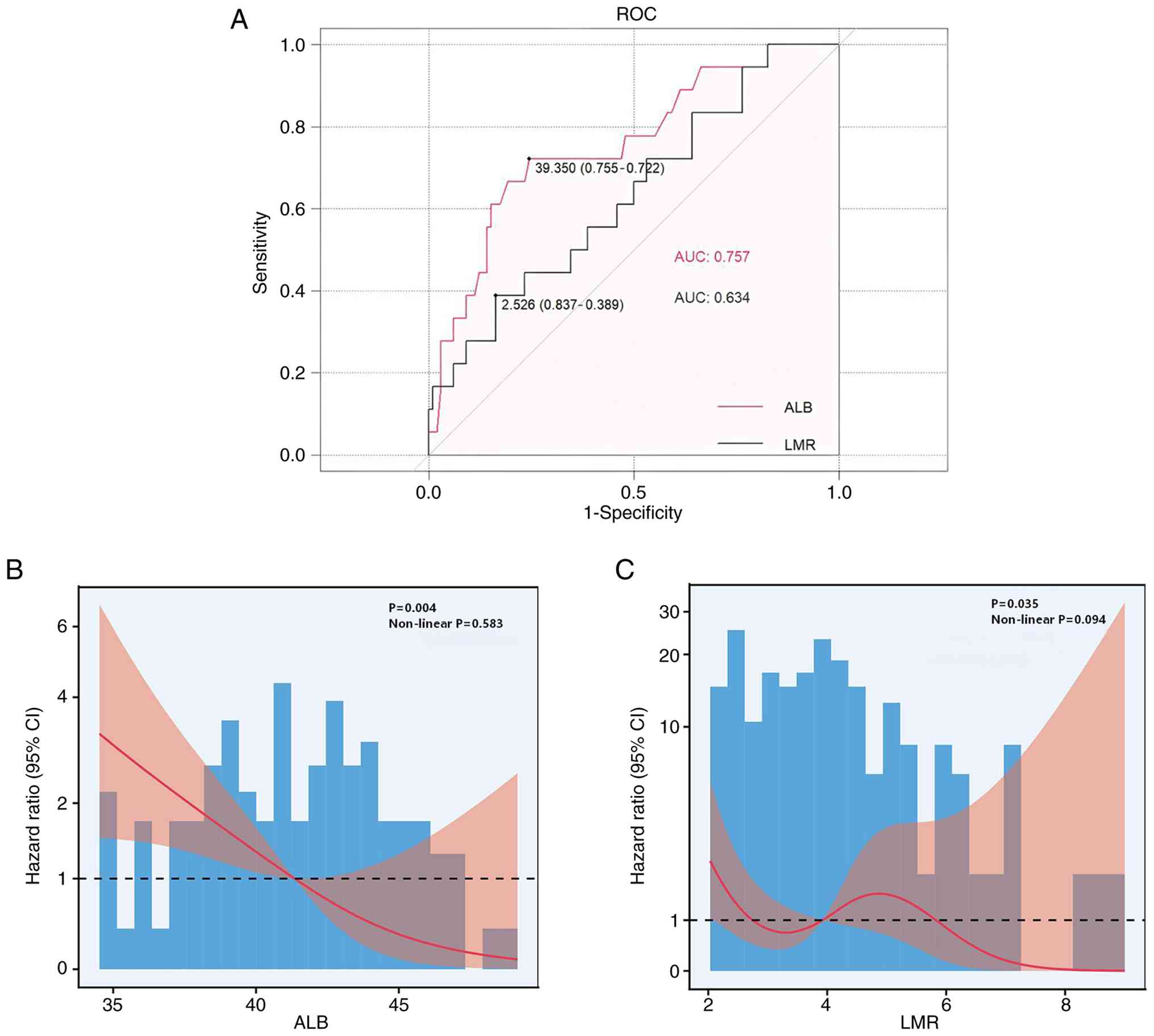
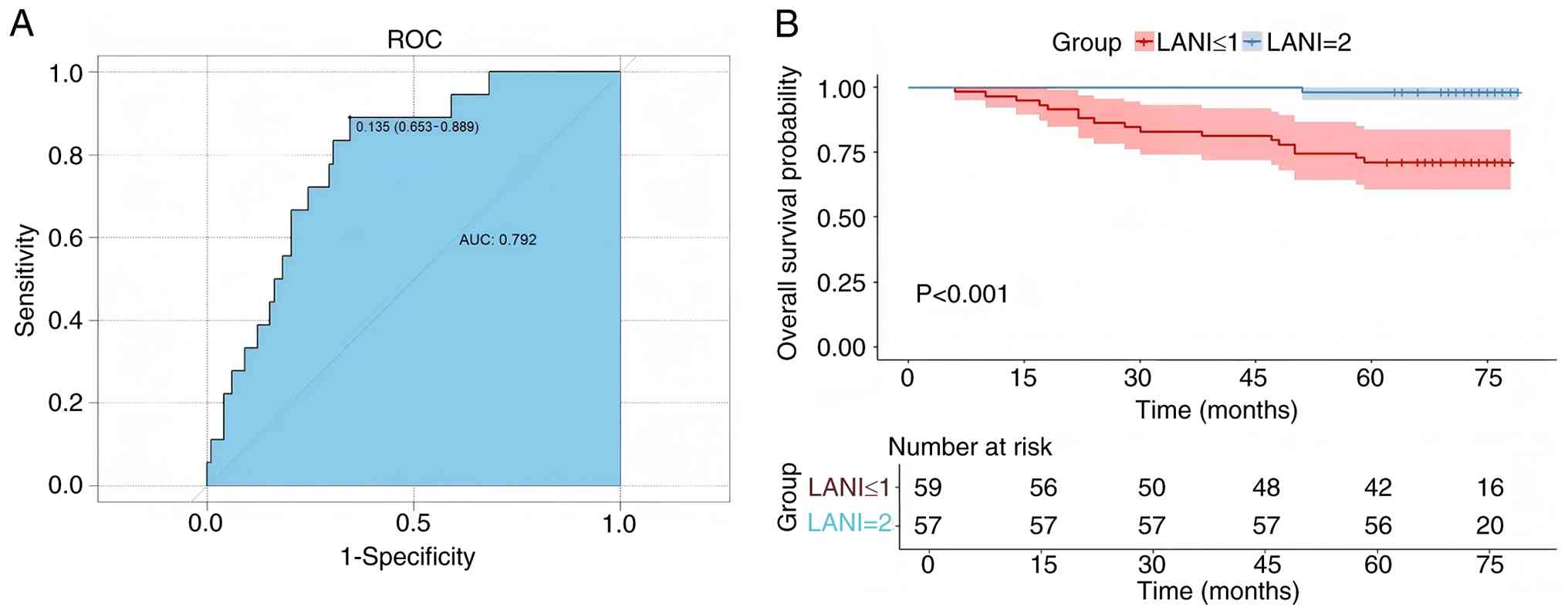
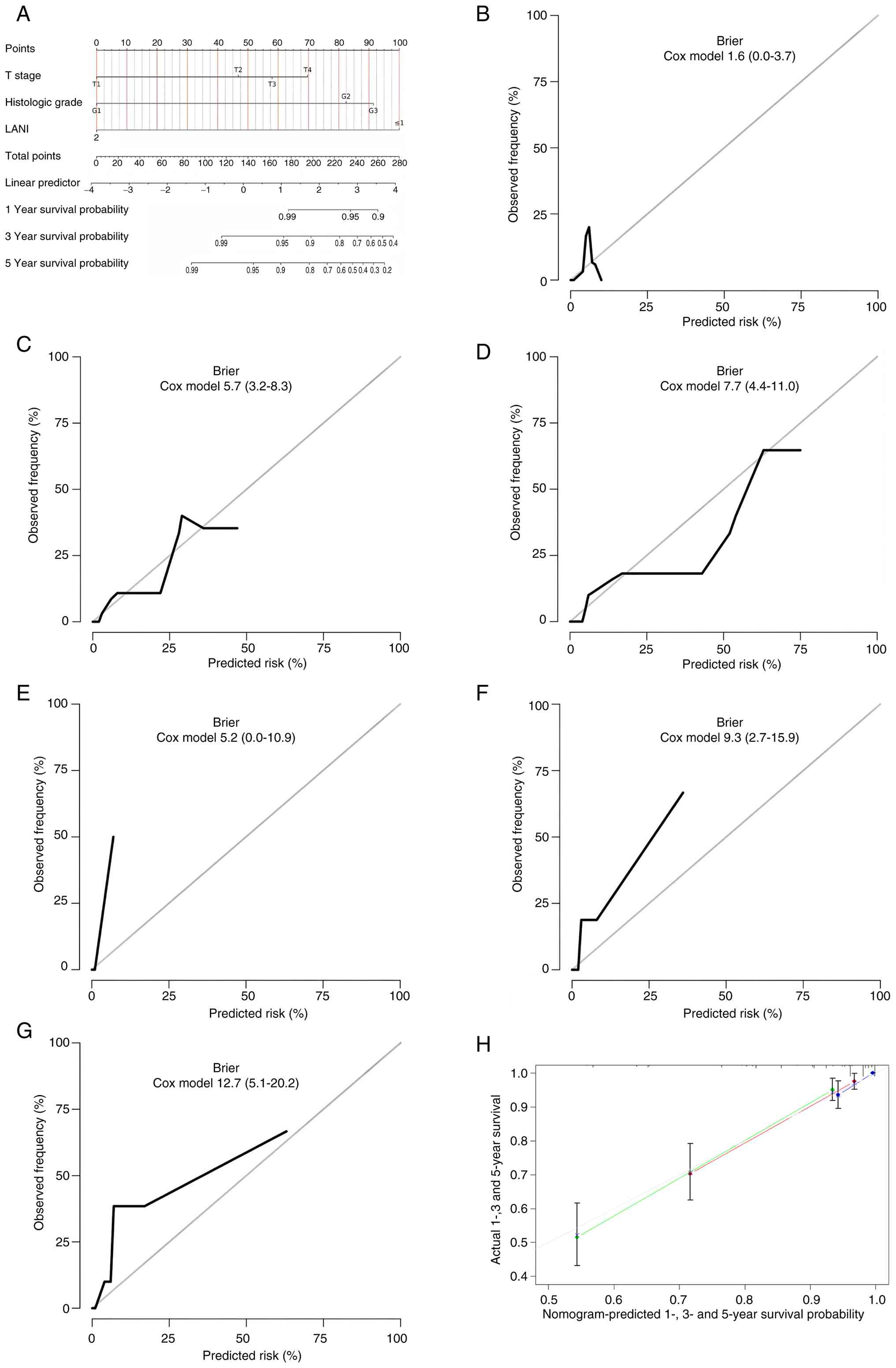
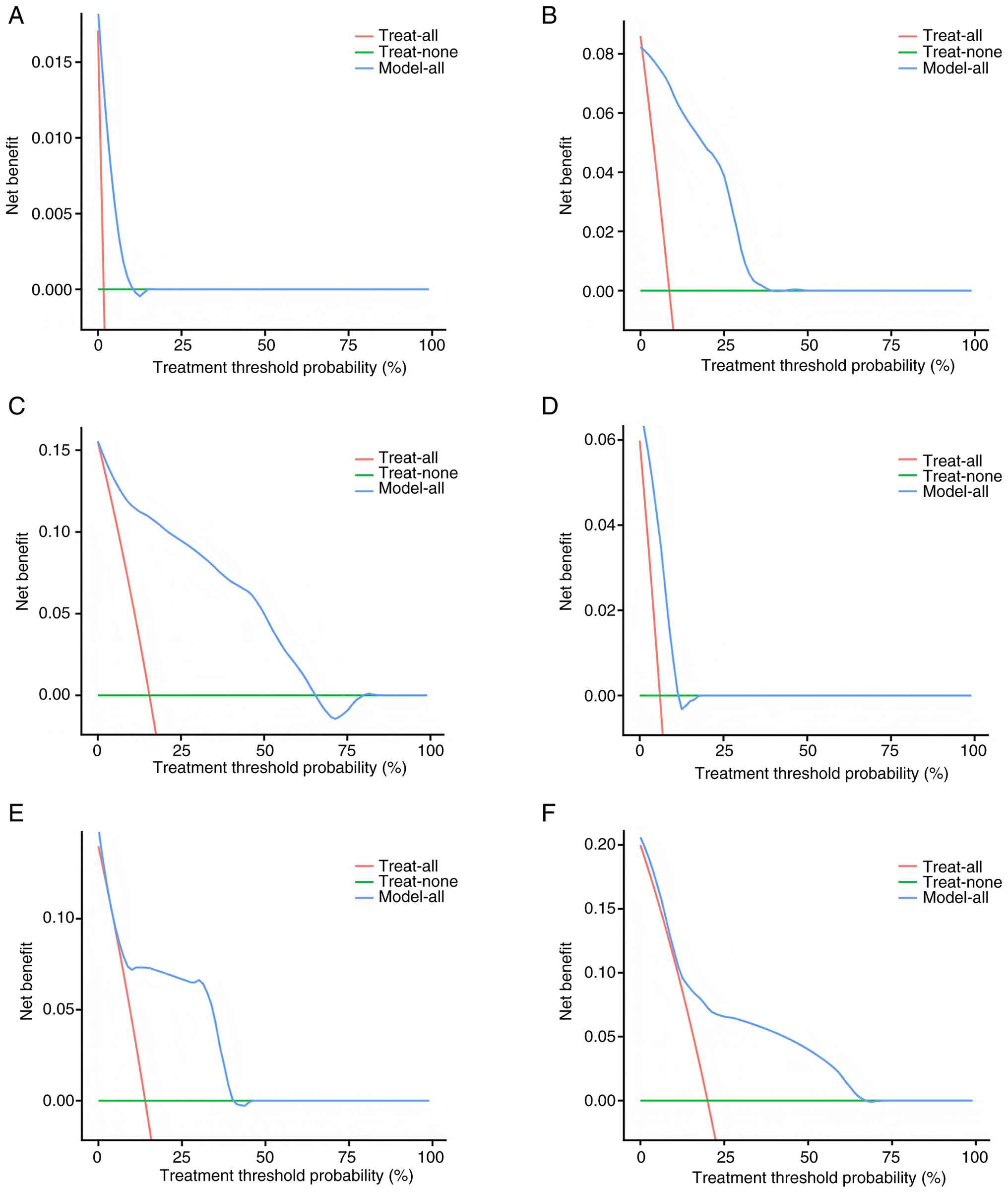
|
1
|
Dogra AK, Prakash A, Gupta S and Gupta M:
Prognostic significance and molecular classification of triple
negative breast cancer: A systematic review. Eur J Breast Health.
21:101–114. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Z, Liu Y, Lyu M, Chan CH, Sun M, Yang
X, Qiao S, Chen Z, Yu S, Ren M, et al: Classifications of
triple-negative breast cancer: insights and current therapeutic
approaches. Cell Biosci. 15:132025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kannan K, Srinivasan A, Kannan A and Ali
N: The underlying mechanisms and emerging strategies to overcome
resistance in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 17:29382025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martorana TM, Ricciardi G, Tralongo P,
Fiorentino V, Pizzimenti C, Franchina M, Marino MA, Santarpia M,
Tuccari G, Ieni A, et al: Targeting the tumor microenvironment in
triple-negative breast cancer: Biological insights and therapeutic
opportunities. Pathol Res Pract. 275:1562262025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen Y, Anwar M, Wang X, Zhang B and Ma B:
Integrative transcriptomic and single-cell analysis reveals IL27RA
as a key immune regulator and therapeutic indicator in breast
cancer. Discov Oncol. 16:9772025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen H, Gui X, Zhou Z, Su F, Gong C, Li S,
Wu W, Rao N, Liu Q and Yao H: Distinct ER and PR expression
patterns significantly affect the clinical outcomes of early
HER2-positive breast cancer: A real-world analysis of 871 patients
treated with neoadjuvant therapy. Breast. 75:1037332024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Zhang H, Merkher Y, Chen L, Liu N,
Leonov S and Chen Y: Recent advances in therapeutic strategies for
triple-negative breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 15:1212022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jiang C, Zhang S, Jiang L, Chen Z, Chen H,
Huang J, Tang J, Luo X, Yang G, Liu J and Chi H: Precision
unveiled: Synergistic genomic landscapes in breast
cancer-Integrating single-cell analysis and decoding drug toxicity
for elite prognostication and tailored therapeutics. Environ
Toxicol. 39:3448–3472. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou Y, Tao L, Qiu J, Xu J, Yang X, Zhang
Y, Tian X, Guan X, Cen X and Zhao Y: Tumor biomarkers for
diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 9:1322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He M, Zhang JX, Jiang YZ, Chen YL, Yang
HY, Tang LC, Shao ZM and Di GH: The lymph node ratio as an
independent prognostic factor for node-positive triple-negative
breast cancer. Oncotarget. 8:44870–44880. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Altea-Manzano P, Decker-Farrell A,
Janowitz T and Erez A: Metabolic interplays between the tumour and
the host shape the tumour macroenvironment. Nat Rev Cancer.
25:274–292. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li B, Lin R, Hua Y, Ma B and Chen Y:
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals TMEM71 as an immunomodulatory
biomarker predicting immune checkpoint blockade response in breast
cancer. Discov Oncol. 16:12562025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tripathi S, Sharma Y and Kumar D:
Unveiling the link between chronic inflammation and cancer. Metabol
Open. 25:1003472025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hassan AF, Kheraldine H, Abujamous L,
Al-Thawadi H and Elhissi A: Inflammation-associated drug resistance
and tumor growth in TNBC. Front Immunol. 16:16231372025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hua S, Wang W, Yao Z, Gu J, Zhang H, Zhu
J, Xie Z and Jiang H: The fatty acid-related gene signature
stratifies poor prognosis patients and characterizes TIME in
cutaneous melanoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 150:402024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li KJ, Zhang ZY, Wang K, Sulayman S, Zeng
XY, Liu J, Chen Y and Zhao ZL: Prognostic scoring system using
inflammation- and nutrition-related biomarkers to predict prognosis
in stage I-III colorectal cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol.
31:1045882025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang M, Liu J, Zhang F, Liang Q and Guo
Z: Comprehensive characterization of neddylation related genes in
cutaneous melanoma identified a novel prognostic signature for
treatment outcomes, immune landscape. Discov Oncol. 15:7222024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Majumdar A, Saraf SK, Sahu C, Verma K and
Vishwakarma P: Current perspectives on malnutrition and
immunomodulators bridging nutritional deficiencies and immune
health. Future J Pharm Sci. 11:502025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kanbur B, Unek IT, Uzun M, Ozturk C, Yarol
RC and Balci A: Association of systemic inflammatory response index
and prognostic nutritional index scores with sarcopenia in patients
with metastatic gastric cancer. Medicina (Kaunas). 61:7852025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shayimu P, Awula M, Wang CY, Jiapaer R,
Pan YP, Wu ZM, Chen Y and Zhao ZL: Serum nutritional predictive
biomarkers and risk assessment for anastomotic leakage after
laparoscopic surgery in rectal cancer patients. World J
Gastrointest Surg. 16:3142–3154. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Stotz M, Gerger A, Eisner F, Szkandera J,
Loibner H, Ress AL, Kornprat P, AlZoughbi W, Seggewies FS, Lackner
C, et al: Increased neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio is a poor
prognostic factor in patients with primary operable and inoperable
pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 109:416–421. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Zhang B, Wang X, Chen Y, Anwar M,
Fan J and Ma B: Prognostic value of preoperative modified Glasgow
prognostic score in predicting overall survival in breast cancer
patients: A retrospective cohort study. Oncol Lett. 29:1802025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee YK, Hsu CY, Wang MY, Kuo WH, Lien HC,
Lee YH, Lo C and Huang CS: Prognostic factors for early-stage
triple-negative breast cancer with a focus on
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio: A single-center retrospective
study. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 64:1030–1036. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alzogaray V, Defante MLR, Celso DSG,
Torres LA, Bearse M and Lopes ACFMM: Prognostic significance of
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with triple-negative
breast cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Diagn
Progn. 5:779–787. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao J, Chen X, Zhang Z, Zhao D, Cao X,
Mao F, Sun Q and Peng L: Prognostic value of the systemic
immune-inflammation index in recurrent/metastatic triple-negative
breast cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Gland Surg.
14:1858–1872. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Guo Q, Wang B, Gao X, Zhao P and Lv S:
Predicting prognosis of patients with triple-negative breast cancer
undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on inflammatory status at
different time points: A propensity score matching analysis. Oncol
Lett. 29:2522025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qiu Y, Chen Y, Shen H, Yan S, Li J and Wu
W: Naples prognostic score: A novel predictor of survival in
patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Inflamm Res.
17:5253–5269. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kotowicz B, Fuksiewicz M, Jodkiewicz M,
Makowka A and Jagiełło-Gruszfeld A: Evaluation of the prognostic
value of obesity, vitamin d concentrations, and systemic
inflammatory response indexes (SIRI, SII, PIV) in patients with
breast cancer scheduled for neoadjuvant treatment. Breast Cancer
(Auckl). 19:117822342513694632025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhu J, Cheng J, Ma Y, Wang Y, Zou Z, Wang
W, Shi H and Meng Y: The value of inflammation-related indicators
in chemotherapy efficacy and disease-free survival of
triple-negative breast cancer. Eur J Med Res. 30:772025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Eckart A, Struja T, Kutz A, Baumgartner A,
Baumgartner T, Zurfluh S, Neeser O, Huber A, Stanga Z, Mueller B
and Schuetz P: Relationship of nutritional status, inflammation,
and serum albumin levels during acute illness: A prospective study.
Am J Med. 133:713–722.e7. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gremese E, Bruno D, Varriano V, Perniola
S, Petricca L and Ferraccioli G: Serum albumin levels: A biomarker
to be repurposed in different disease settings in clinical
practice. J Clin Med. 12:60172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang K, Li K, Zhang Z, Zeng X, Wu Z, Zhang
B, Pan Y, Lau LY, Zhao Z and Chen Y: Combined preoperative
platelet-albumin ratio and cancer inflammation prognostic index
predicts prognosis in colorectal cancer: A retrospective study. Sci
Rep. 15:295002025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Benner B, Scarberry L, Suarez-Kelly LP,
Duggan MC, Campbell AR, Smith E, Lapurga G, Jiang K, Butchar JP,
Tridandapani S, et al: Generation of monocyte-derived
tumor-associated macrophages using tumor-conditioned media provides
a novel method to study tumor-associated macrophages in vitro. J
Immunother Cancer. 7:1402019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang H, Tang S, Biskup E, Zhang Y, Yong
L, Chen L and Cai F: Long-term survival after diverse therapeutic
modalities in malignant phyllodes tumors of the breast. Technol
Cancer Res Treat. 21:153303382211210862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tokumaru Y, Oshi M, Murthy V, Tian W, Yan
L, Angarita FA, Nagahashi M, Matsuhashi N, Futamura M, Yoshida K,
et al: Low intratumoral genetic neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
(NLR) is associated with favorable tumor immune microenvironment
and with survival in triple negative breast cancer (TNBC). Am J
Cancer Res. 11:5743–5755. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bae SJ, Cha YJ, Yoon C, Kim D, Lee J, Park
S, Cha C, Kim JY, Ahn SG, Park HS, et al: Prognostic value of
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in human epidermal growth factor
receptor 2-negative breast cancer patients who received neoadjuvant
chemotherapy. Sci Rep. 10:130782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sun H, Liang J, Xue S, Zhang X, Ding M,
Zhu J, Nanding A, Liu T, Lou G, Gao Y, et al: Establishment and
clinical application of a prognostic index for inflammatory status
in triple-negative breast cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant
therapy using machine learning. BMC Cancer. 24:15592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Giro A, Passildas-Jahanmohan J, Kossai M,
Bidet Y, Molnar I, Bernadach M, Penault-Llorca F, Abrial C, Durando
X and Radosevic-Robin N: Comparison of the predictive and
prognostic capacities of neutrophil, lymphocyte and platelet counts
and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in triple-negative breast
cancer: Preliminary RESULTS of the PERCEPTION study. Anticancer
Res. 44:4983–4994. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fang Q, Jiang H, Deng L, Sun W, Wang M,
Liu Y and Xu J: Constructing and evaluating a predictive model for
the risk of preoperative frailty in breast cancer patients. BMC
Womens Health. 25:5832025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Miao Y, Yang R, Zhang B, Yang J, Yao L,
Wang W, Liu X, Guo X and Jia H: Naples prognostic score (NPS) as a
novel prognostic score for stage III breast cancer patients: A
real-world retrospective study. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press).
17:403–421. 2025.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hou M, Li H, He T, Hui S, Dai W, Hou X,
Zhao J, Zhao J, Wen J, Kan W, et al: Icariside I reduces breast
cancer proliferation, apoptosis, invasion, and metastasis probably
through inhibiting IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol.
76:499–513. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Vu NT, Vu QV, Vo NT, Tanigaki R, Quach HT,
Miyake Y, Shiba T and Kataoka T: Cardamonin inhibits the nuclear
translocation and DNA binding of RelA in the tumor necrosis
factor-α-induced NF-κB signaling pathway in human lung
adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Molecules. 30:43242025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ma H, Liu J, Jin H, Zhang M, Liang Q and
Guo Z: Comprehensive characterization of NK cell-related genes in
cutaneous melanoma identified a novel prognostic signature for
predicting the prognosis, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy efficacy.
Discov Oncol. 16:12432025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Liu Y, Luo R, Wu Z, Zhang W, Liang C, Liu
Z and Zhao H: Association of neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio
with distant metastasis and survival outcomes in breast cancer
patients: A retrospective and prospective cohort study. Sci Rep.
15:454562025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gruys E, Toussaint MJ, Niewold TA and
Koopmans SJ: Acute phase reaction and acute phase proteins. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 6:1045–1056. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Shang Y, Duan Y, Liu J, Guo R, Fang Z, Ma
F and Guo B: Association between albumin-related inflammatory
biomarkers and breast cancer risk: A secondary analysis of NHANES
1998–2018. Medicine (Baltimore). 104:e464822025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhang R, Meng Z, Wu X, Piao Z, Jin T and
Zhang M: MIR4435-2HG promotes breast cancer evolution through
miR-205-5p/UBE2N axis and exosome-mediated macrophage M2-like
polarization. Cell Signal. 139:1122872026. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
He S, Wang Q, He J, Chen Z and Xiao Y: The
Leupaxin/ HDAC6/EGR2 axis facilitates breast cancer progression by
enhancing macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Biol Toxicol.
41:1542025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang J, Huang X, Ma L, Chen Z, Li T, Wang
L, Guo Y, Xu H, Li J, Qin JJ, et al: Micro-organ chip deciphers
tumor-derived G-CSF as remote commander of lung pre-metastatic
niche via VEGFA-KDR cascade. Adv Sci (Weinh). e185842025.(Epub
ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gao S, Tang W, Zuo B, Mulvihill L, Yu J
and Yu Y: The predictive value of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio
for overall survival and pathological complete response in breast
cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Front Oncol.
12:10656062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhang Y, Wu J, Chen W and Liang X:
Pretreatment system inflammation response index (SIRI) is a
valuable marker for evaluating the efficacy of neoadjuvant therapy
in breast cancer patients. Int J Gen Med. 17:4359–4368. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li Y and Fei Y: The predictive value of
serum NLR, SII, and OPNI for lymph node metastasis in breast cancer
patients with internal mammary lymph nodes after thoracoscopic
surgery. Open Life Sci. 19:202207632024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fan S, Xie X, Shen Y, Wang W, Gu X and Yao
Z: The predictive value of preoperative serum
neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and tumor markers for early breast
cancer patients: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore).
101:e300112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao Z, Xu H, Ma B and Dong C: Prognostic
value of platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in breast cancer
patients receiving neoadjuvant therapy: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Front Immunol. 16:16585712025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tan Z, Xin H, Chen J, Lei M, Tu G and Tang
L: SIGLEC15 modulates the immunosuppressive microenvironment and
suppresses malignant phenotypes in triple-negative breast cancer.
Genes Dis. 13:1017992025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liu J, Wang YT, Zeng LL and Chen CL:
Lactate-related genes signature as a novel prognostic landscape in
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma: Insights from 156 machine
learning algorithms and in vitro validation. Int J Biol Macromol.
323:1470982025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang P, Zhang H, Tang J, Ren Q, Zhang J,
Chi H, Xiong J, Gong X, Wang W, Lin H, et al: The integrated
single-cell analysis developed an immunogenic cell death signature
to predict lung adenocarcinoma prognosis and immunotherapy. Aging
(Albany NY). 15:10305–10329. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Imani S, Farghadani R, Roozitalab G,
Maghsoudloo M, Emadi M, Moradi A, Abedi B and Jabbarzadeh Kaboli P:
Reprogramming the breast tumor immune microenvironment: Cold-to-hot
transition for enhanced immunotherapy. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
44:1312025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li Y, Gao Y, Wang L and Si J: NK cell
adaptation in the tumor microenvironment: Insights for NK
cell-based immunotherapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 86:181–198.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chen X, Chi H, Zhao X, Pan R, Wei Y and
Han Y: Role of exosomes in immune microenvironment of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Oncol. 2022:25210252022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xiang Y, Du D, Su Y, Guo L and Chen S:
Integrated pan-cancer analysis and experimental verification of the
roles of retinoid-binding proteins in breast cancer. Cancers
(Basel). 17:37062025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Mardamshina M, Karagach S, Mohan V, Arad
G, Necula D, Golani O, Fellus-Alyagor L, Shenoy A, Krol K, Pirak D,
et al: Integrated spatial proteomic analysis of breast cancer
heterogeneity unravels cancer cell phenotypic plasticity. Nat
Commun. 16:104822025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Cheng T, Wang X, Han Y, Hao J, Hu H and
Hao L: The level of serum albumin is associated with renal
prognosis and renal function decline in patients with chronic
kidney disease. BMC Nephrol. 24:572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Wiedermann CJ: Hypoalbuminemia as
surrogate and culprit of infections. Int J Mol Sci. 22:44962021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|