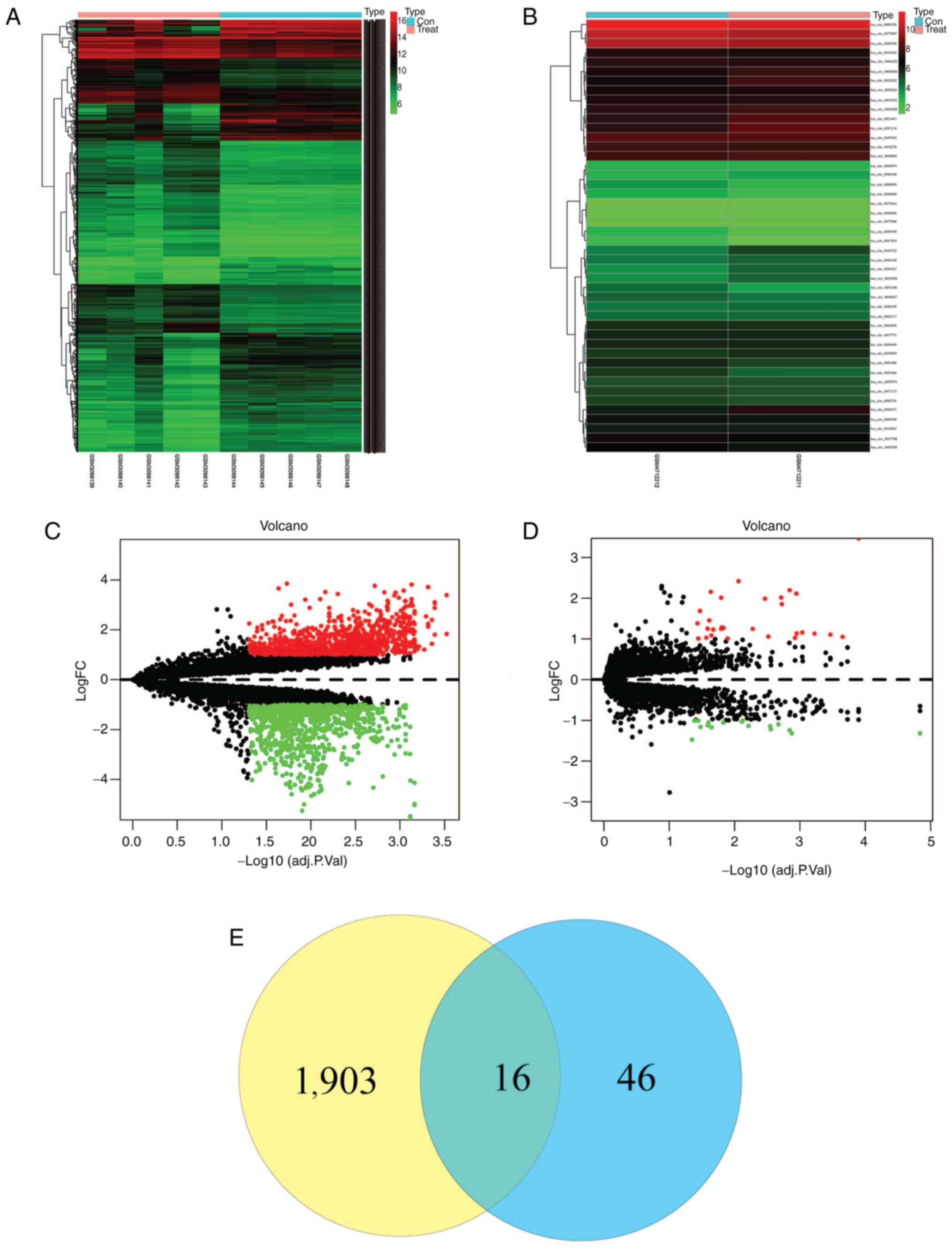
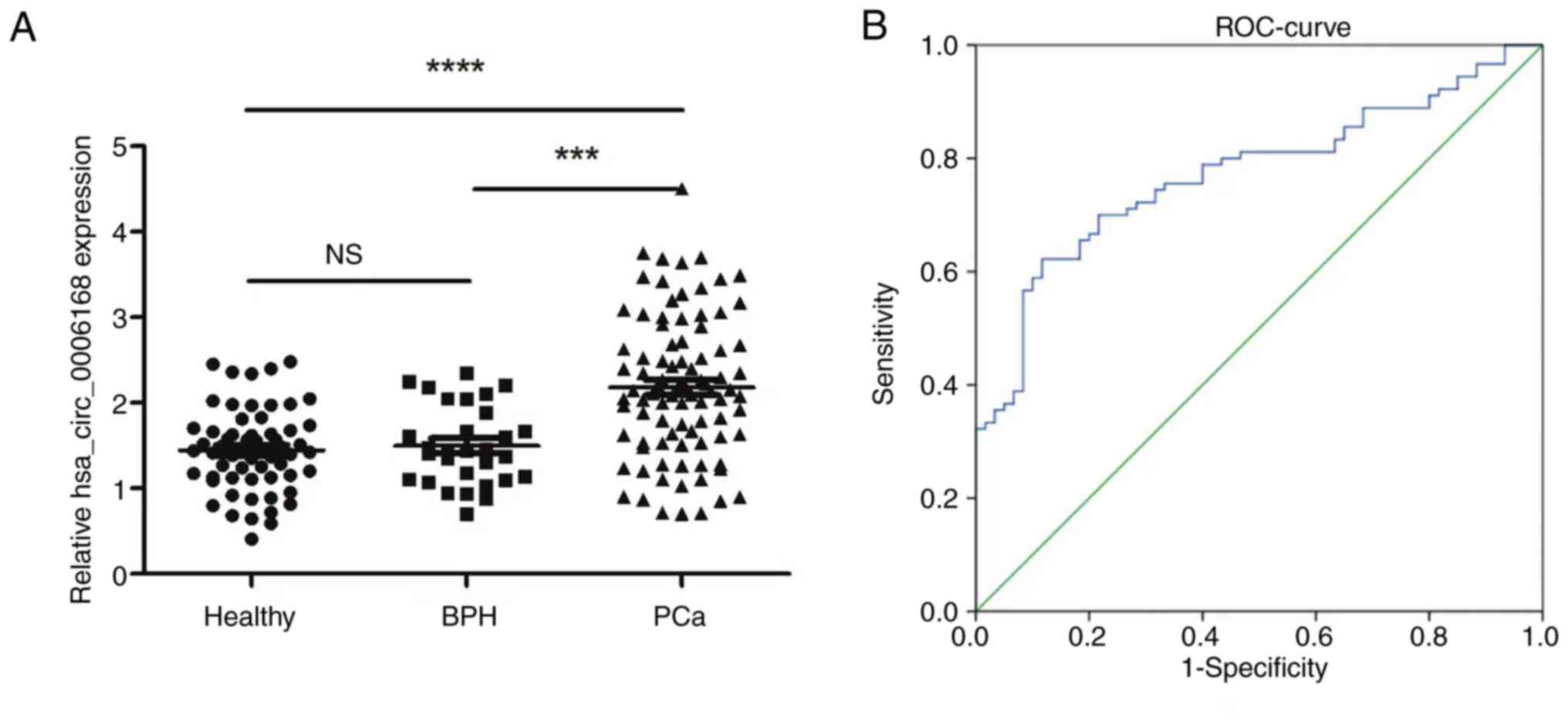
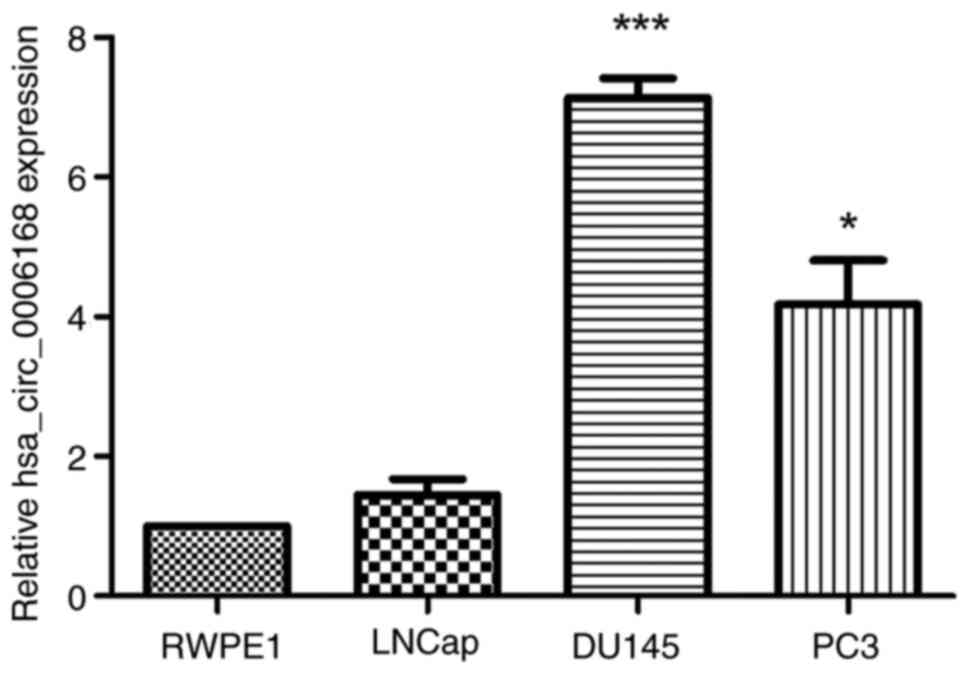
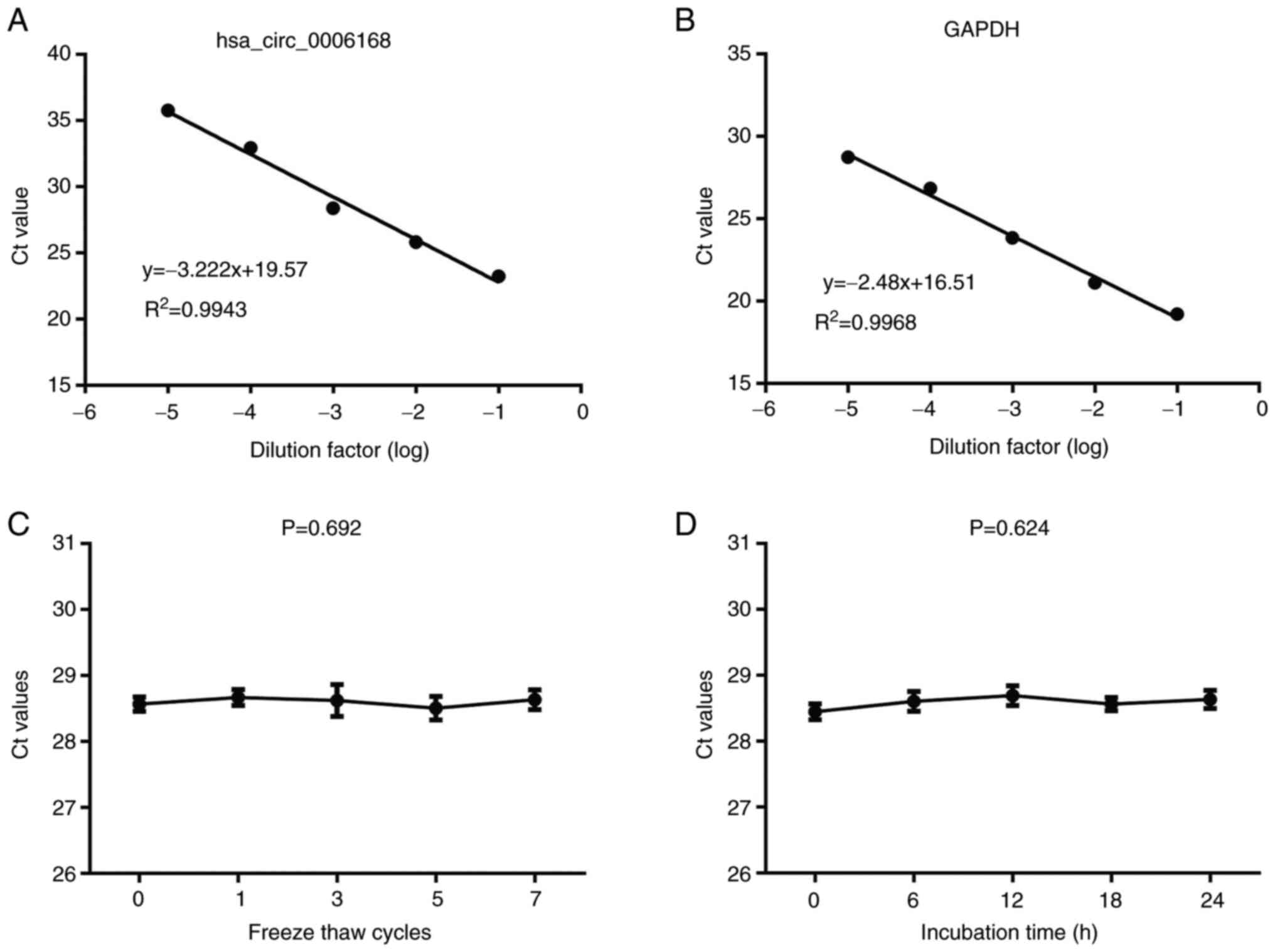
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Sung H,
Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer
statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality
worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin.
74:229–263. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
US Preventive Services Task Force, ;
Grossman DC, Curry SJ, Owens DK, Bibbins-Domingo K, Caughey AB,
Davidson KW, Doubeni CA, Ebell M, Epling JW Jr, et al: Screening
for prostate cancer: US preventive services task force
recommendation statement. JAMA. 319:1901–1913. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang
R, Sun W, Dou K and Li H: Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding
RNAs. Cancer Lett. 365:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lei M, Zheng G, Ning Q, Zheng J and Dong
D: Translation and functional roles of circular RNAs in human
cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li S, Hu W, Deng F, Chen S, Zhu P, Wang M,
Chen X, Wang Y, Hu X, Zhao B, et al: Identification of circular RNA
hsa_circ_0001599 as a novel biomarker for large-artery
atherosclerotic stroke. DNA Cell Boil. 40:457–468. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lv J, Ren L, Han S, Zhang J, Zhao X, Zhang
Y, Fang H, Zhang L, Yang H, Wang S, et al: Peripheral blood
hsa-circRNA5333-4: A novel biomarker for myasthenia gravis. Clin
Immunol. 224:1086762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi J, Liu C, Chen C, Guo K, Tang Z, Luo
Y, Chen L, Su Y and Xu K: Circular RNA circMBOAT2 promotes prostate
cancer progression via a miR-1271-5p/mTOR axis. Aging (Albany NY).
12:13255–13280. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shi Y, Guo Z, Fang N, Jiang W, Fan Y, He
Y, He Y, Ma Z and Chen Y: hsa_circ_0006168 sponges miR-100 and
regulates mTOR to promote the proliferation, migration and invasion
of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother.
117:1091512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang T, Mao P, Feng Y, Cui B, Zhang B,
Chen C, Xu M and Gao K: Blocking hsa_circ_0006168 suppresses cell
proliferation and motility of human glioblastoma cells by
regulating hsa_circ_0006168/miR-628-5p/IGF1R ceRNA axis. Cell
Cycle. 20:1181–1194. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen D, Lu X, Yang F and Xing N: Circular
RNA circHIPK3 promotes cell proliferation and invasion of prostate
cancer by sponging miR-193a-3p and regulating MCL1 expression.
Cancer Manag Res. 11:1415–1423. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gleason DF: Classification of prostatic
carcinomas. Cancer Chemother Rep. 50:125–128. 1966.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Verma S, Pandey M, Shukla GC, Singh V and
Gupta S: Integrated analysis of miRNA landscape and cellular
networking pathways in stage-specific prostate cancer. PLoS One.
14:e02240712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, Wagner
I, Stephan C, Jentzmik F, Miller K, Lein M, Kristiansen G and Jung
K: Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in
prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:1166–1176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Byrd DR,
Brookland RK, Washington MK, Gershenwald JE, Compton CC, Hess KR,
Sullivan DC, et al: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th edition.
Springer; New York, NY: 2017
|
|
16
|
Sobel RE and Sadar MD: Cell lines used in
prostate cancer research: A compendium of old and new lines-part 1.
J Urol. 173:342–359. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Le TK, Duong QH, Baylot V, Fargette C,
Baboudjian M, Colleaux L, Taïeb D and Rocchi P:
Castration-resistant prostate cancer: From uncovered resistance
mechanisms to current treatments. Cancers (Basel). 15:50472023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Watson PA, Arora VK and Sawyers CL:
Emerging mechanisms of resistance to androgen receptor inhibitors
in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:701–711. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang Z, Qu CB, Zhang Y, Zhang WF, Wang DD,
Gao CC, Ma L, Chen JS, Liu KL, Zheng B, et al: Dysregulation of
p53-RBM25-mediated circAMOTL1L biogenesis contributes to prostate
cancer progression through the circAMOTL1L-miR-193a-5p-Pcdha
pathway. Oncogene. 38:2516–2532. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ofner H, Kramer G, Shariat SF and Hassler
MR: TP53 deficiency in the natural history of prostate cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 17:6452025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Teroerde M, Nientiedt C, Duensing A,
Hohenfellner M, Stenzinger A and Duensing S: Chapter 8: Revisiting
the role of p53 in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer. Bott SRJ and
Ng KL: Exon Publications; Brisbane, Australia: pp. 113–123.
2021
|
|
22
|
To KKW, Zhang H and Cho WC: Competing
endogenous RNAs (ceRNAs) and drug resistance to cancer therapy.
Cancer Drug Resist. 7:372024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xu S, Lian Z, Zhang S, Xu Y and Zhang H:
CircGNG4 promotes the progression of prostate cancer by sponging
miR-223 to enhance EYA3/c-myc expression. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:6841252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chao F, Song Z, Wang S, Ma Z, Zhuo Z, Meng
T, Xu G and Chen G: Novel circular RNA circSOBP governs amoeboid
migration through the regulation of the miR-141-3p/MYPT1/p-MLC2
axis in prostate cancer. Clin Transl Med. 11:e3602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Feng Y, Yang Y, Zhao X, Fan Y, Zhou L,
Rong J and Yu Y: Circular RNA circ0005276 promotes the
proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells by interacting
with FUS to transcriptionally activate XIAP. Cell Death Dis.
10:7922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gandellini P, Folini M, Longoni N, Pennati
M, Binda M, Colecchia M, Salvioni R, Supino R, Moretti R, Limonta
P, et al: miR-205 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in human
prostate through down-regulation of protein kinase cepsilon. Cancer
Res. 69:2287–2295. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hagman Z, Haflidadottir BS, Ceder JA,
Larne O, Bjartell A, Lilja H, Edsjö A and Ceder Y: miR-205
negatively regulates the androgen receptor and is associated with
adverse outcome of prostate cancer patients. Br J Cancer.
108:1668–1676. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kalogirou C, Linxweiler J, Schmucker P,
Snaebjornsson MT, Schmitz W, Wach S, Krebs M, Hartmann E, Puhr M,
Müller A, et al: MiR-205-driven downregulation of cholesterol
biosynthesis through SQLE-inhibition identifies therapeutic
vulnerability in aggressive prostate cancer. Nat Commun.
12:50662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gregorich M, Strohmaier S, Dunkler D and
Heinze G: Regression with highly correlated predictors: Variable
omission is not the solution. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
18:42592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|