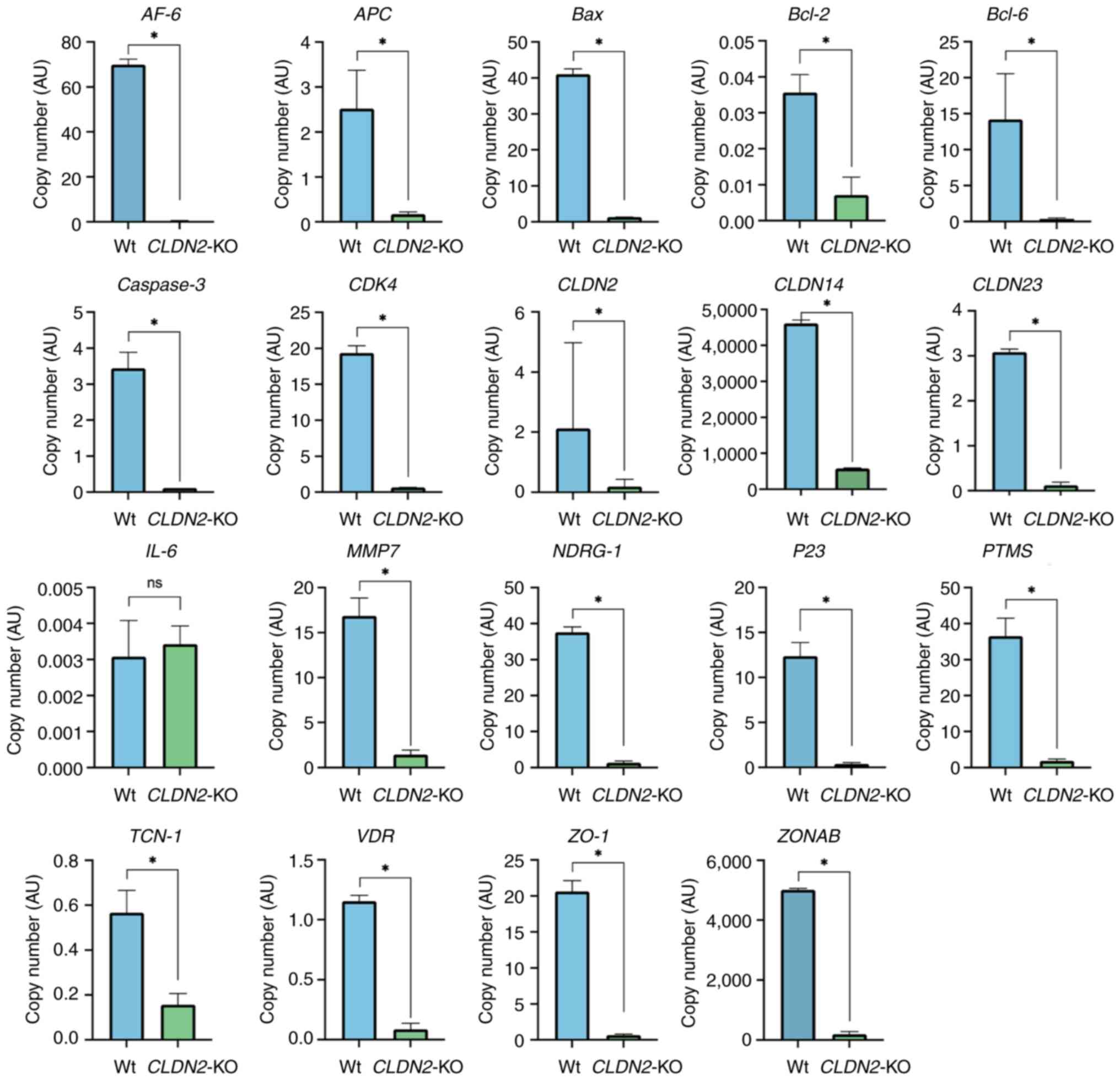
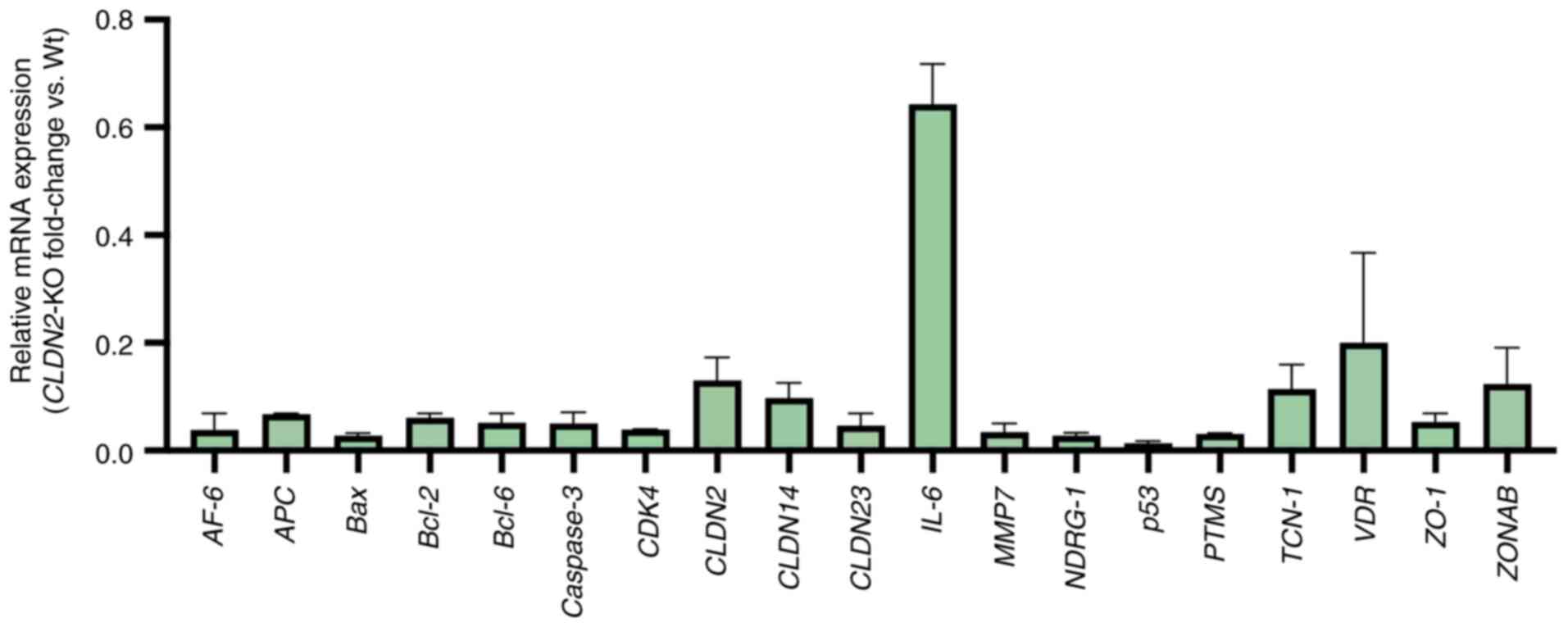
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA
and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin.
73:233–254. 2023.
|
|
2
|
Xi Y and Xu P: Global colorectal cancer
burden in 2020 and projections to 2040. Transl Oncol.
14:1011742021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mousavi SE, Ilaghi M, Hamidi Rad R and
Nejadghaderi SA: Epidemiology and socioeconomic correlates of
colorectal cancer in Asia in 2020 and its projection to 2040. Sci
Rep. 15:266392025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sarkar S: Proteogenomic approaches to
understand gene mutations and protein structural alterations in
colon cancer. Physiologia. 3:11–29. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tabariès S, Dupuy F, Dong Z, Monast A,
Annis MG, Spicer J, Ferri LE, Omeroglu A, Basik M, Amir E, et al:
Claudin-2 promotes breast cancer liver metastasis by facilitating
tumor cell interactions with hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol.
32:2979–2991. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cherradi S, Ayrolles-Torro A, Vezzo-Vié N,
Gueguinou N, Denis V, Combes E, Boissière F, Busson M,
Canterel-Thouennon L, Mollevi C, et al: Antibody targeting of
claudin-1 as a potential colorectal cancer therapy. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 36:892017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tabariès S, Annis MG, Lazaris A, Petrillo
SK, Huxham J, Abdellatif A, Palmieri V, Chabot J, Johnson RM, Van
Laere S, et al: Claudin-2 promotes colorectal cancer liver
metastasis and is a biomarker of the replacement type growth
pattern. Commun Biol. 4:6572021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Venugopal S, Anwer S and Szászi K:
Claudin-2: Roles beyond permeability functions. Int J Mol Sci.
20:56552019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Alghamdi RA and Al-Zahrani MH:
Identification of key claudin genes associated with survival
prognosis and diagnosis in colon cancer through integrated
bioinformatic analysis. Front Genet. 14:12218152023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Weber CR, Nalle SC, Tretiakova M, Rubin DT
and Turner JR: Claudin-1 and claudin-2 expression is elevated in
inflammatory bowel disease and may contribute to early neoplastic
transformation. Lab Invest. 88:1110–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rosenthal R, Milatz S, Krug SM, Oelrich B,
Schulzke JD, Amasheh S, Günzel D and Fromm M: Claudin-2, a
component of the tight junction, forms a paracellular water
channel. J Cell Sci. 123:1913–1921. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dhawan P, Ahmad R, Chaturvedi R, Smith JJ,
Midha R, Mittal MK, Krishnan M, Chen X, Eschrich S, Yeatman TJ, et
al: Claudin-2 expression increases tumorigenicity of colon cancer
cells: Role of epidermal growth factor receptor activation.
Oncogene. 30:3234–3247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wei M, Zhang Y, Yang X, Ma P, Li Y, Wu Y,
Chen X, Deng X, Yang T, Mao X, et al: Claudin-2 promotes colorectal
cancer growth and metastasis by suppressing NDRG1 transcription.
Clin Transl Med. 11:e6672021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Al-Zahrani M, Lary S, Assidi M, Hakamy S,
Dallol A, Alahwal M, Al-Maghrabi J, Sibiany A, Abuzenadah A,
Al-Qahtani M and Buhmeida A: Evaluation of prognostic potential of
CD44, Claudin-2 and EpCAM expression patterns in colorectal
carcinoma. Adv Environmental Biol. 10:147–156. 2016.
|
|
15
|
Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu
VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA Jr and Kinzler KW: Cancer genome landscapes.
Science. 339:1546–1558. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kim D and Cho KH: Hidden patterns of gene
expression provide prognostic insight for colorectal cancer. Cancer
Gene Ther. 30:11–21. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal
cancer. Nature. 487:330–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhao Z, Li C, Tong F, Deng J, Huang G and
Sang Y: Review of applications of CRISPR-Cas9 gene-editing
technology in cancer research. Biol Proced Online. 23:142021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Meng H, Nan M, Li Y, Ding Y, Yin Y and
Zhang M: Application of CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing technology in
basic research, diagnosis and treatment of colon cancer. Front
Endocrinol (Lausanne). 14:11484122023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Neumann E, Schaefer-Ridder M, Wang Y and
Hofschneider P: Gene transfer into mouse lyoma cells by
electroporation in high electric fields. EMBO J. 1:841–845. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Enzmann BL and Wronski A: Synthego's
engineered cells allow scientists to ‘Cut Out’ CRISPR optimization
[SPONSORED]. CRISPR J. 1:255–257. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Roginsky J: Analyzing CRISPR editing
results: Synthego developed a tool called ICE to be more efficient
than other methods. Genet Eng Biotechnol News. 38 (Suppl):S24–S26.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bentley DR, Balasubramanian S, Swerdlow
HP, Smith GP, Milton J, Brown CG, Hall KP, Evers DJ, Barnes CL,
Bignell HR, et al: Accurate whole human genome sequencing using
reversible terminator chemistry. Nature. 456:53–59. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gross A, Schoendube J, Zimmermann S, Steeb
M, Zengerle R and Koltay P: Technologies for single-cell isolation.
Int J Mol Sci. 16:16897–16919. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liang CC, Park AY and Guan JL: In vitro
scratch assay: A convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of
cell migration in vitro. Nat Protoc. 2:329–333. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schneider CA, Rasband WS and Eliceiri KW:
NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods.
9:671–675. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans
J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL,
et al: The MIQE guidelines: Minimum information for publication of
quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 55:611–622.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)). Method. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhu L, Han J, Li L, Wang Y, Li Y and Zhang
S: Claudin family participates in the pathogenesis of inflammatory
bowel diseases and Colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Front
Immunol. 10:14412019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Al-Zahrani MH, Assidi M, Pushparaj PN,
Al-Maghrabi J, Zari A, Abusanad A, Buhmeida A and Abu-Elmagd M:
Expression pattern, prognostic value and potential microRNA
silencing of FZD8 in breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 26:4772023.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ahmad R, Kumar B, Thapa I, Tamang RL,
Yadav SK, Washington MK, Talmon GA, Yu AS, Bastola DK, Dhawan P and
Singh AB: Claudin-2 protects against colitis-associated cancer by
promoting colitis-associated mucosal healing. J Clin Invest.
133:e1707712023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sourisseau T, Georgiadis A, Tsapara A, Ali
RR, Pestell R, Matter K and Balda MS: Regulation of PCNA and Cyclin
D1 expression and epithelial morphogenesis by the ZO-1-regulated
transcription factor ZONAB/DbpA. Mol Cell Biol. 26:2387–2398. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Balda MS: The tight junction protein ZO-1
and an interacting transcription factor regulate ErbB-2 expression.
EMBO J. 19:2024–2033. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kovacevic Z and Richardson DR: The
metastasis suppressor, Ndrg-1: A new ally in the fight against
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 27:2355–2366. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sun J, Zhang D, Bae DH, Sahni S, Jansson
P, Zheng Y, Zhao Q, Yue F, Zheng M, Kovacevic Z and Richardson DR:
Metastasis suppressor, NDRG1, mediates its activity through
signaling pathways and molecular motors. Carcinogenesis.
34:1943–1954. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tao D, Guan B, Li H and Zhou C: Expression
patterns of claudins in cancer. Heliyon. 9:e213382023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Amoozadeh Y, Anwer S, Dan Q, Venugopal S,
Shi Y, Branchard E, Liedtke E, Ailenberg M, Rotstein OD, Kapus A
and Szászi K: Cell confluence regulates claudin-2 expression:
Possible role for ZO-1 and Rac. Am J Physiol Physiol.
314:C366–C378. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Yang L and Zhang W, Li M, Dam J, Huang K,
Wang Y, Qiu Z, Sun T, Chen P, Zhang Z and Zhang W: Evaluation of
the prognostic relevance of differential claudin gene expression
highlights Claudin-4 as Being Suppressed by TGFβ1 inhibitor in
colorectal cancer. Front Genet. 13:7830162022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chen W, Zhu XN, Wang J, Wang YP and Yang
JL: The expression and biological function of claudin-23 in
colorectal cancer. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 49:331–336.
2018.(In Chinese).
|
|
40
|
Tabariès S, McNulty A, Ouellet V, Annis
MG, Dessureault M, Vinette M, Hachem Y, Lavoie B, Omeroglu A, Simon
HG, et al: Afadin cooperates with Claudin-2 to promote breast
cancer metastasis. Genes Dev. 33:180–193. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang X, Wang H, Li Q and Li T: CLDN2
inhibits the metastasis of osteosarcoma cells via down-regulating
the afadin/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 18:1602018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
González-Mariscal L, Miranda J,
Gallego-Gutiérrez H, Cano-Cortina M and Amaya E: Relationship
between apical junction proteins, gene expression and cancer.
Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1862:1832782020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Dang CV: MYC on the path to cancer. Cell.
149:22–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hirota C, Takashina Y, Ikumi N, Ishizuka
N, Hayashi H, Tabuchi Y, Yoshino Y, Matsunaga T and Ikari A:
Inverse regulation of claudin-2 and −7 expression by p53 and
hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α in colonic MCE301 cells. Tissue
Barriers. 9:18604092021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kim HY, Jeon H, Bae CH, Lee Y, Kim H and
Kim S: Rumex japonicus Houtt. alleviates dextran sulfate
sodium-induced colitis by protecting tight junctions in mice.
Integr Med Res. 9:1003982020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Sena P, Mariani F, Benincasa M, De Leon
MP, Di Gregorio C, Mancini S, Cavani F, Smargiassi A, Palumbo C and
Roncucci L: Morphological and quantitative analysis of BCL6
expression in human colorectal carcinogenesis. Oncol Rep.
31:103–110. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Li J: Context-dependent roles of claudins
in tumorigenesis. Front Oncol. 11:6767812021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Nehme Z, Roehlen N, Dhawan P and Baumert
TF: Tight junction protein signaling and cancer biology. Cells.
12:2432023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Miwa N, Furuse M, Tsukita S, Niikawa N,
Nakamura Y and Furukawa Y: Involvement of claudin-1 in the
beta-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway and its frequent upregulation in
human colorectal cancers. Oncol Res. 12:469–476. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Mankertz J, Hillenbrand B, Tavalali S,
Huber O, Fromm M and Schulzke JD: Functional crosstalk between Wnt
signaling and Cdx-related transcriptional activation in the
regulation of the claudin-2 promoter activity. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 314:1001–1007. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Clements WM, Wang J, Sarnaik A, Kim OJ,
MacDonald J, Fenoglio-Preiser C, Groden J and Lowy AM: Beta-Catenin
mutation is a frequent cause of Wnt pathway activation in gastric
cancer. Cancer Res. 62:3503–3506. 2002.
|
|
52
|
Chiurillo MA: Role of the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in gastric cancer: An in-depth literature review. World J
Exp Med. 5:84–102. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Jang JH, Jung J, Kang HG, Kim W, Kim WJ,
Lee H, Cho JY, Hong R, Kim JW, Chung JY, et al: Kindlin-1 promotes
gastric cancer cell motility through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Sci Rep. 15:24812025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang N, Wei P, Gong A, Chiu WT, Lee HT,
Colman H, Huang H, Xue J, Liu M, Wang Y, et al: FoxM1 promotes
β-catenin nuclear localization and controls Wnt target-gene
expression and glioma tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 20:427–442. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Dey N, Young B, Abramovitz M, Bouzyk M,
Barwick B, De P and Leyland-Jones B: Differential activation of
Wnt-β-catenin pathway in triple negative breast cancer increases
MMP7 in a PTEN dependent manner. PLoS One. 8:e774252013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhang YG, Wu S, Lu R, Zhou D, Zhou J,
Carmeliet G, Petrof E, Claud EC and Sun J: Tight junction CLDN2
gene is a direct target of the Vitamin D receptor. Sci Rep.
5:106422015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Pereira F, Fernández-Barral A, Larriba MJ,
Barbáchano A and González-Sancho JM: From molecular basis to
clinical insights: A challenging future for the vitamin D endocrine
system in colorectal cancer. FEBS J. 291:2485–2518. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Mariadason JM, Nicholas C, L'Italien KE,
Zhuang M, Smartt HJM, Heerdt BG, Yang W, Corner GA, Wilson AJ,
Klampfer L, et al: Gene expression profiling of intestinal
epithelial cell maturation along the crypt-villus axis.
Gastroenterology. 128:1081–1088. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|