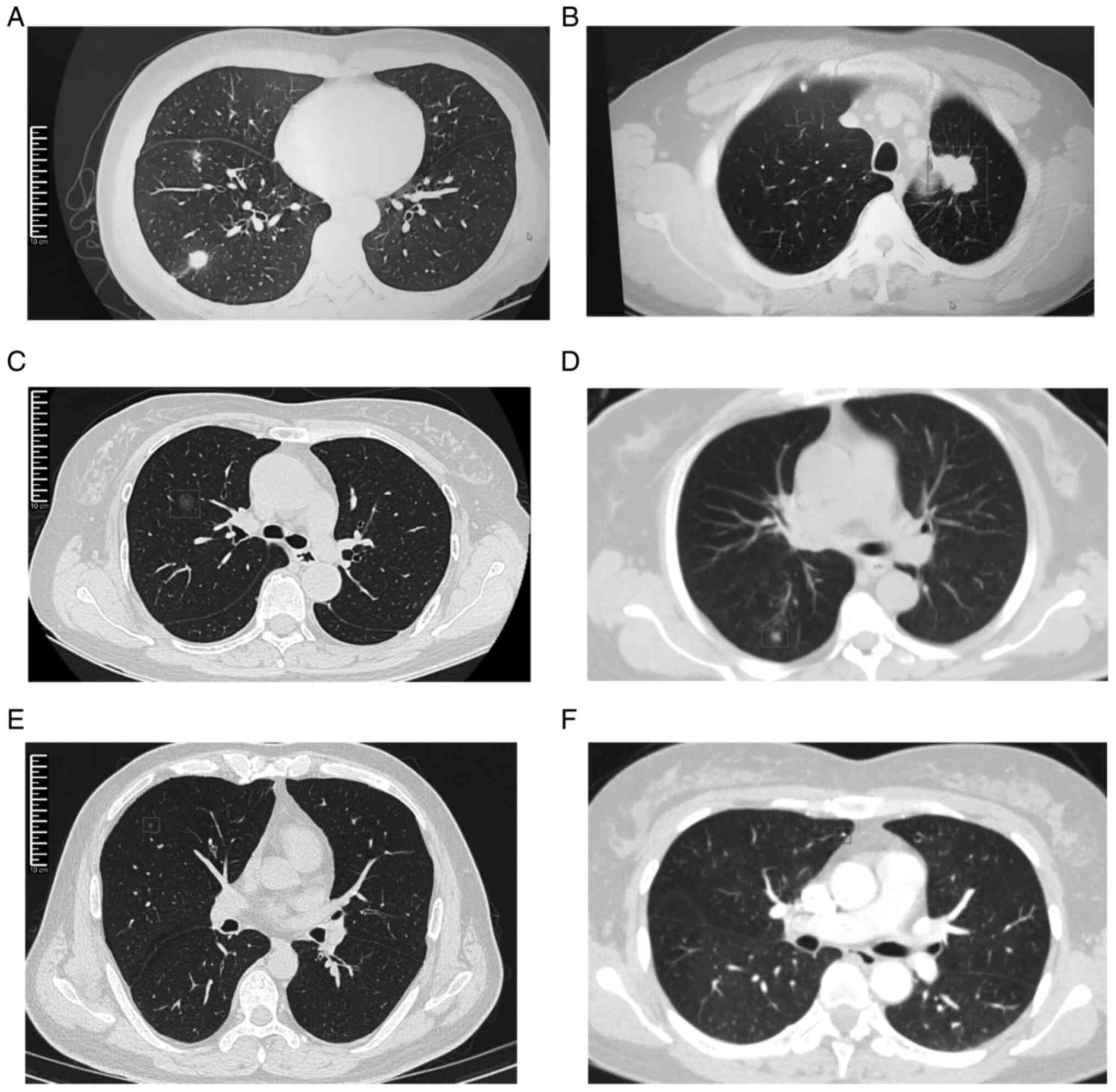
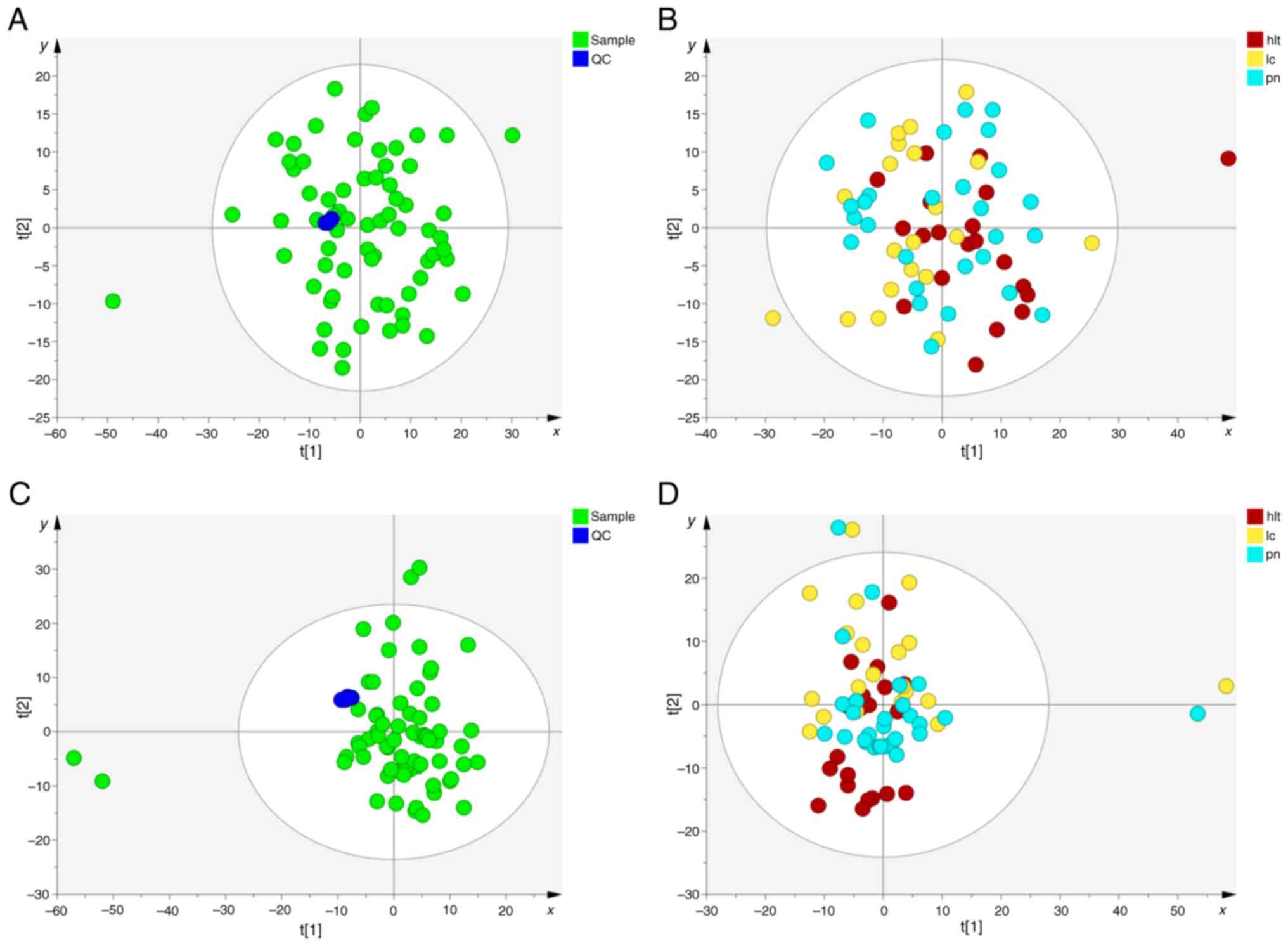
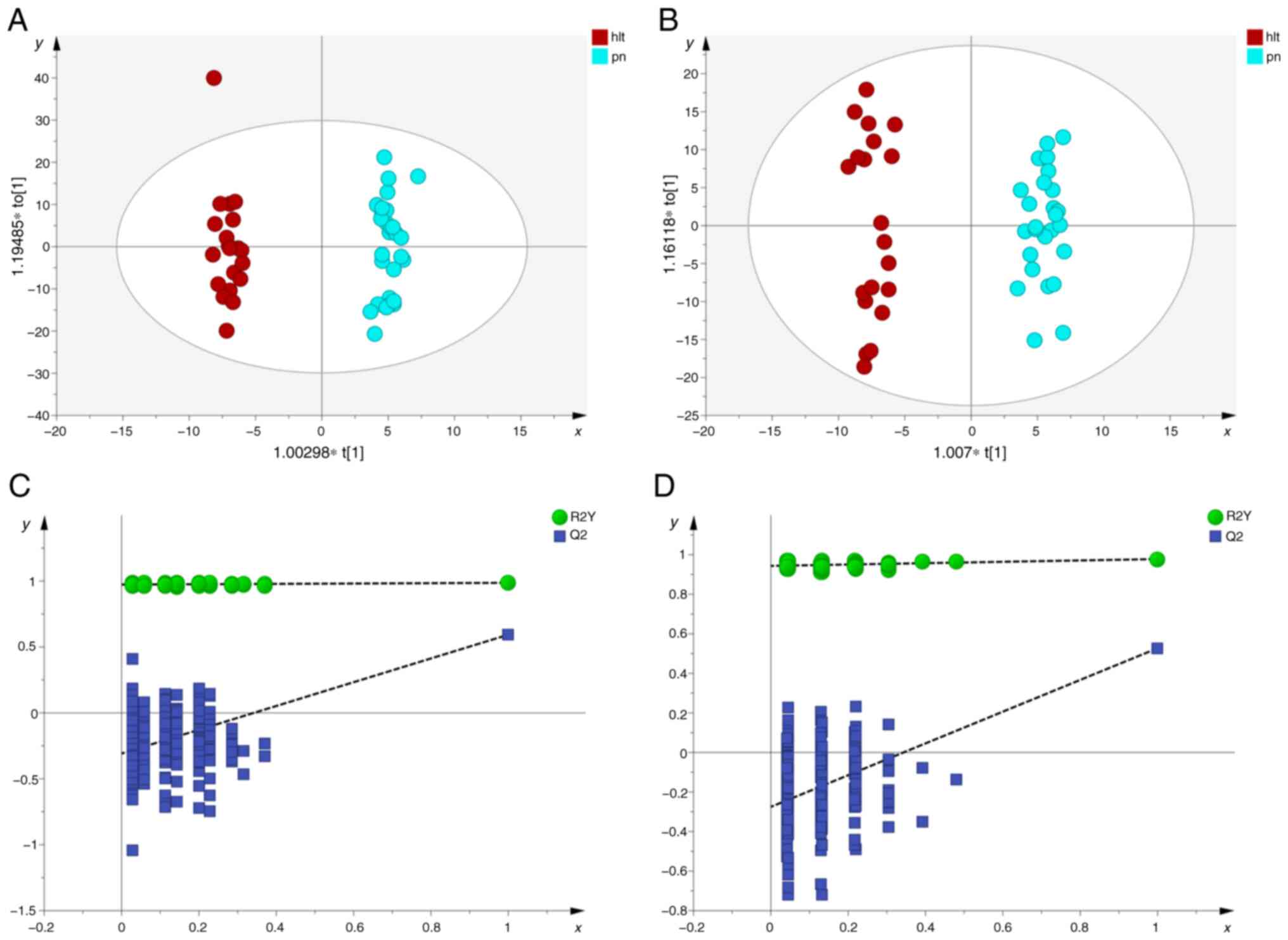
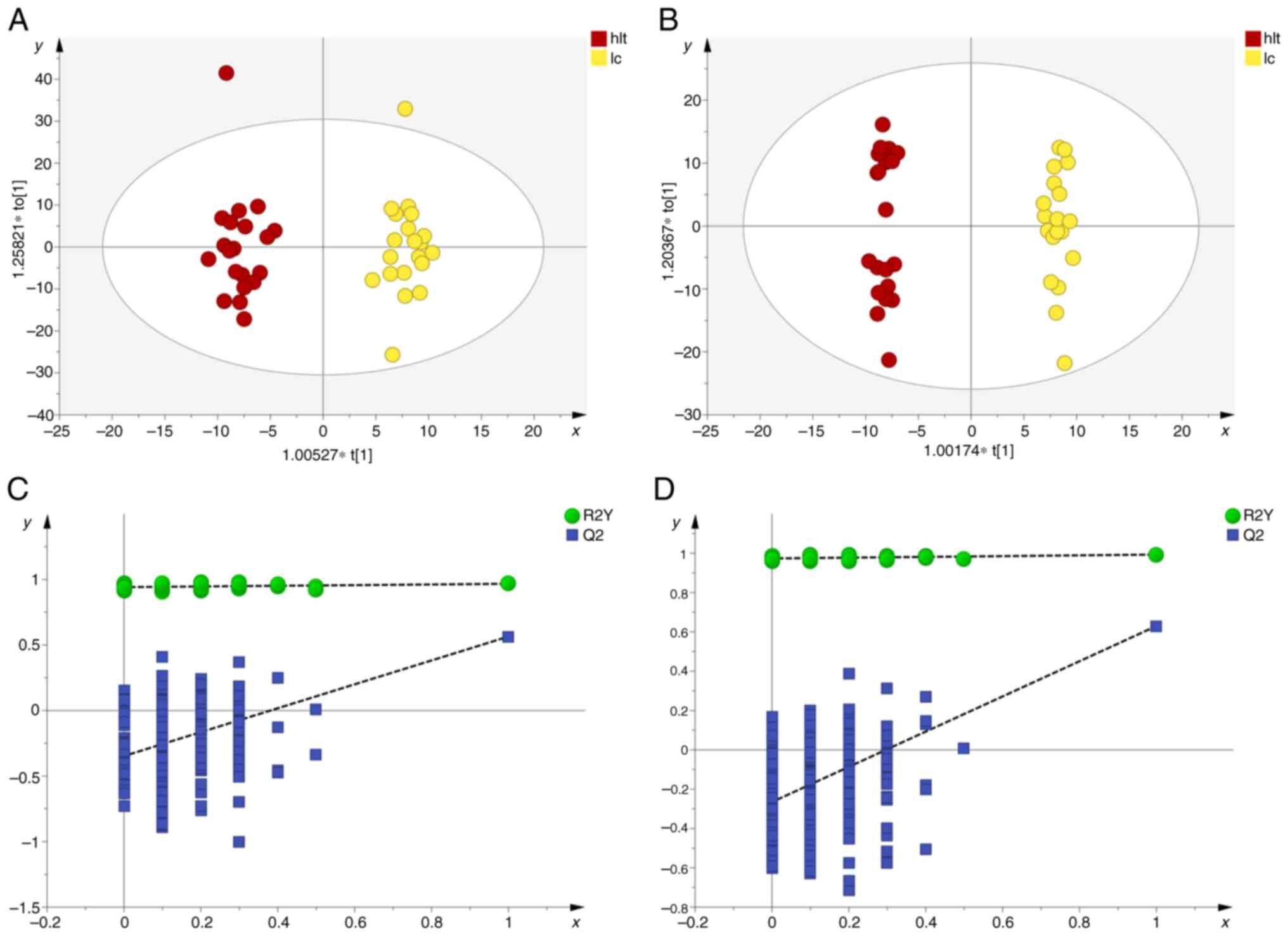
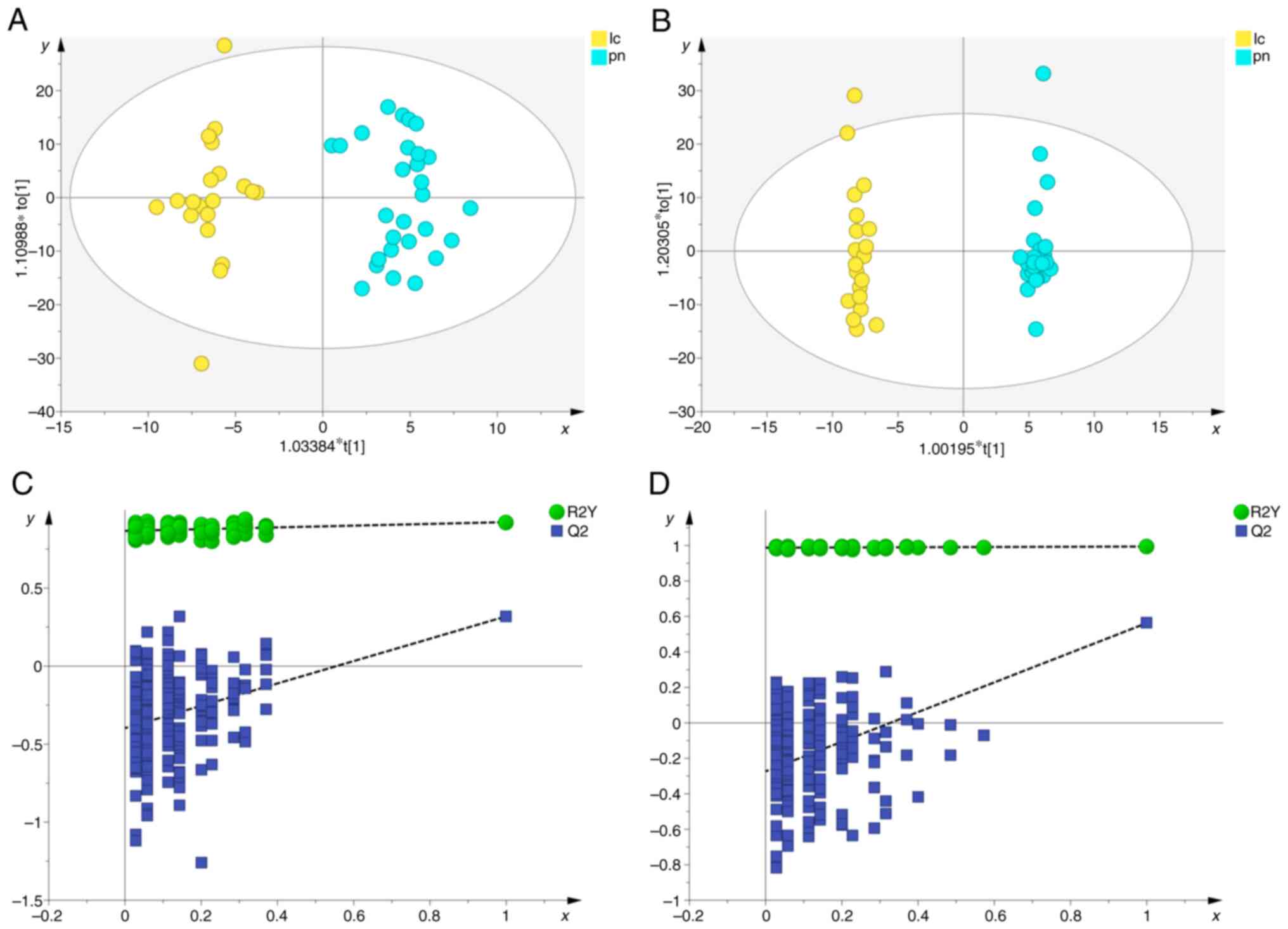
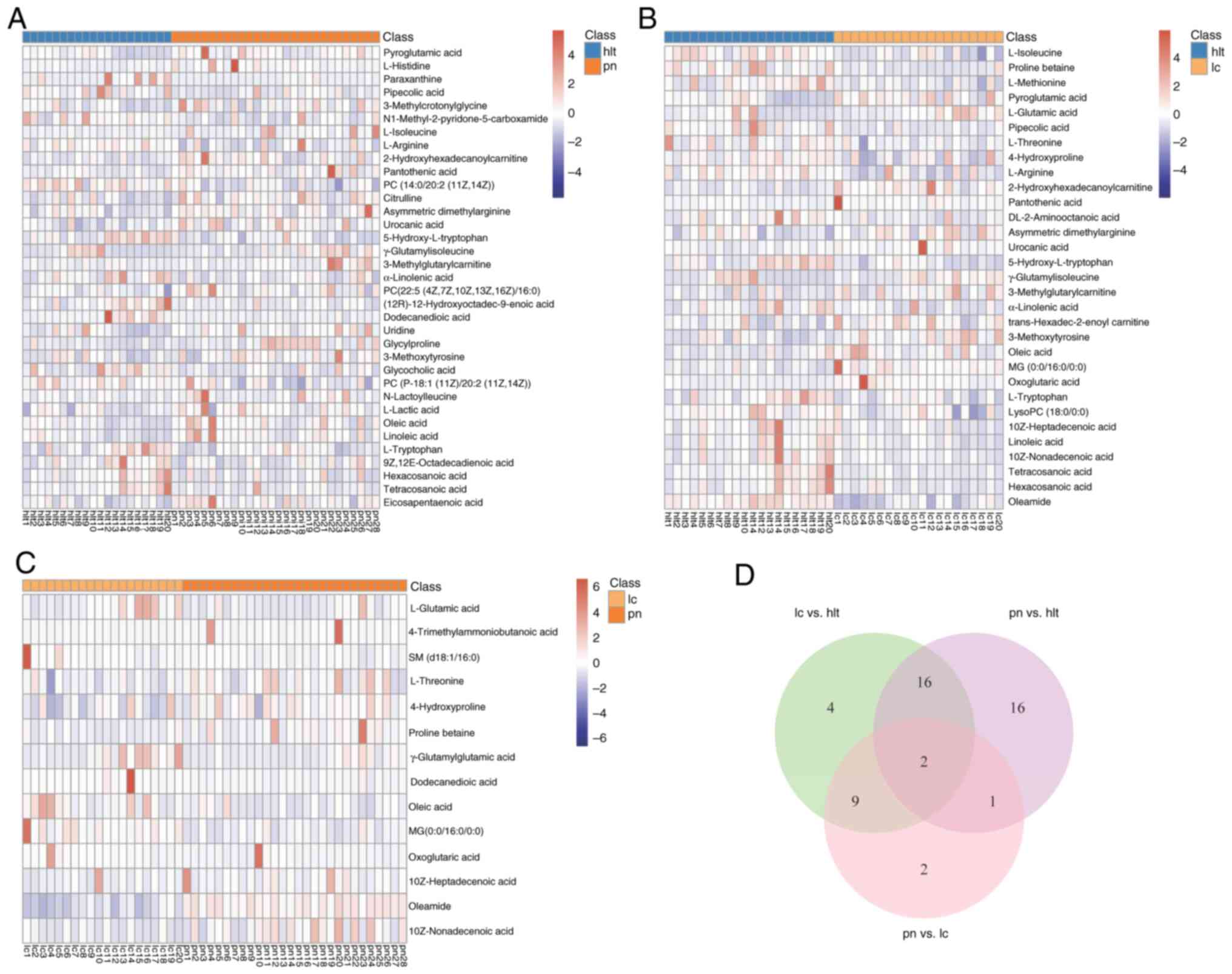
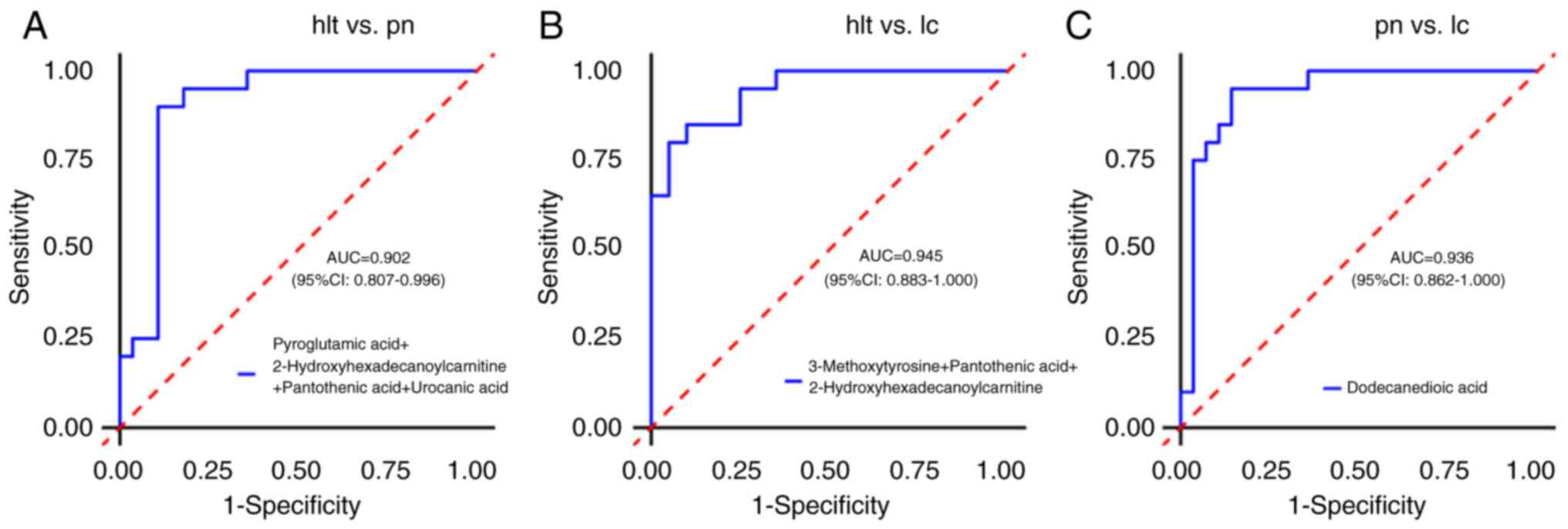
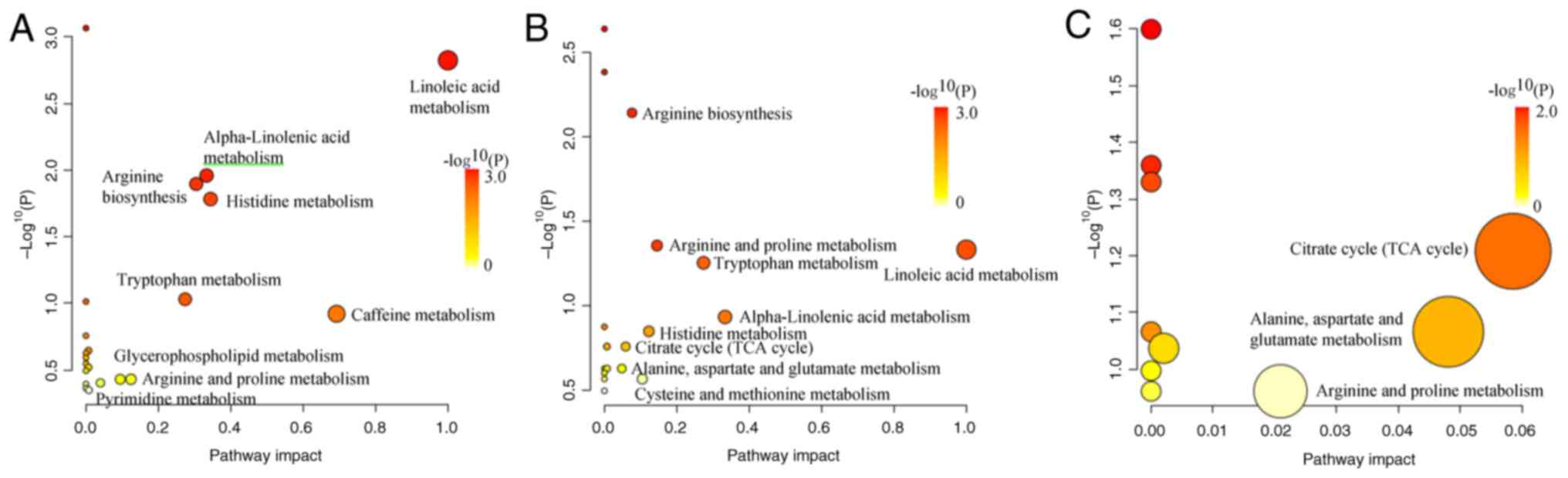
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36
Cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thai AA, Solomon BJ, Sequist LV, Gainor JF
and Heist RS: Lung cancer. Lancet. 398:535–554. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bi H, Yin L, Fang W, Song S, Wu S and Shen
J: Association of CEA, NSE, CYFRA 21-1, SCC-Ag, and ProGRP with
Clinicopathological characteristics and chemotherapeutic outcomes
of lung cancer. Lab Med. 54:372–379. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Guo Q, Huang Z, Song L, Zhao F, Gu
T, Feng Z, Wang H, Li B, Wang D, et al: Cell-free epigenomes
enhanced fragmentomics-based model for early detection of lung
cancer. Clin Transl Med. 15:e702252025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang C, Li J, Huang J and Wu S: Computed
tomography image under convolutional neural network deep learning
algorithm in pulmonary nodule detection and lung function
examination. J Healthc Eng. 2021:34172852021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang J, Ye G, Guo J, Huang Q and Zhang S:
Reducing False-positives in lung nodules detection using balanced
datasets. Front Public Health. 9:6710702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu Z, Wang F, Cao W, Qin C, Dong X, Yang
Z, Zheng Y, Luo Z, Zhao L, Yu Y, et al: Lung cancer risk prediction
models based on pulmonary nodules: A systematic review. Thorac
Cancer. 13:664–677. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zheng J, Hao Y, Guo Y, Du M, Wang P and
Xin J: An 18F-FDG-PET/CT-based radiomics signature for estimating
malignance probability of solitary pulmonary nodule. Clin Respir J.
18:e137512024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhu K, Tang S, Pan D, Wang X, Xu Y, Yan J,
Wang L, Chen C and Yang M: Development and biological evaluation of
a novel CEACAM6-targeted PET tracer for distinguishing malignant
nodules in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol
Imaging. 52:2414–2430. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nooreldeen R and Bach H: Current and
future development in lung cancer diagnosis. Int J Mol Sci.
22:86612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Chen Y, Ma C, Bi L, Su Z, Li W and
Wang Z: Current advances and future prospects of blood-based
techniques for identifying benign and malignant pulmonary nodules.
Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 207:1046082025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang CF, Peng SJ, Liu RQ, Yu YJ, Ge QM,
Liang RB, Li QY, Li B and Shao Y: The combination of CA125 and NSE
is useful for predicting liver metastasis of lung cancer. Dis
Markers. 2020:88508732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Anwardeen NR, Diboun I, Mokrab Y, Althani
AA and Elrayess MA: Statistical methods and resources for biomarker
discovery using metabolomics. BMC Bioinformatics. 24:2502023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang S, He T and Wang H: Non-targeted
metabolomics study for discovery of hepatocellular carcinoma serum
diagnostic biomarker. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 239:1158692024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang X, Chen L, Liu L, Chen H, Gong Z,
Lyu J, Li Y, Jiang Q, Zeng X, Zhang P and Zhou H: Untargeted
metabolomics analysis reveals the potential mechanism of
imatinib-induced skin rash in patients with gastrointestinal
stromal tumor. Int Immunopharmacol. 140:1127282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Johnson CH, Ivanisevic J and Siuzdak G:
Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 17:451–459. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu K, Berthiller F, Metzler-Zebeli BU and
Schwartz-Zimmermann HE: Development and validation of targeted
metabolomics methods using liquid Chromatography-tandem mass
spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) for the quantification of 235 plasma
metabolites. Molecules. 30:7062025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wang R, Hu Q, Wu Y, Guan N, Han X and Guan
X: Intratumoral lipid metabolic reprogramming as a pro-tumoral
regulator in the tumor milieu. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1878:1889622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rispoli MG, Valentinuzzi S, De Luca G, Del
Boccio P, Federici L, Di Ioia M, Digiovanni A, Grasso EA, Pozzilli
V, Villani A, et al: Contribution of metabolomics to multiple
sclerosis diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Int J Mol Sci.
22:111122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liang S, Cao X, Wang Y, Leng P, Wen X, Xie
G, Luo H and Yu R: Metabolomics analysis and diagnosis of lung
cancer: Insights from diverse sample types. Int J Med Sci.
21:234–252. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang Y, Li Z, Lazar L, Fang Z, Tang C and
Zhao J: Metabolomics workflow for lung cancer: Discovery of
biomarkers. Clin Chim Acta. 495:436–445. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chelala L, Hossain R, Kazerooni EA,
Christensen JD, Dyer DS and White CS: Lung-RADS version 1.1:
Challenges and a look ahead, from the AJR special series on
radiology reporting and data systems. AJR Am J Roentgenol.
216:1411–1422. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aunger J, Yip KP, Dosanjh K, Scandrett K,
Ungureanu B, Newnham M and Turner AM: Interventions to improve
adherence to clinical guidelines for the management and Follow-Up
of pulmonary nodules: A systematic review. Chest. 168:248–268.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kramer BS, Berg CD, Aberle DR and Prorok
PC: Lung cancer screening with Low-dose helical CT: Results from
the national lung screening Trial (NLST). J Med Screen. 18:109–111.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
O Reilly D, Roche S, Noonan C, O'Shea J,
Toomey S, Hennessy BT, Fitzmaurice GJ, Egan K, Dunne J, Dowling CM,
et al: Lung health check pilot: Ireland's flagship lung cancer
screening trial. BMJ Open Respir Res. 12:e0030352025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao Y and Wang Z, Liu X, Chen Q, Li C,
Zhao H and Wang Z: Pulmonary nodule detection based on multiscale
feature fusion. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022:89030372022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu J, Tao J, Zhu M, Liu J, Ma C, Chen K,
Wang Y, Lu X, Saito Y and Ni B: Development and validation of CT
radiomics diagnostic models: Differentiating benign from malignant
pulmonary nodules and evaluating malignancy degree. J Thorac Dis.
17:1645–1672. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu L, Chang C, Jiang P, Wei K, Zhang R,
Jin Y, Zhao J, Xu L, Shi Y, Guo S, et al: Metabolomics in
rheumatoid arthritis: Advances and review. Front Immunol.
13:9617082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pham DL, Lim KM, Joo KM, Park HS, Leung
DYM and Ye YM: Increased cis-to-trans urocanic acid ratio in the
skin of chronic spontaneous urticaria patients. Sci Rep.
7:13182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Tan Y, Wang H, Yu XD, Mo Y, Reilly
J, He Z and Shu X: Urocanic acid facilitates acquisition of object
recognition memory in mice. Physiol Behav. 266:1142012023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hart PH and Norval M: The multiple roles
of urocanic acid in health and disease. J Invest Dermatol.
141:496–502. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mi M, Liu Z, Zheng X, Wen Q, Zhu F, Li J,
Mungur ID and Zhang L: Serum metabolomic profiling based on GC/MS
helped to discriminate diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with
different prognosis. Leuk Res. 111:1066932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Vidman L, Zheng R, Bodén S, Ribbenstedt A,
Gunter MJ, Palmqvist R, Harlid S, Brunius C and Van Guelpen B:
Untargeted plasma metabolomics and risk of colorectal cancer-an
analysis nested within a large-scale prospective cohort. Cancer
Metab. 11:172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Peterson CT, Rodionov DA, Osterman AL and
Peterson SN: B vitamins and their role in immune regulation and
cancer. Nutrients. 12:33802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hrubša M, Siatka T, Nejmanová I,
Vopršalová M, Kujovská Krčmová L, Matoušová K, Javorská L, Macáková
K, Mercolini L, Remião F, et al: Biological properties of vitamins
of the B-Complex, part 1: Vitamins B1, B2, B3, and B5. Nutrients.
14:4842022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen G, Bao B, Cheng Y, Tian M, Song J,
Zheng L and Tong Q: Acetyl-CoA metabolism as a therapeutic target
for cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 168:1157412023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou Y, Li X, Long G, Tao Y, Zhou L and
Tang J: Identification and validation of a tyrosine
metabolism-related prognostic prediction model and characterization
of the tumor microenvironment infiltration in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Front Immunol. 13:9942592022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang X, Chen Y, Lan B, Wang Y, Lin W,
Jiang X, Ye J, Shang B, Feng C, Liu J, et al: Heterogeneity of
tyrosine-based melanin anabolism regulates pulmonary and cerebral
organotropic colonization microenvironment of melanoma cells.
Theranostics. 12:2063–2079. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wu T and Dai Y: Tumor microenvironment and
therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 387:61–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zou X, Huang H and Tan Y: Genetically
determined metabolites in allergic conjunctivitis: A Mendelian
randomization study. World Allergy Organ J. 17:1008942024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yang L, Chu Z, Liu M, Zou Q, Li J, Liu Q,
Wang Y, Wang T, Xiang J and Wang B: Amino acid metabolism in immune
cells: Essential regulators of the effector functions, and
promising opportunities to enhance cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol
Oncol. 16:592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang Z, Hu Y, Chen Y, Chen Z, Zhu Y, Chen
M, Xia J, Sun Y and Xu W: Immunometabolism in the tumor
microenvironment and its related research progress. Front Oncol.
12:10247892022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Koundouros N and Poulogiannis G:
Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer.
122:4–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Broadfield LA, Pane AA, Talebi A, Swinnen
JV and Fendt SM: Lipid metabolism in cancer: New perspectives and
emerging mechanisms. Dev Cell. 56:1363–1393. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Radzikh I, Fatica E, Kodger J, Shah R,
Pearce R and Sandlers YI: Metabolic outcomes of anaplerotic
dodecanedioic acid supplementation in very long Chain Acyl-CoA
dehydrogenase (VLCAD) deficient fibroblasts. Metabolites.
11:5382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
He W, Li Q and Li X: Acetyl-CoA regulates
lipid metabolism and histone acetylation modification in cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1878:1888372023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Feron O: The many metabolic sources of
acetyl-CoA to support histone acetylation and influence cancer
progression. Ann Transl Med. 7 (Suppl 8):S2772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Noreldeen HAA: Recent advances in lung
cancer lipidomics: Analytical techniques and their applications.
Clin Chim Acta. 577:1204702025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Rocha CM, Carrola J, Barros AS, Gil AM,
Goodfellow BJ, Carreira IM, Bernardo J, Gomes A, Sousa V, Carvalho
L, et al: Metabolic signatures of lung cancer in biofluids:
NMR-based metabonomics of blood plasma. J Proteome Res.
10:4314–4324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Musharraf SG, Mazhar S, Choudhary MI, Rizi
N and Atta-ur-Rahman: Plasma metabolite profiling and chemometric
analyses of lung cancer along with three controls through gas
chromatography-mass spectrometry. Sci Rep. 5:86072015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li X and Zhang HS: Amino acid metabolism,
redox balance and epigenetic regulation in cancer. FEBS J.
291:412–429. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jin HR, Wang J, Wang ZJ, Xi MJ, Xia BH,
Deng K and Yang JL: Lipid metabolic reprogramming in tumor
microenvironment: From mechanisms to therapeutics. J Hematol Oncol.
16:1032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Liu X, Ren B, Ren J, Gu M, You L and Zhao
Y: The significant role of amino acid metabolic reprogramming in
cancer. Cell Commun Signal. 22:3802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xu X, Peng Q, Jiang X, Tan S, Yang Y, Yang
W, Han Y, Chen Y, Oyang L, Lin J, et al: Metabolic reprogramming
and epigenetic modifications in cancer: From the impacts and
mechanisms to the treatment potential. Exp Mol Med. 55:1357–1370.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lieu EL, Nguyen T, Rhyne S and Kim J:
Amino acids in cancer. Exp Mol Med. 52:15–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Greene LI, Bruno TC, Christenson JL,
D'Alessandro A, Culp-Hill R, Torkko K, Borges VF, Slansky JE and
Richer JK: A Role for Tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase in CD8 T-cell
suppression and evidence of tryptophan catabolism in breast cancer
patient plasma. Mol Cancer Res. 17:131–139. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yang K, Wang X, Song C, He Z, Wang R, Xu
Y, Jiang G, Wan Y, Mei J and Mao W: The role of lipid metabolic
reprogramming in tumor microenvironment. Theranostics.
13:1774–1808. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Snaebjornsson MT, Janaki-Raman S and
Schulze A: Greasing the wheels of the cancer machine: The role of
lipid metabolism in cancer. Cell Metab. 31:62–76. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
An Q, Lin R, Wang D and Wang C: Emerging
roles of fatty acid metabolism in cancer and their targeted drug
development. Eur J Med Chem. 240:1146132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Acharya R, Shetty SS and Kumari NS: Fatty
acid transport proteins (FATPs) in cancer. Chem Phys Lipids.
250:1052692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang Y, Wang D, Lv B, Hou X, Liu Q, Liao
C, Xu R, Zhang Y, Xu F and Zhang P: Oleic acid and insulin as key
characteristics of T2D promote colorectal cancer deterioration in
xenograft mice revealed by functional metabolomics. Front Oncol.
11:6850592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yu M, Wen W, Wang Y, Shan X, Yi X, Zhu W,
Aa J and Wang G: Plasma metabolomics reveals risk factors for lung
adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol. 14:12772062024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang D, Duan JJ, Guo YF, Chen JJ, Chen TQ,
Wang J and Yu SC: Targeting the glutamine-arginine-proline
metabolism axis in cancer. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 39:23671292024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Matos A, Carvalho M, Bicho M and Ribeiro
R: Arginine and arginases modulate metabolism, tumor
microenvironment and prostate cancer progression. Nutrients.
13:45032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Du T and Han J: Arginine metabolism and
its potential in treatment of colorectal cancer. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:6588612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Niu F, Yu Y, Li Z, Ren Y, Li Z, Ye Q, Liu
P, Ji C, Qian L and Xiong Y: Arginase: An emerging and promising
therapeutic target for cancer treatment. Biomed Pharmacother.
149:1128402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|