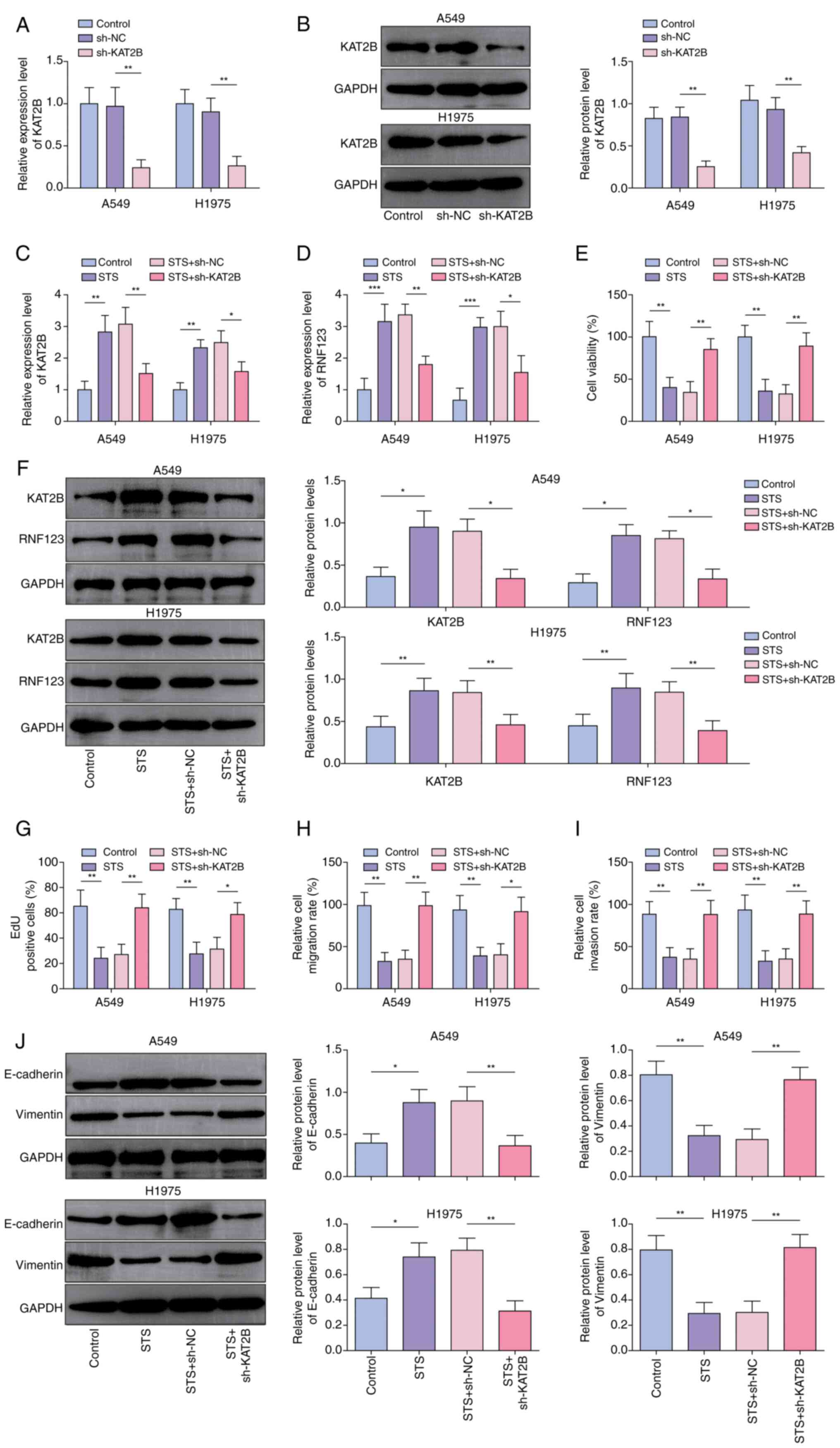
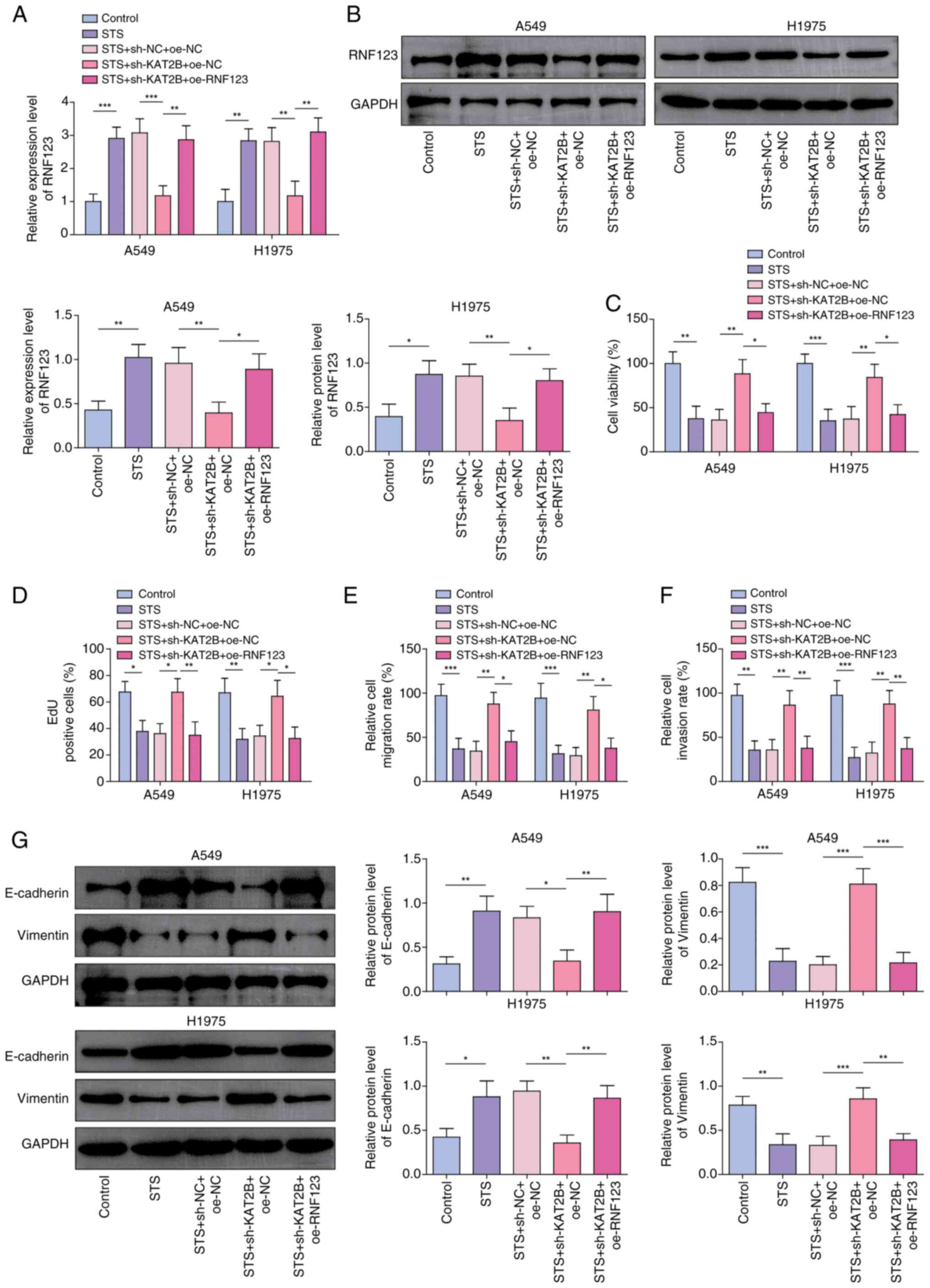
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2022.
|
|
2
|
Feng J, Li J, Qie P, Li Z, Xu Y and Tian
Z: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) PGM5P4-AS1 inhibits lung cancer
progression by up-regulating leucine zipper tumor suppressor
(LZTS3) through sponging microRNA miR-1275. Bioengineered.
12:196–207. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS: Lung cancer
2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med.
41:1–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang LJ, Jeng CJ, Kung HN, Chang CC, Wang
AG, Chau GY, Don MJ and Chau YP: Tanshinone IIA isolated from
Salvia miltiorrhiza elicits the cell death of human
endothelial cells. J Biomed Sci. 12:347–361. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Gao H, Wen T, Gu T, Zhang S and
Yuan Z: Tanshinone IIA attenuates AOM/DSS-induced colorectal
tumorigenesis in mice via inhibition of intestinal inflammation.
Pharm Biol. 59:89–96. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao F, Li M, Liu W and Li W: Inhibition of
EGFR signaling and activation of mitochondrial apoptosis contribute
to tanshinone IIA-mediated tumor suppression in non-small cell lung
cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 13:2757–2769. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang B, Zou F, Xin G, Xiang BL, Zhao JQ,
Yuan SF, Zhang XL and Zhang ZH: Sodium tanshinone IIA sulphate
inhibits angiogenesis in lung adenocarcinoma via mediation of
miR-874/eEF-2K/TG2 axis. Pharm Biol. 61:868–877. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dawson MA and Kouzarides T: Cancer
epigenetics: From mechanism to therapy. Cell. 150:12–27. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guo P, Chen W, Li H, Li M and Li L: The
histone acetylation modifications of breast cancer and their
therapeutic implications. Pathol Oncol Res. 24:807–813. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng Z, Li X, Hou S, Wu Y, Sun Y and Liu
B: K-Ras-ERK1/2 accelerates lung cancer cell development via
mediating H3K18ac through the MDM2-GCN5-SIRT7 axis.
Pharm Biol. 57:701–709. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen G, Zhu X, Li J, Zhang Y, Wang X,
Zhang R, Qin X, Chen X, Wang J, Liao W, et al: Celastrol inhibits
lung cancer growth by triggering histone acetylation and acting
synergically with HDAC inhibitors. Pharmacol Res. 185:1064872022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ma H, Hu ZC, Long Y, Cheng LC, Zhao CY and
Shao MK: Tanshinone IIA microemulsion protects against cerebral
ischemia reperfusion injury via regulating H3K18ac and H4K8ac in
vivo and in vitro. Am J Chin Med. 50:1845–1868. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gulei D, Drula R, Ghiaur G, Buzoianu AD,
Kravtsova-Ivantsiv Y, Tomuleasa C and Ciechanover A: The tumor
suppressor functions of ubiquitin ligase KPC1: From cell-cycle
control to NF-κB regulator. Cancer Res. 83:1762–1767. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Bustos MA, Zhang X, Ramos RI, Tan
C, Iida Y, Chang SC, Salomon MP, Tran K, Gentry R, et al:
Downregulation of the ubiquitin-E3 ligase RNF123 promotes
upregulation of the NF-κB1 target SerpinE1 in aggressive
glioblastoma tumors. Cancers (Basel). 12:10812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Heintzman ND, Hon GC, Hawkins RD,
Kheradpour P, Stark A, Harp LF, Ye Z, Lee LK, Stuart RK, Ching CW,
et al: Histone modifications at human enhancers reflect global
cell-type-specific gene expression. Nature. 459:108–112. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hashemi M, Arani HZ, Orouei S, Fallah S,
Ghorbani A, Khaledabadi M, Kakavand A, Tavakolpournegari A, Saebfar
H, Heidari H, et al: EMT mechanism in breast cancer metastasis and
drug resistance: Revisiting molecular interactions and biological
functions. Biomed Pharmacother. 155:1137742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Serrano-Gomez SJ, Maziveyi M and Alahari
SK: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition through
epigenetic and post-translational modifications. Mol Cancer.
15:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hou YS, Wang JZ, Shi S, Han Y, Zhang Y,
Zhi JX, Xu C, Li FF, Wang GY and Liu SL: Identification of
epigenetic factor KAT2B gene variants for possible roles in
congenital heart diseases. Biosci Rep. 40:BSR201917792020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou X, Wang N, Zhang Y, Yu H and Wu Q:
KAT2B is an immune infiltration-associated biomarker predicting
prognosis and response to immunotherapy in non-small cell lung
cancer. Invest New Drugs. 40:43–57. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Megyesfalvi Z, Gay CM, Popper H, Pirker R,
Ostoros G, Heeke S, Lang C, Hoetzenecker K, Schwendenwein A,
Boettiger K, et al: Clinical insights into small cell lung cancer:
Tumor heterogeneity, diagnosis, therapy, and future directions. CA
Cancer J Clin. 73:620–652. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xu S and Liu P: Tanshinone II-A: New
perspectives for old remedies. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 23:149–153.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song Q, Yang L, Han Z, Wu X, Li R, Zhou L,
Liu N, Sui H, Cai J, Wang Y, et al: Tanshinone IIA inhibits
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through hindering β-arrestin1
mediated β-catenin signaling pathway in colorectal cancer. Front
Pharmacol. 11:5866162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yuan F, Zhao ZT, Jia B, Wang YP and Lei W:
TSN inhibits cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and EMT
through regulating miR-874/HMGB2/β-catenin pathway in gastric
cancer. Neoplasma. 67:1012–1021. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie J, Liu J, Liu H, Liang S, Lin M, Gu Y,
Liu T, Wang D, Ge H and Mo SL: The antitumor effect of tanshinone
IIA on anti-proliferation and decreasing VEGF/VEGFR2 expression on
the human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell line. Acta Pharm Sin
B. 5:554–563. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng CY and Su CC: Tanshinone IIA may
inhibit the growth of small cell lung cancer H146 cells by
up-regulating the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and decreasing mitochondrial
membrane potential. Mol Med Rep. 3:645–650. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fang ZY, Zhang M, Liu JN, Zhao X, Zhang YQ
and Fang L: Tanshinone IIA: A review of its anticancer effects.
Front Pharmacol. 11:6110872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo W: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma ecology
theory: Cancer as multidimensional spatiotemporal ‘unity of ecology
and evolution’ pathological ecosystem. Theranostics. 13:1607–1631.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Berndsen CE and Wolberger C: New insights
into ubiquitin E3 ligase mechanism. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
21:301–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Iida Y, Ciechanover A, Marzese DM, Hata K,
Bustos M, Ono S, Wang J, Salomon MP, Tran K, Lam S, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of KPC1 ubiquitin ligase affects the NF-κB
pathway in melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 23:4831–4842. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shvedunova M and Akhtar A: Modulation of
cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:329–349. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li L, Zhang J and Cao S: Lysine
acetyltransferase 2B predicts favorable prognosis and functions as
anti-oncogene in cervical carcinoma. Bioengineered. 12:2563–2575.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|