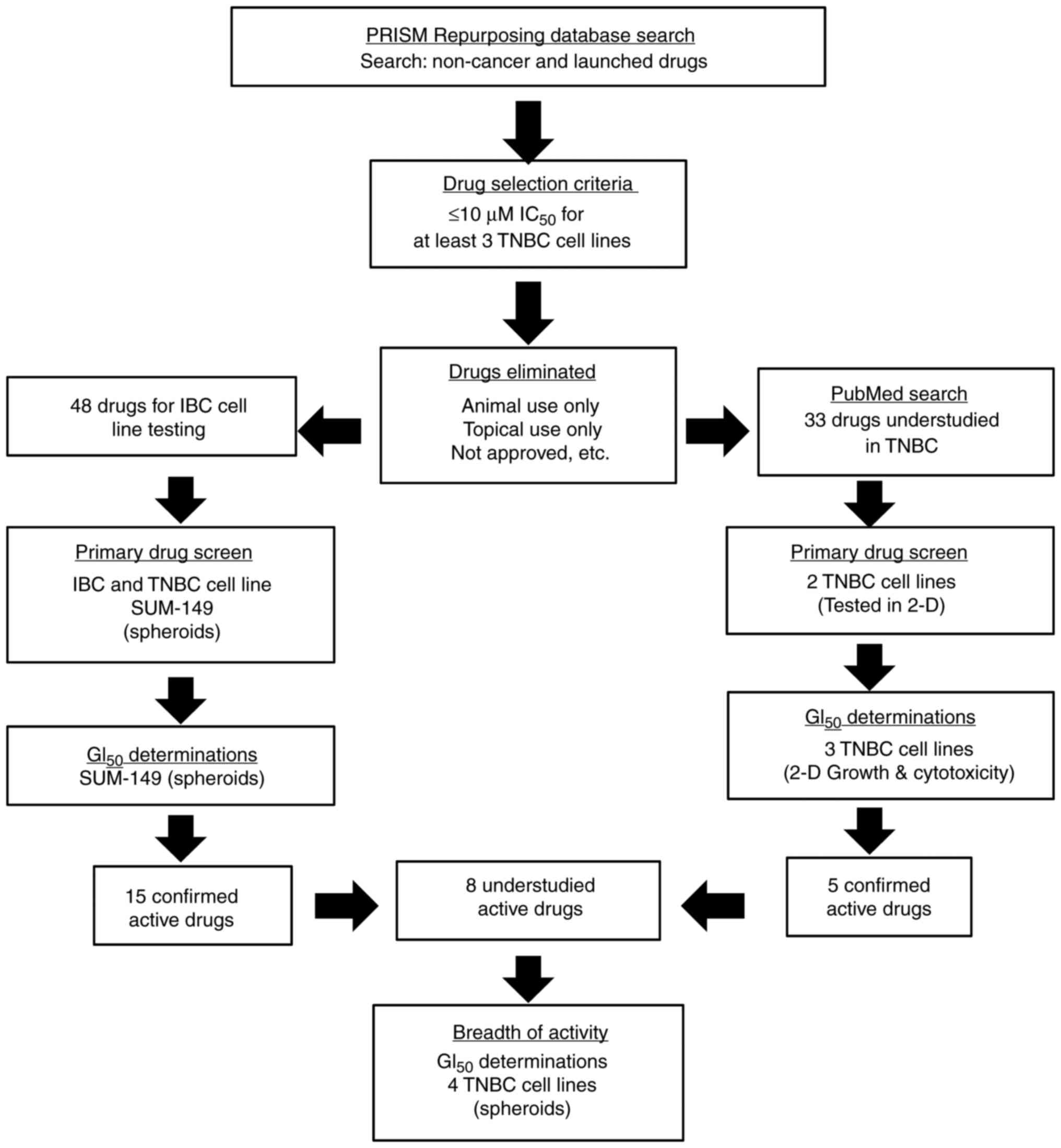
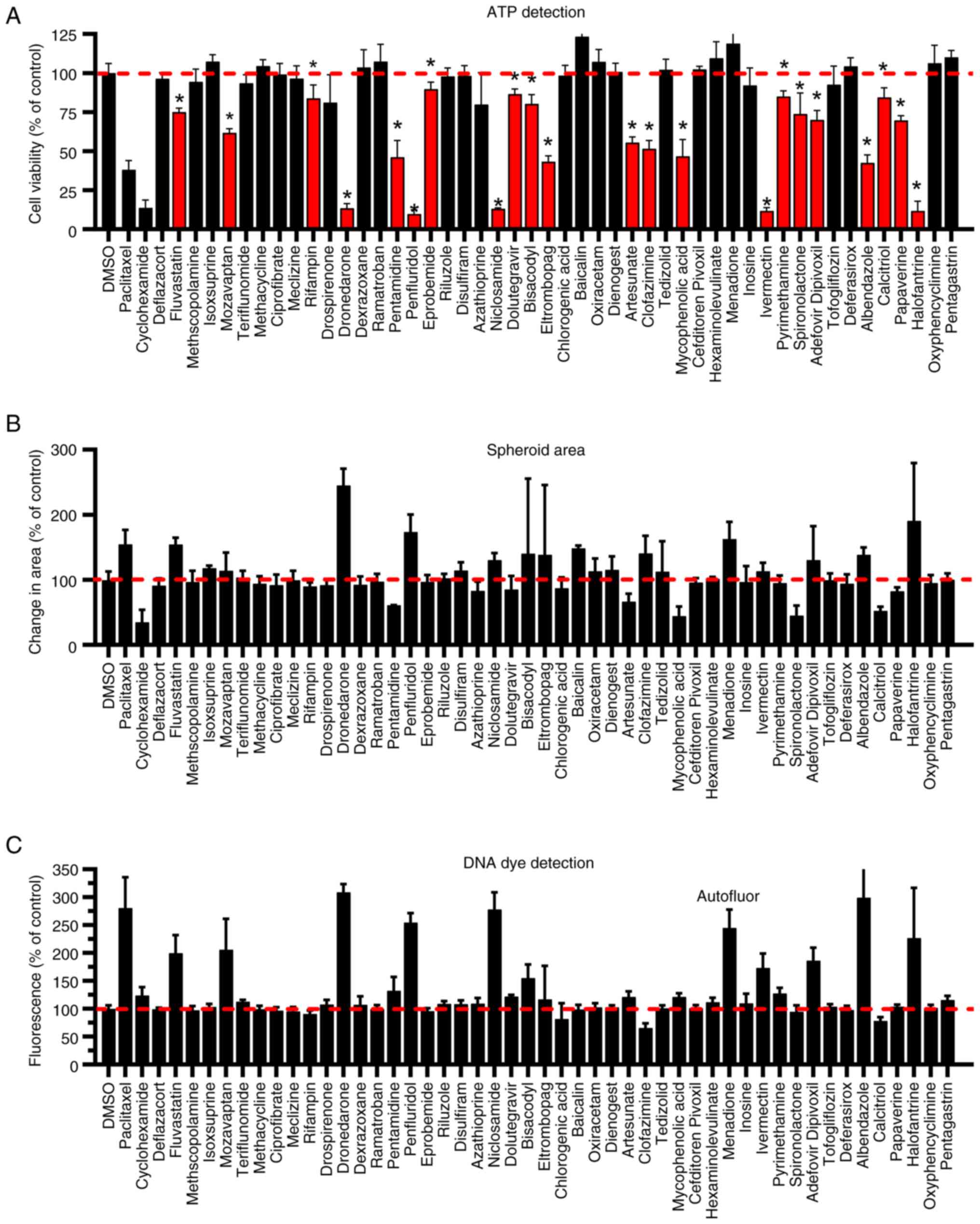
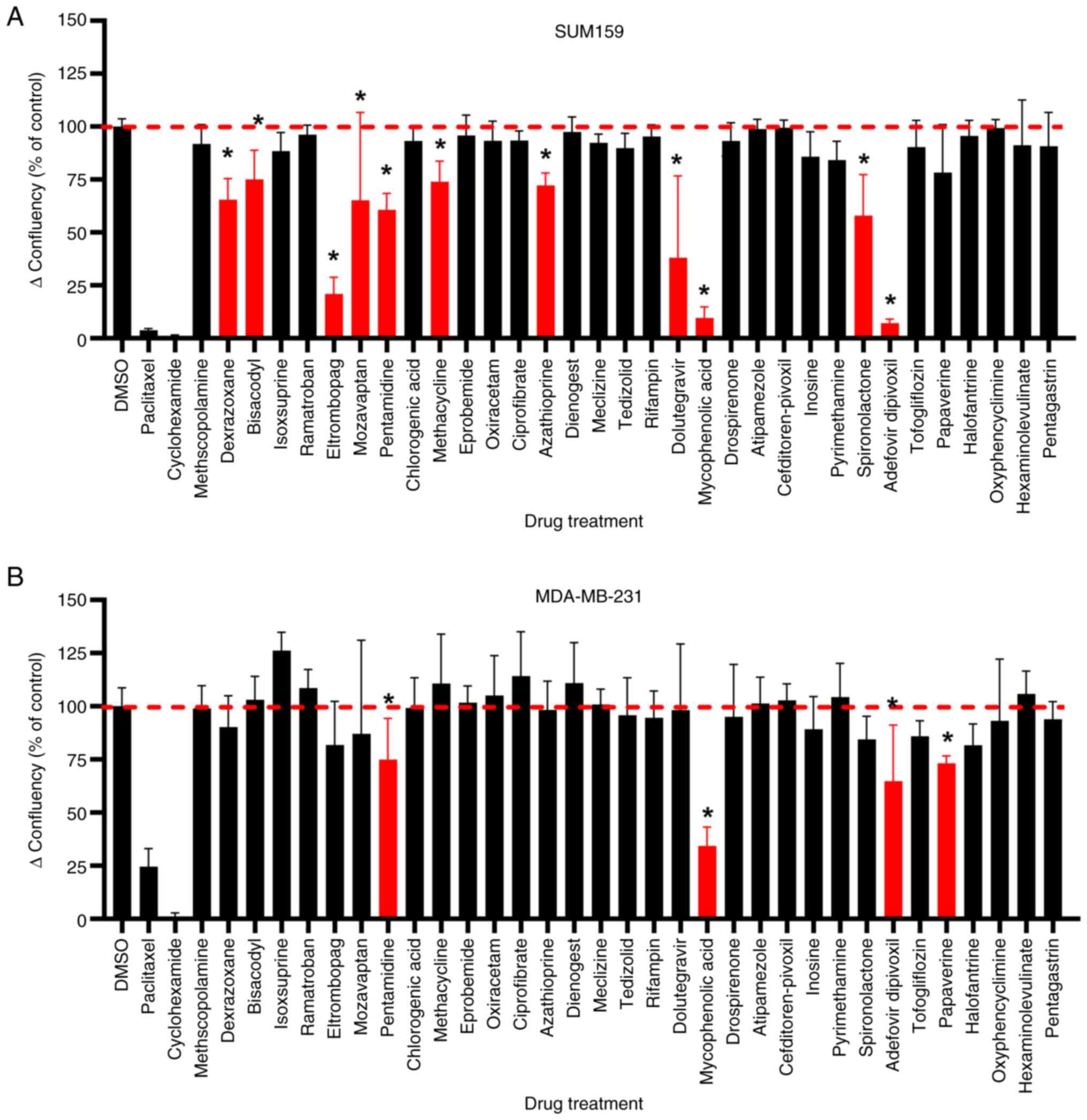
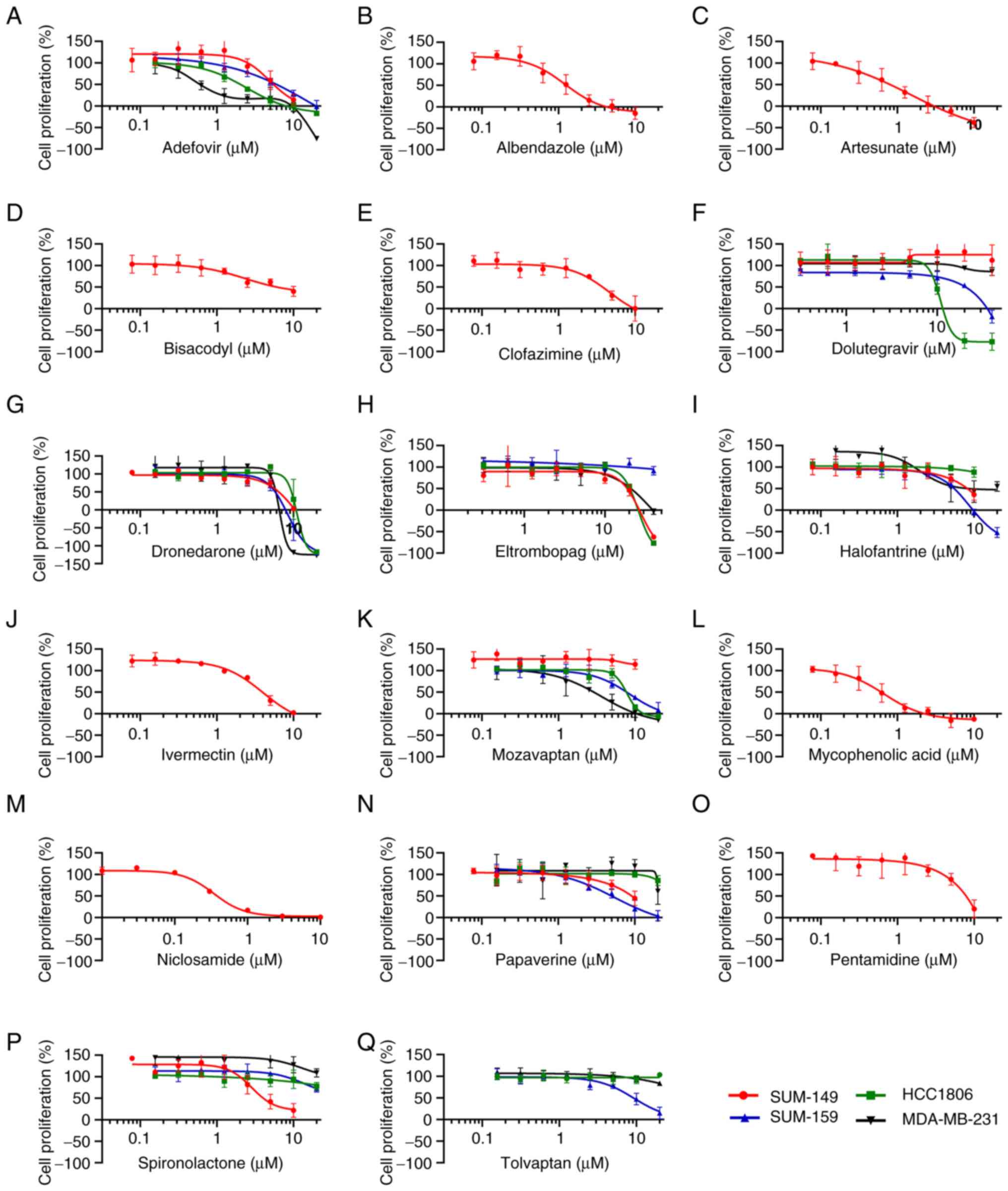
|
1
|
Beňačka R, Szabóová D, Guľašová Z,
Hertelyová Z and Radoňák J: Classic and new markers in diagnostics
and classification of breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 14:54442022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee J: Current treatment landscape for
early triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC). J Clin Med.
12:15242023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Russnes HG, Lingjærde OC, Børresen-Dale AL
and Caldas C: Breast cancer molecular stratification: From
intrinsic subtypes to integrative clusters. Am J Pathol.
187:2152–2162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devi GR, Hough H, Barrett N, Cristofanilli
M, Overmoyer B, Spector N, Ueno NT, Woodward W, Kirkpatrick J,
Vincent B, et al: Perspectives on inflammatory breast cancer (IBC)
research, clinical management and community engagement from the
duke IBC consortium. J Cancer. 10:3344–3351. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boussen H, Berrazaga Y, Sherif K, Manai M,
Berrada N, Mejri N, Siala I, Levine PH and Cristofanilli M:
Inflammatory breast cancer: Epidemiologic data and therapeutic
results. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 384:1–23. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matro JM, Li T, Cristofanilli M, Hughes
ME, Ottesen RA, Weeks JC and Wong YN: Inflammatory breast cancer
management in the national comprehensive cancer network: The
disease, recurrence pattern, and outcome. Clin Breast Cancer.
15:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hester RH, Hortobagyi GN and Lim B:
Inflammatory breast cancer: Early recognition and diagnosis is
critical. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 225:392–396. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Biswas T, Efird JT, Prasad S, James SE,
Walker PR and Zagar TM: Inflammatory TNBC breast cancer: Demography
and clinical outcome in a large cohort of patients with TNBC. Clin
Breast Cancer. 16:212–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chainitikun S, Saleem S, Lim B, Valero V
and Ueno NT: Update on systemic treatment for newly diagnosed
inflammatory breast cancer. J Adv Res. 29:1–12. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Al Khzem AH, Gomaa MS, Alturki MS, Tawfeeq
N, Sarafroz M, Alonaizi SM, Al Faran A, Alrumaihi LA, Alansari FA
and Alghamdi AA: Drug repurposing for cancer treatment: A
comprehensive review. Int J Mol Sci. 25:124412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Szalai P and Engedal N: An image-based
assay for high-throughput analysis of cell proliferation and cell
death of adherent cells. Bio Protoc. 8:e28352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Corsello SM, Nagari RT, Spangler RD,
Rossen J, Kocak M, Bryan JG, Humeidi R, Peck D, Wu X, Tang AA, et
al: Discovering the anti-cancer potential of non-oncology drugs by
systematic viability profiling. Nat Cancer. 1:235–248. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Culley J, Nagle PW, Dawson JC and
Carragher NO: Patient derived glioma stem cell spheroid reporter
assays for live cell high content analysis. SLAS Discov. 28:13–19.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pfab C, Schnobrich L, Eldnasoury S,
Gessner A and El-Najjar N: Repurposing of antimicrobial agents for
cancer therapy: What do we know? Cancers (Basel). 13:31932021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhattacharya U, Kamran M, Manai M,
Cristofanilli M and Ince TA: Cell-of-origin targeted drug
repurposing for triple-negative and inflammatory breast carcinoma
with HDAC and HSP90 inhibitors combined with niclosamide. Cancers
(Basel). 15:3322023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
da Silva Fernandes T, Gillard BM, Dai T,
Martin JC, Chaudhry KA, Dugas SM, Fisher AA, Sharma P, Wu R,
Attwood KM, et al: Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase 2 (IMPDH2)
modulates response to therapy and chemo-resistance in triple
negative breast cancer. Sci Rep. 15:10612025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim JH, Park S, Jung E, Shin J, Kim YJ,
Kim JY, Sessler JL, Seo JH and Kim JS: A dual-action
niclosamide-based prodrug that targets cancer stem cells and
inhibits TNBC metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
120:e23040811202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Greenshields AL, Fernando W and Hoskin DW:
The anti-malarial drug artesunate causes cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis of triple-negative MDA-MB-468 and HER2-enriched SK-BR-3
breast cancer cells. Exp Mol Pathol. 107:10–22. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zadeh T, Lucero M and Kandpal RP:
Artesunate-induced cellular effects are mediated by specific EPH
receptors and ephrin ligands in breast carcinoma cells. Cancer
Genomics Proteomics. 19:19–26. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu H, Sun H, Zhang B, Liu S, Deng S, Weng
Z, Zuo B, Yang J and He Y: 18F-FDG PET imaging for
monitoring the early anti-tumor effect of albendazole on
triple-negative breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 27:372–380. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Priotti J, Baglioni MV, Garcia A, Rico MJ,
Leonardi D, Lamas MC and Menacho Márquez M: Repositioning of
anti-parasitic drugs in cyclodextrin inclusion complexes for
treatment of triple-negative breast cancer. AAPS PharmSciTech.
19:3734–3741. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kieliszek AM, Mobilio D, Bassey-Archibong
BI, Johnson JW, Piotrowski ML, de Araujo ED, Sedighi A, Aghaei N,
Escudero L, Ang P, et al: De novo GTP synthesis is a metabolic
vulnerability for the interception of brain metastases. Cell Rep
Med. 5:1017552024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Benjanuwattra J, Chaiyawat P, Pruksakorn D
and Koonrungsesomboon N: Therapeutic potential and molecular
mechanisms of mycophenolic acid as an anticancer agent. Eur J
Pharmacol. 887:1735802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abdelwahab MT, Wasserman S, Brust JCM,
Gandhi NR, Meintjes G, Everitt D, Diacon A, Dawson R, Wiesner L,
Svensson EM, et al: Clofazimine pharmacokinetics in patients with
TB: Dosing implications. J Antimicrob Chemother. 75:3269–3277.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bullingham RE, Nicholls AJ and Kamm BR:
Clinical pharmacokinetics of mycophenolate mofetil. Clin
Pharmacokinet. 34:429–455. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ceballos L, Alvarez L, Lifschitz A and
Lanusse C: Ivermectin systemic availability in adult volunteers
treated with different oral pharmaceutical formulations. Biomed
Pharmacother. 160:1143912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Friedrich C, Richter E, Trommeshauser D,
de Kruif S, van Iersel T, Mandel K and Gessner U: Absence of
excretion of the active moiety of bisacodyl and sodium picosulfate
into human breast milk: An open-label, parallel-group,
multiple-dose study in healthy lactating women. Drug Metab
Pharmacokinet. 26:458–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Girard PM, Clair B, Certain A, Bidault R,
Matheron S, Regnier B and Farinotti R: Comparison of plasma
concentrations of aerosolized pentamidine in nonventilated and
ventilated patients with pneumocystosis. Am Rev Respir Dis.
140:1607–1610. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kouakou YI, Tod M, Leboucher G, Lavoignat
A, Bonnot G, Bienvenu AL and Picot S: Systematic review of
artesunate pharmacokinetics: Implication for treatment of resistant
malaria. Int J Infect Dis. 89:30–44. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Milton KA, Edwards G, Ward SA, Orme ML and
Breckenridge AM: Pharmacokinetics of halofantrine in man: Effects
of food and dose size. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 28:71–77. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Naccarelli GV, Wolbrette DL, Levin V,
Samii S, Banchs JE, Penny-Peterson E and Gonzalez MD: Safety and
efficacy of dronedarone in the treatment of atrial
fibrillation/flutter. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 5:103–119. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ross LL, Song IH, Arya N, Choukour M, Zong
J, Huang SP, Eley T, Wynne B and Buchanan AM: No clinically
significant pharmacokinetic interactions between dolutegravir and
daclatasvir in healthy adult subjects. BMC Infect Dis. 16:3472016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schulz M and Schmoldt A: Therapeutic and
toxic blood concentrations of more than 800 drugs and other
xenobiotics. Pharmazie. 58:447–474. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Schweizer MT, Haugk K, McKiernan JS,
Gulati R, Cheng HH, Maes JL, Dumpit RF, Nelson PS, Montgomery B,
McCune JS, et al: A phase I study of niclosamide in combination
with enzalutamide in men with castration-resistant prostate cancer.
PLoS One. 13:e01983892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Williams DD, Peng B, Bailey CK, Wire MB,
Deng Y, Park JW, Collins DA, Kapsi SG and Jenkins JM: Effects of
food and antacids on the pharmacokinetics of eltrombopag in healthy
adult subjects: Two single-dose, open-label, randomized-sequence,
crossover studies. Clin Ther. 31:764–776. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu FG, Zhang ZJ, Dong HJ, Tian Y, Liu Y
and Chen Y: Bioequivalence assessment of two formulations of
spironolactone in Chinese healthy male volunteers.
Arzneimittelforschung. 58:117–121. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zou J, Di B, Zhang J, Dai L, Ding L, Zhu
Y, Fan H and Xiao D: Determination of adefovir by LC-ESI-MS-MS and
its application to a pharmacokinetic study in healthy Chinese
volunteers. J Chromatogr Sci. 47:889–894. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Abbas ZN, Al-Saffar AZ, Jasim SM and
Sulaiman GM: Comparative analysis between 2D and 3D colorectal
cancer culture models for insights into cellular morphological and
transcriptomic variations. Sci Rep. 13:183802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Filipiak-Duliban A, Brodaczewska K,
Kajdasz A and Kieda C: Spheroid culture differentially affects
cancer cell sensitivity to drugs in melanoma and RCC models. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:11662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li J, Lin J, Lin JR, Farris M, Robbins L,
Andrada L, Grohol B, Nong S and Liu Y: Dolutegravir inhibits
proliferation and motility of BT-20 tumor cells through inhibition
of human endogenous retrovirus type K. Cureus.
14:e265252022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen M, Hu L, Bao X, Ye K, Li Y, Zhang Z,
Kaufmann SH, Xiao J and Dai H: Eltrombopag directly activates BAK
and induces apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 14:3942023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lin Y, Shi Q, Yang G, Shi F, Zhou Y, Wang
T, Xu P, Li P, Liu Z, Sun H, et al: A small-molecule drug inhibits
autophagy gene expression through the central regulator TFEB. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 120:e22136701202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cui C, Pan Y, Zhang C, Zhu D, Xuan Y, Hao
P, Ke X, Zhou X and Qu Y: Eltrombopag binds SDC4 directly and
enhances MAPK signaling and macropinocytosis in cancer cells. Am J
Cancer Res. 12:2697–2710. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Spitz AZ, Zacharioudakis E, Reyna DE,
Garner TP and Gavathiotis E: Eltrombopag directly inhibits BAX and
prevents cell death. Nat Commun. 12:11342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Cheraghi S, Senel P, Dogan Topal B, Agar
S, Majidian M, Yurtsever M, Bellur Atici E, Gölcü A and Ozkan SA:
Elucidation of DNA-eltrombopag binding: electrochemical,
spectroscopic and molecular docking techniques. Biosensors (Basel).
13:3002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Argenziano M, Di Paola A, Tortora C, Di
Pinto D, Pota E, Di Martino M, Perrotta S, Rossi F and Punzo F:
Effects of iron chelation in osteosarcoma. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 21:443–455. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Argenziano M, Tortora C, Paola AD, Pota E,
Martino MD, Pinto DD, Leva CD and Rossi F: Eltrombopag and its iron
chelating properties in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncotarget. 12:1377–1387. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Waters T, Goss KL, Koppenhafer SL, Terry
WW and Gordon DJ: Eltrombopag inhibits the proliferation of Ewing
sarcoma cells via iron chelation and impaired DNA replication. BMC
Cancer. 20:11712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dogra N, Singh P and Kumar A: A multistep
in silico approach identifies potential glioblastoma drug
candidates via inclusive molecular targeting of glioblastoma stem
cells. Mol Neurobiol. 61:9253–9271. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Erickson-Miller CL, Pillarisetti K,
Kirchner J, Figueroa DJ, Ottesen L, Martin AM, Liu Y, Kamel YM and
Messam C: Low or undetectable TPO receptor expression in malignant
tissue and cell lines derived from breast, lung, and ovarian
tumors. BMC Cancer. 12:4052012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Idlin N, Krishnamoorthy S, Wolczyk M,
Fakhri M, Lechowski M, Stec N, Milek J, Mandal PK, Cendrowski J,
Spanos C, et al: Effects of genetic ablation and pharmacological
inhibition of HuR on gene expression, iron metabolism, and hormone
levels. BMC Biol. 23:242025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Roth M, Will B, Simkin G, Narayanagari S,
Barreyro L, Bartholdy B, Tamari R, Mitsiades CS, Verma A and Steidl
U: Eltrombopag inhibits the proliferation of leukemia cells via
reduction of intracellular iron and induction of differentiation.
Blood. 120:386–394. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhu Y, Yang L, Xu J, Yang X, Luan P, Cui
Q, Zhang P, Wang F, Li R, Ding X, et al: Discovery of the
anti-angiogenesis effect of eltrombopag in breast cancer through
targeting of HuR protein. Acta Pharm Sin B. 10:1414–1425. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen Y, Zhang R, Yang L, Zhang P, Wang F,
Lin G, Zhang J and Zhu Y: Eltrombopag inhibits metastasis in breast
carcinoma by targeting HuR protein. Int J Mol Sci. 24:31642023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Jenkins JM, Williams D, Deng Y, Uhl J,
Kitchen V, Collins D and Erickson-Miller CL: Phase 1 clinical study
of eltrombopag, an oral, nonpeptide thrombopoietin receptor
agonist. Blood. 109:4739–4741. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Shen CL, Hsieh TC, Wang TF, Huang WH, Chu
SC and Wu YF: Designing a scoring system for differential diagnosis
from reactive thrombocytosis and essential thrombocytosis. Front
Med (Lausanne). 8:7361502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Saleh MN, Bussel JB, Cheng G, Meyer O,
Bailey CK, Arning M and Brainsky A; EXTEND Study Group, : Safety
and efficacy of eltrombopag for treatment of chronic immune
thrombocytopenia: Results of the long-term, open-label EXTEND
study. Blood. 121:537–545. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Bhat A, Tan V, Heng B, Chow S, Basappa S,
Essa MM, Chidambaram SB and Guillemin GJ: Papaverine, a
phosphodiesterase 10A inhibitor, ameliorates quinolinic
acid-induced synaptotoxicity in human cortical neurons. Neurotox
Res. 39:1238–1250. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Fontana JA, Miksis G, Miranda DM and
Durham JP: Inhibition of human mammary carcinoma cell proliferation
by retinoids and intracellular cAMP-elevating compounds. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 78:1107–1112. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gomes DA, Joubert AM and Visagie MH: In
vitro effects of papaverine on cell proliferation, reactive oxygen
species, and cell cycle progression in cancer cells. Molecules.
26:63882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Benej M, Hong X, Vibhute S, Scott S, Wu J,
Graves E, Le QT, Koong AC, Giaccia AJ, Yu B, et al: Papaverine and
its derivatives radiosensitize solid tumors by inhibiting
mitochondrial metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:10756–10761.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Laure A, Royet C, Bihel F, Baratte B, Bach
S, Peyressatre M and Morris MC: Ethaverine and papaverine target
cyclin-dependent kinase 5 and inhibit lung cancer cell
proliferation and migration. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 7:1377–1385.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Sahin ID, Christodoulou MS, Guzelcan EA,
Koyas A, Karaca C, Passarella D and Cetin-Atalay R: A small library
of chalcones induce liver cancer cell death through Akt
phosphorylation inhibition. Sci Rep. 10:118142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Huang H, Li LJ, Zhang HB and Wei AY:
Papaverine selectively inhibits human prostate cancer cell (PC-3)
growth by inducing mitochondrial mediated apoptosis, cell cycle
arrest and downregulation of NF-κB/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J
BUON. 22:112–118. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Marciano R, Prasad M, Ievy T, Tzadok S,
Leprivier G, Elkabets M and Rotblat B: High-throughput screening
identified compounds sensitizing tumor cells to glucose starvation
in culture and VEGF inhibitors in vivo. Cancers (Basel).
11:1562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Sajadian S, Vatankhah M, Majdzadeh M,
Kouhsari SM, Ghahremani MH and Ostad SN: Cell cycle arrest and
apoptogenic properties of opium alkaloids noscapine and papaverine
on breast cancer stem cells. Toxicol Mech Methods. 25:388–395.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gardos G, Cole JO and Sniffin C: An
evaluation of papaverine in tardive dyskinesia. J Clin Pharmacol.
16:304–310. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shupack J, Stiller M, Meola T Jr and
Orbuch P: Papaverine hydrochloride in the treatment of atopic
dermatitis: A double-blind, placebo-controlled crossover clinical
trial to reassess safety and efficacy. Dermatologica. 183:21–24.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Reif GA, Yamaguchi T, Nivens E, Fujiki H,
Pinto CS and Wallace DP: Tolvaptan inhibits ERK-dependent cell
proliferation, Cl− secretion, and in vitro cyst growth
of human ADPKD cells stimulated by vasopressin. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 301:F1005–F1013. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tahara A, Saito M, Sugimoto T, Tomura Y,
Wada K, Kusayama T, Tsukada J, Ishii N, Yatsu T, Uchida W and
Tanaka A: Pharmacological characterization of the human vasopressin
receptor subtypes stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells.
Br J Pharmacol. 125:1463–1470. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Garona J, Pifano M, Orlando UD, Pastrian
MB, Iannucci NB, Ortega HH, Podesta EJ, Gomez DE, Ripoll GV and
Alonso DF: The novel desmopressin analogue [V4Q5]dDAVP inhibits
angiogenesis, tumour growth and metastases in vasopressin type 2
receptor-expressing breast cancer models. Int J Oncol.
46:2335–2345. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ectopic ADH Syndrome Therapeutic Research
Group, . Yamaguchi K, Shijubo N, Kodama T, Mori K, Sugiura T,
Kuriyama T, Kawahara M, Shinkai T, Iguchi H and Sakurai M: Clinical
implication of the antidiuretic hormone (ADH) receptor antagonist
mozavaptan hydrochloride in patients with ectopic ADH syndrome. Jpn
J Clin Oncol. 41:148–152. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ferreira JP, Pitt B and Zannad F:
Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in heart failure: An update.
Circ Heart Fail. 17:e0116292024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ethier SP, Guest ST, Garrett-Mayer E,
Armeson K, Wilson RC, Duchinski K, Couch D, Gray JW and Kappler C:
Development and implementation of the SUM breast cancer cell line
functional genomics knowledge base. NPJ Breast Cancer. 6:302020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Alekseev S, Ayadi M, Brino L, Egly JM,
Larsen AK and Coin F: A small molecule screen identifies an
inhibitor of DNA repair inducing the degradation of TFIIH and the
chemosensitization of tumor cells to platinum. Chem Biol.
21:398–407. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Elstrodt F, Hollestelle A, Nagel JHA,
Gorin M, Wasielewski M, van den Ouweland A, Merajver SD, Ethier SP
and Schutte M: BRCA1 mutation analysis of 41 human breast cancer
cell lines reveals three new deleterious mutants. Cancer Res.
66:41–45. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Martín-Bejarano P, Sánchez-Tapia EM,
Jessica P, Martín-Gómez T, Tocino RV, González-Sarmiento R and
Herrero AB: Functional characterization of BRCA1 variants of
unknown significance using homologous recombination repair assays.
Breast Cancer Res. 27:1742025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Baloch T, López-Ozuna VM, Wang Q, Matanis
E, Kessous R, Kogan L, Yasmeen A and Gotlieb WH: Sequential
therapeutic targeting of ovarian cancer harboring dysfunctional
BRCA1. BMC Cancer. 19:442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Mita P, Sun X, Fenyö D, Kahler DJ, Li D,
Agmon N, Wudzinska A, Keegan S, Bader JS, Yun C and Boeke JD: BRCA1
and S phase DNA repair pathways restrict LINE-1 retrotransposition
in human cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 27:179–191. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Keung MY, Wu Y, Badar F and Vadgama JV:
Response of breast cancer cells to PARP inhibitors is independent
of BRCA status. J Clin Med. 9:9402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Bommareddy K, Hamade H, Lopez-Olivo MA,
Wehner M, Tosh T and Barbieri JS: Association of spironolactone use
with risk of cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA
Dermatol. 158:275–282. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Garate D, Thang CJ, Golovko G, Wilkerson
MG and Barbieri JS: A matched cohort study evaluating whether
spironolactone or tetracycline-class antibiotic use among female
acne patients is associated with breast cancer development risk.
Arch Dermatol Res. 316:1962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Lin G, Chen R, Wen C, Li Z, Yan X and Li
L: Analyzing real-world adverse events of spironolactone with the
FAERS database. PLoS One. 20:e03306592025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kayaaslan B and Guner R: Adverse effects
of oral antiviral therapy in chronic hepatitis B. World J Hepatol.
9:227–241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Min S, Sloan L, DeJesus E, Hawkins T,
McCurdy L, Song I, Stroder R, Chen S, Underwood M, Fujiwara T, et
al: Antiviral activity, safety, and
pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of dolutegravir as 10-day
monotherapy in HIV-1-infected adults. AIDS. 25:1737–1745. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Su J, He L and Wang M: Post-marketing
safety concerns with dolutegravir: A pharmacovigilance study based
on the FDA adverse event reporting system database. Front
Pharmacol. 16:16256012025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Tschuppert Y, Buclin T, Rothuizen LE,
Decosterd LA, Galleyrand J, Gaud C and Biollaz J: Effect of
dronedarone on renal function in healthy subjects. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 64:785–791. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wadhani N, Sarma JS, Singh BN, Radzik D
and Gaud C: Dose-dependent effects of oral dronedarone on the
circadian variation of RR and QT intervals in healthy subjects:
Implications for antiarrhythmic actions. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol
Ther. 11:184–190. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Charbit B, Becquemont L, Lepère B,
Peytavin G and Funck-Brentano C: Pharmacokinetic and
pharmacodynamic interaction between grapefruit juice and
halofantrine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 72:514–523. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|