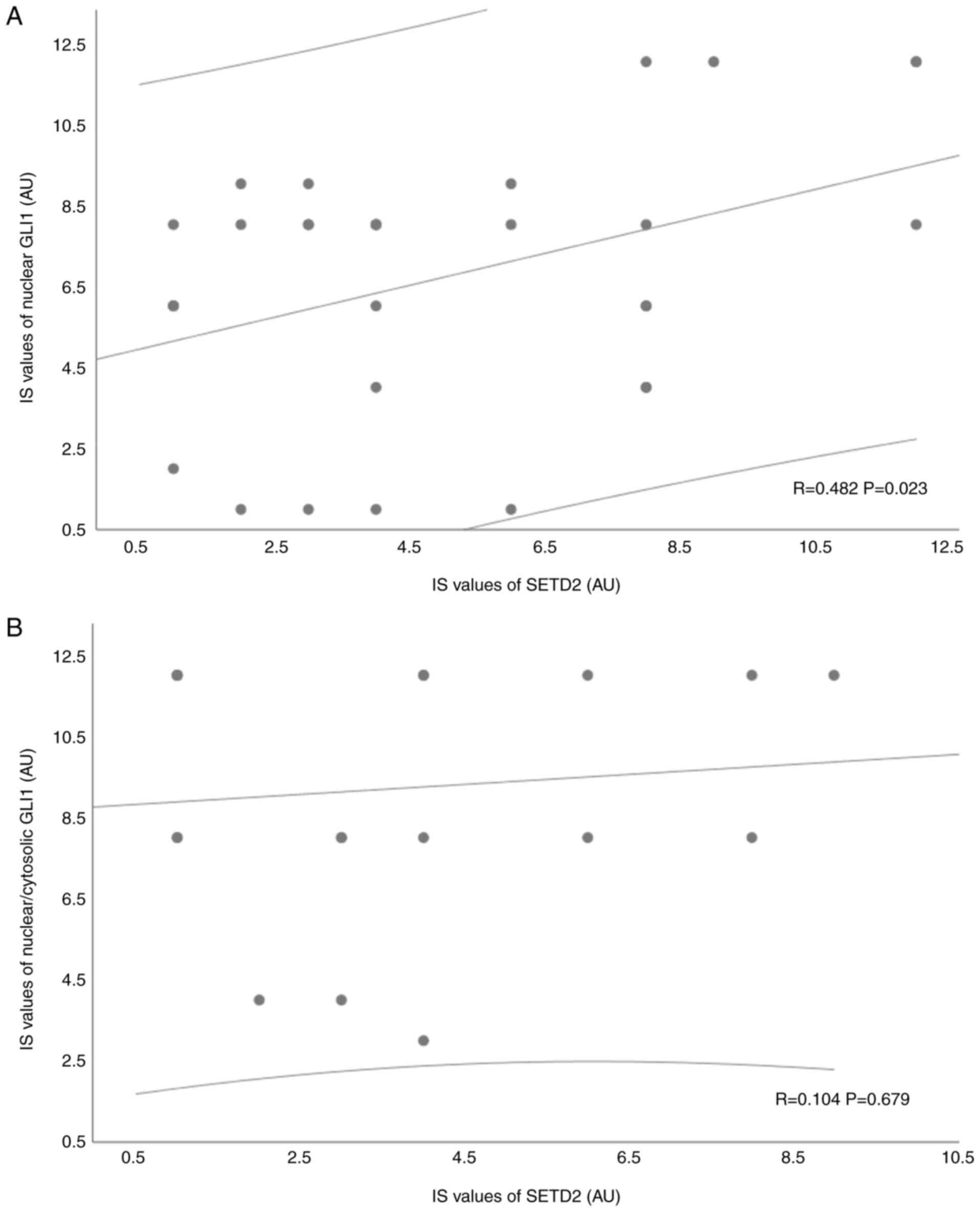
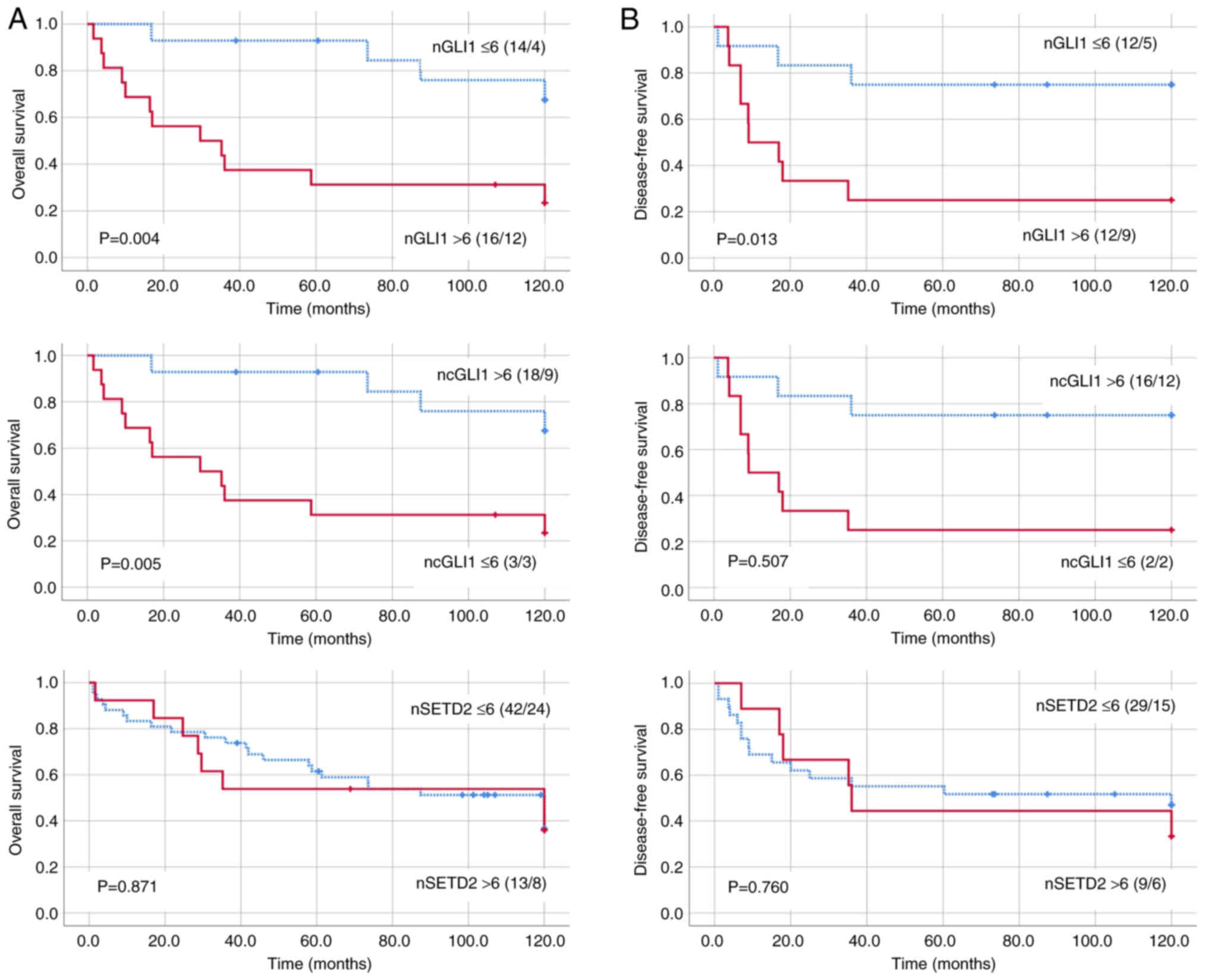
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M,
Colombet M, Mery L, et al: Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today.
Lyon, France, International Agency for Research on Cancer.
2024.https://gco.iarc.who.int/today
|
|
3
|
Hull R, Mbele M, Makhafola T, Hicks C,
Wang S, Reis R, Mehrotra R, Mkhize-Kwitshana Z, Kibiki G, Bates DO
and Dlamini Z: Cervical cancer in low and middle-income countries
(Review). Oncol Lett. 20:2058–2074. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sehnal B, Kmoníčková E, Sláma J, Tomancová
V and Zikán M: Current FIGO staging for carcinoma of the cervix
uteri and treatment of particular stages. Klin Onkol. 32:224–231.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lizano M, Carrillo-García A, De La
Cruz-Hernández E, Castro-Muñoz LJ and Contreras-Paredes A:
Promising predictive molecular biomarkers for cervical cancer
(Review). Int J Mol Med. 53:502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lu M, Zhao B, Liu M, Wu L, Li Y, Zhai Y
and Shen X: Pan-cancer analysis of SETD2 mutation and its
association with the efficacy of immunotherapy. NPJ Precis Oncol.
5:512021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zeng Z, Zhang J, Li J, Li Y, Huang Z, Han
L, Xie C and Gong Y: SETD2 regulates gene transcription patterns
and is associated with radiosensitivity in lung adenocarcinoma.
Front Genet. 13:9356012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Viaene AN, Santi M, Rosenbaum J, Li MM,
Surrey LF and Nasrallah MP: SETD2 mutations in primary central
nervous system tumors. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 6:1232018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jing J, Wu Z, Wang J, Luo G, Lin H, Fan Y
and Zhou C: Hedgehog signaling in tissue homeostasis, cancers and
targeted therapies. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 8:3152023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu C and Wang R: The roles of hedgehog
signaling pathway in radioresistance of cervical cancer. Dose
Response. 17:15593258198852932019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu Z, Huang C, Li R, Li H, Lu H and Lin Z:
PRKCI mediates radiosensitivity via the Hedgehog/GLI1 pathway in
cervical cancer. Front Oncol. 12:8871392022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang C, Lu H, Li J, Xie X, Fan L, Wang D,
Tan W, Wang Y, Lin Z and Yao T: SOX2 regulates radioresistance in
cervical cancer via the hedgehog signaling pathway. Gynecol Oncol.
151:533–541. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chaudary N, Pintilie M, Hedley D, Fyles
AW, Milosevic M, Clarke B, Hill RP and Mackay H: Hedgehog pathway
signaling in cervical carcinoma and outcome after chemoradiation.
Cancer. 118:3105–3115. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chai JY, Sugumar V, Alshanon AF, Wong WF,
Fung SY and Looi CY: Defining the Role of GLI/Hedgehog signaling in
Chemoresistance: Implications in therapeutic approaches. Cancers
(Basel). 13:47462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gennigens C, De Cuypere M, Hermesse J,
Kridelka F and Jerusalem G: Optimal treatment in locally advanced
cervical cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 21:657–671. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J,
Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S,
Mooney M, et al: New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours:
Revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 45:228–247.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vázquez-Ulloa E, Ramos-Cruz AC, Prada D,
Avilés-Salas A, Chávez-Blanco AD, Herrera LA, Lizano M and
Contreras-Paredes A: Loss of nuclear NOTCH1, but not its negative
regulator NUMB, is an independent predictor of cervical malignancy.
Oncotarget. 9:18916–18928. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bohr Mordhorst L, Ahlin C and Sorbe B:
Prognostic impact of the expression of Hedgehog proteins in
cervical carcinoma FIGO stages I–IV treated with radiotherapy or
chemoradiotherapy. Gynecol Oncol. 135:305–311. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lizano M, De la Cruz-Hernández E,
Carrillo-García A, García-Carrancá A, Ponce de Leon-Rosales S,
Dueñas-González A, Hernández-Hernández DM and Mohar A: Distribution
of HPV16 and 18 intratypic variants in normal cytology,
intraepithelial lesions, and cervical cancer in a Mexican
population. Gynecol Oncol. 102:230–235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sotlar K, Diemer D, Dethleffs A, Hack Y,
Stubner A, Vollmer N, Menton S, Menton M, Dietz K, Wallwiener D, et
al: Detection and typing of human papillomavirus by e6 nested
multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 42:3176–3184. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar A, Kumari N, Gupta V and Prasad R:
Renal cell carcinoma: Molecular aspects. Indian J Clin Biochem.
33:246–254. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang C, He C, Wu Z, Li F and Xiao J:
Histone methyltransferase SETD2 regulates osteosarcoma cell growth
and chemosensitivity by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 502:382–388. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen R, Zhao WQ, Fang C, Yang X and Ji M:
Histone methyltransferase SETD2: A potential tumor suppressor in
solid cancers. J Cancer. 11:3349–3356. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li W, Huang Y, Xiao M, Zhao J, Du S, Wang
Z, Hu S, Yang L and Cai J: PBRM1 presents a potential ctDNA marker
to monitor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in cervical cancer.
iScience. 27:1091602024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vishnoi K, Mahata S, Tyagi A, Pandey A,
Verma G, Jadli M, Singh T, Singh SM and Bharti AC: Cross-talk
between Human Papillomavirus Oncoproteins and hedgehog signaling
synergistically promotes stemness in cervical cancer cells. Sci
Rep. 6:343772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gautam D, Johnson BA, Mac M and Moody CA:
SETD2-dependent H3K36me3 plays a critical role in epigenetic
regulation of the HPV31 life cycle. PLoS Pathog. 14:e10073672018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Asthana S, Busa V and Labani S: Oral
contraceptives use and risk of cervical cancer-A systematic review
& meta-analysis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 247:163–175.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gadducci A, Cosio S and Fruzzetti F:
Estro-progestin contraceptives and risk of cervical cancer: A
debated issue. Anticancer Res. 40:5995–6002. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wei X, Hong L, Liang H, Ren K, Man W, Zhao
Y and Guo P: Estrogen and viral infection. Front Immunol.
16:15567282025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gashu C, Tasfa B, Alemu C and Kassa Y:
Assessing survival time of outpatients with cervical cancer: At the
university of Gondar referral hospital using the Bayesian approach.
BMC Womens Health. 23:592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
International Collaboration of
Epidemiological Studies of Cervical Cancer, . Appleby P, Beral V,
Berrington de González A, Colin D, Franceschi S, Goodhill A, Green
J, Peto J, Plummer M and Sweetland S: Cervical cancer and hormonal
contraceptives: Collaborative reanalysis of individual data for
16,573 women with cervical cancer and 35,509 women without cervical
cancer from 24 epidemiological studies. Lancet. 370:1609–1621.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yamamichi F, Shigemura K, Behnsawy HM,
Meligy FY, Huang WC, Li X, Yamanaka K, Hanioka K, Miyake H, Tanaka
K, et al: Sonic hedgehog and androgen signaling in tumor and
stromal compartments drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
prostate cancer. Scand J Urol. 48:523–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lubik AA, Nouri M, Truong S, Ghaffari M,
Adomat HH, Corey E, Cox ME, Li N, Guns ES, Yenki P, et al:
Paracrine sonic hedgehog signaling contributes significantly to
acquired steroidogenesis in the prostate tumor microenvironment.
Int J Cancer. 140:358–369. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaushal JB, Sankhwar P, Kumari S, Popli P,
Shukla V, Hussain MK, Hajela K and Dwivedi A: The regulation of
Hh/Gli1 signaling cascade involves Gsk3β-mediated mechanism in
estrogen-derived endometrial hyperplasia. Sci Rep. 7:65572017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cui Y, Cui CA, Yang ZT, Ni WD, Jin Y and
Xuan YH: Gli1 expression in cancer stem-like cells predicts poor
prognosis in patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma. Exp Mol
Pathol. 102:347–353. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sinicrope FA, Ruan SB, Cleary KR, Stephens
LC, Lee JJ and Levin B: Bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression during
colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 55:237–241. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xuan YH, Jung HS, Choi YL, Shin YK, Kim
HJ, Kim KH, Kim WJ, Lee YJ and Kim SH: Enhanced expression of
hedgehog signaling molecules in squamous cell carcinoma of uterine
cervix and its precursor lesions. Mod Pathol. 19:1139–1147. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yu X, Zhao H, Wang R, Chen Y, Ouyang X, Li
W, Sun Y and Peng A: Cancer epigenetics: From laboratory studies
and clinical trials to precision medicine. Cell Death Discov.
10:282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tinsley E, Bredin P, Toomey S, Hennessy BT
and Furney SJ: KMT2C and KMT2D aberrations in breast cancer. Trends
Cancer. 10:519–530. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Na F, Pan X, Chen J, Chen X, Wang M, Chi
P, You L, Zhang L, Zhong A, Zhao L, et al: KMT2C deficiency
promotes small cell lung cancer metastasis through DNMT3A-mediated
epigenetic reprogramming. Nat Cancer. 3:753–767. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Niu Y, Du C, Zhou Y, Zhang M, Guo Q and
Zhou H: A comparative analysis of survival outcomes and adverse
effects between preoperative brachytherapy with radical surgery and
concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with locally advanced
cervical cancer. Front Oncol. 15:15117482025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|