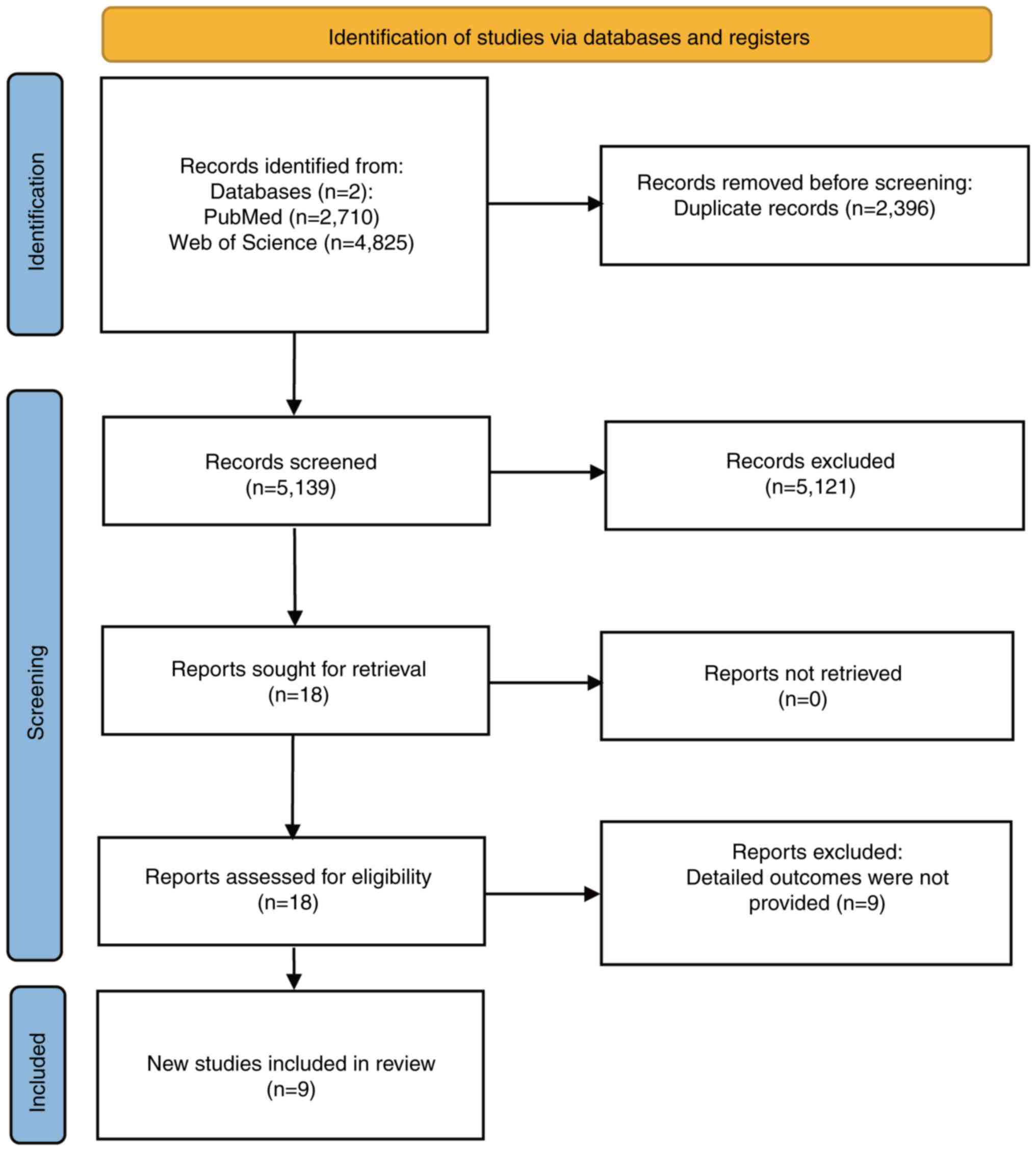
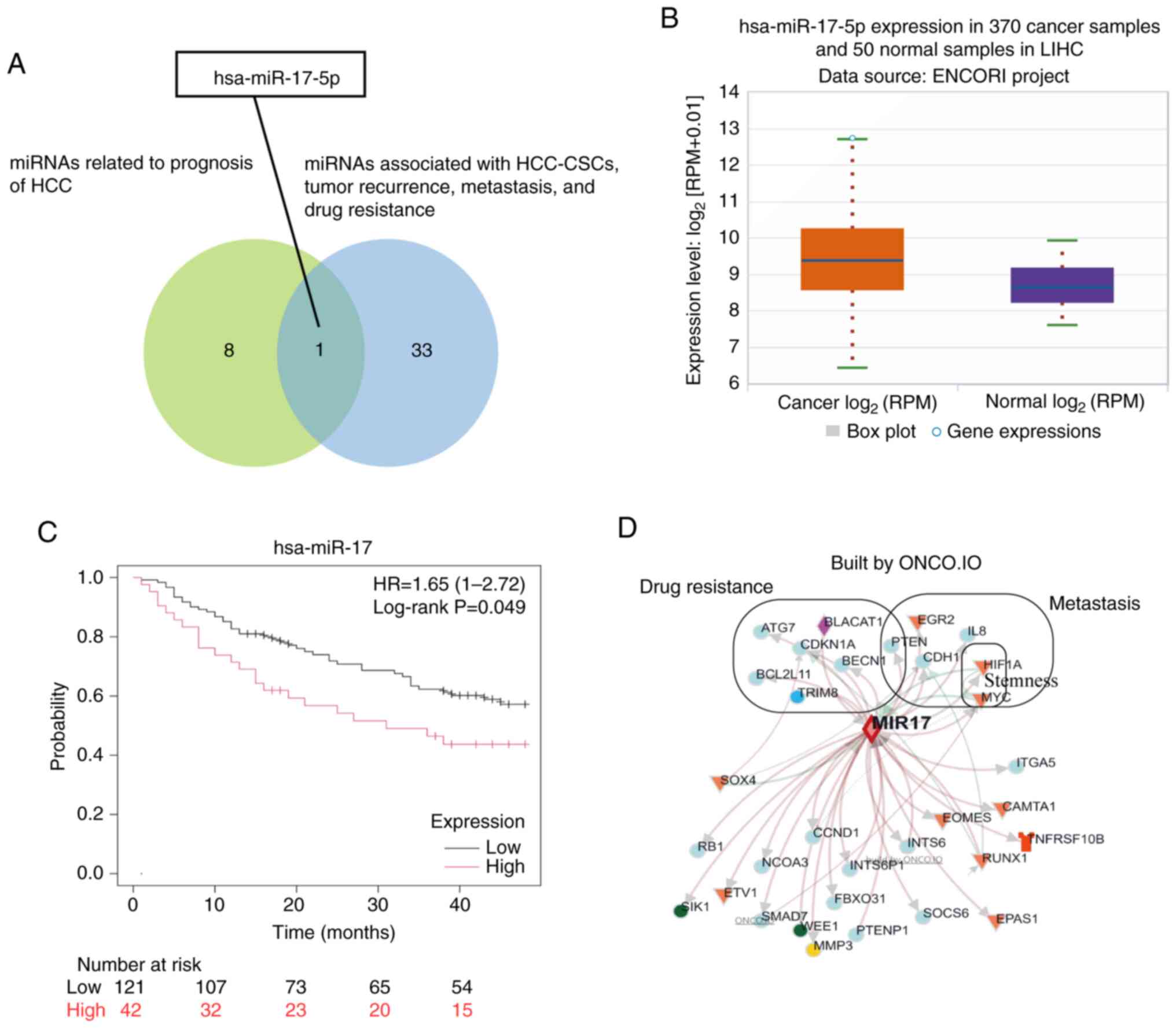
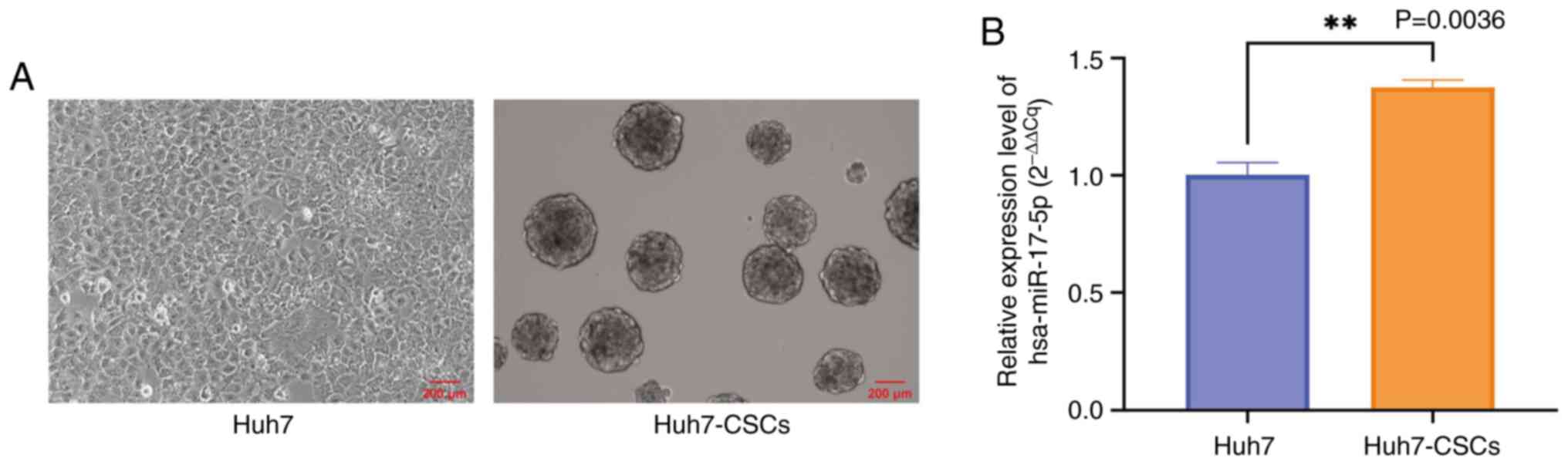
|
1
|
Villanueva A: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 380:1450–1462. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Qi J, Li M, Wang L, Hu Y, Liu W, Long Z,
Zhou Z, Yin P and Zhou M: National and subnational trends in cancer
burden in China, 2005–20: An analysis of national mortality
surveillance data. Lancet Public Health. 8:e943–e955. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim E and Viatour P: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Old friends and new tricks. Exp Mol Med. 52:1898–1907.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anwanwan D, Singh SK, Singh S, Saikam V
and Singh R: Challenges in liver cancer and possible treatment
approaches. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1873:1883142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhong Y, Yang Y, He L, Zhou Y, Cheng N,
Chen G, Zhao B, Wang Y, Wang G and Liu X: Development of prognostic
evaluation model to predict the overall survival and early
recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma.
8:301–312. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Makary MS, Khandpur U, Cloyd JM, Mumtaz K
and Dowell JD: Locoregional therapy approaches for hepatocellular
carcinoma: Recent advances and management strategies. Cancers
(Basel). 12:19142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nakano S, Eso Y, Okada H, Takai A,
Takahashi K and Seno H: Recent advances in immunotherapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 12:7752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Niu L, Liu L, Yang S, Ren J, Lai PBS and
Chen GG: New insights into sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular
carcinoma: Responsible mechanisms and promising strategies. Biochim
Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1868:564–570. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu J, Liao K and Zhou W: Exosomes regulate
the transformation of cancer cells in cancer stem cell homeostasis.
Stem Cells Int. 2018:48373702018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Y, Wu G, Fu X, Xu S, Wang T, Zhang Q
and Yang Y: Aquaporin 3 maintains the stemness of CD133+
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating STAT3. Cell Death Dis.
10:4652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bai X, Ni J, Beretov J, Graham P and Li Y:
Cancer stem cell in breast cancer therapeutic resistance. Cancer
Treat Rev. 69:152–163. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen C, Zhao S, Karnad A and Freeman JW:
The biology and role of CD44 in cancer progression: Therapeutic
implications. J Hematol Oncol. 11:642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Glumac PM and LeBeau AM: The role of CD133
in cancer: A concise review. Clin Transl Med. 7:182018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xiang DM, Sun W, Zhou T, Zhang C, Cheng Z,
Li SC, Jiang W, Wang R, Fu G, Cui X, et al: Oncofetal HLF
transactivates c-Jun to promote hepatocellular carcinoma
development and sorafenib resistance. Gut. 68:1858–1871. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Akbari S, Kunter I, Azbazdar Y, Ozhan G,
Atabey N, Firtina Karagonlar Z and Erdal E: LGR5/R-Spo1/Wnt3a axis
promotes stemness and aggressive phenotype in hepatoblast-like
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cell Signal. 82:1099722021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Wu Y, Zhou Z, Huang M, Deng W, Wang
Y, Zhou X, Chen L, Li Y, Zeng T, et al: Celecoxib inhibits the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in bladder cancer via the
miRNA-145/TGFBR2/Smad3 axis. Int J Mol Med. 44:683–693.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lv T, Jiang L, Kong L and Yang J:
MicroRNA-29c-3p acts as a tumor suppressor gene and inhibits tumor
progression in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting TRIM31. Oncol
Rep. 43:953–964. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG; PRISMA Group, : Preferred reporting items for systematic
reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med.
6:e10000972009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Methley AM, Campbell S, Chew-Graham C,
McNally R and Cheraghi-Sohi S: PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: A comparison
study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for
qualitative systematic reviews. BMC Health Serv Res. 14:5792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Torre-Healy LA, Berezovsky A and Lathia
JD: Isolation, characterization, and expansion of cancer stem
cells. Methods Mol Biol. 1553:133–143. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xie RT, Cong XL, Zhong XM, Luo P, Yang HQ,
Lu GX, Luo P, Chang ZY, Sun R, Wu TM, et al: MicroRNA-33a
downregulation is associated with tumorigenesis and poor prognosis
in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett.
15:4571–4577. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhuang L, Xu L, Wang P and Meng Z: Serum
miR-128-2 serves as a prognostic marker for patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01172742015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun J, Fang K, Shen H and Qian Y:
MicroRNA-9 is a ponderable index for the prognosis of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:17748–17756.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen HY, Han ZB, Fan JW, Xia J, Wu JY, Qiu
GQ, Tang HM and Peng ZH: miR-203 expression predicts outcome after
liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic
liver. Med Oncol. 29:1859–1865. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou N, Wu J, Wang X, Sun Z, Han Q and
Zhao L: Low-level expression of microRNA-375 predicts poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 37:2145–2152.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo C, Pu J, Liu F, Long X, Wang C, Wei H
and Tang Q: MicroRNA-200c expression is decreased in hepatocellular
carcinoma and associated with poor prognosis. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 43:715–721. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ha SY, Yu JI, Choi C, Kang SY, Joh JW,
Paik SW, Kim S, Kim M, Park HC, Park CK, et al: Prognostic
significance of miR-122 expression after curative resection in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Sci Rep. 9:147382019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu HT, Dong QZ, Sheng YY, Wei JW, Wang G,
Zhou HJ, Ren N, Jia HL, Ye QH and Qin LX: MicroRNA-29a-5p is a
novel predictor for early recurrence of hepatitis B virus-related
hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection. PLoS One.
7:e523932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen L, Jiang M, Yuan W and Tang H:
miR-17-5p as a novel prognostic marker for hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Invest Surg. 25:156–161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zenlander R, Salter H, Gilg S, Eggertsen G
and Stål P: MicroRNAs as plasma biomarkers of hepatocellular
carcinoma in patients with liver cirrhosis-A cross-sectional study.
Int J Mol Sci. 25:24142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Friedman RC, Farh KKH, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Gebrie A: Disease progression role as well
as the diagnostic and prognostic value of microRNA-21 in patients
with cervical cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS
One. 17:e02684802022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li D, Wang T, Sun FF, Feng JQ, Peng JJ, Li
H, Wang C, Wang D, Liu Y, Bai YD, et al: MicroRNA-375 represses
tumor angiogenesis and reverses resistance to sorafenib in
hepatocarcinoma. Cancer Gene Ther. 28:126–140. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang D and Yang J: MiR-375 attenuates
sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inhibiting cell autophagy. Acta Biochim Pol. 70:239–246.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen Y, Xu H, Tang H, Li H, Zhang C, Jin S
and Bai D: miR-9-5p expression is associated with vascular invasion
and prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma, and in vitro
verification. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:14657–14671. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lu Z, Li X, Xu Y, Chen M, Chen W, Chen T,
Tang Q and He Z: microRNA-17 functions as an oncogene by
downregulating Smad3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Death Dis. 10:7232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang X, Li F, Cheng J, Hou N, Pu Z, Zhang
H, Chen Y and Huang C: MicroRNA-17 family targets RUNX3 to increase
proliferation and migration of hepatocellular carcinoma. Crit Rev
Eukaryot Gene Expr. 33:71–84. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shan SW, Fang L, Shatseva T, Rutnam ZJ,
Yang X, Du W, Lu WY, Xuan JW, Deng Z and Yang BB: Mature miR-17-5p
and passenger miR-17-3p induce hepatocellular carcinoma by
targeting PTEN, GalNT7 and vimentin in different signal pathways. J
Cell Sci. 126:1517–1530. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu YC, Yeh CT and Lin KH: Cancer stem
cell functions in hepatocellular carcinoma and comprehensive
therapeutic strategies. Cells. 9:13312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim YJ, Yuk N, Shin HJ and Jung HJ: The
natural pigment violacein potentially suppresses the proliferation
and stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro. Int J Mol
Sci. 22:107312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Prager BC, Xie Q, Bao S and Rich JN:
Cancer stem cells: The architects of the tumor ecosystem. Cell Stem
Cell. 24:41–53. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li L and Bhatia R: Molecular pathways:
Stem cell quiescence. Clin Cancer Res. 17:4936–4941. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Song S, Ma D, Xu L, Wang Q, Liu L, Tong X
and Yan H: Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound-generated singlet oxygen
induces telomere damage leading to glioma stem cell awakening from
quiescence. iScience. 25:1035582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zou R, Liu Y, Qiu S, Lu Y, Chen Y, Yu H,
Zhu H, Zhu W, Zhu L, Feng J and Han J: The identification of
N6-methyladenosine-related miRNAs predictive of hepatocellular
carcinoma prognosis and immunotherapy efficacy. Cancer Biomark.
38:551–566. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lequeux A, Noman MZ, Xiao M, Van Moer K,
Hasmim M, Benoit A, Bosseler M, Viry E, Arakelian T, Berchem G, et
al: Targeting HIF-1 alpha transcriptional activity drives cytotoxic
immune effector cells into melanoma and improves combination
immunotherapy. Oncogene. 40:4725–4735. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cui CP, Wong CCL, Kai AKL, Ho DWH, Lau
EYT, Tsui YM, Chan LK, Cheung TT, Chok KSH, Chan ACY, et al: SENP1
promotes hypoxia-induced cancer stemness by HIF-1α deSUMOylation
and SENP1/HIF-1α positive feedback loop. Gut. 66:2149–2159. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
EI Tayebi HM, Omar K, Hegy S, EI Maghrabi
M, EI Brolosy M, Hosny KA, Esmat G and Abdelaziz AI: Repression of
miR-17-5p with elevated expression of E2F-1 and c-MYC in
non-metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma and enhancement of cell
growth upon reversing this expression pattern. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 434:421–427. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Shachaf CM and Felsher DW: Tumor dormancy
and MYC inactivation: Pushing cancer to the brink of normalcy.
Cancer Res. 65:4471–4474. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ebrahimi KH, Gilbert-Jaramillo J, James WS
and McCullagh JSO: Interferon-stimulated gene products as
regulators of central carbon metabolism. FEBS J. 288:3715–3726.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Snyder V, Reed-Newman TC, Arnold L, Thomas
SM and Anant S: Cancer stem cell metabolism and potential
therapeutic targets. Front Oncol. 8:2032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xia H, Huang Z, Xu Y, Yam JWP and Cui Y:
Reprogramming of central carbon metabolism in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 153:1134852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen YY, Wang WH, Che L, Lan Y, Zhang LY,
Zhan DL, Huang ZY, Lin ZN and Lin YC: BNIP3L-dependent mitophagy
promotes hbx-induced cancer stemness of hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via glycolysis metabolism reprogramming. Cancers (Basel).
12:6552020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fan J, Tian R, Yang X, Wang H, Shi Y, Fan
X, Zhang J, Chen Y, Zhang K, Chen Z and Li L: KCNN4 promotes the
stemness potentials of liver cancer stem cells by enhancing glucose
metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 23:69582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu G, Luo Q, Li H, Liu Q, Ju Y and Song
G: Increased oxidative phosphorylation is required for stemness
maintenance in liver cancer stem cells from hepatocellular
carcinoma cell line HCCLM3 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 21:52762020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang T, Liang N, Zhang J, Bai Y, Li Y,
Zhao Z, Chen L, Yang M, Huang Q, Hu P, et al: OCTN2 enhances
PGC-1α-mediated fatty acid oxidation and OXPHOS to support stemness
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Metabolism. 147:1556282023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wang W, Han N, Xu Y, Zhao Y, Shi L, Filmus
J and Li F: Assembling custom side chains on proteoglycans to
interrogate their function in living cells. Nat Commun.
11:59152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Yao G and Yang Z: Glypican-3 knockdown
inhibits the cell growth, stemness, and glycolysis development of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells under hypoxic microenvironment
through lactylation. Arch Physiol Biochem. 130:546–554.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Aguilar-Chaparro MA, Rivera-Pineda SA,
Hernández-Galdámez HV, Ríos-Castro E, Garibay-Cerdenares OL,
Piña-Vázquez C and Villa-Treviño S: Transforming growth factor-β
modulates cancer stem cell traits on CD44 subpopulations in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 126:e700032025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|