|
1
|
Lee R, Feinbaum R and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with
antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993.
|
|
2
|
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, et al:
The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in
Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 403:901–906. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W
and Tuschl T: Identification of novel genes coding for small
expressed RNAs. Science. 294:853–858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG and Bartel
DP: An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles
in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 294:858–862. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vetter G, Saumet A, Moes M, et al: miR-661
expression in SNAI1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition
contributes to breast cancer cell invasion by targeting Nectin-1
and StarD10 messengers. Oncogene. 29:4436–4448. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ambros V: MicroRNA pathways in flies and
worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 113:673–676.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Palatnik JF, Allen E, Wu X, et al: Control
of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature. 425:257–263. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hatfield SD, Shcherbata HR, Fischer KA,
Nakahara K, Carthew RW and Ruohola-Baker H: Stem cell division is
regulated by the microRNA pathway. Nature. 435:974–978. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O’Donnell KA, Wentzel EA, Zeller KI, Dang
CV and Mendell JT: c-Myc-regulated microRNAs modulate E2F1
expression. Nature. 435:839–843. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tong AW and Nemunaitis J: Modulation of
miRNA activity in human cancer: a new paradigm for cancer gene
therapy? Cancer Gene Ther. 15:341–355. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Calin G, Dumitru C, Shimizu M, et al:
Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro-RNA genes miR15 and
miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:15524–15529. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, et al:
MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Al-Hajj M: Cancer stem cells and oncology
therapeutics. Curr Opin Oncol. 19:61–64. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Al-Hajj M and Clarke MF: Self-renewal and
solid tumor stem cells. Oncogene. 23:7274–7282. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
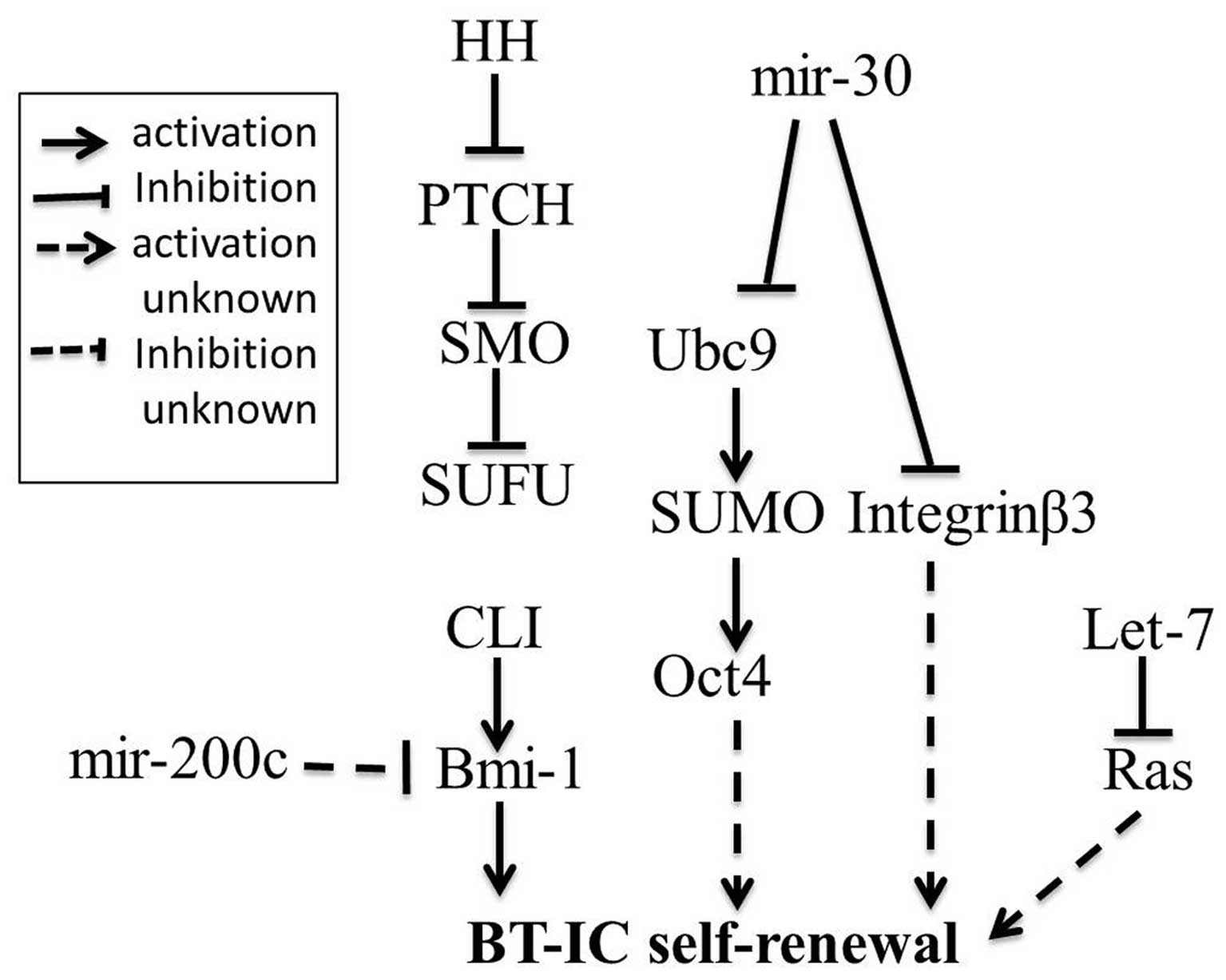
Liu S, Dontu G, Mantle ID, et al: Hedgehog
signaling and Bmi-1 regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant
human mammary stem cells. Cancer Res. 66:6063–6071. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dimri GP, Martinez JL, Jacobs JJL, et al:
The Bmi-1 oncogene induces telomerase activity and immortalizes
human mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 62:4736–4745.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shimono Y, Zabala M, Cho RW, et al:
Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with
normal stem cells. Cell. 138:592–603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, et al: let-7 regulates
self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell.
131:1109–1123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu F, Deng H, Yao H, Liu Q, Su F and Song
E: Mir-30 reduction maintains self-renewal and inhibits apoptosis
in breast tumor-initiating cells. Oncogene. 29:4194–4204. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Müller S, Hoege C, Pyrowolakis G and
Jentsch S: SUMO, ubiquitin’s mysterious cousin. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 2:202–213. 2001.
|
|
24
|
Park SW, Hu X, Gupta P, Lin YP, Ha SG and
Wei LN: SUMOylation of Tr2 orphan receptor involves Pml and
fine-tunes Oct4 expression in stem cells. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
14:68–75. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
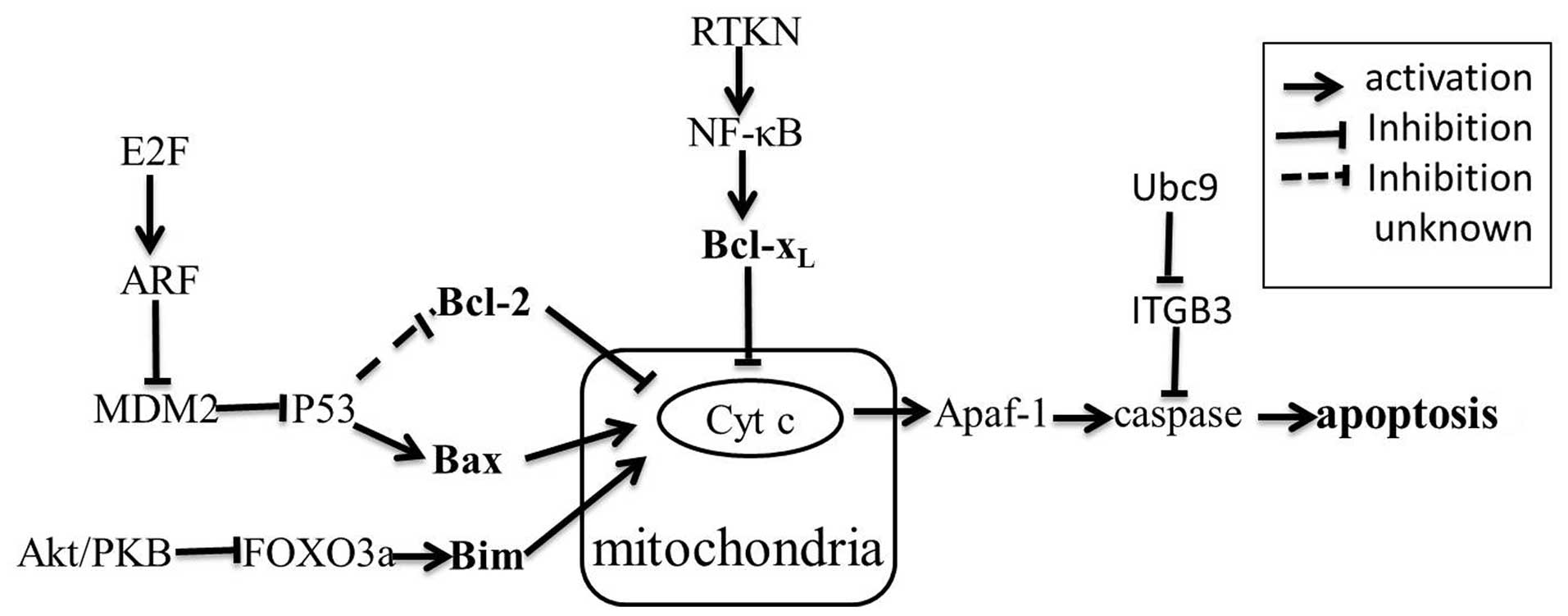
Stupack DG, Puente XS, Boutsaboualoy S,
Storgard CM and Cheresh DA: Apoptosis of adherent cells by
recruitment of caspase-8 to unligated integrins. J Cell Biol.
155:459–470. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pontier SM and Muller WJ: Integrins in
mammary-stem-cell biology and breast-cancer progression - a role in
cancer stem cells? J Cell Sci. 122:207–214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF and
Weissman IL: Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature.
414:105–111. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu CA, Wang MJ, Chi CW, Wu CW and Chen
JY: Rho/Rhotekin-mediated NF-kappaB activation confers resistance
to apoptosis. Oncogene. 23:8731–8742. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Raver-Shapira N, Marciano E, Meiri E, et
al: Transcriptional activation of miR-34a contributes to
p53-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell. 26:731–743. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Antonsson B and Martinou JC: The Bcl-2
protein family. Exp Cell Res. 256:50–57. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cimmino A, Calin G, Fabbri M, et al:
miR-15 and miR-16 induce apoptosis by targeting BCL2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 102:13944–13949. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
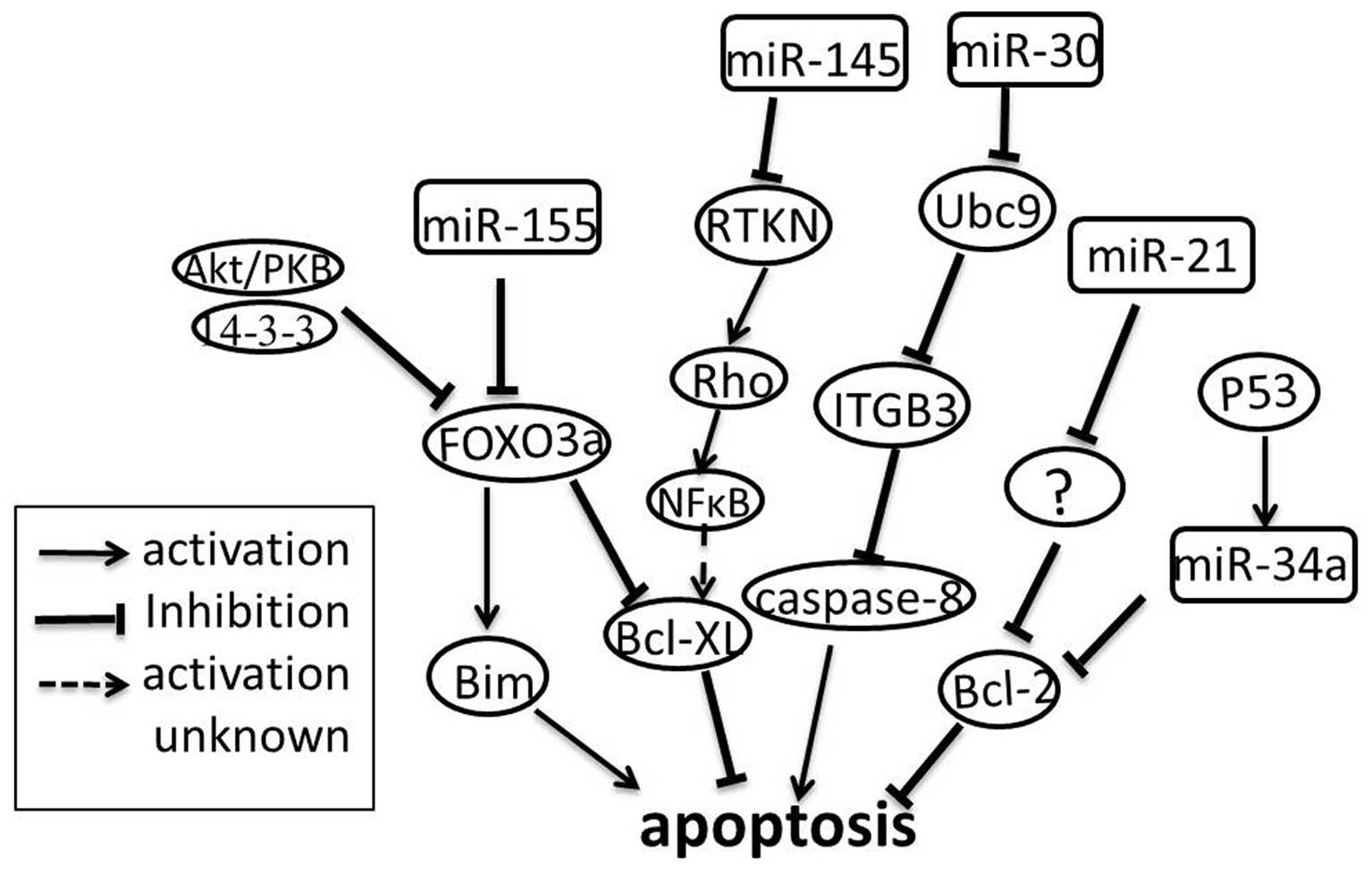
Si ML, Zhu S, Wu H, Lu Z, Wu F and Mo YY:
miR-21-mediated tumor growth. Oncogene. 26:2799–2803. 2006.
|
|
34
|
Chan J, Krichevsky A and Kosik K:
MicroRNA-21 is an antiapoptotic factor in human glioblastoma cells.
Cancer Res. 65:6029–6033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang S, Bian C, Yang Z, et al: miR-145
inhibits breast cancer cell growth through RTKN. Int J Oncol.
34:1461–1466. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kong W, He L, Coppola M, et al:
MicroRNA-155 regulates cell survival, growth, and chemosensitivity
by targeting FOXO3a in breast cancer. J Biol Chem. 285:17869–17879.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sunters A, Fernández de Mattos S, Stahl M,
et al: FoxO3a transcriptional regulation of Bim controls apoptosis
in paclitaxel-treated breast cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem.
278:49795–49805. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Le MT, Teh C, Shyh-Chang N, et al:
MicroRNA-125b is a novel negative regulator of p53. Genes Dev.
23:862–876. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kato M, Paranjape T, Ullrich R, et al: The
mir-34 microRNA is required for the DNA damage response in vivo in
C. elegans and in vitro in human breast cancer cells.
Oncogene. 28:2419–2424. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
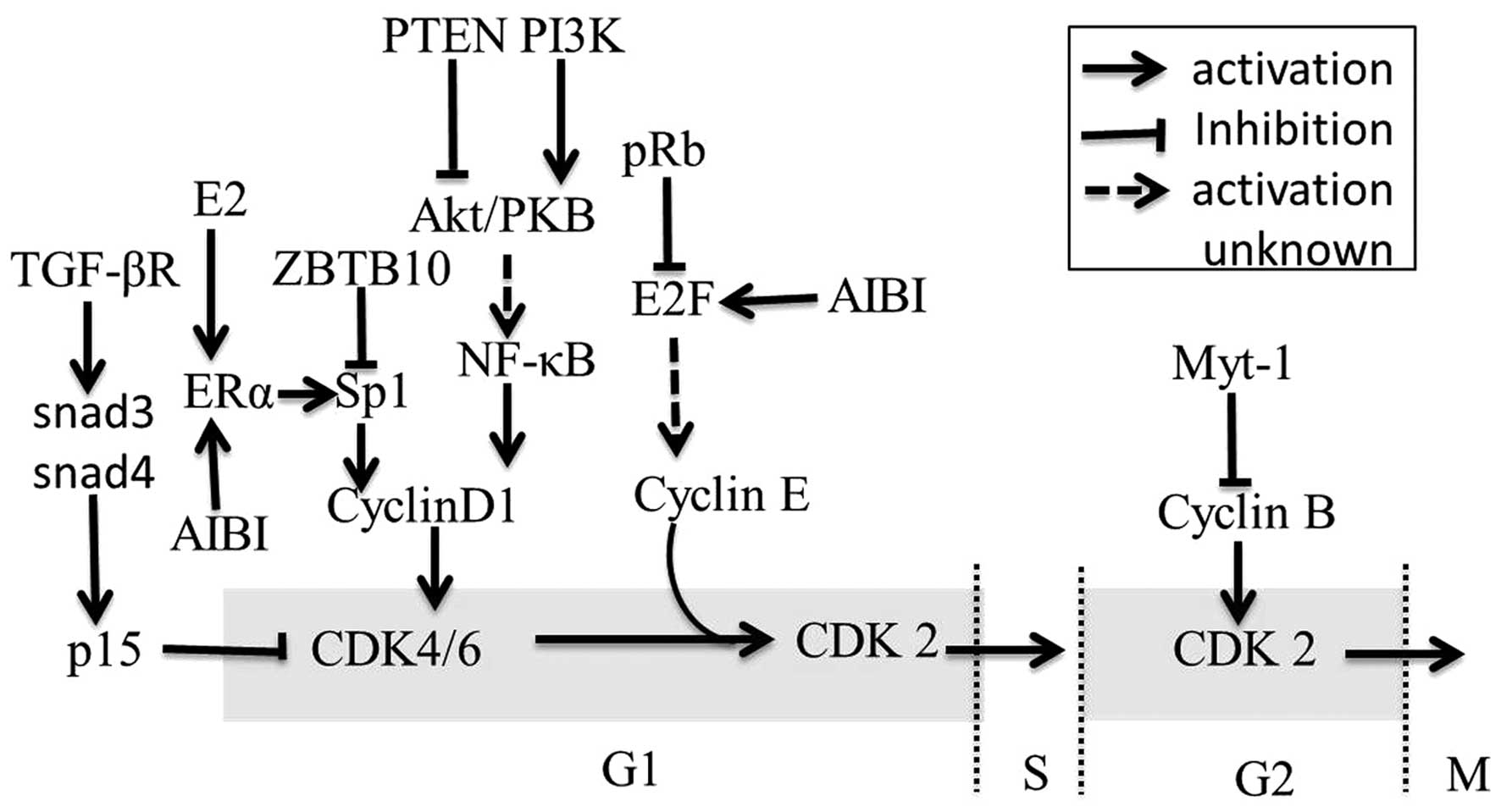
Fu M: Minireview: cyclin D1: normal and
abnormal functions. Endocrinology. 145:5439–5447. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu Z, Wang C, Wang M, et al: A cyclin
D1/microRNA 17/20 regulatory feedback loop in control of breast
cancer cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 182:509–517. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mertens-Talcott SU, Chintharlapalli S, Li
X and Safe S: The oncogenic microRNA-27a targets genes that
regulate specificity protein transcription factors and the G2-M
checkpoint in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Res.
67:11001–11011. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hossain A, Kuo MT and Saunders GF:
Mir-17-5p regulates breast cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting
translation of AIB1 mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 26:8191–8201. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Brosh R, Shalgi R, Liran A, et al:
p53-Repressed miRNAs are involved with E2F in a feed-forward loop
promoting proliferation. Mol Syst Biol. 4:2292008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Castro-Rivera E, Samudio I and Safe S:
Estrogen regulation of cyclin D1 gene expression in ZR-75 breast
cancer cells involves multiple enhancer elements. J Biol Chem.
276:30853–30861. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Adams BD, Furneaux H and White BA: The
micro-ribonucleic acid (miRNA) miR-206 targets the human estrogen
receptor-(ER) and represses ER messenger RNA and protein expression
in breast cancer cell lines. Mol Endocrinol. 21:1132–1147. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Leivonen SK, Makela R, Ostling P, et al:
Protein lysate microarray analysis to identify microRNAs regulating
estrogen receptor signaling in breast cancer cell lines. Oncogene.
28:3926–3936. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhao JJ, Lin J, Yang H, et al:
MicroRNA-221/222 negatively regulates estrogen receptor alpha and
is associated with tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Biol
Chem. 283:31079–31086. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Bhat-Nakshatri P, Wang G, Collins NR, et
al: Estradiol-regulated microRNAs control estradiol response in
breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:4850–4861. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wickramasinghe NS, Manavalan TT, Dougherty
SM, Riggs KA, Li Y and Klinge CM: Estradiol downregulates miR-21
expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7
breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:2584–2595. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gupta GP and Massague J: Cancer
metastasis: building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, et al:
The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and
metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:202–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Vincent-Salomon A and Thiery JP:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer development.
Breast Cancer Res. 5:101–106. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tryndyak VP, Beland FA and Pogribny IP:
E-cadherin transcriptional down-regulation by epigenetic and
microRNA-200 family alterations is related to mesenchymal and
drug-resistant phenotypes in human breast cancer cells. Int J
Cancer. 126:2575–2583. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ma L, Young J, Prabhala H, et al: miR-9, a
MYC/MYCN-activated microRNA, regulates E-cadherin and cancer
metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 12:247–256. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Blagosklonny MV, Dykxhoorn DM, Wu Y, et
al: miR-200 enhances mouse breast cancer cell colonization to form
distant metastases. PLoS One. 4:e71812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gregory PA, Bert AG, Paterson EL, et al:
The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal
transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat Cell Biol. 10:593–601.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Valastyan S, Reinhardt F, Benaich N, et
al: A pleiotropically acting microRNA, miR-31, inhibits breast
cancer metastasis. Cell. 137:1032–1046. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kong W, Yang H, He L, et al: MicroRNA-155
is regulated by the transforming growth factor beta/Smad pathway
and contributes to epithelial cell plasticity by targeting RhoA.
Mol Cell Biol. 28:6773–6784. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Baker AH, George SJ, Zaltsman AB, Murphy G
and Newby AC: Inhibition of invasion and induction of apoptotic
cell death of cancer cell lines by overexpression of TIMP-3. Br J
Cancer. 79:1347–1355. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Bode W, Reinemer P, Huber R, Kleine T,
Schnierer S and Tschesche H: The X-ray crystal structure of the
catalytic domain of human neutrophil collagenase inhibited by a
substrate analogue reveals the essentials for catalysis and
specificity. EMBO J. 13:1263–1269. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Gabriely G, Wurdinger T, Kesari S, et al:
MicroRNA 21 promotes glioma invasion by targeting matrix
metalloproteinase regulators. Mol Cell Biol. 28:5369–5380. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Selaru FM, Olaru AV, Kan T, et al:
MicroRNA-21 is overexpressed in human cholangiocarcinoma and
regulates programmed cell death 4 and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase 3. Hepatology. 49:1595–1601. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Song B, Wang C, Liu J, et al: MicroRNA-21
regulates breast cancer invasion partly by targeting tissue
inhibitor of metalloproteinase 3 expression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
29:292010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhu S, Wu H, Wu F, Nie D, Sheng S and Mo
YY: MicroRNA-21 targets tumor suppressor genes in invasion and
metastasis. Cell Res. 18:350–359. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Perry SV: Vertebrate tropomyosin:
distribution, properties and function. J Muscle Res Cell Motil.
22:5–49. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hall A: Rho GTPases and the actin
cytoskeleton. Science. 279:509–514. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Varga AE, Stourman NV, Zheng Q, et al:
Silencing of the Tropomyosin-1 gene by DNA methylation alters tumor
suppressor function of TGF-beta. Oncogene. 24:5043–5052. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, et al:
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the
programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene. 27:4373–4379. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Asangani IA, Rasheed SAK, Nikolova DA, et
al: MicroRNA-21 (miR-21) post-transcriptionally downregulates tumor
suppressor Pdcd4 and stimulates invasion, intravasation and
metastasis in colorectal cancer. Oncogene. 27:2128–2136. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Yang HS, Matthews CP, Clair T, et al:
Tumorigenesis suppressor Pdcd4 down-regulates mitogen-activated
protein kinase kinase kinase kinase 1 expression to suppress colon
carcinoma cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol. 26:1297–1306. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Benbow U and Brinckerhoff CE: The AP-1
site and MMP gene regulation: what is all the fuss about? Matrix
Biol. 15:519–526. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Murai T, Maruyama Y, Mio K, Nishiyama H,
Suga M and Sato C: Low cholesterol triggers membrane
microdomain-dependent CD44 shedding and suppresses tumor cell
migration. J Biol Chem. 286:1999–2007. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Lesley J, Hyman R and Kincade PW: CD44 and
its interaction with extracellular matrix. Adv Immunol. 54:271–335.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Tavazoie S, Alarcón C, Oskarsson T, et al:
Endogenous human microRNAs that suppress breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 451:147–152. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hakem A: RhoC is dispensable for
embryogenesis and tumor initiation but essential for metastasis.
Genes Dev. 19:1974–1979. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Clark E, Golub T, Lander E and Hynes R:
Genomic analysis of metastasis reveals an essential role for RhoC.
Nature. 406:532–535. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J and Weinberg RA:
Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast
cancer. Nature. 449:682–688. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Myers C, Charboneau A, Cheung I, Hanks D
and Boudreau N: Sustained expression of homeobox D10 inhibits
angiogenesis. A J Pathol. 161:2099–2109. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lehtonen ST, Svensk A-M, Soini Y, et al:
Peroxiredoxins, a novel protein family in lung cancer. Int J
Cancer. 111:514–521. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Chang XZ, Li DQ, Hou YF, et al:
Identification of the functional role of peroxiredoxin 6 in the
progression of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 9:R762007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kümin A, Huber C, Rülicke T, Wolf E and
Werner S: Peroxiredoxin 6 is a potent cytoprotective enzyme in the
epidermis. Am J Pathol. 169:1194–1205. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chang XZ, Li DQ, Hou YF, et al:
Identification of the functional role of peroxiredoxin 6 in the
progression of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 9:R762007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Suarez Y and Sessa WC: MicroRNAs as novel
regulators of angiogenesis. Circ Res. 104:442–454. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Xie H, et al:
Endothelial-specific intron-derived miR-126 is down-regulated in
human breast cancer and targets both VEGFA and PIK3R2. Mol Cell
Biochem. 351:157–164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gerber HP, McMurtrey A, Kowalski J, et al:
Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates endothelial cell
survival through the phosphatidylinositol 3′-Kinase/Akt signal
transduction pathway. J Biol Chem. 273:30336–30343. 1998.
|
|
89
|
Iva N and Karl-Heinz P: EGFL7 meets
miRNA-126: an angiogenesis alliance. J Angiogenes Res. 2:92010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, et al:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Boudreau N and Myers C: Breast
cancer-induced angiogenesis: multiple mechanisms and the role of
the microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 5:140–146. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Cascio S, D’Andrea A, Ferla R, et al:
miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1α and STAT3 in
MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 224:242–249.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Bos R, Zhong H, Hanrahan CF, et al: Levels
of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α during breast carcinogenesis. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 93:3092001.
|
|
94
|
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, et al:
Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nature Genet.
37:495–500. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar
|