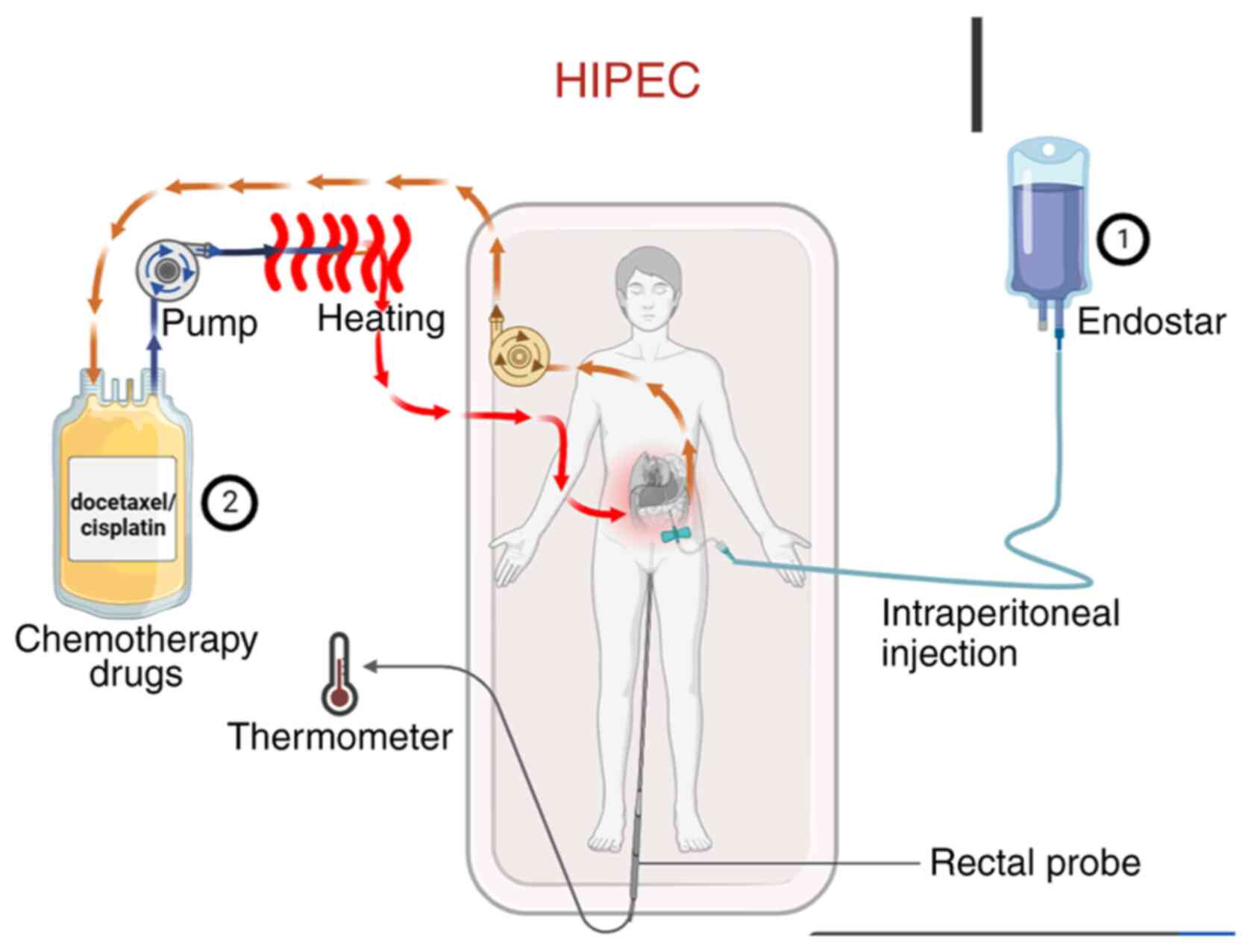
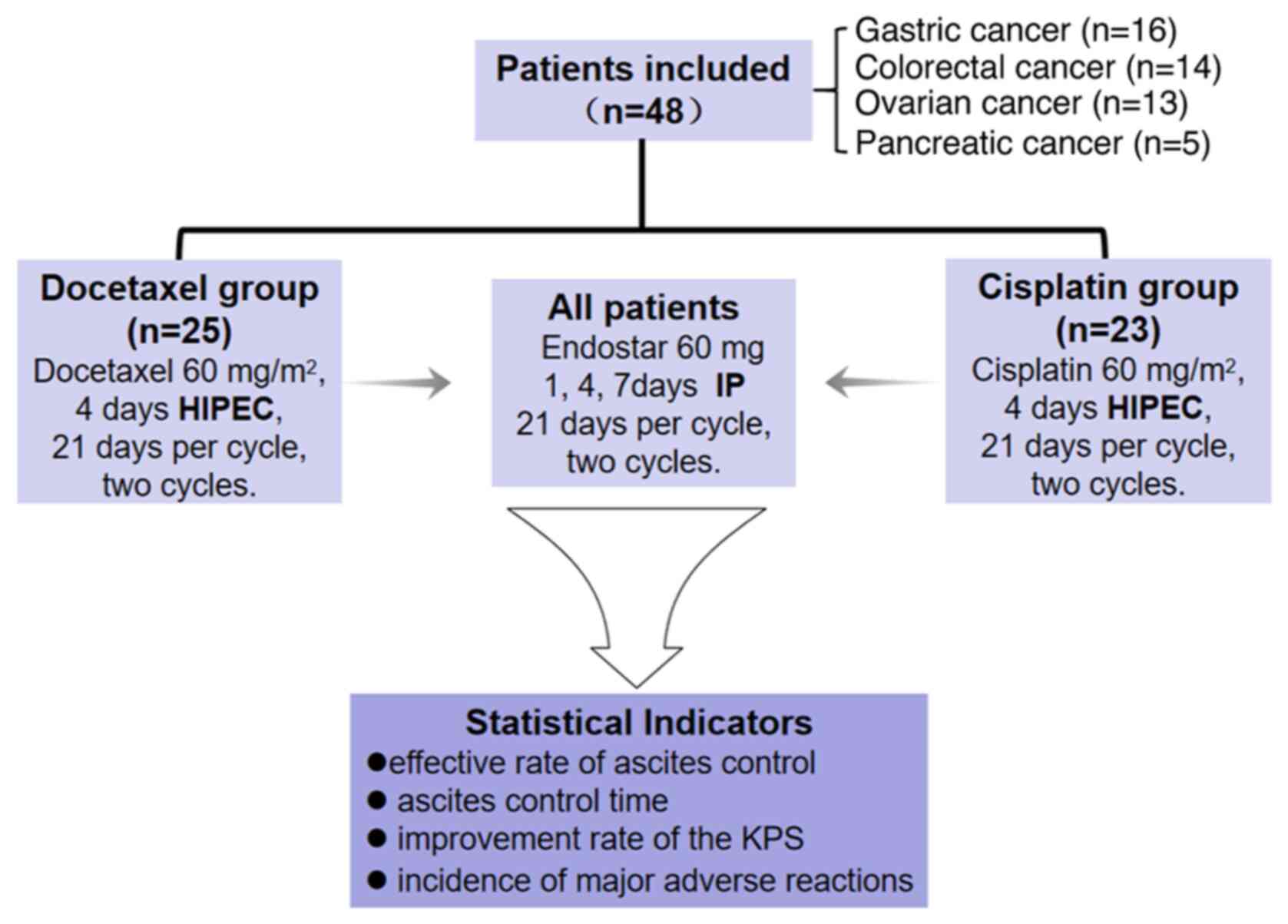
Introduction
Peritoneal metastases (PM), typically originating
from colorectal cancer (1), gastric
cancer (2,3), ovarian cancer (4), pancreatic cancer (5) and other abdominal tumors, are
typically regarded as the terminal stage of cancer (6). Uncontrolled malignant ascites (MA) is
the main complication of PM, leading to abdominal distension,
abdominal pain, dyspnea, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and
decreased mobility, which seriously affects quality of life
(7). The effectiveness of existing
treatment methods for PM, including extended frequent high-volume
puncture drainage, peritoneal venous shunt, diuretics, systemic
chemotherapy, intraperitoneal (IP) chemotherapy and immunotherapy,
remains limited and does not meet the needs of patients. Given the
significantly higher incidence of renal injury observed in the
cisplatin group in the present study, clinicians should be cautious
about nephrotoxicity when considering this agent for high-risk
patients with PM.
Hyperthermic IP chemotherapy (HIPEC) is a
specialized treatment method that targets and directly eliminates
malignant cells within the abdominal cavity by circulating heated
chemotherapy drugs within the peritoneal cavity, especially in
patients who have experienced systemic therapy failure (8,9). This
technique aims to eliminate free cancer cells, fibrin and other
cellular debris by flushing these substances out of the body, which
can reduce adhesion. Additionally, HIPEC can enhance the absorption
and sensitivity of tumor cells to chemotherapy drugs, increasing
the penetration of chemotherapy at the peritoneal surface,
resulting in efficient tumor cell death for advanced peritoneal
cavity cancers (10). In 1980,
Spratt first reported (11) the use
of HIPEC specifically for the treatment of abdominal and pelvic
malignant tumors, and residual tumors, and this technique has
proven to be a promising treatment modality (12). HIPEC is used to treat
gastrointestinal cancer, ovarian cancer, pseudomyxoma peritonei and
other peritoneal cancer types (13,14).
However, this technology is currently underdeveloped, and there are
no clear guidelines for drug selection.
Endostar is a vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) inhibitor that has been shown to significantly reduce
visible ascites formation and tumor burden (15). VEGF overexpression is commonly
observed in malignant cancer metastases affecting the abdominal
region (16). Prospective
multicenter clinical studies have confirmed the efficacy of
Endostar and cisplatin injections for controlling malignant pleural
effusions (17,18). In recent years, docetaxel has also
been reported to control MA (19).
In addition, hyperthermia is known to enhance tumor perfusion and
increase drug penetration after IP delivery (20).
The present study retrospectively assessed the
effectiveness and adverse effects of HIPEC using
docetaxel/cisplatin, combined with IP Endostar injections, for
treating MA in patients who had failed at least two rounds of
systemic chemotherapy regimens. The findings provide valuable
insights for improving and developing new therapies for this
condition.
Materials and methods
Study design and patients
The present retrospective study involved patients
treated between July 2019 and December 2020 at the Sandun Campus of
Zhejiang Hospital (Hangzhou, China). The eligibility criteria were
as follows: i) Patients must have been diagnosed with a malignant
tumor, with evidence of cytology or tumor cells in an ascites cell
block; ii) patients must have previously undergone systemic
chemotherapy of second line or higher, and not undergone a HIPEC
procedure in the past 6 months; iii) patients must not have
received docetaxel, cisplatin or Endostar before receiving the
protocol under investigation; iv) hemoglobin level must be ≥90 g/l
(normal range, 120–160 g/l for women and 130–170 g/l for men); v)
absolute neutrophil count must be ≥1.5×109/l (normal
range, 1.8–7.7×109/l); vi) white blood cell count must
be >3.5×109/l (normal range,
4.0–10.0×109/l); vii) platelet count must be
≥85×109/l (normal range, 150–400×109/l);
viii) total bilirubin must be ≤1.5 times the upper limit of normal
(ULN) (normal range, 3.4–20.5 µmol/l or 0.2–1.2 mg/dl); ix)
aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase must both
be ≤2.5 times the ULN (normal range for AST, 8–40 U/l; normal range
for ALT, 7–56 U/l); x) patients must have an expected survival time
of >3 months; and xi) patients should have failed at least two
rounds of systemic chemotherapy regimens. The exclusion criteria
were: i) Uncontrolled central nervous system metastases with
manifestations of intracranial hypertension; ii) bleeding tendency,
especially marked gastrointestinal bleeding within the past 4
weeks, or currently undergoing thrombolytic or anticoagulant
therapy; iii) prior IP infusion of docetaxel, cisplatin or Endostar
within 6 months, or concurrent participation in other clinical
studies; iv) myocardial infarction within the past 6 months, or
current unstable angina pectoris or cardiac insufficiency; v)
severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and/or respiratory
failure, or severe intestinal adhesions; vi) currently uncontrolled
severe infection; vii) known allergy to the investigational drug(s)
or their excipients; viii) fertile patients unwilling to adopt
contraception, and pregnant or lactating women; ix) poor compliance
or diagnosed with significant psychiatric disorders causing lack of
self-control.
All patients provided written informed consent prior
to catheterization and underwent HIPEC via abdominal puncture as
part of routine clinical treatment for malignant ascites. This
study was approved by the Scientific Research Board of Zhejiang
Hospital, who waived the requirement for informed patient consent
for study participation.
Treatment procedure
Abdominal circumference was measured in all patients
before and after treatment. The treatment protocol is outlined in
Fig. 1. First, the volume of
ascites was assessed via abdominal ultrasonography. Under
ultrasound guidance, a single-lumen central venous catheter or an
external drainage catheter (6F or 8F) was percutaneously inserted
into the abdominal cavity for continuous drainage. Ascites was
drained slowly over 1–3 days with the flow regulated not to exceed
1,000 ml/h to prevent complications. Endostar was administered by
intraperitoneal injection on days 1, 4 and 7 of the treatment
cycle. On day 4, HIPEC was performed immediately following the
Endostar injection. The chemotherapeutic agent (docetaxel or
cisplatin) was prepared in a perfusion solution, which was then
circulated through a closed-loop system equipped with a pump and a
heating module. The solution was heated to the target therapeutic
temperature (42–43°C) and infused into the abdominal cavity; it was
maintained in circulation for the prescribed duration to allow for
continuous hyperthermic perfusion of the peritoneal surface, before
being returned to the system for reheating and recirculation. Core
body temperature was monitored in real-time throughout the HIPEC
procedure using a rectal temperature probe. Ascites drainage
statistics were collected. HIPEC was administered using a
thermochemotherapy perfusion device (RHL-2000A; Jilin Maida Medical
Device Co., Ltd.) with careful temperature control of the body
between 43 and 45°C. Prior to chemotherapeutic drug infusion, the
abdominal cavity was effectively rinsed with 1,000-2,000 ml of warm
normal saline.
All patients received IP injections of Endostar (60
mg) on days 1, 4 and 7 of a 21-day cycle, for a total of two
cycles. The Endostar timing was decided based on the vascular
normalization window principle, as recombinant human endostatin can
temporarily normalize the structure and function of the tumor
vasculature, with this optimal window typically occurring between 3
to 5 days after administration. Therefore, the concurrent IP
administration of Endostar and HIPEC chemotherapeutic agents on day
4 was designed to leverage this transient window to reduce
interstitial pressure and promote the deep and uniform penetration
of chemotherapeutic drugs into the tumor tissues, achieving
spatiotemporal synergism. This regimen aligns with the
recommendations of the Expert Consensus on the Clinical Application
of Recombinant Human Endostatin for the Treatment of Malignant
Serous Cavity Effusions (21) and
has been validated as effective in multiple clinical studies
(22–25). As well as Endostar, 25 patients in
the docetaxel group received 60 mg/m2 docetaxel
intraperitoneally on day 4 as circulating hyperthermic perfusion
chemotherapy, with 21 days per cycle, for a total of two cycles.
Oral administration of 4 mg dexamethasone tablets was started the
day before docetaxel treatment, for a total of 3 days. In the
cisplatin group, 23 patients received 60 mg/m2 cisplatin
on day 4 as IP circulating hyperthermic perfusion chemotherapy,
with 21 days per cycle, for a total of two cycles. During the
course of treatment, diuresis and albumin supplementation were
administered as supportive treatments according to specific
conditions, routine blood tests were performed, liver and kidney
functions were monitored, and adverse reactions were observed.
The selection of the treatment approach was not
randomized. Within Zhejiang Hospital, patients with gastric,
ovarian and pancreatic cancer are recommended either cisplatin or
docetaxel treatment, while for patients with colon cancer, only
cisplatin is used. These recommendations are based on clinical
practice guidelines and individual patient characteristics.
Moreover, in line with standard clinical practice to avoid
cisplatin-associated nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity, patients
with renal insufficiency (eGFR <60 ml/min) or neuropathy
received docetaxel rather than cisplatin.
Outcomes
The ascites control time was defined as the duration
from achieving a complete response (CR) or partial response (PR)
until the first documented evidence of progressive disease (PD) and
was calculated from the end of the second cycle of treatment. The
abdominal circumference was measured twice a week, and follow-up
examinations were conducted at the hospital 4 weeks after the end
of treatment, followed by collection of abdominal circumference
measurements by telephone. The World Health Organization evaluation
standard (26) classifies ascites
that has completely subsided for >4 weeks as a CR, ascites that
has decreased by >50% and been maintained for >4 weeks as a
PR, ascites that has decreased by <50% or increased by <25%
and been maintained for >4 weeks as SD, and ascites that has
increased by >25% as PD. Objective response rate (ORR)=(CR +
PR)/total number of cases ×100. Disease control rate (DCR)=(CR + PR
+ SD)/total number of cases ×100. If the ascites reached PD,
follow-up was terminated after 90 days. During the follow-up
period, there were no deaths or patients lost to follow-up.
The changes in Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS)
score before and after treatment were evaluated according to the
Karnofsky scoring standard (27).
After treatment, a KPS increase of ≥10 points was evaluated as an
improvement in quality of life (QOL), a change of <10 points was
evaluated as stable and a decrease of ≥10 points was evaluated as
decreased QOL (28).
According to the National Cancer Institute Common
Toxic Reaction Standard CTC V4.0, the toxicity grading standard is
divided into grades 1–5, of which grades 1–2 are low-grade
reactions, grades 3–4 are severe reactions and grade 5 indicates
death (29).
Follow-up
The follow-up protocol was defined as follows: Once
PD was reached, the endpoint was determined. Further intensive
follow-up was therefore unnecessary for scientific reasons, and
also to reduce the burden on patients. Follow-up was terminated 90
days after PD, or earlier if the patient died or was lost to
follow-up, while patients without PD were followed until death,
loss to follow-up or study end.
Statistical analysis
Statistical software SPSS (version 26.0; IBM Corp.)
was used for the data analysis. The ascites control time was
defined as the duration from achieving a CR or PR until the first
documented evidence of PD and was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier
method and differences between groups were compared using the
log-rank test. Normally distributed continuous variables (as
assessed using quantile-quantile plots) are expressed as the mean ±
standard deviation and compared using an unpaired t-test, while
non-normally distributed variables are presented as the median
(interquartile range) and compared using the Wilcoxon rank-sum
test. Count data were compared between the groups using the
χ2 test or Fisher's exact probability method. P<0.05
is considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Patient's basic characteristics
As illustrated in Fig.
2, a collective total of 48 patients were included in this
research, with 16 patients diagnosed with gastric cancer, 14
patients diagnosed with colorectal cancer, 13 patients diagnosed
with ovarian cancer and 5 patients diagnosed with pancreatic
cancer. Comparing the cisplatin and docetaxel groups, the age
(55.9±15.4 vs. 55.5±13.8 years; t=0.350; P=0.927), sex [male: 11
(47.8%) vs. 10 (40.0%); χ2=0.298; P=0.585], primary
tumor type (the most common type was gastric cancer: 8 (34.8%) vs.
8 (32.0%); χ2=0.480; P=0.923), KPS score [≥60 points: 14
(60.9%) vs. 16 (64.0%); χ2=0.050; P=0.823], ascites
volume [<3,000 ml: 10 (43.5%) vs. 9 (36.0%);
χ2=0.280; P=0.597] and previous treatment option
[second-line: 9 (39.1%) vs. 8 (32.0%); χ2=0.266;
P=0.606] of the two groups were evenly distributed and the results
were comparable (Table I).
 | Table I.Comparison of general conditions
between the docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups. |
Table I.
Comparison of general conditions
between the docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups.
| Variables | Docetaxel
group | Cisplatin
group |
χ2/t | P-value |
|---|
| Sex, n (%) |
|
| 0.298 | 0.585 |
|
Male | 10 (40.0) | 11 (47.8) |
|
|
|
Female | 15 (60.0) | 12 (52.2) |
|
|
| Age, years |
|
| 0.350 | 0.927 |
| Average
age | 55.5±13.8 | 55.9±15.4 |
|
|
| Age
distribution | 28-78 | 30-78 |
|
|
| KPS, n (%) |
|
| 0.050 | 0.823 |
|
≥60 | 16 (64.0) | 14 (60.9) |
|
|
|
<60 | 9 (36.0) | 9 (39.1) |
|
|
| Ascites volume, n
(%) |
|
| 0.280 | 0.597 |
|
<3,000 ml | 9 (36.0) | 10 (43.5) |
|
|
| ≥3,000
ml | 16 (64.0) | 13 (56.5) |
|
|
| Prior treatment, n
(%) |
|
| 0.266 | 0.606 |
|
Second-line | 8 (32.0) | 9 (39.1) |
|
|
|
>Second-line | 17 (68.0) | 14 (60.9) |
|
|
| Primary tumor, n
(%) |
|
| 0.480 | 0.923 |
| Gastric
cancer | 8 (32.0) | 8 (34.8) |
|
|
|
Colorectal cancer | 8 (32.0) | 6 (26.1) |
|
|
| Ovarian
cancer | 6 (24.0) | 7 (30.4) |
|
|
|
Pancreatic cancer | 3 (12.0) | 2 (8.7) |
|
|
Objective efficacy evaluation
In Table II, among
the participants in the docetaxel group, 3 patients achieved a CR,
13 achieved a PR, 7 were stable and 2 exhibited PD, with an ORR of
64.0% and a DCR of 92.0%. In the cisplatin group, 2 patients
achieved a CR, 11 achieved a PR, 8 were stable and 2 exhibited PD,
with an ORR of 56.5% and a DCR of 91.3%. There were no
statistically significant differences between the two groups in
terms of either ORR (χ2=0.280, P=0.597) or DCR
(P>0.999, Fisher's exact test).
 | Table II.Comparison of curative effects
between the docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups. |
Table II.
Comparison of curative effects
between the docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups.
| Response | Docetaxel
group | Cisplatin
group | χ2 | P-value |
|---|
| CR, n (%) | 3 (12.0) | 2 (8.7) |
|
|
| PR, n (%) | 13 (52.0) | 11 (47.8) |
|
|
| SD, n (%) | 7 (28.0) | 8 (34.8) |
|
|
| PD, n (%) | 2 (8.0) | 2 (8.7) |
|
|
| ORR, n (%) | 16 (64.0) | 13 (56.5) | 0.280 | 0.597 |
| DCR, n (%) | 23 (92.0) | 21 (91.3) | - |
>0.999a |
QOL of patients
KPS scores were utilized to gauge the QOL. As shown
in Table III, KPS improvement
rates were 48.0 and 43.5% for the docetaxel and cisplatin groups,
respectively. There was no significant difference in the QOL
between the two groups (χ2=0.967;
P=0.617).
 | Table III.Improvement of quality of life
between the docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups. |
Table III.
Improvement of quality of life
between the docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups.
| Status | Docetaxel
group | Cisplatin
group | χ2 | P-value |
|---|
| Improvement, n
(%) | 12 (48.0) | 10 (43.5) |
|
|
| Stabilization, n
(%) | 11 (44.0) | 9 (39.1) |
|
|
| Declined, n
(%) | 2 (8.0) | 4 (17.4) | 0.967 | 0.617 |
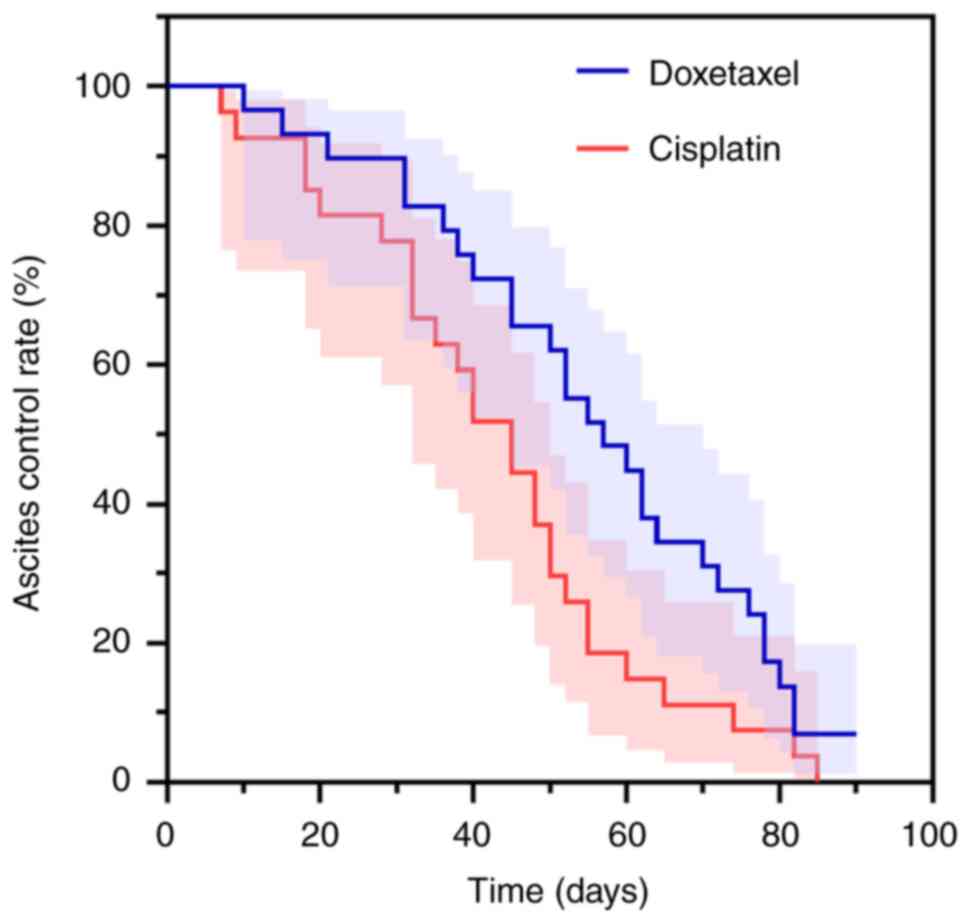
The median ascites control time was 55 days (95% CI:
46.892–63.108) in the docetaxel group and 46 days (95% CI:
34.261–57.739) in the cisplatin group. When comparing the control
time between the two groups, the difference was not statistically
significant (log-rank χ2=0.934; P=0.334)
(Fig. 3).
Security analysis
There were no significant differences between the
two groups in terms of the incidence of leukopenia
(χ2=0.680; P=0.712), anemia
(χ2=0.473; P=0.789), thrombocytopenia
(χ2=0.762; P=0.683), nausea and vomiting
(χ2=1.451; P=0.484), anorexia
(χ2=0.309; P=0.857), fatigue
(χ2=0.071; P=0.965), constipation
(χ2=0.371; P=0.573), abdominal pain and diarrhea
(χ2=0.285; P=0.867), hepatic damage
(χ2=0.084; P=0.772), or palpitation/chest
tightness (χ2=0.084; P=0.772). However, the
incidence of kidney damage was significantly higher in the
cisplatin group than in the docetaxel group
(χ2=6.194; P=0.045). Additionally, there was a
significant difference between the two groups with regard to the
elevation of blood pressure (χ2=5.135; P=0.023)
(Table IV).
 | Table IV.Adverse reactions between the
docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups. |
Table IV.
Adverse reactions between the
docetaxel (n=25) and cisplatin (n=23) groups.
| Variables | Docetaxel
group | Cisplatin
group | χ2 | P-value |
|---|
| Leukopenia, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 6 (24.0) | 4 (17.4) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 2 (8.0) | 1 (4.3) | 0.680 | 0.712 |
| Anemia, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 5 (20.0) | 4 (17.4) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 1 (4.0) | 2 (8.7) | 0.473 | 0.789 |
| Thrombopenia, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 4 (16.0) | 6 (26.1) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 1 (4.0) | 2 (8.7) | 0.762 | 0.683 |
| Nausea and
vomiting, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 4 (16.0) | 5 (21.7) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 0 (0.0) | 1 (4.3) | 1.451 | 0.484 |
| Anorexia, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 8 (32.0) | 9 (39.1) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 2 (8.0) | 2 (8.7) | 0.309 | 0.857 |
| Fatigue, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 14 (56.0) | 12 (52.2) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 2 (8.0) | 1 (4.3) | 0.071 | 0.965 |
| Constipation, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 6 (24.0) | 4 (17.4) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.371 | 0.573 |
| Abdominal pain and
diarrhea, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 4 (16.0) | 5 (21.7) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 2 (8.0) | 2 (8.7) | 0.285 | 0.867 |
| Hepatic damage, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 4 (16.0) | 3 (13.0) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.084 | 0.772 |
| Kidney damage, n
(%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 1 (4.0) | 5 (21.7) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 0 (0.0) | 2 (8.7) | 6.194 | 0.045 |
| Palpitation/chest
tightness, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 4 (16.0) | 3 (13.0) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.084 | 0.772 |
| Elevation of blood
pressure, n (%) |
|
|
|
|
|
I–II | 5 (20.0) | 0 (0.0) |
|
|
|
III–IV | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 5.135 | 0.023 |
Discussion
Advanced tumor PM can result in the development of
MA, which significantly impairs patient survival and QOL (30). The development of MA is a
multifaceted and intricate physiological process that is
intricately linked to the impediment of lymphatic drainage, tumor
angiogenesis and alterations in microvascular permeability
(31). VEGF stimulates tumor cells
and mesothelial cells, causing vascular growth factors such as
TNF-α, TGF-β, VEGF and IL-8 to increase in malignant effusions
(32). The VEGF level of MA is
significantly higher than that of benign ascites and VEGF levels
are correlated with a worse prognosis (33). The ‘peritoneal-plasma barrier’
restricts macromolecular drug absorption via the peritoneum, which
enables a high drug concentration in the abdominal cavity while
maintaining low peripheral blood drug levels (34). HIPEC, a recent therapeutic strategy,
promotes deep tissue penetration of chemotherapeutic drugs,
enhancing their concentration in tumor cells, and achieving a
positive therapeutic effect.
As shown in Fig. 4,
the general mechanism of Endostar combined with docetaxel/cisplatin
HIPEC in the treatment of MA may be as follows: i) Endostar
inhibits vascular endothelium proliferation, differentiation and
migration, reducing blood vessel filtration area and permeability,
reducing material exudation and controlling MA osmotic pressure,
thereby reducing effusion (7,35,36).
ii) HIPEC treatment kills MA tumor cells by repeated washing,
causing anoikis and tumor cell detachment. Heat changes the tumor
cell membrane and vascular permeability, reducing drug metabolism
and increasing drug concentration (37,38).
Heat shock protein activation by heat can induce an autoimmune
attack on tumor cells, block angiogenesis and cause protein
denaturation (39). iii) Cisplatin
can directly enter the tumor cell nucleus to prevent DNA
replication and transcription to achieve the purpose of killing
tumor cells (40). iv) Docetaxel
binds to tubulin subunits after entering the body, stably
accumulates tubulin, prevents depolymerization and inhibits tumor
cell proliferation (41).
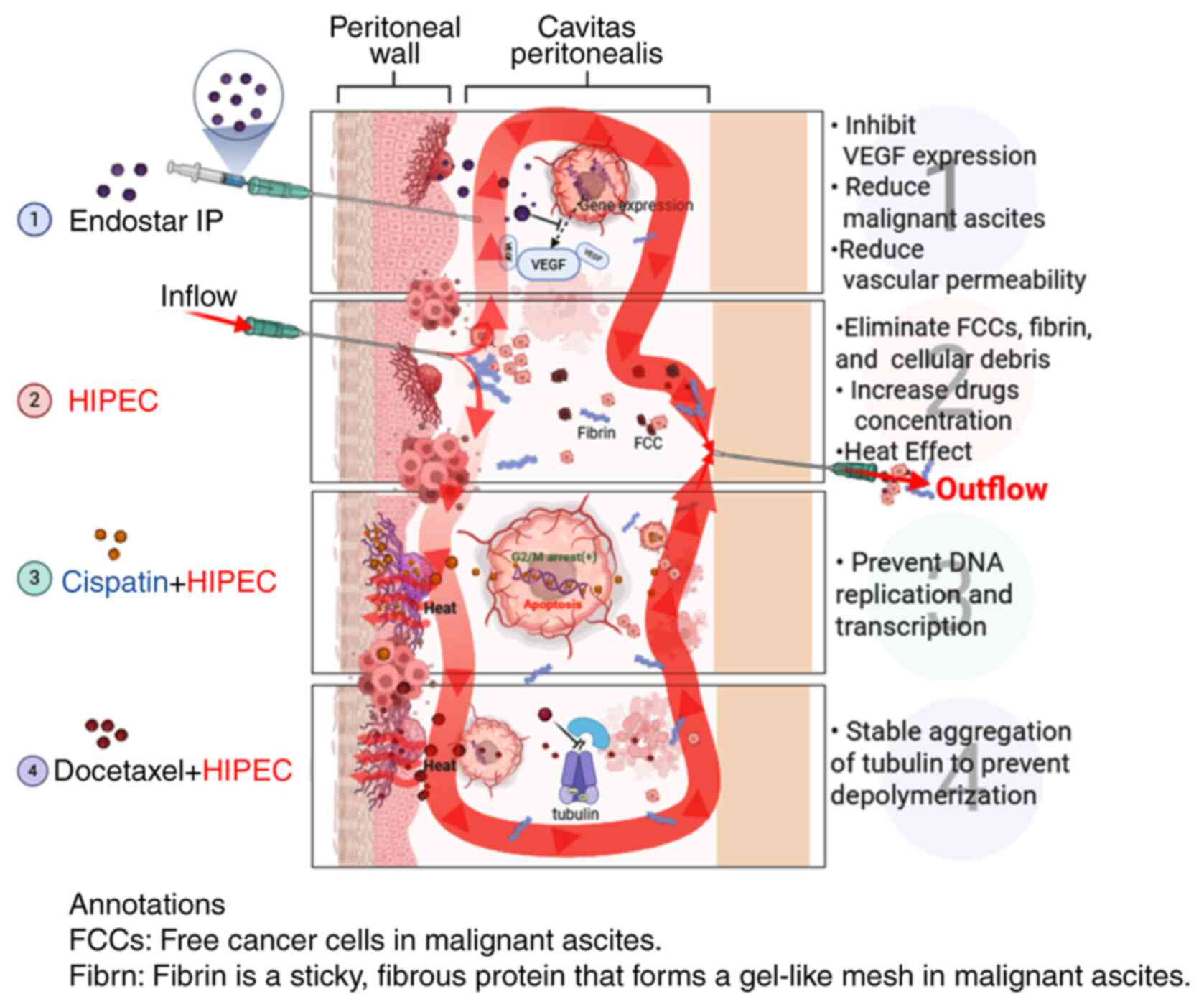 | Figure 4.Mechanisms of docetaxel/cisplatin
HIPEC combined with IP Endostar in the treatment of MA. As shown in
point 1, the IP Endostar injection inhibits VEGF expression,
reduces MA and reduces vascular permeability. A shown in point 2,
when HIPEC is performed, drug concentration and temperature
increase. As shown in points 3 and 4, the addition of cisplatin can
prevent DNA replication and transcription, while the addition of
docetaxel can stabilize the aggregation of tubulin and prevent
depolymerization. MA, malignant ascites; IP, intraperitoneal;
HIPEC, hyperthermic IP chemotherapy; FCC, free cancer cell. Created
in BioRender, https://app.biorender.com/illustrations/64297f7a20eede8ed30124a8?slideId=3d6d849d-02c8-4b18-b5ee-18396b8d452e. |
Cisplatin and Endostar are both commonly used drugs
for HIPEC and have various indications for use. Cisplatin is
conventionally indicated for peritoneal malignancies, particularly
ovarian cancer (42), whereas
Endostar is commonly employed in the management of malignant
ascites (43). Zhao et al
(35) reported that the disease
control rate was 87.0% for pleural effusion and ascites using
Endostar combined with cisplatin, while Fu et al (44) showed that patients who received
HIPEC with cisplatin plus docetaxel had a longer median overall
survival time compared with those who received cisplatin plus
mitomycin. A previous study revealed that detectable cisplatin
concentrations persisted for at least 6 h post-HIPEC (45), while Endostar was proven effective
for reducing the expression of VEGF and other factors, including
fibroblast growth factor-2, transforming growth factor-β1, and
platelet-derived growth factor-B (46). However, the major side effects of
cisplatin include acute and chronic nephrotoxicity, both systemic
and IP. Hakeam et al (47)
reported that 3.7% of patients experienced acute kidney injury
after HIPEC with cisplatin, while Gómez-Ruiz et al (48) showed that 7.2% of patients developed
acute renal dysfunction after HIPEC. Cisplatin can induce early
proximal tubular injury, leading to acute or subacute tubular
necrosis. In addition, cisplatin can cause a gradual and
irreversible decline in the long-term filtration capacity of the
glomerulus, leading to chronic renal failure. This toxicity is the
main reason for limiting the IP injection of cisplatin (37). Previous studies showed that the
incidence of acute renal failure after HIPEC combined with
cisplatin was from 1.3 to 40.4%, and 8.5% developed into grade 3–4
kidney injury; moreover, these acute or chronic renal failures
contributed to 4.3% of long-term dialysis patients (49,50),
which seriously affected subsequent consolidation therapy with
other anticancer drugs or further treatment after recurrence. In
the present study, the incidence of renal impairment in the
cisplatin group was 30.4%, which is similar to that reported in the
aforementioned previous studies. Docetaxel is a semi-synthetic
taxoid drug that is widely used to treat non-small cell lung,
breast, gastric and ovarian cancer (51). Studies have shown that the area
under the curve (AUC) of peritoneal injection is nearly 1,000 times
higher than that of intravenous injection, and the peak
concentration in the peritoneum is ~200 times higher than that in
the plasma, making docetaxel a suitable drug for HIPEC application
(52,53). The present study retrospectively
evaluated the efficacy and safety of docetaxel/cisplatin combined
with Endostar for the treatment of MA. The objective remission rate
(64.0 vs. 56.5%), DCR (92.0 vs. 91.3%), improvement in the KPS
score (48 vs. 43.5%) and median control time of ascites (55 days
vs. 46 days) in the two groups were similar. However, in terms of
the occurrence of adverse reactions, the cisplatin group had higher
renal toxicity; 5 patients had grade 1–2 renal damage, and after
symptomatic treatments such as diuresis and kidney protection (such
as reduced glutathione Bailing capsule use), the renal function
recovered to normal. Overall, 2 patients had grade 3–4 renal
damage, and 1 patient developed chronic renal failure and received
hemodialysis maintenance treatment. The incidence of renal
impairment was much lower in the docetaxel group than in the
cisplatin group, and the underlying reason could be associated with
the different metabolism of the two drugs. Miller et al
(54) reported that cisplatin is
primarily excreted through the kidneys and may lead to the damage
and necrosis of renal tubular epithelial cells (54). Meanwhile, docetaxel is primarily
metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system and
has low direct toxicity to the kidneys (55). A more direct comparison was shown in
the study performed by Kurokawa et al (56), where increased creatinine levels
were only observed in patients receiving cisplatin plus S-1, while
patients with docetaxel plus S-1 exhibited normal creatinine levels
(56).
Other adverse effects were similar between the two
groups in the present study, and there was no significant
difference in efficacy. In comparison to cisplatin, the treatment
of MA with docetaxel combined with HIPEC can improve patients' QOL,
induce minimal adverse effects on renal function and display fewer
adverse reactions. Notably, psychological and social factors are
also important for patients' QOL, while the KPS score used in the
present study focuses more on physical function. In future studies,
the Medical Outcomes Study Social Support Survey (57), Symptom Checklist 90 (58) and other tools should also be
evaluated.
The present study had several limitations. Firstly,
the sample size was relatively small, with only 48 participants
included in the final analysis. This limited number resulted in
insufficient statistical power, which may have reduced the ability
to detect true differences in ORR, improvement of KPS scores and
ascites control time between the two groups. Furthermore, although
an attempt was made to perform multivariable analyses to adjust for
potential confounding factors, these models failed to converge due
to data sparsity issues, which was a direct consequence of the
small sample size, therefore yielding no reliable results.
Consequently, these findings require rigorous examination in future
large-scale cohorts. Secondly, key potential confounders such as
the peritoneal cancer index, baseline renal function and specific
details of personalized treatment plans were not available for
inclusion in the analysis. Thirdly, the retrospective nature of the
study means that treatment methods were non-randomly determined
based on established guidelines, patients' medical history and
current clinical status; therefore, the results remain susceptible
to indication bias, emphasizing the necessity for future randomized
controlled trials to further validate the findings. Finally, the
study relied solely on the KPS score for QOL evaluation. Future
studies should employ more comprehensive, multidimensional QOL
assessment tools to better capture the full spectrum of patients'
psychological and social wellbeing.
In conclusion, the present retrospective study
revealed that HIPEC with docetaxel and Endostar exhibited
comparable efficacy to a cisplatin-based regimen for controlling
MA, but with a significantly more favorable safety profile,
particularly with a lower incidence of nephrotoxicity. This
indicates that docetaxel may be a preferable agent for MA; however,
the finding warrants investigation in future prospective
trials.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Zhibing Wu
(Department of Oncology, Affiliated Zhejiang Hospital, Hangzhou,
China) for their suggestions on study design.
Funding
This study was funded by the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science
Nation of China (grant no. LQN25H290003), the Medical Science and
Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (grant no. 2023RC124), the
Traditional Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Project of
Zhejiang Province (grant no. 2023ZR061), the Medical Science and
Technology Project of Zhejiang Province (grant no. 2024KY594) and
the Zhejiang Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine for
Chinese Medicine Expert's Wan Xiaoging Inheritance Studio Project
(grant no. GZS2021028).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
JW was responsible for conceptualization, data
curation (lead), formal analysis (preliminary) and writing the
original draft (lead). JQ and YZ performed data curation
(collecting and organising clinical data) (supporting) and
validation, and helped to review and edit the manuscript
(supporting). DY performed the formal analysis (lead, conducted
final statistical analysis) and was in involved with the
methodology (statistical). GZ contributed to the study
conceptualization and design, and the analysis and interpretation
of data, provided critical revision of the manuscript for important
intellectual content and approved the final version to be
published. Additionally, GZ led the project administration and
supervision, and secured funding; they are responsible for the
communication and integrity of the work. YW was responsible for
conceptualization, interpretation (clinical data) and reviewing and
editing the manuscript (supporting). JW, YW and GZ confirm the
authenticity of all the raw data. All authors have read and
approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
This study was performed in accordance with the
Declaration of Helsinki (2000) of the World Medical Association.
All methods were performed in accordance with the relevant
guidelines. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee
of Zhejiang Hospital (Hangzhou, China; approval no. 2021-41K).
Informed consent was obtained from all participants for the HIPEC
treatment, and informed consent to participate in the study was
waived due to the retrospective nature of the study.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Soliman F, Ye L, Jiang W and Hargest R:
O17: Hyaluronic acid dependent adhesion in colorectal cancer
peritoneal metastasis. Br J Surg. 108 (Suppl 1):znab117.017. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhu L, Xu Z, Wu Y, Liu P, Qian J, Yu S,
Xia B, Lai J, Ma S and Wu Z: Prophylactic chemotherapeutic
hyperthermic intraperitoneal perfusion reduces peritoneal
metastasis in gastric cancer: A retrospective clinical study. BMC
Cancer. 20:8272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhu L, Xu Y, Shan Y, Zheng R, Wu Z and Ma
S: Intraperitoneal perfusion chemotherapy and whole abdominal
hyperthermia using external radiofrequency following radical D2
resection for treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Int J
Hyperthermia. 36:403–407. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mei S, Chen X, Wang K and Chen Y: Tumor
microenvironment in ovarian cancer peritoneal metastasis. Cancer
Cell Int. 23:112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Avula LR, Hagerty B and Alewine C:
Molecular mediators of peritoneal metastasis in pancreatic cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 39:1223–1243. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Roth L, Russo L, Ulugoel S, Freire Dos
Santos R, Breuer E, Gupta A and Lehmann K: Peritoneal metastasis:
Current status and treatment options. Cancers (Basel). 14:602021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hu L, Hofmann J, Holash J, Yancopoulos GD,
Sood AK and Jaffe RB: Vascular endothelial growth factor trap
combined with paclitaxel strikingly inhibits tumor and ascites,
prolonging survival in a human ovarian cancer model. Clin Cancer
Res. 11:6966–6971. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Wu J and Wu C: Direct and
indirect anticancer effects of hyperthermic intraperitoneal
chemotherapy on peritoneal malignancies (Review). Oncol Rep.
45:232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Karimi M, Shirsalimi N and Sedighi E:
Challenges following CRS and HIPEC surgery in cancer patients with
peritoneal metastasis: A comprehensive review of clinical outcomes.
Front Surg. 11:14985292024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jung H: Interaction of thermotolerance and
thermosensitization induced in CHO cells by combined hyperthermic
treatments at 40 and 43 degrees C. Radiat Res. 91:433–446. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Spratt JS, Adcock RA, Muskovin M, Sherrill
W and McKeown J: Clinical delivery system for intraperitoneal
hyperthermic chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 40:256–260. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cortes-Guiral D and Glehen O: Expanding
uses of hipec for locally advanced colorectal cancer: A European
perspective. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 33:253–257. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Braam HJ, Schellens JH, Boot H, van
Sandick JW, Knibbe CA, Boerma D and van Ramshorst B: Selection of
chemotherapy for hyperthermic intraperitoneal use in gastric
cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 95:282–296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
de Bree E and Michelakis D: An overview
and update of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy in ovarian
cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 21:1479–1492. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ding Y, Wang Y, Cui J and Si T: Endostar
blocks the metastasis, invasion and angiogenesis of ovarian cancer
cells. Neoplasma. 67:595–603. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shaheen RM, Davis DW, Liu W, Zebrowski BK,
Wilson MR, Bucana CD, McConkey DJ, McMahon G and Ellis LM:
Antiangiogenic therapy targeting the tyrosine kinase receptor for
vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibits the growth of
colon cancer liver metastasis and induces tumor and endothelial
cell apoptosis. Cancer Res. 59:5412–5416. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hu Y, Zhou Z and Luo M: Efficacy and
safety of endostar combined with cisplatin in treatment of
non-small cell lung cancer with malignant pleural effusion: A
meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 101:e322072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Biaoxue R, Xiguang C, Hua L, Wenlong G and
Shuanying Y: Thoracic perfusion of recombinant human endostatin
(Endostar) combined with chemotherapeutic agents versus
chemotherapeutic agents alone for treating malignant pleural
effusions: A systematic evaluation and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer.
16:8882016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guchelaar NAD, Noordman BJ, Koolen SLW,
Mostert B, Madsen EVE, Burger JWA, Brandt-Kerkhof ARM, Creemers GJ,
de Hingh IHJT, Luyer M, et al: Intraperitoneal chemotherapy for
unresectable peritoneal surface malignancies. Drugs. 83:159–180.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chia DKA, Demuytere J, Ernst S, Salavati H
and Ceelen W: Effects of hyperthermia and hyperthermic
intraperitoneal chemoperfusion on the peritoneal and tumor immune
contexture. Cancers (Basel). 15:43142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology
Antitumor Drug Safety Management Expert Committee and Chinese
Society of Clinical Oncology Vascular Targeted Therapy Expert
Committee, . Expert consensus on the clinical application of
recombinant human endostatin for the treatment of malignant serous
effusions. Chinese Clinical Oncology. 25:849–856. 2020.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ning T, Jiang M, Peng Q, Yan X, Lu ZJ,
Peng YL, Wang HL, Lei N, Zhang H, Lin HJ, et al: Low-dose
endostatin normalizes the structure and function of tumor
vasculature and improves the delivery and anti-tumor efficacy of
cytotoxic drugs in a lung cancer xenograft murine model. Thorac
Cancer. 3:229–238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lv Y, Jiang R, Ma C, Li J, Wang B, Sun L
and Mu N: Clinical observation of recombinant human vascular
endostatin durative transfusion combined with window period
arterial infusion chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced lung
squamous carcinoma. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 18:500–504. 2015.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lin MI and Sessa WC: Antiangiogenic
therapy: Creating a unique ‘window’ of opportunity. Cancer Cell.
6:529–531. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiang XD, Dai P, Qiao Y, Wu J, Song DA and
Li SQ: Clinical study on the recombinant human endostatin regarding
improving the blood perfusion and hypoxia of non-small-cell lung
cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 14:437–443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M and
Winkler A: Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer.
47:207–214. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Karnofsky DA and Burchenal JH: The
clinical evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer. MacLeod
CM: Evaluation of Chemotherapeutic Agents. Columbia University
Press; New York: pp. 191–205. 1949
|
|
28
|
Schag CC, Heinrich RL and Ganz PA:
Karnofsky performance status revisited: Reliability, validity, and
guidelines. J Clin Oncol. 2:187–193. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
US Department of Health and Human
Services, National Institutes of Health and National Cancer
Institute. Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).
Version 4.0. 2009.
|
|
30
|
Deraco M, Kusamura S, Virzì S, Puccio F,
Macrì A, Famulari C, Solazzo M, Bonomi S, Iusco DR and Baratti D:
Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy
as upfront therapy for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer:
Multi-institutional phase-II trial. Gynecol Oncol. 122:215–220.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Matsusaki K, Aridome K, Emoto S, Kajiyama
H, Takagaki N, Takahashi T, Tsubamoto H, Nagao S, Watanabe A,
Shimada H and Kitayama J: Clinical practice guideline for the
treatment of malignant ascites: Section summary in clinical
practice guideline for peritoneal dissemination (2021). Int J Clin
Oncol. 27:1–6. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Horikawa N, Abiko K, Matsumura N,
Hamanishi J, Baba T, Yamaguchi K, Yoshioka Y, Koshiyama M and
Konishi I: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in
ovarian cancer inhibits tumor immunity through the accumulation of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Clin Cancer Res. 23:587–599.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhan N, Dong WG and Wang J: The clinical
significance of vascular endothelial growth factor in malignant
ascites. Tumour Biol. 37:3719–3725. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chiva LM and Gonzalez-Martin A: A critical
appraisal of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) in
the treatment of advanced and recurrent ovarian cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 136:130–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao WY, Chen DY, Chen JH and Ji ZN:
Effects of intracavitary administration of Endostar combined with
cisplatin in malignant pleural effusion and ascites. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 70:623–628. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei H, Qin S, Yin X, Chen Y, Hua H, Wang
L, Yang N, Chen Y and Liu X: Endostar inhibits ascites formation
and prolongs survival in mouse models of malignant ascites. Oncol
Lett. 9:2694–2700. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Laplace N, Kepenekian V, Friggeri A,
Vassal O, Ranchon F, Rioufol C, Gertych W, Villeneuve L, Glehen O
and Bakrin N: Sodium thiosulfate protects from renal impairement
following hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) with
cisplatin. Int J Hyperthermia. 37:897–902. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goodman MD, McPartland S, Detelich D and
Saif MW: Chemotherapy for intraperitoneal use: A review of
hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy and early post-operative
intraperitoneal chemotherapy. J Gastrointest Oncol. 7:45–57.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu P, Wu Y, Xu X, Fan X, Sun C, Chen X,
Xia J, Bai S, Qu L, Lu H, et al: Microwave triggered
multifunctional nanoplatform for targeted photothermal-chemotherapy
in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nano Res. 16:9688–9700.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Li Y, Köpper F and Dobbelstein M:
Inhibition of MAPKAPK2/ MK2 facilitates DNA replication upon cancer
cell treatment with gemcitabine but not cisplatin. Cancer Lett.
428:45–54. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pu YS, Huang CY, Wu HL, Wu JH, Su YF, Yu
CTR, Lu CY, Wu WJ, Huang SP, Huang YT and Hour TC: EGFR-mediated
hyperacetylation of tubulin induced docetaxel resistance by
downregulation of HDAC6 and upregulation of MCAK and PLK1 in
prostate cancer cells. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 40:23–34. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Van Driel WJ, Koole SN, Sikorska K,
Schagen van Leeuwen JH, Schreuder HWR, Hermans RHM, de Hingh IHJT,
van der Velden J, Arts HJ, Massuger LFAG, et al: Hyperthermic
intraperitoneal chemotherapy in ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med.
378:230–240. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhan ZW, Wang XJ, Yu JM, Zheng JX, Zeng Y,
Sun MY, Peng L, Guo ZQ and Chen BJ: Intraperitoneal Infusion of
Recombinant Human Endostatin Improves Prognosis in Gastric Cancer
Ascites. Future Oncol. 18:1259–1271. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fu YB, Yang R, Su YD, Ma R, Wei T, Yu Y,
Li B and Li Y: Cisplatin + docetaxel improves survival over
cisplatin + mitomycin C in hyperthermic intraperitoneal
chemotherapy for pseudomyxoma peritonei: A retrospective study
based on propensity score matching. Int J Hyperthermia.
42:24672962025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Harlev C, Bue M, Petersen EK, Jørgensen
AR, Bibby BM, Hanberg P, Schmedes AV, Petersen LK and Stilling M:
Dynamic assessment of local abdominal tissue concentrations of
cisplatin during a HIPEC procedure: Insights from a porcine model.
Ann Surg Oncol. 32:3804–3813. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wang Y and Ren H: Multi-omics sequencing
revealed endostar combined with cisplatin treated non small cell
lung cancer via anti-angiogenesis. BMC Cancer. 24:1872024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hakeam HA, Breakiet M, Azzam A, Nadeem A
and Amin T: The incidence of cisplatin nephrotoxicity post
hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) and cytoreductive
surgery. Ren Fail. 36:1486–1491. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gómez-Ruiz ÁJ, González-Gil A, Gil J,
Alconchel F, Navarro-Barrios Á, Gil-Gómez E, Martínez J, Nieto A,
García-Palenciano C and Cascales-Campos PA: Acute renal disease in
patients with ovarian peritoneal carcinomatosis treated with
cytoreduction and HIPEC: The influence of surgery and the
cytostatic agent used. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 406:2449–2456. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ye J, Ren Y, Wei Z, Peng J, Chen C, Song
W, Tan M, He Y and Yuan Y: Nephrotoxicity and long-term survival
investigations for patients with peritoneal carcinomatosis using
hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy with cisplatin: A
retrospective cohort study. Surg Oncol. 27:456–461. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sin EI, Chia CS, Tan GHC, Soo KC and Teo
MC: Acute kidney injury in ovarian cancer patients undergoing
cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intra-peritoneal
chemotherapy. Int J Hyperthermia. 33:690–695. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Koemans WJ, van der Kaaij RT, Wassenaar
ECE, Grootscholten C, Boot H, Boerma D, Los M, Imhof O, Schellens
JHM, Rosing H, et al: Systemic exposure of oxaliplatin and
docetaxel in gastric cancer patients with peritonitis
carcinomatosis treated with intraperitoneal hyperthermic
chemotherapy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 47:486–489. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Morgan RJ Jr, Doroshow JH, Synold T, Lim
D, Shibata S, Margolin K, Schwarz R, Leong L, Somlo G, Twardowski
P, et al: Phase I trial of intraperitoneal docetaxel in the
treatment of advanced malignancies primarily confined to the
peritoneal cavity: Dose-limiting toxicity and pharmacokinetics.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:5896–5901. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Marchettini P, Stuart OA, Mohamed F, Yoo D
and Sugarbaker PH: Docetaxel: Pharmacokinetics and tissue levels
after intraperitoneal and intravenous administration in a rat
model. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 49:499–503. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G and
Reeves WB: Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins (Basel).
2:2490–2518. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Clarke SJ and Rivory LP: Clinical
pharmacokinetics of docetaxel. Clin Pharmacokinet. 36:99–114. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kurokawa Y, Matsuyama J, Nishikawa K,
Takeno A, Kimura Y, Fujitani K, Kawabata R, Makari Y, Terazawa T,
Kawakami H, et al: Docetaxel plus S-1 versus cisplatin plus S-1 in
unresectable gastric cancer without measurable lesions: A
randomized phase II trial (HERBIS-3). Gastric Cancer. 24:428–434.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Alyami MM and Alasmari AA: Exploratory and
confirmatory factor analysis of the arabic medical outcomes
study-social support Survey-6 among Saudi adults. Saudi J Med Med
Sci. 13:197–204. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Derogatis LR, Rickels K and Rock AF: The
SCL-90 and the MMPI: A step in the validation of a new self-report
scale. Br J Psychiatry. 128:280–289. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|