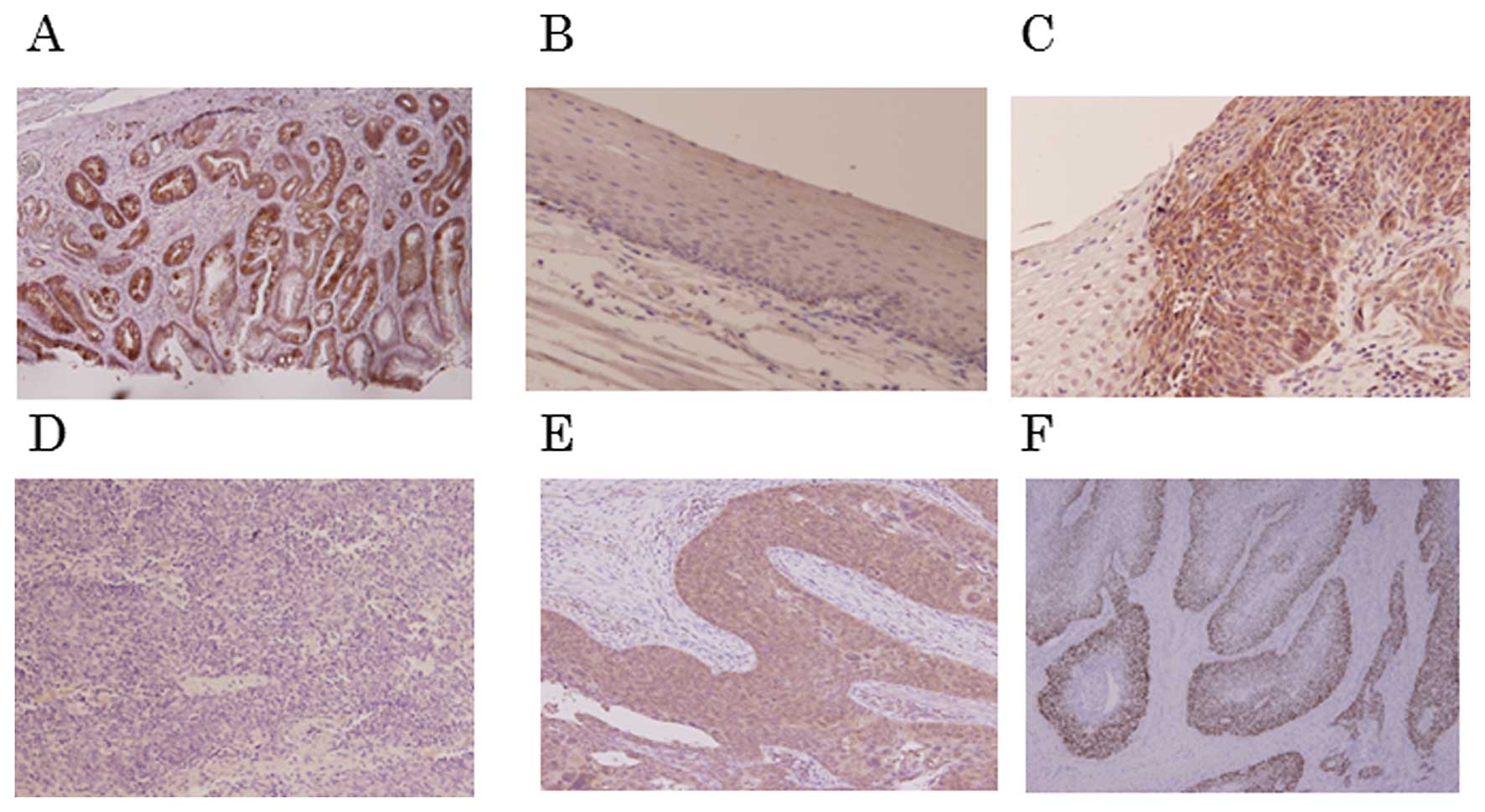
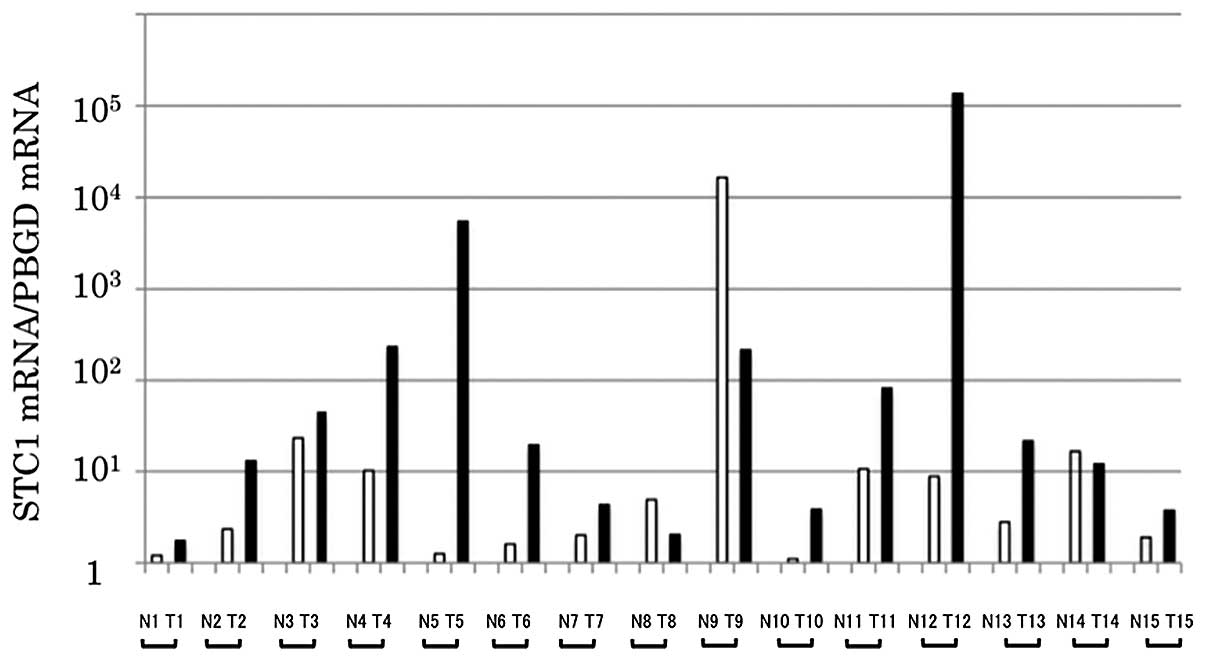
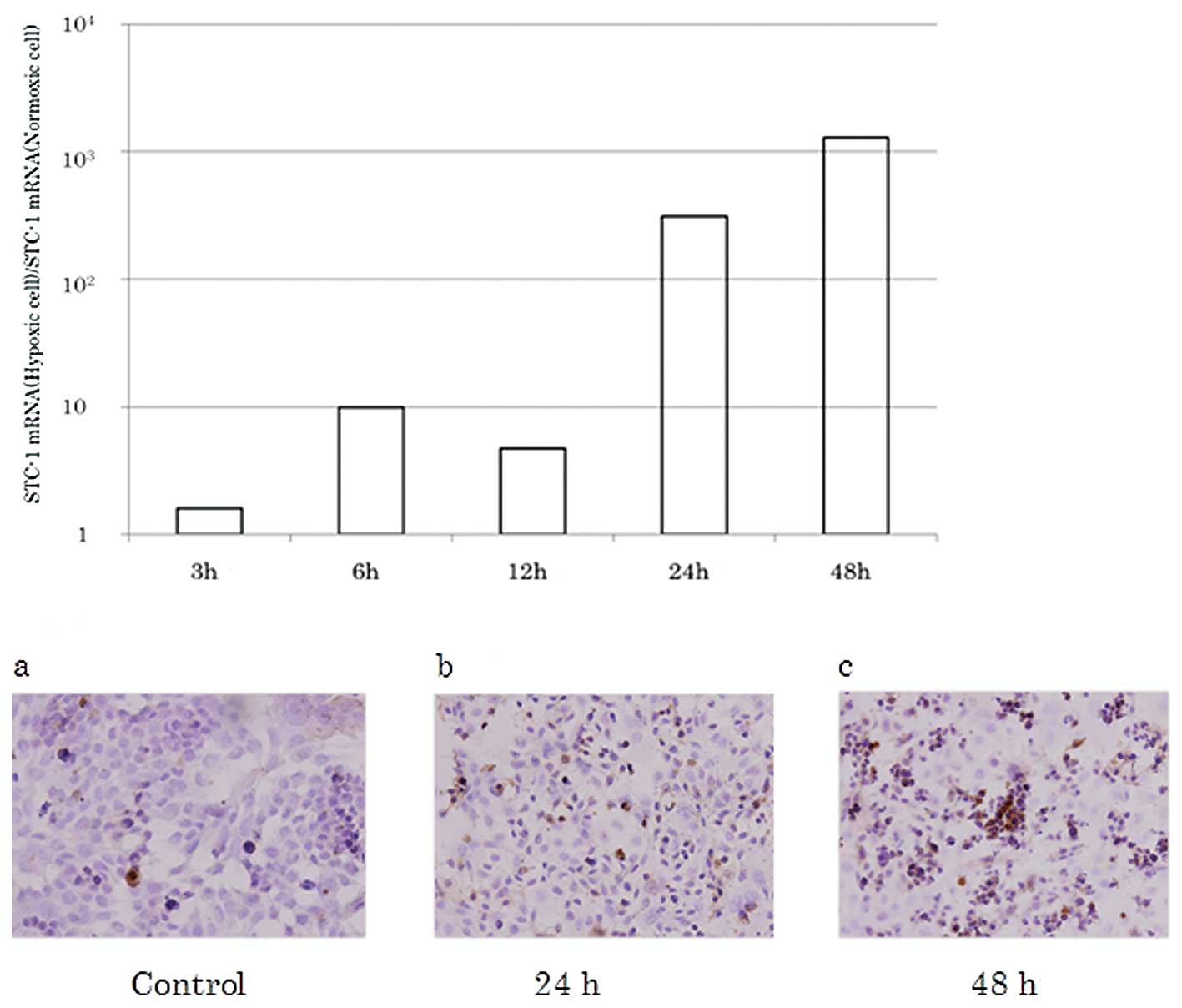
|
1
|
Sugimachi K, Matsuura H, Kai H, et al:
Prognostic factors of esophageal carcinoma: univariate and
multivariate analyses. J Surg Oncol. 31:108–112. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Natsugoe S, Matsumoto M, Okumura H, et al:
Prognostic factors in patients with submucosal esophageal cancer. J
Gastrointest Surg. 8:631–635. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ando N, Iizuka T, Ide H, et al: Surgery
plus chemotherapy compared with surgery alone for localized
squamous cell carcinoma of the thoracic esophagus: a Japan Clinical
Oncology Group Study-JCOG9204. J Clin Oncol. 15:4592–4596. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tepper J, Krasna MJ, Niedzwiecki D, et al:
Phase III trial of trimodality therapy with cisplatin,
fluorouracil, radiotherapy, and surgery compared with surgery alone
for esophageal cancer: CALGB 9781. J Clin Oncol. 26:1086–1092.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fontaine M: Stannius’ corpuscles and ionic
(Ca, K, Na) of the interior environment of the eel (Anguilla
Anguilla L). C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 259:875–878. 1964.
|
|
6
|
Chang ACM, Janosi J, Hulsbeek M, et al: A
novel human cDNA highly homologous to the fish hormone
stanniocalcin. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 112:241–247. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chang AC and Reddel RR: Identification of
a second Stanniocalcin cDNA in mouse and human: stanniocalcin 2.
Mol Cell Endocrinol. 141:95–99. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fujiwara Y, Sugita Y, Nakamori S, et al:
Assessment of Stanniocalcin-1 mRNA as a molecular marker for
micrometastases of various human cancers. Int J Oncol. 16:799–804.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nakagawa T, Martinez SR, Goto Y, et al:
Detection of circulating tumor cells in early-stage breast cancer
metastasis to axillary lymph nodes. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4105–4110.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Joensuu K, Heikkilä P and Andersson LC:
Tumor dormancy: elevated expression of stanniocalcins in late
relapsing breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 265:76–83. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Law AY, Ching LY, Lai KP, et al:
Identification and characterization of the hypoxia-responsive
element in human stanniocalcin-1 gene. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
314:118–127. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsuyama J, Doki Y, Yasuda T, et al: The
effect of neoadjuvant chemotherapy on lymph node micrometastases in
squamous cell carcinomas of the thoracic esophagus. Surgery.
141:570–580. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yano M, Takachi K, Doki Y, et al:
Preoperative chemotherapy for clinically node-positive patients
with squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Dis Esophagus.
19:158–163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamasaki M, Miyata H, Fujiwara Y, et al:
p53 genotype predicts response to chemotherapy in patients with
squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Ann Surg Oncol.
17:634–642. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Makino T, Yamasaki M, Miyata H, et al: p53
Mutation status predicts pathological response to chemoradiotherapy
in locally advanced esophageal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:804–811.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wascher RA, Huynh KT, Giuliano AE, et al:
Stanniocalcin-1: a novel molecular blood and bone marrow marker for
human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1427–1435. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Paulitschke V, Kunstfeld R, Mohr T, et al:
Entering a new era of rational biomarker discovery for early
detection of melanoma metastases: secretome analysis of associated
stroma cells. J Proteome Res. 8:2501–2510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chang AC, Jellinek DA and Reddel RR:
Mammalian stanniocalcins and cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer.
10:359–373. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McCudden CR, James KA, Hasilo C and Wagner
GF: Characterization of mammalian stanniocalcin receptors.
Mitochondrial targeting of ligand and receptor for regulation of
cellular metabolism. J Biol Chem. 277:45249–45258. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maxwell PH, Dachs GU, Gleadle JM, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 modulates gene expression in solid
tumors and influences both angiogenesis and tumor growth. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 94:8104–8109. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang GL, Jiang BH and Semenza GL: Effect
of altered redox states on expression and DNA-binding activity of
hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
212:550–556. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yeung HY, Lai KP, Chan HY, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-mediated activation of stanniocalcin-1
in human cancer cells. Endocrinology. 146:4951–4960. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M and Bunn HF:
Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is mediated by an
O2-dependent degradation domain via the
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:7987–7992.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lai KP, Law AY, Yeung HY, et al: Induction
of stanniocalcin-1 expression in apoptotic human nasopharyngeal
cancer cells by p53. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 356:968–975. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brown JM and Wilson WR: Exploiting tumor
hypoxia in cancer treatment. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:437–447. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vaupel P, Thews O and Hoeckel M: Treatment
resistance of solid tumors: role of hypoxia and anemia. Med Oncol.
18:243–259. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cohen P and Frame S: The renaissance of
GSK3 (Review). Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:769–776. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Thompson JE and Thompson CB: Putting the
rap on Akt. J Clin Oncol. 22:4217–4226. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Comerford KM, Wallace TJ, Karhausen J, et
al: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent regulation of the
multidrug resistance (MDR1) gene. Cancer Res. 62:3387–3394.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sullivan R, Paré GC, Frederickson LJ, et
al: Hypoxia-induced resistance to anticancer drugs is associated
with decreased senescence and requires hypoxia-inducible factor-1
activity. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:1961–1973. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kita Y, Mimori K, Iwatsuki M, et al: STC2:
A predictive marker for lymph node metastasis in esophageal
squamous-cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:261–272. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Law AY and Wong CK: Stanniocalcin-2 is a
HIF-1 target gene that promotes cell proliferation in hypoxia. Exp
Cell Res. 316:466–476. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|