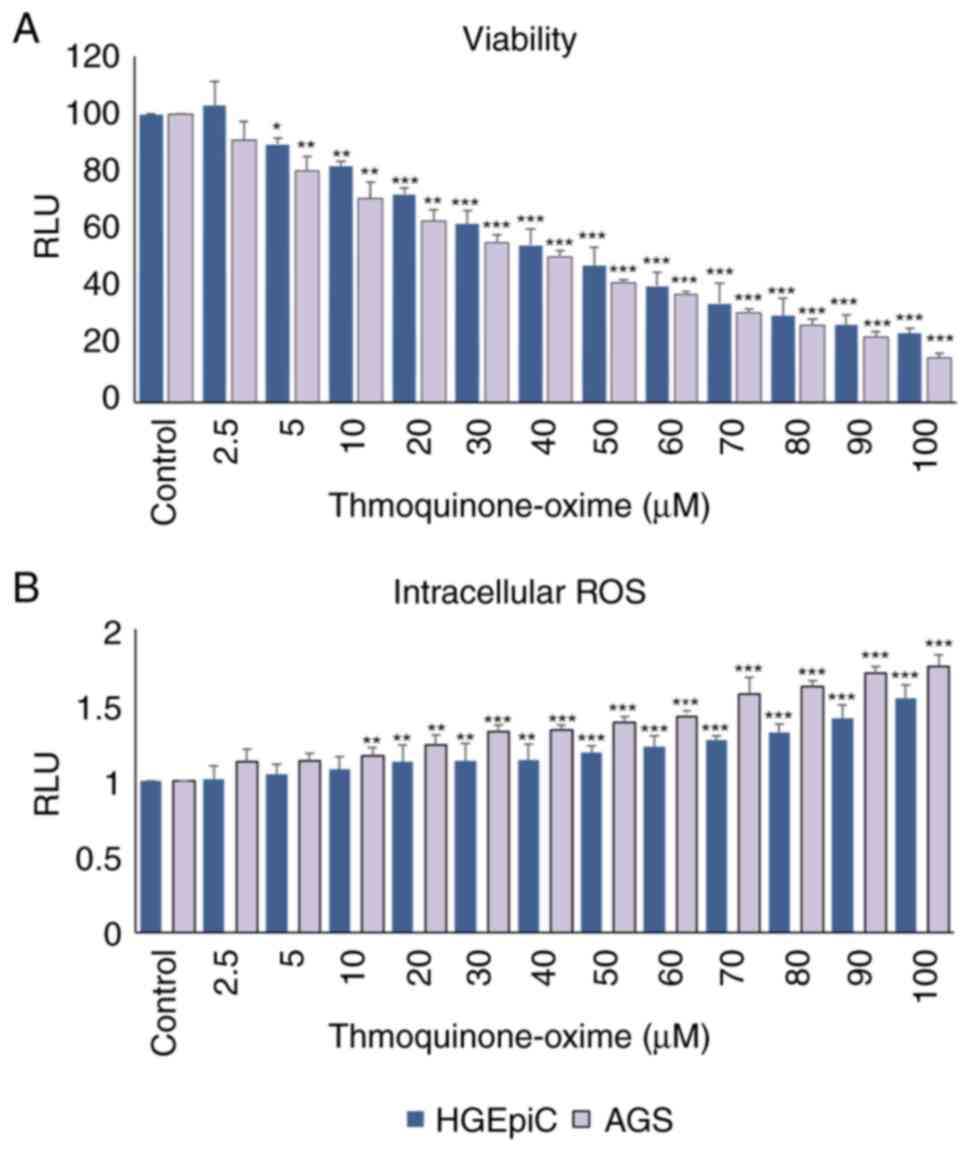
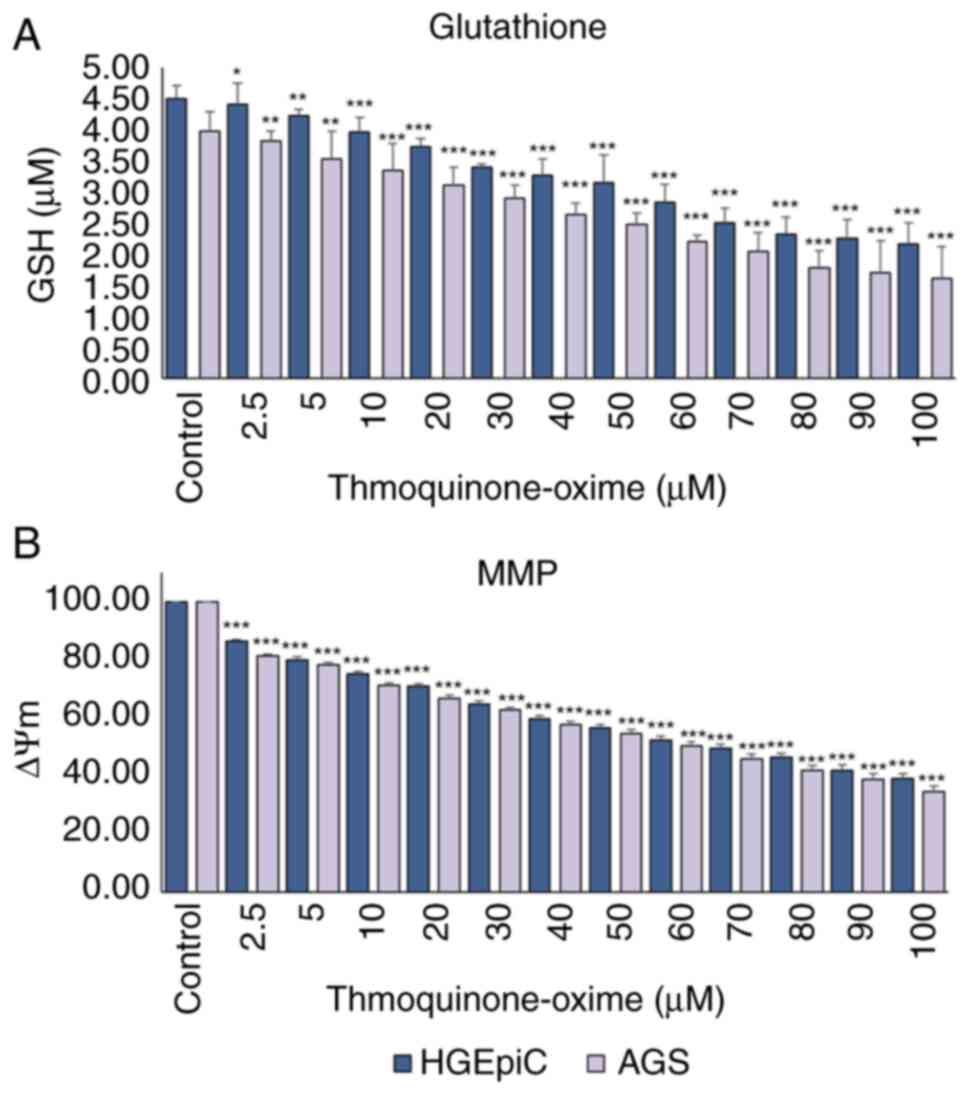
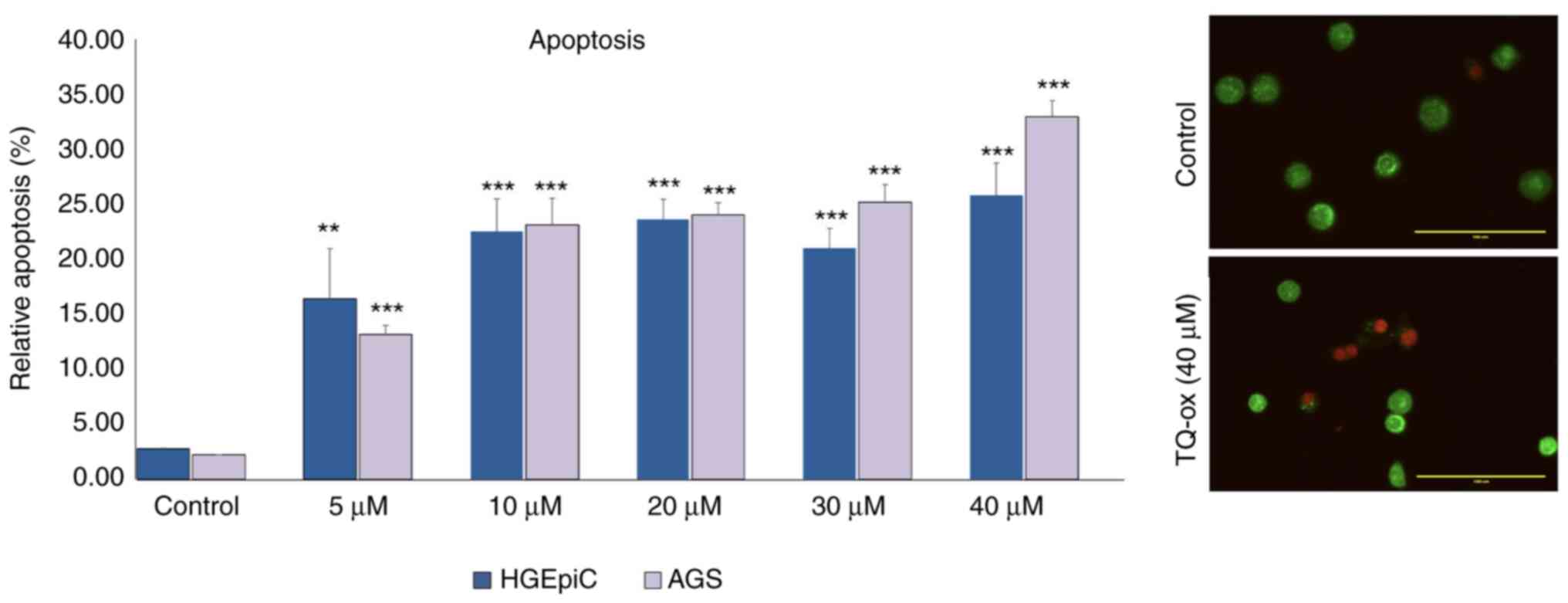
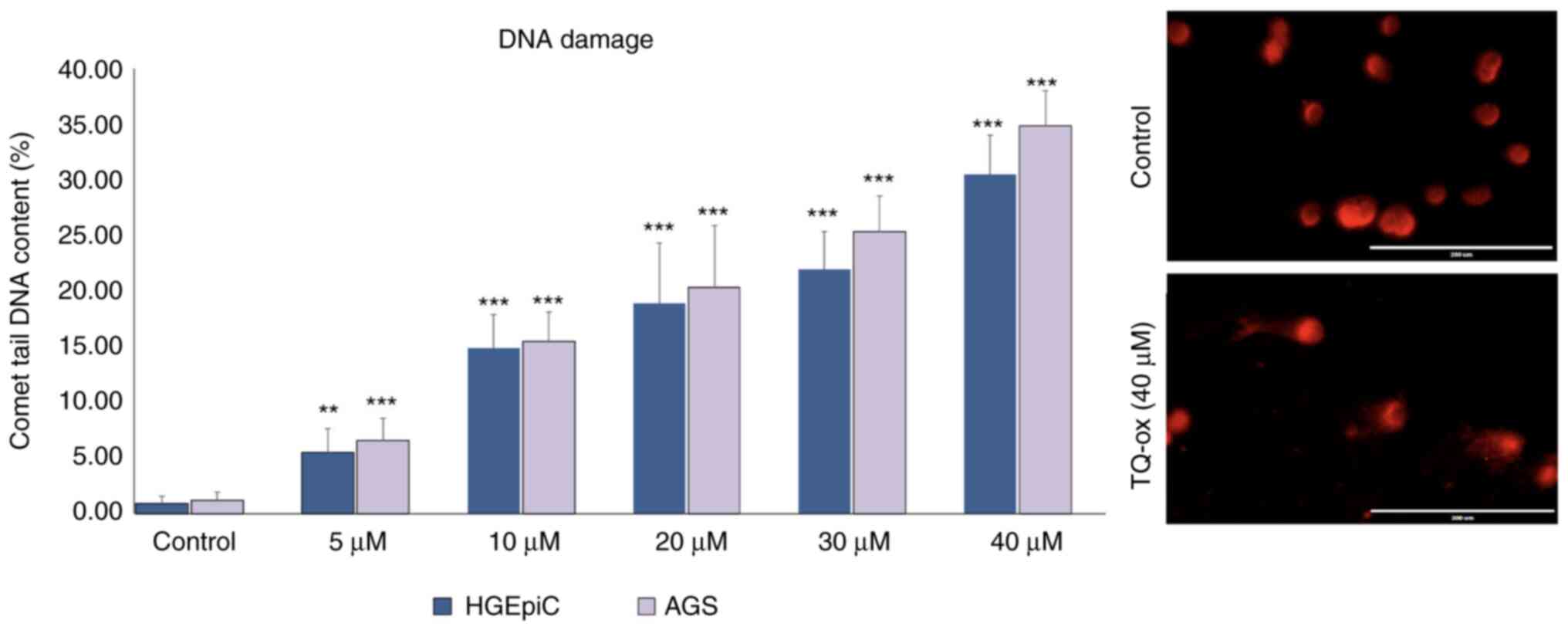
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guan WL, He Y and Xu RH: Gastric cancer
treatment: Recent progress and future perspectives. J Hematol
Oncol. 16:572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Burz C, Pop V, Silaghi C, Lupan I and
Samasca G: Prognosis and treatment of gastric cancer: A 2024
update. Cancers (Basel). 16:17082024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lordick F, Carneiro F, Cascinu S, Fleitas
T, Haustermans K, Piessen G, Vogel A and Smyth EC; ESMO Guidelines
Committee. Gastric cancer, : ESMO clinical practice guideline for
diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 33:1005–1020. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Imran M, Rauf A, Khan IA, Shahbaz M,
Qaisrani TB, Fatmawati S, Abu-Izneid T, Imran A, Rahman KU and
Gondal TA: Thymoquinone: A novel strategy to combat cancer: A
review. Biomed Pharmacother. 106:390–402. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tabassum S, Thakur V, Rosli N, Ichwan SJA,
Mishra P and Suriyah WH: Therapeutic implications of thymoquinone
and its molecular and functional mechanisms against oral and lung
cancer. Gene Rep. 27:1–9. 2022.
|
|
7
|
Butnariu M, Quispe C, Herrera-Bravo J,
Helon P, Kukula-Koch W, López V, Les F, Vergara CV, Alarcón-Zapata
P, Alarcón-Zapata B, et al: The effects of thymoquinone on
pancreatic cancer: Evidence from preclinical studies. Biomed
Pharmacother. 153:1133642022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kale E, Kale A, Bozali K, Gulgec AS,
Ozdemir M, Yalcin B and Guler EM: TQ-Ox, a novel synthetic
derivative of thymoquinone on ovarian cancer cells in vitro. Nat
Prod Res. 37:3015–3024. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang HM, Zhao YL, Sun Q, Ouyang XH and Li
JH: Recent advances in N-O bond cleavage of oximes and
hydroxylamines to construct N-heterocycle. Molecules. 28:17752023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dudchak R, Podolak M, Holota S,
Szewczyk-Roszczenko O, Roszczenko P, Bielawska A, Lesyk R and
Bielawski K: Click chemistry in the synthesis of antibody-drug
conjugates. Bioorg Chem. 143:1069822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guler EM and Bozali K: Synthesised
thymoquinone-oxime induces cytotoxicity, genotoxicity and apoptosis
in hepatocellular cancer cells: In vitro study. Nat Prod Res.
38:1695–1703. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Feng LM, Wang XF and Huang QX:
Thymoquinone induces cytotoxicity and reprogramming of EMT in
gastric cancer cells by targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. J Biosci.
42:547–554. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lei X, Lv X, Liu M, Yang Z, Ji M, Guo X
and Dong W: Thymoquinone inhibits growth and augments
5-fluorouracil-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells both in
vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 417:864–868. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu WQ, Wang J, Guo XF, Liu Z and Dong WG:
Thymoquinone inhibits proliferation in gastric cancer via the STAT3
pathway in vivo and in vitro. World J Gastroenterol. 22:4149–4159.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma J, Hu X, Li J, Wu D, Lan Q, Wang Q,
Tian S and Dong W: Enhancing conventional chemotherapy drug
cisplatin-induced anti-tumor effects on human gastric cancer cells
both in vitro and in vivo by Thymoquinone targeting PTEN gene.
Oncotarget. 8:85926–85939. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
He P, He Y, Ma J, Liu Y, Liu C, Baoping Y
and Dong W: Thymoquinone induces apoptosis and protective autophagy
in gastric cancer cells by inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway.
Phytother Res. 37:3467–3480. 2023. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bozali K, Koc S, Beyaztas H, Ozdemir M,
Ozkan BN, Dumlu FS, Yalcin B and Guler EM: Thymoquinone oxime
synthesis and its effects on melanoma cells: Cytotoxic, genotoxic,
and apoptotic evaluation. Nat Prod Res. 39:5768–5776. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McGahon AJ, Martin SJ, Bissonnette RP,
Mahboubi A, Shi Y, Mogil RJ, Nishioka WK and Green DR: The end of
the (cell) line: Methods for the study of apoptosis in vitro.
Methods Cell Biol. 46:153–185. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Singh NP, Danner DB, Tice RR, Brant L and
Schneider EL: DNA damage and repair with age in individual human
lymphocytes. Mutat Res. 237:123–130. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gomes AR, Pires AS, Abrantes AM, Gonçalves
AC, Costa SC, Varela CL, Silva ET, Botelho MF and Roleira FMF:
Design, synthesis, and antitumor activity evaluation of steroidal
oximes. Bioorg Med Chem. 46:1163602021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vágvölgyi M, Laczkó D, Santa-Maria AR,
Vigh JP, Walter FR, Berkecz R, Deli MA, Tóth G and Hunyadi A:
17-Oxime ethers of oxidized ecdysteroid derivatives modulate
oxidative stress in human brain endothelial cells and
dose-dependently might protect or damage the blood-brain barrier.
PLoS One. 19:e02905262024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gomes AR, Pires AS, Roleira FMF and
Tavares-da-Silva EJ: The structural diversity and biological
activity of steroid oximes. Molecules. 28:16902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zińczuk J, Zaręba K, Kamińska J,
Koper-Lenkiewicz OM, Dymicka-Piekarska V, Pryczynicz A,
Guzińska-Ustymowicz K, Kędra B, Matowicka-Karna J,
Żendzian-Piotrowska M, et al: Association of tumour
microenvironment with protein glycooxidation, DNA damage, and
nitrosative stress in colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res.
13:6329–6348. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chavda V, Chaurasia B, Garg K, Deora H,
Umana GE, Palmisciano P, Scalia G and Lu B: Molecular mechanisms of
oxidative stress in stroke and cancer. Brain Disorders.
5:1000292022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kolsi LE, Leal AS, Yli-Kauhaluoma J, Liby
KT and Moreira VM: Dehydroabietic oximes halt pancreatic cancer
cell growth in the G1 phase through induction of p27 and
downregulation of cyclin D1. Sci Rep. 8:159232018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schepetkin IA, Plotnikov MB, Khlebnikov
AI, Plotnikova TM and Quinn MT: Oximes: Novel therapeutics with
anticancer and anti-inflammatory potential. Biomolecules.
11:7772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Beyaztas H, Babaoglu B, Demirkol B,
Cetinkaya E and Metin Guler E: Synthesis and characterization of
thymoquinone-oxime (TQ-Ox) from thymoquinone and evaluation of its
cytotoxic, genotoxic, and apoptotic potential in lung cancer cells
(A549) in vitro. ChemistrySelect:. 9:e2023049402024. View Article : Google Scholar
|