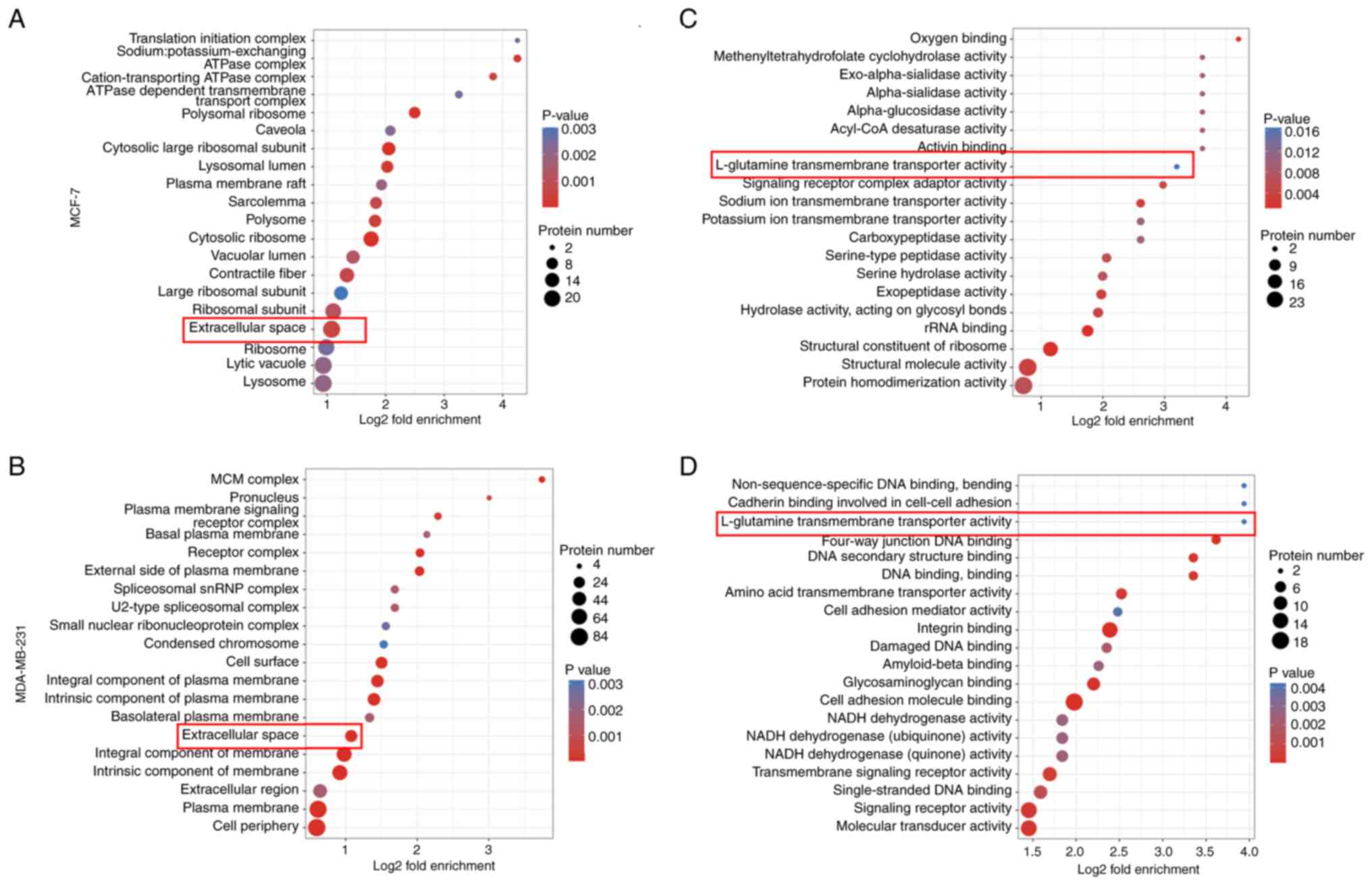
|
1
|
Katsura C, Ogunmwonyi I, Kankam HK and
Saha S: Breast cancer: Presentation, investigation and management.
Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 83:1–7. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Avti PK, Singh J, Dahiya D and Khanduja
KL: Dual functionality of pyrimidine and flavone in targeting
genomic variants of EGFR and ER receptors to influence the
differential survival rates in breast cancer patients. Integr Biol
(Camb). 15:zyad0142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fortin J, Leblanc M, Elgbeili G, Cordova
MJ, Marin MF and Brunet A: The mental health impacts of receiving a
breast cancer diagnosis: A meta-analysis. Br J Cancer.
125:1582–1592. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ye F, Dewanjee S, Li Y, Jha NK, Chen ZS,
Kumar A, Vishakha Behl T, Jha SK and Tang H: Advancements in
clinical aspects of targeted therapy and immunotherapy in breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Castellote-Huguet P, Ruiz-Espana S,
Galan-Auge C, Santabarbara JM, Maceira AM and Moratal D: Breast
cancer diagnosis using texture and shape features in MRI. Annu Int
Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2023:1–4. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nunnery SE and Mayer IA: Targeting the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in hormone-positive breast cancer. Drugs.
80:1685–1697. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kotsopoulos J, Gronwald J, Huzarski T,
Aeilts A, Armel SR, Karlan B, Singer CF, Eisen A, Tung N, Olopade
O, et al: Tamoxifen and the risk of breast cancer in women with a
BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 201:257–264.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Masci D, Naro C, Puxeddu M, Urbani A,
Sette C, La Regina G and Silvestri R: Recent advances in drug
discovery for triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Molecules.
28:75132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu C, Feng Q, Yang H, Wang G, Huang L, Bai
Q, Zhang C, Wang Y, Chen Y, Cheng Q, et al: A light-triggered
mesenchymal stem cell delivery system for photoacoustic imaging and
chemo-photothermal therapy of triple negative breast cancer. Adv
Sci (Weinh). 5:18003822018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hwang KT, Kim J, Jung J, Chang JH, Chai
YJ, Oh SW, Oh S, Kim YA, Park SB and Hwang KR: Impact of breast
cancer subtypes on prognosis of women with operable invasive breast
cancer: A population-based study using SEER database. Clin Cancer
Res. 25:1970–1979. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Al-Azhri J, Zhang Y, Bshara W, Zirpoli G,
McCann SE, Khoury T, Morrison CD, Edge SB, Ambrosone CB and Yao S:
Tumor expression of vitamin D receptor and breast cancer
histopathological characteristics and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res.
23:97–103. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sun Z, Zhou D, Yang J and Zhang D:
Doxorubicin promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion via
DCAF13. FEBS Open Bio. 12:221–230. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang D, Qiu T, Peng J, Li S, Tala Ren W,
Yang C, Wen Y, Chen CH, Sun J, et al: YB-1 is a positive regulator
of KLF5 transcription factor in basal-like breast cancer. Cell
Death Differ. 29:1283–1295. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Katzenellenbogen BS, Guillen VS and
Katzenellenbogen JA: Targeting the oncogenic transcription factor
FOXM1 to improve outcomes in all subtypes of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 25:762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Francois M, Donovan P and Fontaine F:
Modulating transcription factor activity: Interfering with
protein-protein interaction networks. Semin Cell Dev Biol.
99:12–19. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu TT, Yang H, Zhuo FF, Yang Z, Zhao MM,
Guo Q, Liu Y, Liu D, Zeng KW and Tu PF: Atypical E3 ligase ZFP91
promotes small-molecule-induced E2F2 transcription factor
degradation for cancer therapy. EBioMedicine. 86:1043532022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pang X, Zhou Z, Yu Z, Han L, Lin Z, Ao X,
Liu C, He Y, Ponnusamy M, Li P and Wang J: Foxo3a-dependent miR-633
regulates chemotherapeutic sensitivity in gastric cancer by
targeting Fas-associated death domain. RNA Biol. 16:233–248. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Meng XY, Wang KJ, Ye SZ, Chen JF, Chen ZY,
Zhang ZY, Yin WQ, Jia XL, Li Y, Yu R and Ma Q: Sinularin stabilizes
FOXO3 protein to trigger prostate cancer cell intrinsic apoptosis.
Biochem Pharmacol. 220:1160112024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Khoshinani HM, Afshar S, Pashaki AS,
Mahdavinezhad A, Nikzad S, Najafi R, Amini R, Gholami MH,
Khoshghadam A and Saidijam M: Involvement of miR-155/FOXO3a and
miR-222/PTEN in acquired radioresistance of colorectal cancer cell
line. Jpn J Radiol. 35:664–672. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wolfe AR, Debeb BG, Lacerda L, Larson R,
Bambhroliya A, Huang X, Bertucci F, Finetti P, Birnbaum D, Van
Laere S, et al: Simvastatin prevents triple-negative breast cancer
metastasis in pre-clinical models through regulation of FOXO3a.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 154:495–508. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chen S, Li YQ, Yin XZ, Li SZ, Zhu YL, Fan
YY, Li WJ, Cui YL, Zhao J, Li X, et al: Recombinant adenoviruses
expressing apoptin suppress the growth of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
and affect cell autophagy. Oncol Rep. 41:2818–2832. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang BG, Shende M, Inci G, Park SH, Jung
JS, Kim SB, Kim JH, Mo YW, Seo JH, Feng JH, et al: Combination of
metformin/efavirenz/fluoxetine exhibits profound anticancer
activity via a cancer cell-specific ROS amplification. Cancer Biol
Ther. 24:20–32. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Khan MA, Sadaf Ahmad I, Aloliqi AA, Eisa
AA, Najm MZ, Habib M, Mustafa S, Massey S, Malik Z, et al: FOXO3
gene hypermethylation and its marked downregulation in breast
cancer cases: A study on female patients. Front Oncol.
12:10780512022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yang L, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Xu Y, Li Y, Xie
Z, Wang H, Lin Y, Lin Q, Gong T, et al: Live macrophage-delivered
doxorubicin-loaded liposomes effectively treat triple-negative
breast cancer. ACS Nano. 16:9799–9809. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ansari L, Shiehzadeh F, Taherzadeh Z,
Nikoofal-Sahlabadi S, Momtazi-Borojeni AA, Sahebkar A and Eslami S:
The most prevalent side effects of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin
monotherapy in women with metastatic breast cancer: A systematic
review of clinical trials. Cancer Gene Ther. 24:189–193. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wei Y, Guo Y, Zhou J, Dai K, Xu Q and Jin
X: Nicotinamide overcomes doxorubicin resistance of breast cancer
cells through deregulating SIRT1/Akt pathway. Anticancer Agents Med
Chem. 19:687–696. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun L, Liu J, Bao D, Hu C, Zhao Y and Chen
S: Progress in the study of FOXO3a interacting with microRNA to
regulate tumourigenesis development. Front Oncol. 13:12939682023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen YF, Pandey S, Day CH, Chen YF, Jiang
AZ, Ho TJ, Chen RJ, Padma VV, Kuo WW and Huang CY: Synergistic
effect of HIF-1α and FoxO3a trigger cardiomyocyte apoptosis under
hyperglycemic ischemia condition. J Cell Physiol. 233:3660–3671.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yadav RK, Chauhan AS, Zhuang L and Gan B:
FoxO transcription factors in cancer metabolism. Semin Cancer Biol.
50:65–76. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu H, Yin J, Wang H, Jiang G, Deng M,
Zhang G, Bu X, Cai S, Du J and He Z: FOXO3a modulates WNT/β-catenin
signaling and suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in
prostate cancer cells. Cell Signal. 27:510–518. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li H, Tang X, Sun Z, Qu Z and Zou X:
Integrating bioinformatics and experimental models to investigate
the mechanism of the chelidonine-induced mitotic catastrophe via
the AKT/FOXO3/FOXM1 axis in breast cancer cells. Biomol Biomed.
24:560–574. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gauthier-Coles G, Bröer A, McLeod MD,
George AJ, Hannan RD and Bröer S: Identification and
characterization of a novel SNAT2 (SLC38A2) inhibitor reveals
synergy with glucose transport inhibition in cancer cells. Front
Pharmacol. 13:9630662022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Petry ÉR, Dresch DF, Carvalho C, Medeiros
PC, Rosa TG, de Oliveira CM, Martins LAM, Guma FCR, Marroni NP and
Wannmacher CMD: Oral glutamine supplementation relieves muscle loss
in immobilized rats, altering p38MAPK and FOXO3a signaling
pathways. Nutrition. 118:1122732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yuan Q, Wang Q, Li J, Yin L, Liu S, Zu X
and Shen Y: CCT196969 inhibits TNBC by targeting the
HDAC5/RXRA/ASNS axis to down-regulate asparagine synthesis. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 44:2312025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao X, Lai H, Li G, Qin Y, Chen R, Labrie
M, Stommel JM, Mills GB, Ma D, Gao Q and Fang Y: Rictor
orchestrates β-catenin/FOXO balance by maintaining redox
homeostasis during development of ovarian cancer. Oncogene.
44:1820–1832. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Park S, Yoo JE, Yeon GB, Kim JH, Lee JS,
Choi SK, Hwang YG, Park CW, Cho MS, Kim J, et al: Trophoblast
glycoprotein is a new candidate gene for Parkinson's disease. NPJ
Parkinsons Dis. 7:1102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He P, Jiang S, Ma M, Wang Y, Li R, Fang F,
Tian G and Zhang Z: Trophoblast glycoprotein promotes pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma cell metastasis through Wnt/planar cell
polarity signaling. Mol Med Rep. 12:503–509. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Su H, Yu S, Sun F, Lin D, Liu P and Zhao
L: LINC00342 induces metastasis of lung adenocarcinoma by targeting
miR-15b/TPBG. Acta Biochim Pol. 69:291–297. 2022.
|
|
40
|
Ye F, Liang Y, Wang Y, Yang RL, Luo D, Li
Y, Jin Y, Han D, Chen B, Zhao W, et al: Cancer-associated
fibroblasts facilitate breast cancer progression through exosomal
circTBPL1-mediated intercellular communication. Cell Death Dis.
14:4712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu G, Leal M, Lin Q, Affolter T, Sapra P,
Bates B and Damelin M: Phenotype of TPBG gene replacement in the
mouse and impact on the pharmacokinetics of an antibody-drug
conjugate. Mol Pharm. 12:1730–1737. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stern PL, Brazzatti J, Sawan S and McGinn
OJ: Understanding and exploiting 5T4 oncofoetal glycoprotein
expression. Semin Cancer Biol. 29:13–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kandasamy P, Zlobec I, Nydegger DT,
Pujol-Giménez J, Bhardwaj R, Shirasawa S, Tsunoda T and Hediger MA:
Oncogenic KRAS mutations enhance amino acid uptake by colorectal
cancer cells via the hippo signaling effector YAP1. Mol Oncol.
15:2782–2800. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kandasamy P, Gyimesi G, Kanai Y and
Hediger MA: Amino acid transporters revisited: New views in health
and disease. Trends Biochem Sci. 43:752–789. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Morotti M, Zois CE, El-Ansari R, Craze ML,
Rakha EA, Fan SJ, Valli A, Haider S, Goberdhan DCI, Green AR and
Harris AL: Increased expression of glutamine transporter
SNAT2/SLC38A2 promotes glutamine dependence and oxidative stress
resistance, and is associated with worse prognosis in
triple-negative breast cancer. Br J Cancer. 124:494–505. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Morotti M, Bridges E, Valli A, Choudhry H,
Sheldon H, Wigfield S, Gray N, Zois CE, Grimm F, Jones D, et al:
Hypoxia-induced switch in SNAT2/SLC38A2 regulation generates
endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:12452–12461. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Stretton C, Lipina C, Hyde R, Cwiklinski
E, Hoffmann TM, Taylor PM and Hundal HS: CDK7 is a component of the
integrated stress response regulating SNAT2 (SLC38A2)/System A
adaptation in response to cellular amino acid deprivation. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1866:978–991. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Shen Y, Li M, Xiong Y, Gui S, Bai J, Zhang
Y and Li C: Proteomics analysis identified ASNS as a novel
biomarker for predicting recurrence of skull base chordoma. Front
Oncol. 11:6984972021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Du F, Chen J, Liu H, Cai Y, Cao T, Han W,
Yi X, Qian M, Tian D, Nie Y, et al: SOX12 promotes colorectal
cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating asparagine
synthesis. Cell Death Dis. 10:2392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Knott SRV, Wagenblast E, Khan S, Kim SY,
Soto M, Wagner M, Turgeon MO, Fish L, Erard N, Gable AL, et al:
Asparagine bioavailability governs metastasis in a model of breast
cancer. Nature. 554:378–381. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yang H, He X, Zheng Y, Feng W, Xia X, Yu X
and Lin Z: Down-regulation of asparagine synthetase induces cell
cycle arrest and inhibits cell proliferation of breast cancer. Chem
Biol Drug Des. 84:578–584. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Qin C, Yang X and Zhan Z: High expression
of asparagine synthetase is associated with poor prognosis of
breast cancer in Chinese population. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
35:581–585. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nishikawa G, Kawada K, Hanada K, Maekawa
H, Itatani Y, Miyoshi H, Taketo MM and Obama K: Targeting
asparagine synthetase in tumorgenicity using patient-derived
tumor-initiating cells. Cells. 11:32732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen W, Qin Y, Qiao L, Liu X, Gao C, Li
TR, Luo Y, Li D, Yan H, Han L, et al: FAM50A drives breast cancer
brain metastasis through interaction with C9ORF78 to enhance
L-asparagine production. Sci Adv. 11:eadt30752025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Reis LMD, Adamoski D, Souza RO, Ascenção
CF, de Oliveira KR, Corrêa-da-Silva F, de Sá, Patroni FM, Dias MM,
Consonni SR, de Moraes-Vieira PMM, et al: Dual inhibition of
glutaminase and carnitine palmitoyltransferase decreases growth and
migration of glutaminase inhibition-resistant triple-negative
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 294:9342–9357. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Partynska A, Gomulkiewicz A, Dziegiel P
and Podhorska-Okolow M: The role of zyxin in carcinogenesis.
Anticancer Res. 40:5981–5988. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kotb A, Hyndman ME and Patel TR: The role
of zyxin in regulation of malignancies. Heliyon. 4:e006952018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cai T, Bai J, Tan P, Huang Z, Liu C, Wu Z,
Cheng Y, Li T, Chen Y, Ruan J, et al: Zyxin promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression via the activation of AKT/mTOR signaling
pathway. Oncol Res. 31:805–817. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mohammadi H, Shakiba E, Rostampour R,
Bahremand K, Goodarzi MT, Bashiri H, Ghobadi KN and Asadi S: Down
expression of zyxin is associated with down expression of p53 in
colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Cell Med. 14:461–471. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ma B, Cheng H, Gao R, Mu C, Chen L, Wu S,
Chen Q and Zhu Y: Zyxin-Siah2-Lats2 axis mediates cooperation
between Hippo and TGF-β signalling pathways. Nat Commun.
7:111232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|