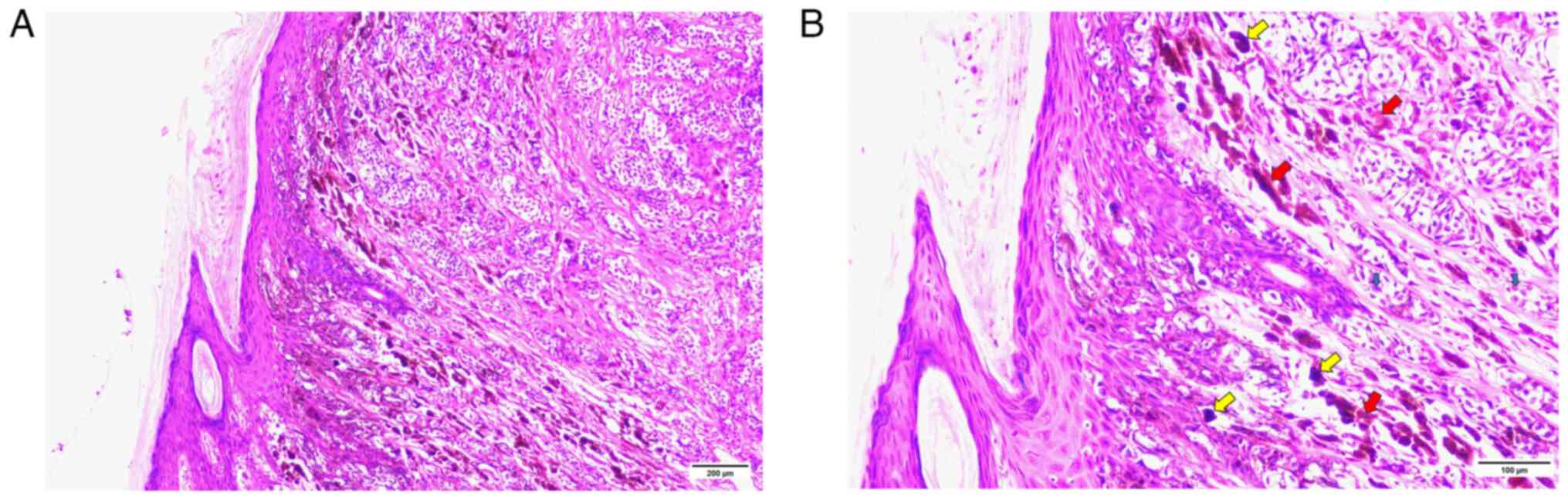
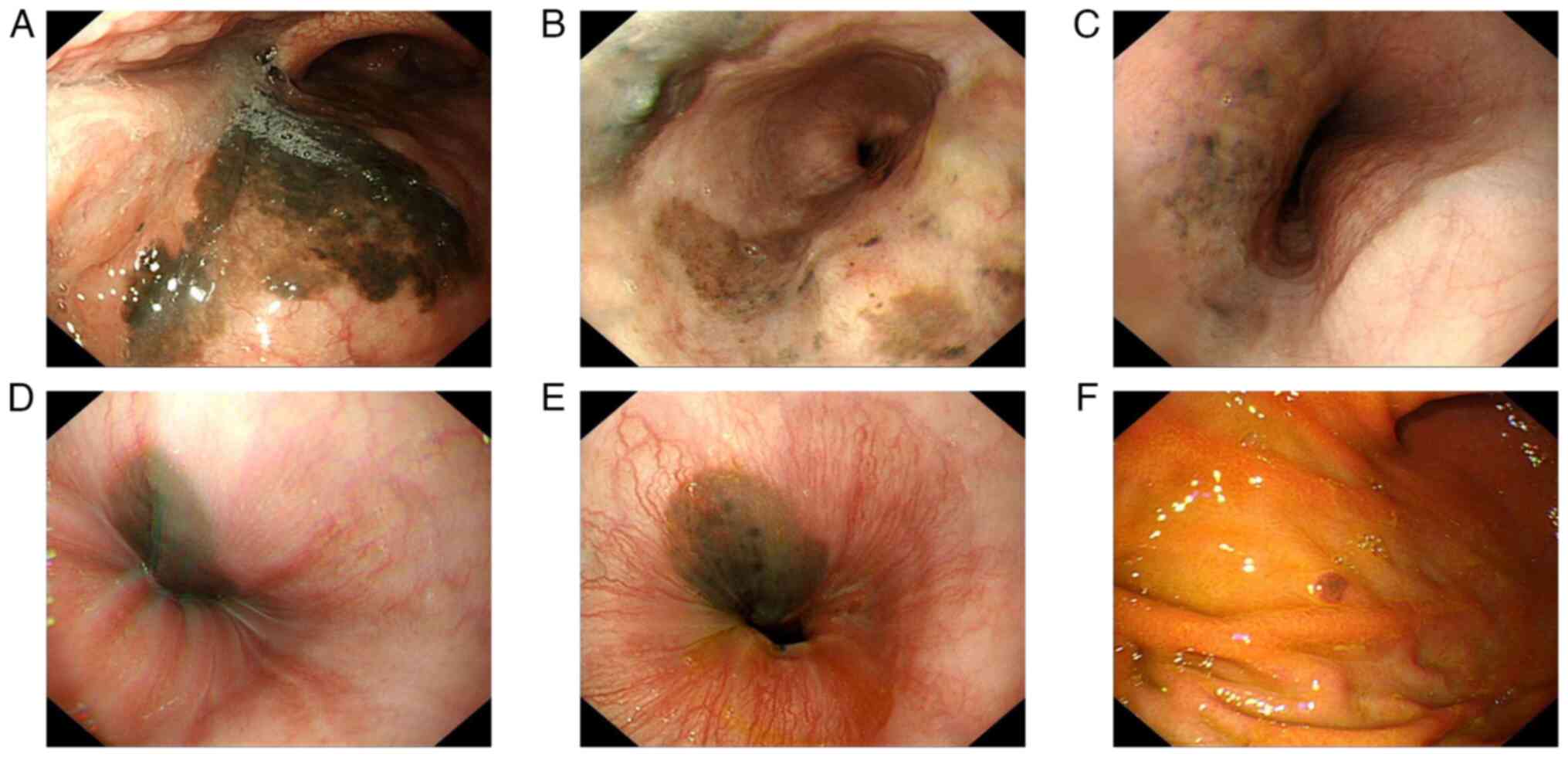
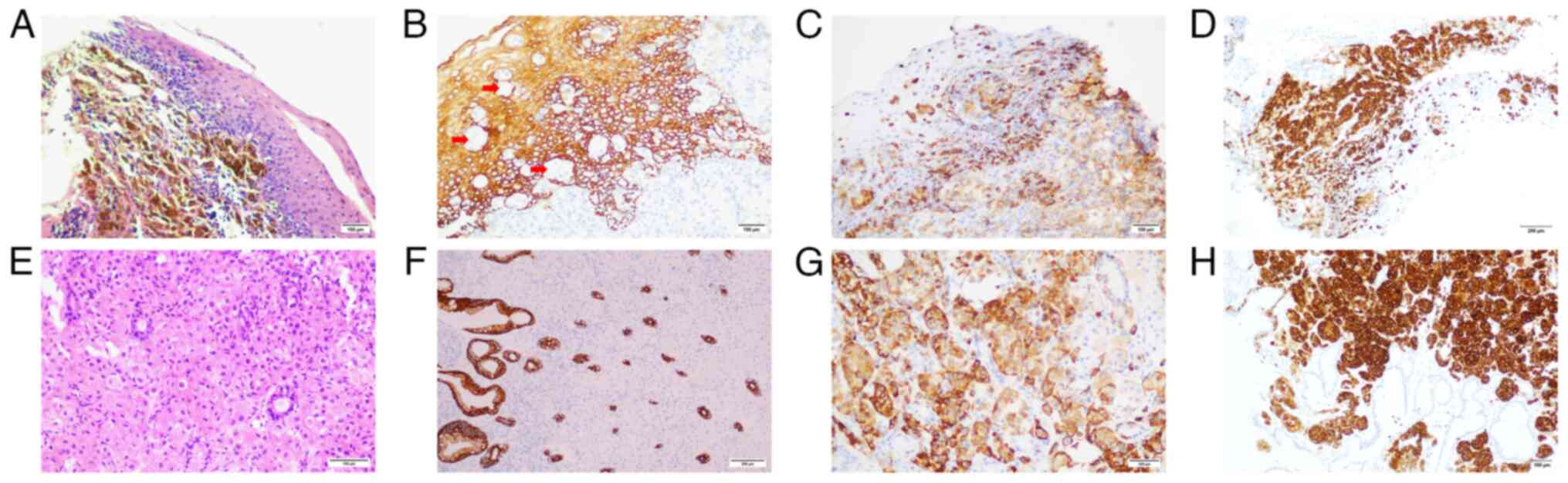
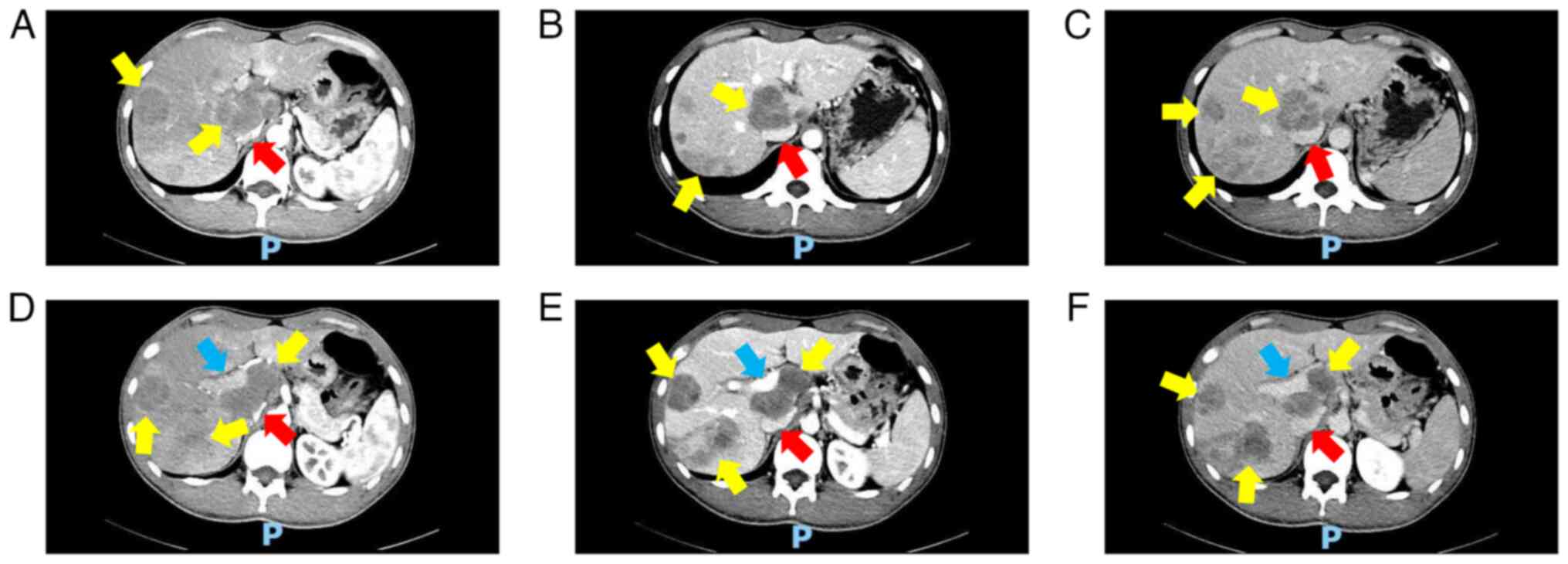
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer (IARC), . WHO Classification of Skin Tumours. Elder DE,
Massi D, Scolyer RA and Willemze R: 11. 4th Edition. IARC; Lyon:
2018
|
|
3
|
Elder DE, Bastian BC, Cree IA, Massi D and
Scolyer RA: The 2018 World Health Organization classification of
cutaneous, mucosal, and uveal melanoma: Detailed analysis of 9
distinct subtypes defined by their evolutionary pathway. Arch
Pathol Lab Med. 144:500–522. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gandini S, Sera F, Cattaruzza MS, Pasquini
P, Abeni D, Boyle P and Melchi CF: Meta-analysis of risk factors
for cutaneous melanoma: I. Common and atypical naevi. Eur J Cancer.
41:28–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Switzer B, Piperno-Neumann S, Lyon J,
Buchbinder E and Puzanov I: Evolving management of stage IV
melanoma. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 43:e3974782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang T, Xiao M, Ge Y, Krepler C, Belser E,
Lopez-Coral A, Xu X, Zhang G, Azuma R, Liu Q, et al: BRAF
inhibition stimulates melanoma-associated macrophages to drive
tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res. 21:1652–1664. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sanchez IM, Purwin TJ, Chervoneva I, Erkes
DA, Nguyen MQ, Davies MA, Nathanson KL, Kemper K, Peeper DS and
Aplin AE: In vivo ERK1/2 reporter predictively models response and
resistance to combined BRAF and MEK inhibitors in melanoma. Mol
Cancer Ther. 18:1637–1648. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
American Joint Committee on Cancer, . AJCC
Cancer Staging Manual. 6th Edition. Springer New York; NY: 2002
|
|
9
|
Taal BG, Westerman H, Boot H and Rankin
EM: Clinical and endoscopic features of melanoma metastases in the
upper GI tract. Gastrointest Endosc. 50:261–263. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu H, Yan Y and Jiang CM: Primary
malignant melanoma of the esophagus with unusual endoscopic
findings: A case report and literature review. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95:e34792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer and Global Cancer Observatory, Cancer Today Globocan 2022, .
Melanoma of Skin. https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/cancers/16-melanoma-of-skin-fact-sheet.pdfApril
29–2025
|
|
12
|
International Agency for Research on
Cancer, Global Cancer Observatory and Cancer Today Globocan 2022, .
Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer. https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/cancers/17-non-melanoma-skin-cancer-fact-sheet.pdfApril
29–2025
|
|
13
|
National Cancer Institute Surveillance and
Epidemiology, End Results Program, . Cancer Stat Facts: Melanoma of
the Skin. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/melan.htmlMay
7–2025
|
|
14
|
Karimkhani C, Dellavalle RP, Coffeng LE,
Flohr C, Hay RJ, Langan SM, Nsoesie EO, Ferrari AJ, Erskine HE,
Silverberg JI, et al: Global skin disease morbidity and mortality:
An update from the global burden of disease study 2013. JAMA
Dermatol. 153:406–412. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Di Carlo V, Eberle A, Stiller C, Bennett
D, Katalinic A, Marcos-Gragera R, Girardi F, Larønningen S, Schultz
A, Lima CA, et al: Sex differences in survival from melanoma of the
skin: The role of age, anatomic location and stage at diagnosis: A
CONCORD-3 study in 59 countries. Eur J Cancer. 217:1152132025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jayasinghe D, Nufer KL, Betz-Stablein B,
Soyer HP and Janda M: Body site distribution of acquired
melanocytic naevi and associated characteristics in the general
population of caucasian adults: A scoping review. Dermatol Ther
(Heidelb). 12:2453–2488. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lallas K, Kyrgidis A, Chrysostomidis A,
Vakirlis E, Apalla Z and Lallas A: Clinical, dermatoscopic,
histological and molecular predictive factors of distant melanoma
metastasis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 202:1044582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Olsen CM, Thompson JF, Pandeya N and
Whiteman DC: Evaluation of sex-specific incidence of melanoma. JAMA
Dermatol. 156:553–560. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Calomarde-Rees L, García-Calatayud R,
Requena Caballero C, Manrique-Silva E, Traves V, García-Casado Z,
Soriano V, Kumar R and Nagore E: Risk factors for lymphatic and
hematogenous dissemination in patients with stages I to II
cutaneous melanoma. JAMA Dermatol. 155:679–687. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Waseh S and Lee JB: Advances in melanoma:
Epidemiology, diagnosis, and prognosis. Front Med (Lausanne).
10:12684792023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
PDQ Adult Treatment Editorial Board, .
Melanoma Treatment (PDQ®): Health Professional Version.
PDQ Cancer Information Summaries. National Cancer Institute (US);
Bethesda, MD, USA: 2025
|
|
22
|
American Cancer Society, . Key Statistics
for Melanoma Skin Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/melanoma-skin-cancer/about/key-statistics.htmlMay
7–2025
|
|
23
|
Indini A, Didoné F, Massi D, Puig S,
Casadevall JR, Bennett D, Katalinic A, Sanvisens A, Ferrari A,
Lasalvia P, et al: Incidence and prognosis of cutaneous melanoma in
European adolescents and young adults (AYAs): EUROCARE-6
retrospective cohort results. Eur J Cancer 1990.
213:1150792024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balch CM, Soong SJ, Murad TM, Smith JW,
Maddox WA and Durant JR: A multifactorial analysis of melanoma. IV.
Prognostic factors in 200 melanoma patients with distant metastases
(stage III). J Clin Oncol. 1:126–134. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gordon R: Skin cancer: An overview of
epidemiology and risk factors. Semin Oncol Nurs. 29:160–169. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wunderlich K, Suppa M, Gandini S, Lipski
J, White JM and Del Marmol V: Risk factors and innovations in risk
assessment for melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 16:10162024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Conforti C and Zalaudek I: Epidemiology
and risk factors of melanoma: A review. Dermatol Pract Concept. 11
(Suppl 1):e2021161S2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Raimondi S, Suppa M and Gandini S:
Melanoma Epidemiology and Sun Exposure. Acta Derm Venereol.
100:57462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rutkowski P and Mandala M: Perioperative
therapy of melanoma: Adjuvant or neoadjuvant treatment. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 50:1079692024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Maher NG, Vergara IA, Long GV and Scolyer
RA: Prognostic and predictive biomarkers in melanoma. Pathology.
56:259–273. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ernst M and Giubellino A: The current
state of treatment and future directions in cutaneous malignant
melanoma. Biomedicines. 10:8222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Russano F, Rastrelli M, Dall'Olmo L, Del
Fiore P, Gianesini C, Vecchiato A, Mazza M, Tropea S and Mocellin
S: Therapeutic treatment options for in-transit metastases from
melanoma. Cancers (Basel). 16:30652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Long GV, Swetter SM, Menzies AM,
Gershenwald JE and Scolyer RA: Cutaneous melanoma. Lancet.
402:485–502. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chatziioannou E, Leiter U, Thomas I, Keim
U, Seeber O, Meiwes A, Boessenecker I, Gonzalez SS, Torres FM,
Niessner H, et al: Features and long-term outcomes of stage IV
melanoma patients achieving complete response under anti-PD-1-based
immunotherapy. Am J Clin Dermatol. 24:453–467. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hodi FS, O'Day SJ, McDermott DF, Weber RW,
Sosman JA, Haanen JB, Gonzalez R, Robert C, Schadendorf D, Hassel
JC, et al: Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with
metastatic melanoma. N Engl J Med. 363:711–723. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Brandlmaier M, Hoellwerth M, Koelblinger
P, Lang R and Harrer A: Adjuvant PD-1 checkpoint inhibition in
early cutaneous melanoma: Immunological mode of action and the role
of ultraviolet radiation. Cancers (Basel). 16:14612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ascierto PA, Del Vecchio M, Mandalá M,
Gogas H, Arance AM, Dalle S, Cowey CL, Schenker M, Grob JJ,
Chiarion-Sileni V, et al: Adjuvant nivolumab versus ipilimumab in
resected stage IIIB-C and stage IV melanoma (CheckMate 238): 4-Year
results from a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, controlled,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 21:1465–1477. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Larkin J, Del Vecchio M, Mandalá M, Gogas
H, Arance Fernandez AM, Dalle S, Cowey CL, Schenker M, Grob JJ,
Chiarion-Sileni V, et al: Adjuvant Nivolumab versus Ipilimumab in
resected stage III/IV melanoma: 5-year efficacy and biomarker
results from CheckMate 238. Clin Cancer Res. 29:3352–3361. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bührer E, Kicinski M, Mandala M, Pe M,
Long GV, Atkinson V, Blank CU, Haydon A, Dalle S, Khattak A, et al:
Adjuvant pembrolizumab versus placebo in resected stage III
melanoma (EORTC 1325-MG/KEYNOTE-054): Long-term, health-related
quality-of-life results from a double-blind, randomised,
controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 25:1202–1212. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Long GV, Luke JJ, Khattak MA, de la Cruz
Merino L, Del Vecchio M, Rutkowski P, Spagnolo F, Mackiewicz J,
Chiarion-Sileni V, Kirkwood JM, et al: Pembrolizumab versus placebo
as adjuvant therapy in resected stage IIB or IIC melanoma
(KEYNOTE-716): Distant metastasis-free survival results of a
multicentre, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
23:1378–1388. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Luke JJ, Rutkowski P, Queirolo P, Del
Vecchio M, Mackiewicz J, Chiarion-Sileni V, de la Cruz Merino L,
Khattak MA, Schadendorf D, Long GV, et al: Pembrolizumab versus
placebo as adjuvant therapy in completely resected stage IIB or IIC
melanoma (KEYNOTE-716): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial.
Lancet. 399:1718–1729. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ochenduszko S, Puskulluoglu M,
Pacholczak-Madej R and Ruiz-Millo O: Adjuvant anti-PD1
immunotherapy of resected skin melanoma: An example of
non-personalized medicine with no overall survival benefit. Crit
Rev Oncol Hematol. 202:1044432024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Knox T, Sahakian E, Banik D, Hadley M,
Palmer E, Noonepalle S, Kim J, Powers J, Gracia-Hernandez M,
Oliveira V, et al: Selective HDAC6 inhibitors improve anti-PD-1
immune checkpoint blockade therapy by decreasing the
anti-inflammatory phenotype of macrophages and down-regulation of
immunosuppressive proteins in tumor cells. Sci Rep. 9:61362019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Phoon YP, Wolfarth AA, Funchain P, Ko JS,
Choi D, Dedkova E, Bateman DD, Corvin J, Melenhorst JJ and Gastman
BR: NT-I7, a novel long-acting interleukin-7, promotes anti-PD-1
efficacy in an autologous humanized melanoma model. Sci Rep.
15:379502025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lorentzen CL, Kjeldsen JW, Ehrnrooth E,
Andersen MH and Marie Svane I: Long-term follow-up of anti-PD-1
naïve patients with metastatic melanoma treated with IDO/PD-L1
targeting peptide vaccine and nivolumab. J Immunother Cancer.
11:e0067552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ribas A, Milhem MM, Hoimes CJ, Amin A, Lao
CD, Conry RM, Hunt JP, Daniels GA, Almubarak M, Shaheen M, et al:
Phase 2, open-label, multicenter study of nelitolimod in
combination with pembrolizumab in anti-PD-1 treatment-Naïve
advanced melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 31:4070–4078. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hodi FS, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R,
Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Cowey CL, Lao CD, Schadendorf D, Wagstaff J,
Dummer R, et al: Nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone
versus ipilimumab alone in advanced melanoma (CheckMate 067):
4-Year outcomes of a multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet
Oncol. 19:1480–1492. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Mullick N and Nambudiri VE:
Relatlimab-nivolumab: A practical overview for dermatologists. J Am
Acad Dermatol. 89:1031–1037. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Chan PY and Corrie PG: Curing stage IV
melanoma: Where Have we been and where are we? Am Soc Clin Oncol
Educ Book. 44:e4386542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Smalley KSM: Understanding melanoma
signaling networks as the basis for molecular targeted therapy. J
Invest Dermatol. 130:28–37. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Garnett MJ and Marais R: Guilty as
charged: B-RAF is a human oncogene. Cancer Cell. 6:313–319. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Demidov LV, Jouary
T, Gutzmer R, Millward M, Rutkowski P, Blank CU, Miller WH Jr,
Kaempgen E, et al: Dabrafenib in BRAF-mutated metastatic melanoma:
A multicentre, open-label, phase 3 randomised controlled trial.
Lancet. 380:358–365. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Long GV, Weber JS, Infante JR, Kim KB,
Daud A, Gonzalez R, Sosman JA, Hamid O, Schuchter L, Cebon J, et
al: Overall survival and durable responses in patients with BRAF
V600-mutant metastatic melanoma receiving dabrafenib combined with
trametinib. J Clin Oncol. 34:871–878. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Robert C, Karaszewska B, Schachter J,
Rutkowski P, Mackiewicz A, Stroiakovski D, Lichinitser M, Dummer R,
Grange F, Mortier L, et al: Improved overall survival in melanoma
with combined dabrafenib and trametinib. N Engl J Med. 372:30–39.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sierra-Davidson K and Boland GM: Advances
in adjuvant and neoadjuvant therapy for melanoma. Hematol Oncol
Clin North Am. 38:953–971. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Corrie P, Meyer N, Berardi R, Guidoboni M,
Schlueter M, Kolovos S, Macabeo B, Trouiller JB and Laramée P:
Comparative efficacy and safety of targeted therapies for
BRAF-mutant unresectable or metastatic melanoma: Results from a
systematic literature review and a network meta-analysis. Cancer
Treat Rev. 110:1024632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Haist M, Stege H, Kuske M, Bauer J, Klumpp
A, Grabbe S and Bros M: Combination of immune-checkpoint inhibitors
and targeted therapies for melanoma therapy: The more, the better?
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 42:481–505. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gutzmer R, Stroyakovskiy D, Gogas H,
Robert C, Lewis K, Protsenko S, Pereira RP, Eigentler T, Rutkowski
P, Demidov L, et al: Atezolizumab, vemurafenib, and cobimetinib as
first-line treatment for unresectable advanced BRAFV600
mutation-positive melanoma (IMspire150): Primary analysis of the
randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial.
Lancet. 395:1835–1844. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Atkins MB, Lee SJ, Chmielowski B, Tarhini
AA, Cohen GI, Truong TG, Moon HH, Davar D, O'Rourke M, Stephenson
JJ, et al: Combination dabrafenib and trametinib versus combination
nivolumab and ipilimumab for patients with advanced BRAF-mutant
melanoma: The DREAMseq trial-ECOG-ACRIN EA6134. J Clin Oncol.
41:186–197. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ziogas DC, Martinos A, Petsiou DP,
Anastasopoulou A and Gogas H: Beyond immunotherapy: Seizing the
momentum of oncolytic viruses in the ideal platform of skin
cancers. Cancers (Basel). 14:28732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Puzanov I, Milhem MM, Minor D, Hamid O, Li
A, Chen L, Chastain M, Gorski KS, Anderson A, Chou J, et al:
Talimogene laherparepvec in combination with ipilimumab in
previously untreated, unresectable stage IIIB-IV melanoma. J Clin
Oncol. 34:2619–2626. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Gorry C, McCullagh L, O'Donnell H, Barrett
S, Schmitz S, Barry M, Curtin K, Beausang E, Barry R and Coyne I:
Neoadjuvant treatment for stage III and IV cutaneous melanoma.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 1:CD0129742023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Patel SP, Othus M, Chen Y, Wright GP Jr,
Yost KJ, Hyngstrom JR, Hu-Lieskovan S, Lao CD, Fecher LA, Truong
TG, et al: Neoadjuvant-adjuvant or adjuvant-only pembrolizumab in
advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 388:813–823. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Amaria RN, Prieto PA, Tetzlaff MT, Reuben
A, Andrews MC, Ross MI, Glitza IC, Cormier J, Hwu WJ, Tawbi HA, et
al: Neoadjuvant plus adjuvant dabrafenib and trametinib versus
standard of care in patients with high-risk, surgically resectable
melanoma: A single-centre, open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 19:181–193. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Amaria RN, Menzies AM, Burton EM, Scolyer
RA, Tetzlaff MT, Antdbacka R, Ariyan C, Bassett R, Carter B, Daud
A, et al: Neoadjuvant systemic therapy in melanoma: Recommendations
of the international neoadjuvant melanoma consortium. Lancet Oncol.
20:e378–e389. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Swetter SM, Johnson D, Albertini MR,
Barker CA, Bateni S, Baumgartner J, Bhatia S, Bichakjian C, Boland
G, Chandra S, et al: NCCN guidelines® insights:
Melanoma: Cutaneous, version 2.2024. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
22:290–298. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Spagnolo F, Ghiorzo P, Orgiano L,
Pastorino L, Picasso V, Tornari E, Ottaviano V and Queirolo P:
BRAF-mutant melanoma: Treatment approaches, resistance mechanisms,
and diagnostic strategies. OncoTargets Ther. 8:157–168. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Haugh AM and Johnson DB: Management of
V600E and V600K BRAF-mutant melanoma. Curr Treat Options Oncol.
20:812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Long GV, Trefzer U, Davies MA, Kefford RF,
Ascierto PA, Chapman PB, Puzanov I, Hauschild A, Robert C, Algazi
A, et al: Dabrafenib in patients with Val600Glu or Val600Lys
BRAF-mutant melanoma metastatic to the brain (BREAK-MB): A
multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:1087–1095.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Dummer R, Goldinger SM, Turtschi CP,
Eggmann NB, Michielin O, Mitchell L, Veronese L, Hilfiker PR,
Felderer L and Rinderknecht JD: Vemurafenib in patients with
BRAF(V600) mutation-positive melanoma with symptomatic brain
metastases: Final results of an open-label pilot study. Eur J
Cancer. 50:611–621. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Davies MA, Saiag P, Robert C, Grob JJ,
Flaherty KT, Arance A, Chiarion-Sileni V, Thomas L, Lesimple T,
Mortier L, et al: Dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with
BRAFV600-mutant melanoma brain metastases (COMBI-MB): A
multicentre, multicohort, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:863–873. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Margolin K, Ernstoff MS, Hamid O, Lawrence
D, McDermott D, Puzanov I, Wolchok JD, Clark JI, Sznol M, Logan TF,
et al: Ipilimumab in patients with melanoma and brain metastases:
An open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 13:459–465. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Jensen IS, Zacherle E, Blanchette CM,
Zhang J and Yin W: Evaluating cost benefits of combination
therapies for advanced melanoma. Drugs Context. 5:2122972016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Paraiso KHT, Xiang Y, Rebecca VW, Abel EV,
Chen YA, Munko AC, Wood E, Fedorenko IV, Sondak VK, Anderson AR, et
al: PTEN loss confers BRAF inhibitor resistance to melanoma cells
through the suppression of BIM expression. Cancer Res.
71:2750–2760. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Xing F, Persaud Y, Pratilas CA, Taylor BS,
Janakiraman M, She QB, Gallardo H, Liu C, Merghoub T, Hefter B, et
al: Concurrent loss of the PTEN and RB1 tumor suppressors
attenuates RAF dependence in melanomas harboring (V600E)BRAF.
Oncogene. 31:446–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Whittaker SR, Theurillat JP, Van Allen E,
Wagle N, Hsiao J, Cowley GS, Schadendorf D, Root DE and Garraway
LA: A genome-scale RNA interference screen implicates NF1 loss in
resistance to RAF inhibition. Cancer Discov. 3:350–362. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nissan MH, Pratilas CA, Jones AM, Ramirez
R, Won H, Liu C, Tiwari S, Kong L, Hanrahan AJ, Yao Z, et al: Loss
of NF1 in cutaneous melanoma is associated with RAS activation and
MEK dependence. Cancer Res. 74:2340–2350. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Pratilas CA, Taylor BS, Ye Q, Viale A,
Sander C, Solit DB and Rosen N: (V600E)BRAF is associated with
disabled feedback inhibition of RAF-MEK signaling and elevated
transcriptional output of the pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
106:4519–4524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shi H, Moriceau G, Kong X, Koya RC,
Nazarian R, Pupo GM, Bacchiocchi A, Dahlman KB, Chmielowski B,
Sosman JA, et al: Preexisting MEK1 exon 3 mutations in V600E/KBRAF
melanomas do not confer resistance to BRAF inhibitors. Cancer
Discov. 2:414–424. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Poulikakos PI, Persaud Y, Janakiraman M,
Kong X, Ng C, Moriceau G, Shi H, Atefi M, Titz B, Gabay MT, et al:
RAF inhibitor resistance is mediated by dimerization of aberrantly
spliced BRAF(V600E). Nature. 480:387–390. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Shi H, Moriceau G, Kong X, Lee MK, Lee H,
Koya RC, Ng C, Chodon T, Scolyer RA, Dahlman KB, et al: Melanoma
whole-exome sequencing identifies (V600E)B-RAF
amplification-mediated acquired B-RAF inhibitor resistance. Nat
Commun. 3:7242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Augustin RC and Luke JJ: Rapidly evolving
pre- and post-surgical systemic treatment of melanoma. Am J Clin
Dermatol. 25:421–434. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|