|
1
|
Reid PA, Wilson P, Li Y, Marcu LG and
Bezak E: Current understanding of cancer stem cells: Review of
their radiobiology and role in head and neck cancers. Head Neck.
39:1920–1932. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Johnson DE, Burtness B, Leemans CR, Lui
VWY, Bauman JE and Grandis JR: Head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 6:922020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mody MD, Rocco JW, Yom SS, Haddad RI and
Saba NF: Head and neck cancer. Lancet. 398:2289–2299. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chi AC, Day TA and Neville BW: Oral cavity
and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma-an update. CA Cancer J
Clin. 65:401–421. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wuerdemann N, Wittekindt C, Sharma SJ,
Prigge ES, Reuschenbach M, Gattenlöhner S, Klussmann JP and Wagner
S: Risk factors for overall survival outcome in surgically treated
human Papillomavirus-Negative and positive patients with
oropharyngeal cancer. Oncol Res Treat. 40:320–327. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu W, Chen Y, Putluri N, Osman A, Coarfa
C, Putluri V, Kamal AHM, Asmussen JK, Katsonis P, Myers JN, et al:
Evolution of cisplatin resistance through coordinated metabolic
reprogramming of the cellular reductive state. Br J Cancer.
128:2013–2024. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Azharuddin M, Roberg K, Dhara AK, Jain MV,
Darcy P, Hinkula J, Slater NKH and Patra HK: Dissecting multi drug
resistance in head and neck cancer cells using multicellular tumor
spheroids. Sci Rep. 9:200662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu H, Li B, Wang J, Tan Y, Xu M, Xu W and
Lu H: New advances into cisplatin resistance in head and neck
squamous carcinoma: Mechanisms and therapeutic aspects. Biomed
Pharmacother. 163:1147782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mackenzie IC: Stem cell properties and
epithelial malignancies. Eur J Cancer. 42:1204–1212. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Norouzi A, Liaghat M, Bakhtiyari M,
Noorbakhsh Varnosfaderani SM, Zalpoor H, Nabi-Afjadi M and Molania
T: The potential role of COVID-19 in progression, chemo-resistance,
and tumor recurrence of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC). Oral
Oncol. 144:1064832023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kang SH, Oh SY, Lee KY, Lee HJ, Kim MS,
Kwon TG, Kim JW, Lee ST, Choi SY and Hong SH: Differential effect
of cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles on
cisplatin resistance in oral squamous cell carcinoma via
miR-876-3p. Theranostics. 14:460–479. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Usman S, Waseem NH, Nguyen TKN, Mohsin S,
Jamal A, The MT and Waseem A: Vimentin is at the heart of
epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT) mediated metastasis.
Cancers (Basel). 13:49852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gong Y, Fan Z, Luo G, Yang C, Huang Q, Fan
K, Cheng H, Jin K, Ni Q, Yu X and Liu C: The role of necroptosis in
cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer. 18:1002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hsu SK, Li CY, Lin IL, Syue WJ, Chen YF,
Cheng KC, Teng YN, Lin YH, Yen CH and Chiu CC: Inflammation-related
pyroptosis, a novel programmed cell death pathway, and its
crosstalk with immune therapy in cancer treatment. Theranostics.
11:8813–8835. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu J, Kuang F, Kang R and Tang D:
Alkaliptosis: A new weapon for cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther.
27:267–269. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tong X, Tang R, Xiao M, Xu J, Wang W,
Zhang B, Liu J, Yu X and Shi S: Targeting cell death pathways for
cancer therapy: Recent developments in necroptosis, pyroptosis,
ferroptosis, and cuproptosis research. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1742022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang C, Liu X, Jin S, Chen Y and Guo R:
Ferroptosis in cancer therapy: A novel approach to reversing drug
resistance. Mol Cancer. 21:472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun
X, Kang R and Tang D: Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death
Differ. 23:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Conrad M and Pratt DA: Publisher
correction: The chemical basis of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol.
16:223–224. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis turns 10:
Emerging mechanisms, physiological functions, and therapeutic
applications. Cell. 185:2401–2421. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xue Y, Jiang X, Wang J, Zong Y, Yuan Z,
Miao S and Mao X: Effect of regulatory cell death on the occurrence
and development of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Biomark
Res. 11:22023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim EH, Shin D, Lee J, Jung AR and Roh JL:
CISD2 inhibition overcomes resistance to sulfasalazine-induced
ferroptotic cell death in head and neck cancer. Cancer Lett.
432:180–190. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Roh JL, Kim EH, Jang HJ, Park JY and Shin
D: Induction of ferroptotic cell death for overcoming cisplatin
resistance of head and neck cancer. Cancer Lett. 381:96–103. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ye J, Jiang X, Dong Z, Hu S and Xiao M:
Low-Concentration PTX And RSL3 inhibits tumor cell growth
synergistically by inducing ferroptosis in mutant p53
hypopharyngeal squamous carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 11:9783–9792.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dersh D, Hollý J and Yewdell JW: A few
good peptides: MHC class I-based cancer immunosurveillance and
immunoevasion. Nat Rev Immunol. 21:116–128. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mohme M, Riethdorf S and Pantel K:
Circulating and disseminated tumour Cells-mechanisms of immune
surveillance and escape. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:155–167. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zou W: Immunosuppressive networks in the
tumour environment and their therapeutic relevance. Nat Rev Cancer.
5:263–274. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, Gijón M, Kennedy
PD, Johnson JK, Liao P, Lang X, Kryczek I, Sell A, et al:
CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer
immunotherapy. Nature. 569:270–274. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li C, Wang X, Qin R, Zhong Z and Sun C:
Identification of a ferroptosis gene set that mediates the
prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Front
Genet. 12:6980402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu W, Wu Y, Huang S and Zhang D: A
Ferroptosis-related gene signature for predicting the prognosis and
drug sensitivity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Front
Genet. 12:7554862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hoadley KA, Yau C, Hinoue T, Wolf DM,
Lazar AJ, Drill E, Shen R, Taylor AM, Cherniack AD, Thorsson V, et
al: Cell-of-Origin patterns dominate the molecular classification
of 10,000 tumors from 33 types of cancer. Cell. 173:291–304.e6.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Martens-de Kemp SR BB, Smeets S, Voorham
Q, Rustenburg F, de Boer VD, Brink A, van Wieringen WN and
Brakenhoff RH: GEO accession number [GSE83519]. NCBI(GEO) (ed.), .
2017.
|
|
35
|
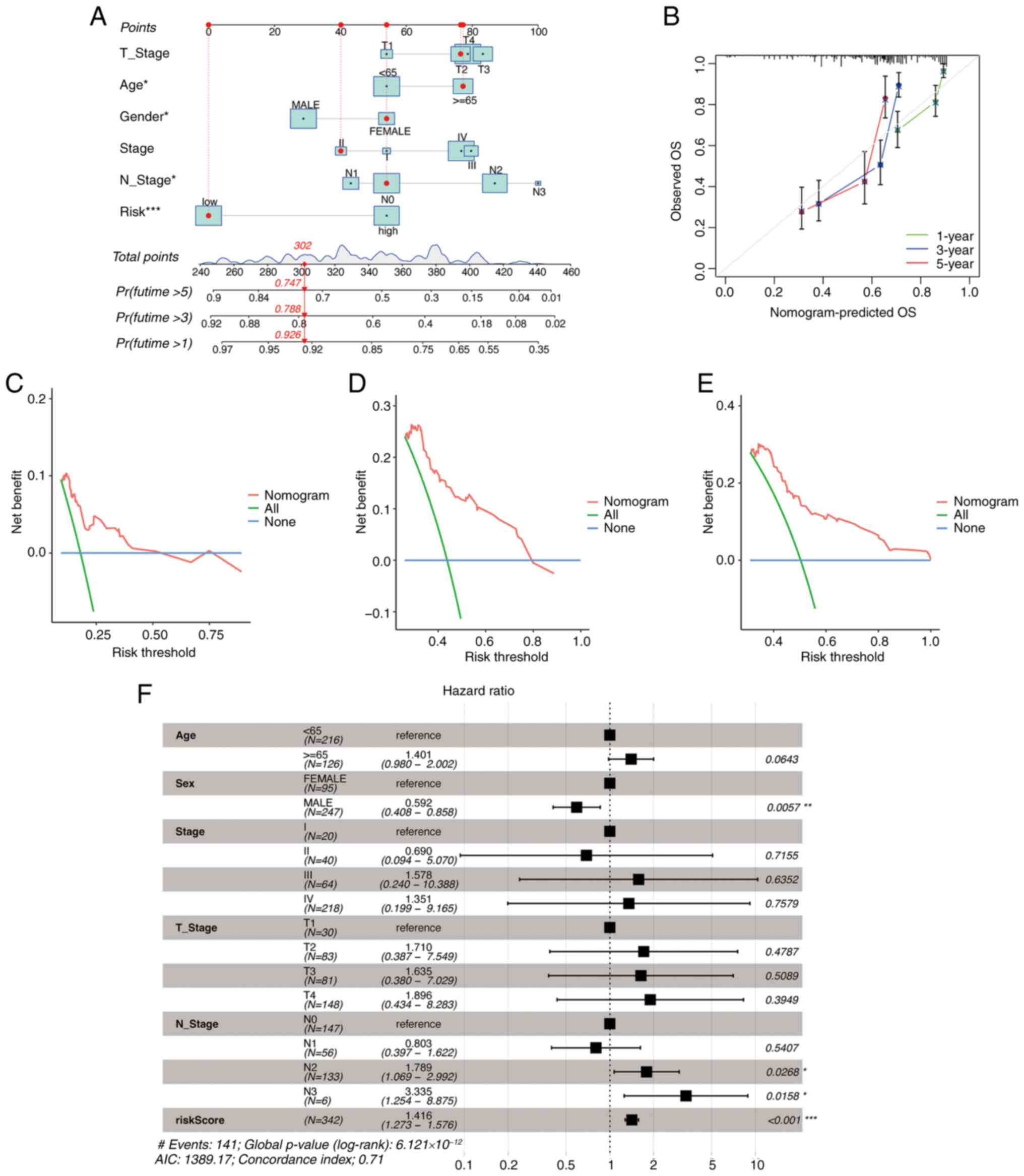
Vickers AJ, Cronin AM, Elkin EB and Gonen
M: Extensions to decision curve analysis, a novel method for
evaluating diagnostic tests, prediction models and molecular
markers. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 8:532008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Maeser D, Gruener RF and Huang RS:
oncoPredict: An R package for predicting in vivo or cancer patient
drug response and biomarkers from cell line screening data. Brief
Bioinform. 22:bbab2602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen XJ, Guo CH, Yang Y, Wang ZC, Liang
YY, Cai YQ, Cui XF, Fan LS and Wang W: HPV16 integration regulates
ferroptosis resistance via the c-Myc/miR-142-5p/HOXA5/SLC7A11 axis
during cervical carcinogenesis. Cell Biosci. 14:1292024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang J and Gu Z: Ferroptosis in head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma: From pathogenesis to treatment. Front
Pharmacol. 15:12834652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hamid S, Khan MS, Khan MA, Muhammad N,
Singh M, Al-Shabeeb Akil AS, Bhat AA and Macha MA: Human papilloma
virus infection drives unique metabolic and immune profiles in head
and neck and cervical cancers: Implications for targeted therapies
and prognostic markers. Discov Oncol. 16:6762025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
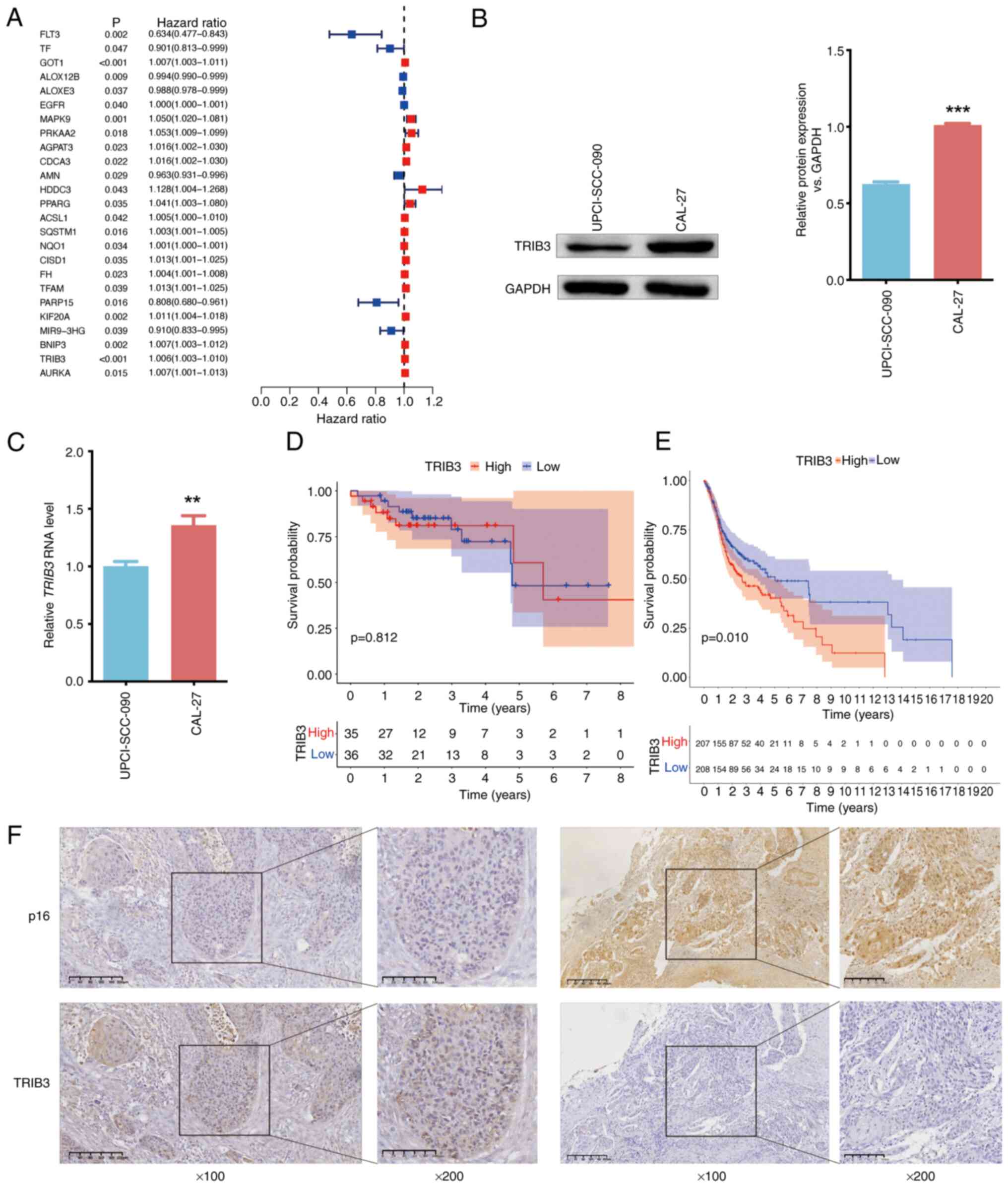
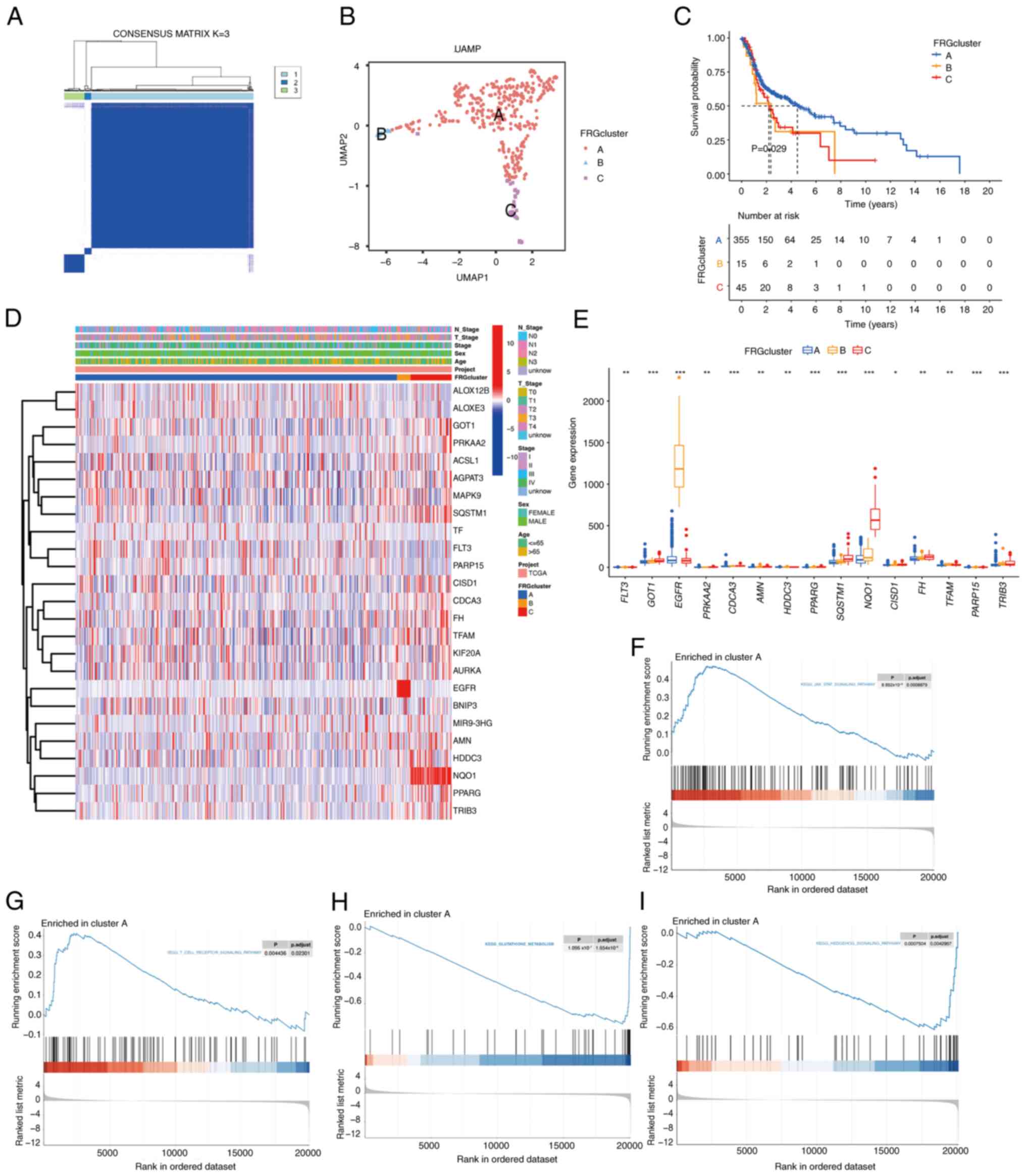
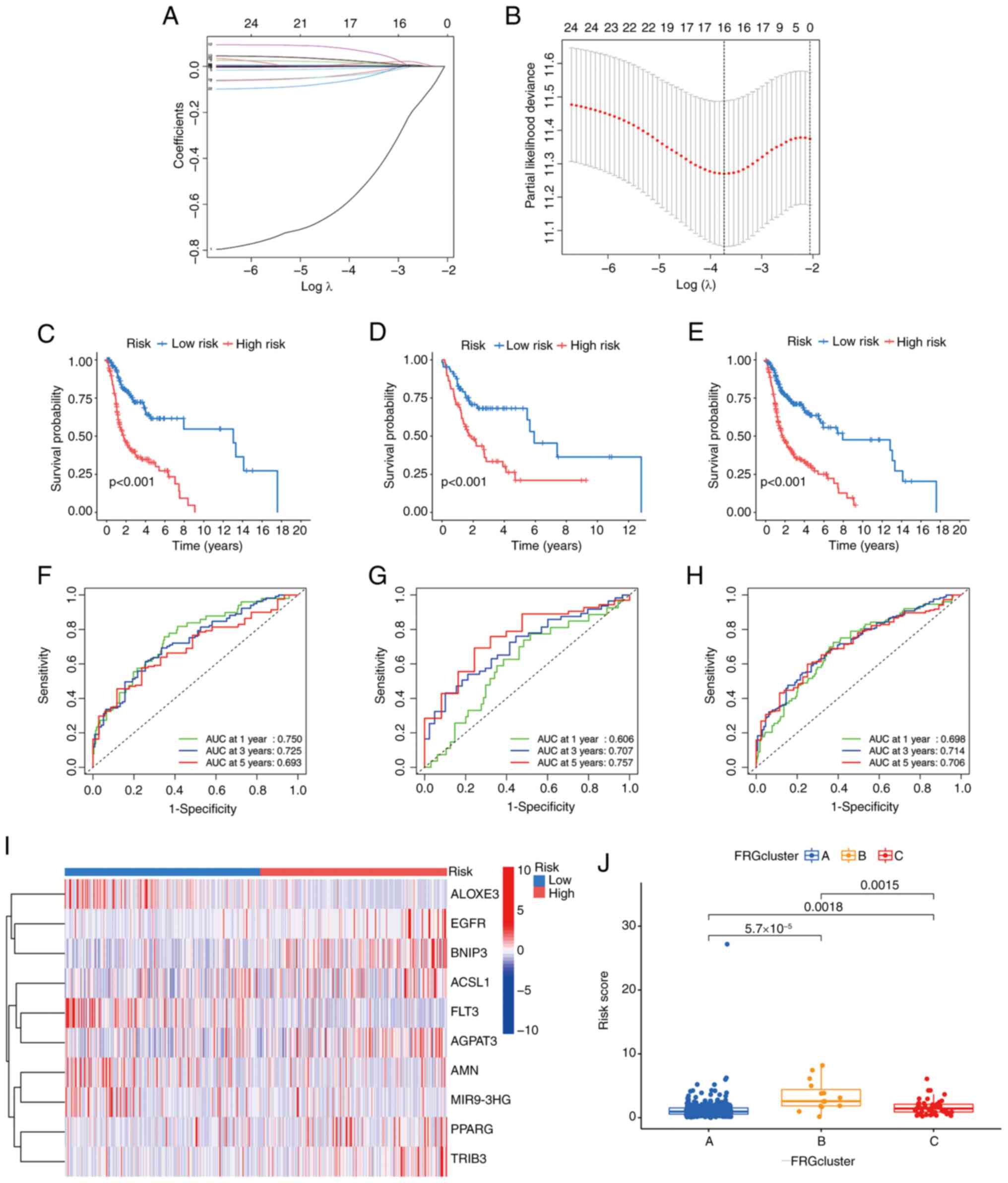
Shen P, Zhang TY and Wang SY: TRIB3
promotes oral squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation by
activating the AKT signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 21:3132021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wennemers M, Bussink J, Scheijen B,
Nagtegaal ID, van Laarhoven HW, Raleigh JA, Varia MA, Heuvel JJ,
Rouschop KM, Sweep FC and Span PN: Tribbles homolog 3 denotes a
poor prognosis in breast cancer and is involved in hypoxia
response. Breast Cancer Res. 13:R822011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhou H, Luo Y, Chen JH, Hu J, Luo YZ, Wang
W, Zeng Y and Xiao L: Knockdown of TRB3 induces apoptosis in human
lung adenocarcinoma cells through regulation of Notch 1 expression.
Mol Med Rep. 8:47–52. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hong B, Zhou J, Ma K, Zhang J, Xie H,
Zhang K, Li L, Cai L, Zhang N, Zhang Z and Gong K: TRIB3 promotes
the proliferation and invasion of renal cell carcinoma cells via
activating MAPK signaling pathway. Int J Biol Sci. 15:587–597.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Miyoshi N, Ishii H, Mimori K, Takatsuno Y,
Kim H, Hirose H, Sekimoto M, Doki Y and Mori M: Abnormal expression
of TRIB3 in colorectal cancer: A novel marker for prognosis. Br J
Cancer. 101:1664–1670. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Tang Z, Chen H, Zhong D, Wei W, Liu L,
Duan Q, Han B and Li G: TRIB3 facilitates glioblastoma progression
via restraining autophagy. Aging (Albany NY). 12:25020–25034. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Izrailit J, Jaiswal A, Zheng W, Moran MF
and Reedijk M: Cellular stress induces TRB3/USP9×-dependent Notch
activation in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1048–1057. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hua F, Mu R, Liu J, Xue J, Wang Z, Lin H,
Yang H, Chen X and Hu Z: TRB3 interacts with SMAD3 promoting tumor
cell migration and invasion. J Cell Sci. 124:3235–3246. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang XD, Liu ZY, Wang MS, Guo YX, Wang
XK, Luo K, Huang S and Li RF: Mechanisms and regulations of
ferroptosis. Front Immunol. 14:12694512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhu X, Zhang F, Zhang W, He J, Zhao Y and
Chen X: Prognostic role of epidermal growth factor receptor in head
and neck cancer: A meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 108:387–397. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lv D, Zhong C, Dixit D, Yang K, Wu Q,
Godugu B, Prager BC, Zhao G, Wang X and Xie Q: EGFR promotes ALKBH5
nuclear retention to attenuate N6-methyladenosine and protect
against ferroptosis in glioblastoma. Mol Cell. 83:4334–4351.e7.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang Q, Li N, Deng L, Jiang X, Zhang Y,
Lee LTO and Zhang H: ACSL1-induced ferroptosis and platinum
resistance in ovarian cancer by increasing FSP1 N-myristylation and
stability. Cell Death Discov. 9:832023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Qin Y, Pei Z, Feng Z, Lin P, Wang S, Li Y,
Huo F, Wang Q, Wang Z, Chen ZN, et al: Oncogenic activation of YAP
signaling sensitizes ferroptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma via
ALOXE3-mediated lipid peroxidation accumulation. Front Cell Dev
Biol. 9:7515932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Han L, Bai L, Qu C, Dai E, Liu J, Kang R,
Zhou D, Tang D and Zhao Y: PPARG-mediated ferroptosis in dendritic
cells limits antitumor immunity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
576:33–39. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sabatier M, Birsen R, Lauture L, Mouche S,
Angelino P, Dehairs J, Goupille L, Boussaid I, Heiblig M, Boet E,
et al: C/EBPα confers dependence to fatty acid anabolic pathways
and vulnerability to lipid oxidative Stress-induced ferroptosis in
FLT3-Mutant leukemia. Cancer Discov. 13:1720–1747. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cui Z, Fu Y, Yang Z, Gao Z, Feng H, Zhou
M, Zhang L and Chen C: Comprehensive analysis of a ferroptosis
pattern and associated prognostic signature in acute myeloid
leukemia. Front Pharmacol. 13:8663252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Meng J, Du H, Lu J and Wang H:
Construction and validation of a predictive nomogram for
ferroptosis-related genes in osteosarcoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
149:14227–14239. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang J, Deng Y, Zhang H, Zhang Z, Jin X,
Xuan Y, Zhang Z and Ma X: Single-cell RNA-Seq analysis reveals
ferroptosis in the tumor microenvironment of clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 24:90922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Jiang W, Song Y, Zhong Z, Gao J and Meng
X: Ferroptosis-related long Non-Coding RNA signature contributes to
the prediction of prognosis outcomes in head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. Front Genet. 12:7858392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Friedmann Angeli JP, Krysko DV and Conrad
M: Ferroptosis at the crossroads of Cancer-acquired drug resistance
and immune evasion. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:405–414. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|